Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (3): 474-479.doi: 10.12307/2022.078
Previous Articles Next Articles
Screw placement in posterior route pedicle on subaxial cervical spine: how to improve the therapeutic effect with the development of artificial intelligence
Li Lu1, Tang Wen2
- 1Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China
-
Received:2021-02-27Revised:2021-03-02Accepted:2021-04-09Online:2022-01-28Published:2021-10-29 -
Contact:Tang Wen, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China -
About author:Li Lu, Master candidate, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Project of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Education, No. GJJ190810 (to TW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Lu, Tang Wen. Screw placement in posterior route pedicle on subaxial cervical spine: how to improve the therapeutic effect with the development of artificial intelligence[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 474-479.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
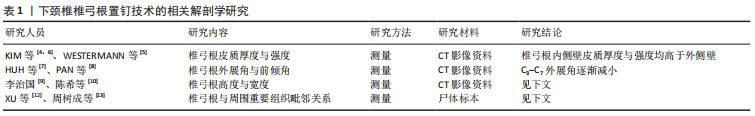
2.1.1 下颈椎椎弓根的解剖结构测量 (1)椎弓根皮质的厚度与强度:椎弓根钉置入颈椎后的稳定性依赖于椎弓根区域的结构强度大小,而椎弓根皮质的厚度决定了其结构强度。KIM等[4]通过CT图像测量了77例患者C3-C7的椎弓根内外侧壁皮质骨厚度,内侧为(1.40± 0.21) mm,外侧为(1.02±0.23) mm;在所有病例中椎弓根皮质在不同椎体均不等厚,内侧壁在各椎体均显著厚于外侧壁。WESTERMANN等[5]分析了100例患者的颈椎CT图像得出了相似的结论,椎弓根内侧壁皮质厚度为(1.77±0.43) mm,外侧为(0.90±0.36) mm。Kim等[6]分析了99例患者CT影像中C3-C7椎弓根皮质骨的CT值,同时测量了10具新鲜尸体标本的椎弓根皮质骨强度,发现椎弓根内侧壁的CT值及皮质骨强度均高于外侧壁。 (2)椎弓根的角度:椎弓根结构的中轴线与椎体矢状面和水平面的角度关系,是椎弓根钉置入过程的重要参考因素。HUH等[7]用44名成人C3-C6的CT图像制作颈椎模型,以每个椎体后壁作为参考平面,定义与椎体后壁垂线在水平面与矢状面的夹角分别为外展角、前倾角;测得C3-C6外展角分别为(50.60±6.22)°,(51.42±7.44)°,(47.79±7.61)°及(41.24±7.76)°,从C3-C6外展角逐渐减小;前倾角分别为(9.72±6.73)°,(5.09±6.39)°,(0.08±6.06)°及(1.67±6.06)°。PAN等[8]测量了棘突平面与椎弓根平面在水平面上的夹角,得出C3-C7外展角分别为(46.70±3.20)°,(47.90±3.70)°,(45.7±4.00)°,(41.50±3.50)°及(32.90±3.10)°。 (3)椎弓根的高度与宽度:椎弓根结构的高度与宽度决定了所需置入椎弓根钉的直径。一般而言,椎弓根钉的直径大小必须适配于椎弓根区域的结构尺寸,才能取得最稳定的固定效果。李治国[9]在CT图像下测量了48例成人C3-C6椎弓根的宽度与高度,其中椎弓根的宽度C3-C6分别为(5.47±0.86), (5.39±0.83),(5.82±1.47)及(5.76±1.03) mm;椎弓根的高度C3-C6分别为(6.45±1.25),(7.03±1.38),(7.62±1.40)及(7.78± 1.35) mm。陈希等[10]分析了50例健康人的CT数据,椎弓根的宽度C3-C7分别为(5.35±0.74),(5.56±0.67),(5.99±0.61), (6.34±0.61)及(6.86±0.74) mm。ZHOU等[11]采用三维CT重建了20例成人颈椎,将椎体从前向后分为10等份,测量得C3-C7在90%临界深度处的内切圆半径分别为(2.94±0.55),(3.04±0.40),(3.15±0.36),(3.28±0.47) 及(3.89±0.54) mm。 2.1.2 下颈椎椎弓根与周围重要组织之间的毗邻关系 椎弓根复杂的位置毗邻是手术过程中造成重要血管与神经损伤的解剖基础,对该问题的研究是防范与减少手术并发症的关键点。XU等[12]测量了20具标本C3-C7椎弓根距其上、下位神经根及硬膜囊的距离,结果显示,椎弓根上缘与其上位神经根之间、椎弓根内侧壁与硬膜囊之间无距离;椎弓根下缘距其下位神经根为1.4-1.6 mm。周树成等[13]测量了32具标本C3-C7椎弓根与周围重要组织之间的距离,结果显示,椎弓根上缘距其上位神经根为1.18-1.40 mm,从C3-C7逐渐增大;椎弓根下缘距其下位神经根为2.33-3.11 mm,从C3-C7逐渐减小;椎弓根内侧壁距硬脊膜为2.75-3.33 mm,椎弓根前外侧壁紧贴椎动脉,椎弓根前内侧壁紧贴硬膜外窦。 2.2 下颈椎椎弓根与下颈椎椎弓根钉的生物力学特点 生物力学测试是判断一项技术或材料是否可靠、有效的标准之一,颈椎椎弓根钉从诞生之初,就有许多学者对其进行生物力学测试。目前,对于下颈椎椎弓根置钉技术相关生物力学特点的研究主要关注于对下颈椎椎弓根与下颈椎椎弓根钉的生物力学测试,见表2。"
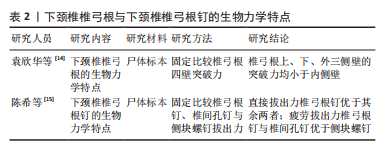
