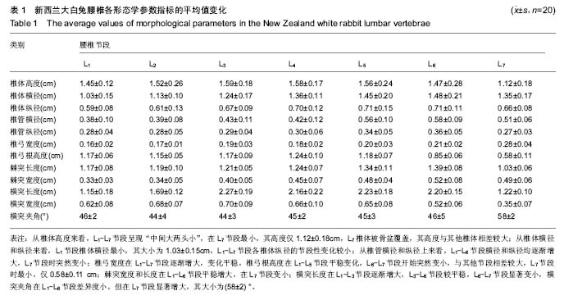
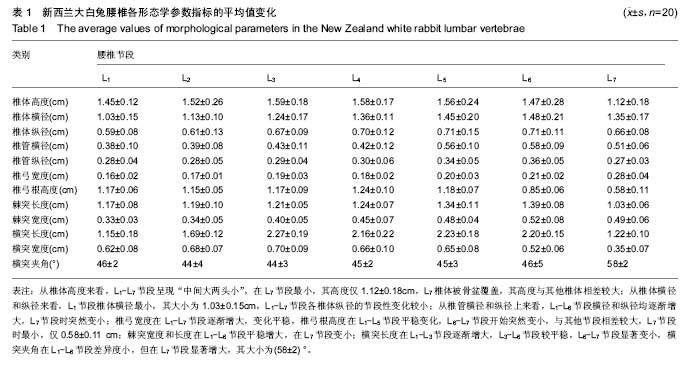
| [1] 王成旭,中国北方地区成人椎骨形态的测量研究[D].大连:大连医科大学,2007.[2] 贺用礼,刘平均,王长青,等,胸腰椎影像学测量及其临床意义[J].中国现代医药杂志,2012,14(9):7-10.[3] 孙舰.正常国人椎管MRL影像解剖学研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2003.[4] 鲁世荣,赵健,秦晓霖,等,腰椎横突与第三腰椎横突综合征的相关性研究[J].中国航天医学杂志,2011,22(6):644-646.[5] 李兵,姜保国,傅中国,等.腰椎横突形态学研究[J].中国骨肿瘤骨病杂志,2003,2(2):94-97.[6] 王汉琴,王配军,陈家强,等.腰椎横突的应用解剖[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2001,19(3):226-228.[7] 沈洪林,腰椎椎板形态学测量[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2013.[8] 张德,方先来,孟志华,等,带棘突钛钉腰椎弓根螺旋CT三维测量的解剖学研究及临床应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2004,12(25): 774-776.[9] Kothe R, O’Holleran JD, Liu W, et al. Internal architecture of the thoracicpedicle. Ananatomic study. Spine. 1996;21(3): 264-270.[10] 赵廷宝,范清宇,李云庆.T10-L5椎体标本和X射线片测量及其临床意义[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2001,19(41):302-304.[11] 西永明,胡有谷.椎间盘退变模型的建立及其历史和现状[J].中华骨科杂志,2000,20(6):378-380.[12] 谢卯,熊蠡茗,周建国,等,椎间盘退变模型研究进展[J].国际骨科杂志,2009,30(2):124-126.[13] 彭城,任先军,梅芳瑞,等.实验性椎间盘退变的放射影像学与病理学观察[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2004,19(1):28-30.[14] 吴健,唐天驷,王根,等.兔腰椎间盘退变模型的建立及影像学分析[J].苏州大学学报,2007,27(4):552-554.[15] Grobler LJ, Robertson PA, Novotny JE, et al. Etiology of spondylolisthesis. Assessment of the role played by lumbar facet joint morphology. Spine. 1993;18(1)10-14.[16] 边卫国,党晓谦,汤少杰,等,计算机辅助下腰椎CT图像自动化测量及其临床价值[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2007,17(10):749-752.[17] 王亮,罗卓荆,罗莉静,等,幼犬胸腰椎形态与椎弓根螺钉置入相关数据的CT测量研究[J],中国临床解剖学杂志, 2008,26(6): 642-646.[18] 白皓天,韩宏志,孔宁,等,鹿羊作为脊椎内固定动物模型的可行性研究[J].中国实验诊断学,2013,17(1):7-11.[19] 王靖,唐天驷,姚啸生.纤维环穿刺诱导椎间盘退变动物模型的实验研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(4):284-286.[20] Niinimaki J, Rnohonen J, Silfverhuth M. et al. Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging of experimentally injured porcine intervertebral disc. Aeta Radilogica. 2007;48(6): 643-649.[21] Dullerud R. Naksiad HCT changes after congervative treatment for lunbar disk herniation. Acta Radiol. 1994;35(5): 415-419.[22] 刘正津,陈尔瑜,临床解剖学丛书-胸部和脊柱分肼[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,1989.[23] Misenhimer CR, Peek RD, Wiltee LL, et al. Anatmic analysis of pedicl cortical and cancellous diamiter as related screw size. Spine. 1989;14:367-372.[24] 方先来,张德,孟志华,等,螺旋CT三维测量在腰椎椎弓根置钉中的应用研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2004,14(2):96-98.[25] Li Bing, Jiang BG, Fu ZG, et al. Accurate determination of lumbar pedicle: amorphometric study by reformatted CT images. Spine. 2004;29:21:2438-2444.[26] 杨敬,常鑫,王强,等,腰椎“人”字嵴顶点定位的三维CT影像研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2013,31(1):60-63.[27] 李智多,袁峰,盛晓磊,等.3D打印导板辅助腰椎皮质骨螺钉置入的可行性[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(48):7232-7238. [28] Phan K, Mobbs RJ, Rao PJ. Foraminal height measurement techniques. J Spine Surg. 2015;1(1):35-43.[29] Chen X, Feng S, Guan H, et al. Radiological characteristics and clinical manifestation of isolated lumbar foraminal stenosis. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015;53(8):584-588. [30] Lee SJ, Binkley N, Lubner MG, et al. Opportunistic screening for osteoporosis using the sagittal reconstruction from routine abdominal CT for combined assessment of vertebral fractures and density. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(3):1131-1136.[31] Siepe CJ, Stosch-Wiechert K, Heider F, et al. Anterior stand-alone fusion revisited: a prospective clinical, X-ray and CT investigation. