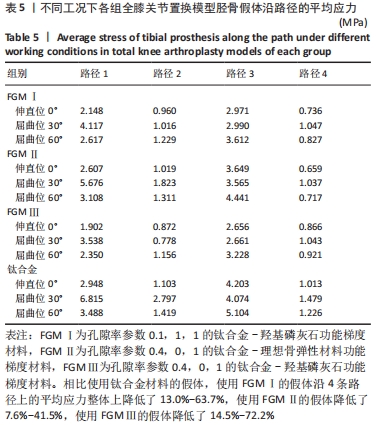
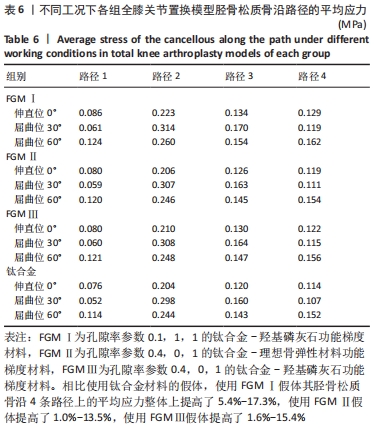
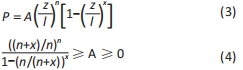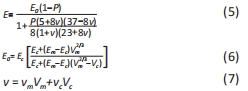[1] 相昌鑫.不同偏移角度荷载下膝关节假体的接触压力有限元分析[D].太原:太原理工大学,2019.
[2] 黄萍,陈博,刘志宏,等.膝关节置换后患者的三维步态特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(35):5596-5601.
[3] OLIVER G, JALDIN L, CAMPRUBÍ E, et al. Observational Study of Total Knee Arthroplasty in Aseptic Revision Surgery: Clinical Results. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(1):177-183.
[4] 贾巍,张满栋,陈维毅,等.股骨假体材料对人工膝关节置换性能的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(10):1477-1481.
[5] 相昌鑫,纪斌平,陈维毅,等.不同偏移角度荷载下膝关节假体接触压力的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(28):4522-4528.
[6] PANG HN, RAZAK H, JAMIECSON P, et al. Factors Affecting Wear of Constrained Polyethylene Tibial Inserts in Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(6):1340-1345.
[7] JIA Z, GONG H, HU S, et al. Influence of design features of tibial stems in total knee arthroplasty on tibial bone remodeling behaviors. Med Eng Phys. 2017;48:103-113.
[8] WATANABE T, KOGA H, HORIE M, et al. Post-Cam Design and Contact Stress on Tibial Posts in Posterior-Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses: Comparison Between a Rounded and a Squared Design. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(12):3757-3762.
[9] WANG CJ, SHI JF, MORGAN C, et al. Design and Simulation of a Femoral Component Peg in Total Knee Replacement. Key Eng Mater. 2010;450: 111-114.
[10] BAHRAMINASAB M, SAHARI BB, EDWARDS KL, et al. Material tailoring of the femoral component in a total knee replacement to reduce the problem of aseptic loosening. Mater Design. 2013;52(dec.):441-451.
[11] Ayatollahi MR, Davari MH, Shirazi HA, et al. To Improve Total Knee Prostheses Performance Using Three-Phase Ceramic-Based Functionally Graded Biomaterials. Front Mater. 2019. doi:10.3389/fmats.2019.00107
[12] ENAB TA. A comparative study of the performance of metallic and FGM tibia tray components in total knee replacement joints. Comput Mater Sci. 2012;53(1):94-100.
[13] HEDIA HS, MAHMOUD NA. Design optimization of functionally graded dental implant. Biomed Mater Eng. 2004;14(2):133-143.
[14] ENAB TA, BONDOK NE. Material selection in the design of the tibia tray component of cemented artificial knee using finite element method. Mater Design. 2013;44:454-460.
[15] 贾政斌.胫骨假体的构型与材料对胫骨骨重建行为影响的数值仿真研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2017.
[16] SERAL B, PEREZ MA, GARCIA-AZNAR JM, et al. Periprosthetic Bone Remodeling. A Finite Element Study of the Influence of the Implant Design. J Appl Biomater Biomech. 2005;3(2):117-127.
[17] HEDIA HS, SHABARA MAN, EL-MIDANY TT, et al. A Method of Material Optimization of Cementless Stem Through Functionally Graded Material. Int J Mech Mater Des. 2004;1(4):329-346.
[18] NEMAT-ALLA M. Reduction of thermal stresses by developing two-dimensional functionally graded materials. Int J Solids Struct. 2003; 40(26):7339-7356.
[19] LIN D, LI Q, LI W, et al. Design optimization of functionally graded dental implant for bone remodeling. Compos Part B-Eng. 2009;40(7): 668-675.
[20] BAHRAMINASAB M, SAHARI BB, EDWARDS KL, et al. On the influence of shape and material used for the femoral component pegs in knee prostheses for reducing the problem of aseptic loosening. Mater Design. 2014;55:416-428.
[21] HEDIA HS, ALDOUSARI SM, FOUDA N. Material optimization of cemented tibia tray using functionally graded material. Mater Test. 2016;3(58):260-268.
[22] 李新宇,王长江,陈维毅.一种新型膝关节假体设计及稳定性评估[J].太原理工大学学报,2018,49(1):152-157.
[23] 王俊然.膝关节在屈曲和步态运动下胫-股关节生物力学的有限元分析[D].太原:太原理工大学,2018.
[24] 李新宇.一种新型人工膝关节置换假体的设计及力学评估[D].太原:太原理工大学,2017.
[25] LUM ZC, SHIEH AK, DORR LD. Why total knees fail-A modern perspective review. World J Orthop. 2018;9(4):60-64.
[26] THOMAS B, BINKLEY N, ANDERSON PA, et al. DXA Measured Distal Femur Bone Mineral Density in Patients After Total Knee Arthroplasty: Method Development and Reproducibility. J Clin Densitom. 2019; 22(1):67-73.
[27] 李超,程静波,冯明利.从生物力学角度认识股骨解剖结构对膝关节置换的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(36):116-123.
[28] BIN QASIM SS, ZAFAR MS, NIAZI FH, et al. Functionally graded biomimetic biomaterials in dentistry: an evidence-based update. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2020;31(9):1144-1162. |