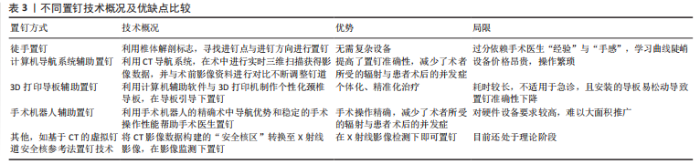
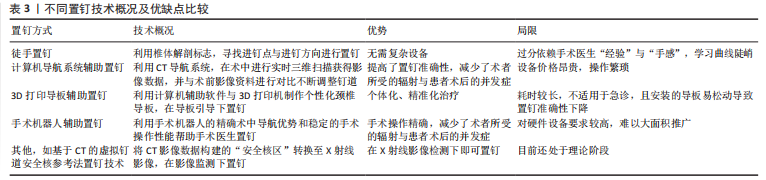
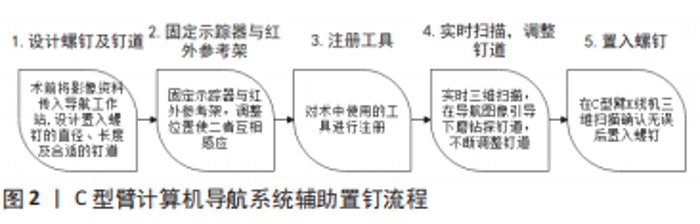
袁欣华等[14]用Abumi法于6具标本C3-C7上置钉,将标本固定并用2 mm探子施加轴向压缩负荷,以探子突破椎弓根时的载荷为实验结果。结果显示,C3-C7的平均穿透力为(-187.35±42.28) N,从C3-C7逐渐减小;C3-C7上下内外四侧壁的平均突破力分别为(-319.59±65.73),(-264.01±63.16),(-283.93±75.00) 及(-283.33±70.41) N,椎弓根上、下、外三侧壁的突破力均小于内侧壁。 陈希等[15]将30个C3-C6椎体随机分为3组,分别于双侧置入椎弓根钉、椎间孔钉与侧块螺钉;随机选取一侧进行直接拔出力测试,另一侧进行疲劳测试。结果显示,椎弓根钉、椎间孔钉与侧块螺钉的直接拔出力平均分别为(635.67±22.82),(327.10±17.07)及(305.71±11.63) N,椎弓根钉的直接拔出力大于其余2种螺钉;椎弓根钉、椎间孔钉与侧块螺钉的疲劳拔出力末次循环载荷分别为(187.06±18.04),(199.63±16.93) 及(161.75±14.71) N,侧块螺钉的疲劳拔出力小于椎弓根钉与椎间孔钉,椎弓根钉与椎间孔钉之间无明显差异。 2.3 下颈椎后路椎弓根钉置钉技术 目前下颈椎后路椎弓根钉置钉技术主要包括徒手置钉、计算机导航辅助置钉、3D打印导板辅助置钉、手术机器人辅助置钉等,不同的置钉方式各有其优缺点,见表3。"
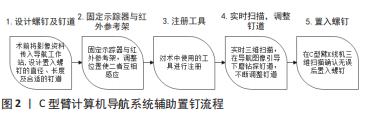
2.3.1 徒手置钉技术 下颈椎后路椎弓根钉徒手置入法由ABUMI等[3]于1994年首次提出,目前徒手置钉技术主要分为探查法与解剖定位法两种。探查法是一类利用磨钻或刮匙工具,在已知大概的进钉点及进钉方向的前提下,通过探查不断调整进钉点及进钉方向的技术。解剖定位法是一类利用椎体解剖标志作为参考,从而寻找椎弓根钉进钉点及进钉方向的技术。另外,通过改良手术入路进行的徒手置钉技术也被相继报道。 (1)利用椎体解剖标志参考的徒手置钉技术:薛晓北等[16]用区域法徒手置钉,即进钉点为一块区域:分别于侧块内外缘做2条垂线,上、下关节突下缘做2条水平线,以2条垂线及2条水平线围成的矩形的中点为原点,建立一直角坐标系,进钉点则位于坐标系的外上象限。进钉方向一般为内倾45°、头尾倾0°,共置钉618枚,准确率97.6%。 PAN等[8]、WU等[17]、LUO等[18]提出侧块切迹参考法徒手置钉。侧块切迹即侧块上关节间部嵴的最内侧部分,切迹始终位于椎弓根外侧壁与下颈椎上关节突到下关节突的交汇点。进钉点在C3-C6约为侧块切迹内侧2.2 mm,较侧块切迹低1.4 mm;在C7大多为侧块切迹内侧2.2 mm,较侧块切迹高1.2 mm;进钉方向在轴向平面,内倾角为49°-34°,从头侧到尾侧逐渐减小,平行于椎骨上终板。PAN等[8]置钉718枚,准确率92.9%。 LIU等[19]、LI等[20]、邹云龙等[21]提出局部解剖定位法徒手置钉,定义椎体上关节突内外缘、上关节突下缘、下关节突上缘在侧块上所围成的区域为“峡部”,进钉点定为过横突根部中点的水平线与过峡部中外1/3的垂线的交点。