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(4):838-851. [32] Allain J, Delecrin J, Beaurain J, et al. Stand-alone ALIF with integrated intracorporeal anchoring plates in the treatment of degenerative lumbar disc disease: a prospective study on 65 cases. Eur Spine J. 2014;23(10):2136-2143.[33] Khiami F, Aziria SA, Ragot S, et al. Reliability and validity of a new measurement of lumbar foraminal volume using a computed tomography. Surg Radiol Anat. 2015;37(1):93-99. [34] Schnake KJ, Stavridis SI, Kandziora F. Five-year clinical and radiological results of combined anteroposterior stabilization of thoracolumbar fractures. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;20(5): 497-504. [35] Xu J, Mao K, Wang Y, et al. A feasibility research of minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion using unilateral incision and hybrid internal fixation for dural-level lumbar degenerative disease. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013;27(8):955-959. [36] Gong Q, Kong Q, Li T, et al. Application of reduction by posterior approach to treat severe spondylolisthesis. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013;27(4): 393-398.[37] Matsukawa K, Yato Y, Nemoto O, et al. Morphometric measurement of cortical bone trajectory for lumbar pedicle screw insertion using computed tomography. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(6):E248-E253. [38] Zhang Y, Yang H, Liu Y, et al. Percutaneous kyphoplasty in hyperextension position for treatment of middle and late period Kümmell disease. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012;26(4):411-415. [39] Makino T, Kaito T, Fujiwara H, et al. Analysis of lumbar pedicle morphology in degenerative spines using multiplanar reconstruction computed tomography: what can be the reliable index for optimal pedicle screw diameter? Eur Spine J. 2012;21(8):1516-1521. [40] Zweig T, Aghayev E, Melloh M, et al. Influence of preoperative leg pain and radiculopathy on outcomes in mono-segmental lumbar total disc replacement: results from a nationwide registry. Eur Spine J. 2012;21 Suppl 6:S729-736.[41] Delécrin J, Allain J, Beaurain J, et al. Effects of lumbar artificial disc design on intervertebral mobility: in vivo comparison between mobile-core and fixed-core. Eur Spine J. 2012;21 Suppl 5:S630-640. [42] Yan L, Li J, Zhao W, et al. The study of epidurography and multispiral CT scanning examinations in the diagnosis of lumbar nerve root canal stenosis. Orthopedics. 2010;33(10): 732. [43] Lin Y, Zhao YS, Li Q, et al. Clinical analysis of vertebral laminae reconstruction after laminectomy and pedicle screw fixation in treating lumbar spinal stenosis. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2010;23(7):511-513. [44] Beck M, Mittlmeier T, Gierer P, et al. Which is the ideal point of time to perform intraoperative 3D imaging in dorsal stabilisation of thoracolumbar spine fractures? A matched pair analysis. Injury. 2010;41(10):996-1001.[45] Fokter SK, Repse-Fokter A, Takac I. Case report: femoral neuropathy secondary to total hip arthroplasty wear debris. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(11):3032-3035. [46] Knop C, Kranabetter T, Reinhold M, et al. Combined posterior-anterior stabilisation of thoracolumbar injuries utilising a vertebral body replacing implant. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(7):949-963. [47] Kolta S, Quiligotti S, Ruyssen-Witrand A, et al. In vivo 3D reconstruction of human vertebrae with the three-dimensional X-ray absorptiometry (3D-XA) method. Osteoporos Int. 2008; 19(2):185-192. |