C3-C5的进钉方向在水平面与峡部后外侧面成角分别为(95.10±3.96)°、(86.60±3.35)°及(84.60±4.95)°,在矢状面与峡部后侧面成角分别为(71.25±4.54)°、(69.90±5.06)°及(76.15±5.11)°;C6-C7的进钉方向在水平面与峡部后外侧面成角分别为(59.71±1.10)°及(89.61±1.24)°,在矢状面与峡部后侧面成角均为(75.86±1.12)°。邹云龙等[21]置钉296枚,准确率为97.6%。 LEE等[22]提出“内侧漏斗法”置钉。“漏斗法”置钉技术[23],即移除椎弓根入口处的侧块,形成一个漏斗形缺口,暴露椎弓根的松质骨,在直视椎弓根松质骨的前提下置钉。“内侧漏斗法”是对“漏斗法”的改良,通过在椎板和侧块内侧钻孔,暴露椎弓根的松质骨,在椎板上部行切开术,分离黄韧带,暴露椎弓根内侧皮质。侧位透视引导下于侧块外上象限创建进钉点,从进钉点到去皮质的椎弓根松质骨做一个假想轨迹后,通过直视暴露的椎弓根内侧皮质及松质骨插入螺钉。相较于“漏斗法”,该法最大限度地保留进钉点的骨皮质,从而维持螺钉的拔出强度,其报道置钉88枚,准确率94.3%。 LIU等[24]利用“滑动技术”徒手置钉,将目标椎体侧块按纵线分为3等份,在外侧纵线偏上一点和关节突关节下缘稍下方选择最佳进入点。先用头部弯曲的探针从进入点进入,头部向内弯曲,旋转探针,同时向内侧以最大角度行进超过45°,遇到阻力时探针停止。后旋转探针180°,使头部向外弯曲,使探针推进至椎体。一旦探头达到15 mm深度,再次旋转180°,使其头部向内弯曲;继续插入椎弓根探子推进至20 mm深度,后将探针旋转360° 2次,以扩大通路,确认无误后置入螺钉,在此过程中,椎弓根内侧缘的皮质起到滑块的作用;其于C3-C7置钉257枚,准确率97.3%。LEE等[25]使用类似的方法,先在预定入口点钻取一个小的导向孔,利用弯曲探针使插入轨迹更宽、更直,再用球针探测,确认无误后放置螺钉;其报道置钉724枚,准确率95.9%。 BURCEV等[26]经CT测量得出最佳进钉点位于距侧块后表面外缘2 mm及上缘2 mm处;进钉方向平行于同一椎骨的对侧椎板,垂直于侧块后表面。其报道置钉32枚,准确率93.75%。 (2)徒手置钉技术的手术入路改良:PARK等[27]经关节旁小切口徒手置钉,先经关节旁小切口暴露椎弓根内上壁,将黄韧带和硬膜外静脉丛解剖游离,明确椎弓根上、内侧缘及椎弓根与椎体后壁交界;通过术前3D-CT扫描中对椎弓根的测量以及手术区域来确定进入点,然后在入口点上方打一个深度约为3 mm的孔,在直视椎弓根内侧壁的情况下,通过探针探查椎弓根的松质骨通道,确定无误后置入螺钉;其报道置钉78枚,准确率92.3%。黄晓东等[28]、方弘伟等[29]经头、颈半棘肌间隙入路置钉,取后正中切口,切开斜方肌及夹肌在项韧带、棘突的附着,暴露头颈半棘肌间隙,分别向内、外侧牵开颈半棘肌及头半棘肌,将周围组织解剖游离,暴露侧块及关节突,根据术前影像徒手置钉。黄晓东等[28]报道置钉58枚,准确率94.8%。方弘伟等[29]报道置钉49枚,准确率96.0%。相较于一般后正中入路,经肌间隙入路具有创伤小、置钉容易、术后并发症减少等优点。 目前,对于徒手置钉技术的报道众多,但缺乏大量的临床病例来证实或处于理论与标本阶段。徒手置钉技术不依赖于先进的设备与高质量的图像,更依赖于操作者的“手感”与“经验”;但同时误置率与术后并发症如颈髓、血管及神经的损伤,螺钉松动、断裂,颈部术后常年疼痛等也随之提高。 2.3.2 计算机导航系统辅助置钉技术 计算机导航系统辅助置钉技术是一类利用CT导航系统,在术中进行实时三维扫描获得影像数据,并与术前影像资料进行对比不断调整钉道的技术。C型臂计算机导航系统主要包括用于成像、导航的工具以及图像处理的系统[30-31]。手术过程包括:术前将影像资料传入导航工作站,设计置入螺钉的直径、长度及合适的钉道;固定示踪器与红外参考架,调整位置使二者互相感应;对术中使用的工具进行注册;进行实时三维扫描并传输数据,在导航图像引导下磨除骨皮质并钻探钉道,与术前影像资料进行对比不断调整钉道,在C型臂X射线机三维扫描确认无误后置入螺钉,见图2。"
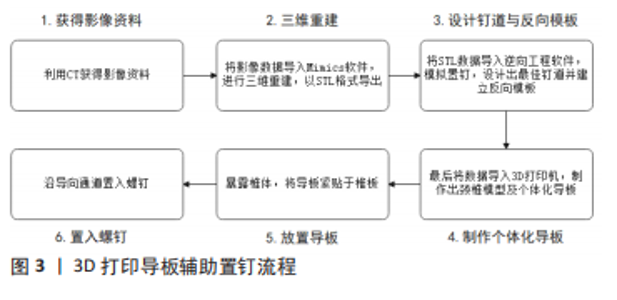
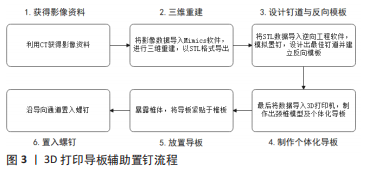
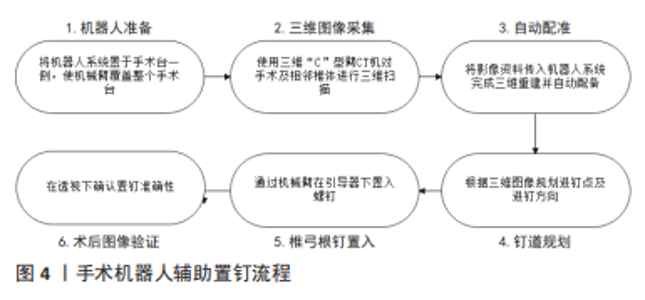
余伟等[30]置钉128枚,优良率95.3%。姜廷华等[32]置钉186枚,优良率为96.2%。Shimokawa等[33]使用术中3D-CT导航系统置钉310枚,准确率97.1%。计算机导航系统辅助置钉技术与传统X射线透视置钉比较,在置钉用时、出血量上劣于后者,但在置钉优良率、辐射量上明显优于后者。 近年来O型臂导航系统在下颈椎椎弓根钉置入过程中的使用被广泛报道[34-36]。黄圣斌等[34]报道置钉142枚,0级96.5%,1级3.5%。SOURABH等[35]报道置钉241枚,准确率96.68%。Wada等[36]报道置钉317枚,准确率96.2%。相较于C型臂导航系统,O型臂导航系统具有精确度高、成像质量好、扫描时间短等优势。 2.3.3 3D打印导板辅助置钉技术 3D打印导板辅助置钉技术是一类通过计算机辅助软件与3D打印机制作个性化颈椎导板,在导板引导下置钉的技术。通道型3D打印导板辅助置钉技术的关键在于个体化的导板制作[37-38],利用CT获得影像资料,将影像数据导入Mimics软件,进行三维重建,以STL格式导出;再将STL数据导入逆向工程软件,以3.5 mm圆柱体模拟置钉,设计出最佳钉道并建立反向模板;最后将数据导入3D打印机,制作出颈椎模型及个体化导板。手术操作则先暴露椎体,将导板紧贴于椎板,沿导向通道置入螺钉,见图3。毛克政等[37]于标本置钉64枚,准确率97%;YU等[38]于标本置钉164枚,准确率96.3%;郝申申等[39]置钉132枚,准确率94.7%;Sugawara等[40]置钉358枚,准确率98.32%。该法简化了手术操作,做到了个体化治疗;但是该法耗时较长,无法用于急诊手术,同时导板的精确性会在三维建模、3D打印、导板固定等过程中受到影响。"
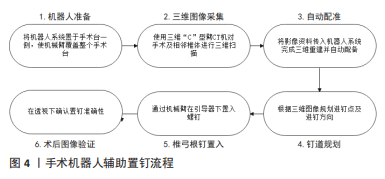
姜良海等[41]用标杆型3D打印导板辅助置钉技术置钉,相较于通道型导板,标杆型导板以导向标杆和导向孔取代了通道型导板的导向通道,进钉点以导向孔为准,进钉方向以导向标杆为准;其报道置钉304枚,准确率99.3%。相较于通道型导板,该法最大的优势在于可在术中对标杆方向进行调整,减少置钉偏差。同通道型导板一样,该法存在一定的局限,一是需要充分剥离软组织;二是术中需要保持导板与椎板等结构紧密贴合;三是不适用于肿瘤、严重骨质增生导致椎板等结构严重破坏者。 张东升等[42]采用改良金属导板置入螺钉,与传统树脂导板相比,金属导板除材料不同外,还多出2个固定孔,可防止置钉时导板移位;其报道于人体椎体标本置钉48枚,准确率87.5%。该法的置钉准确率比传统树脂导板更高,但是该法仍处于标本实验阶段,还需临床试验进一步验证。 2.3.4 手术机器人辅助置钉技术 手术机器人辅助置钉是一类借助手术机器人的精确术中导航优势和稳定的手术操作性能帮助手术医生置钉的技术。手术机器人系统由机械臂与工作站组成,手术过程主要包括6个部分[43-44]:①机器人准备:将机器人系统置于手术台一侧,使机械臂覆盖整个手术台;②三维图像采集:使用三维“C”型臂CT机对手术及相邻椎体进行三维扫描;③自动配准:将影像资料传入机器人系统完成三维重建并自动配备;④钉道规划:根据三维图像规划进钉点及进钉方向;⑤椎弓根钉置入:通过机械臂在引导器下置入螺钉;⑥术后图像验证:透视下确认置钉准确性,见图4。 吕振东等[44]比较了机器人辅助置钉与传统徒手置钉的差异,其中前者置钉49枚,准确率98.0%,后者置钉61枚,准确率83.6%。SU等[45]比较了机器人辅助置钉与透视引导下置钉,置钉准确率分别为97.2%及90.7%,手术机器人辅助置钉的准确率显著提高,并且减少了术者及患者的X射线暴露,且一次成功率明显高于其他置钉方式;但该法对硬件设备要求较高,难以大面积推广。 ZHU等[46]应用基于结构光跟踪的无标记机器人辅助置钉,相较于一般手术机器人辅助置钉,该法不同点在于将结构光扫描获得的图像与CT扫描获得的图像对照,算法分析后直接根据相对位置生成机器人运动命令,规划手术路径,而不需要依靠光学标记建立手术工具和手术路径之间的空间关系;据其报道进钉点的平均位置误差仅为(0.28±0.16) mm, 平均角度误差仅为(0.49±0.24)°。该法目前还处于体外模测试阶段,期待进一步的尸体实验及临床应用结果。 2.3.5 其他置钉技术 (1)经皮微创的置钉技术:李绪辉[47]利用后路经皮微创置钉,经后正中入路暴露病变节段至双侧关节突,在切口两侧,找到椎弓根在皮肤的投影,作1.5-2.0 cm的纵行切口直至皮下筋膜。将穿刺针敲进椎弓根内,确保矢状面X射线透视不穿过椎弓根内壁、水平面与上下终板保持水平,延穿刺针套入导针,通过软通道置入螺钉,其报道置钉122枚,准确率98.36%。 郎昭等[48]利用导航系统经皮微创置钉,在导航系统的引导下于邻近椎体同侧椎弓根体表投影连线中点做一小切口,用微创套筒扩张钉道至骨表面,开路器钻探钉道,确认无误后置钉,共置钉34枚,准确率82.4%。KOMATSUBARA等[49]在导航下经外侧入路微创置钉,置钉120枚,准确率98%。 该法只需行一小切口即可完成手术,避免了对周围软组织的过度损伤,但同时因操作空间受到限制,对手术医生的解剖知识与置钉技术提出了较高的要求。与传统置钉技术相比,该法同样有损伤颈髓及椎血管的可能,因此对该法适应证的掌握尤为重要。 (2)基于CT的虚拟钉道安全核参考法置钉技术:唐文 等[50]提出基于CT影像虚拟构建的“安全核区”参考法置钉技术,将60例成人C3、C4颈椎的CT影像资料导入Mimics软件虚拟构建安全核区,并以安全核区为置钉参考置钉,总有效率为97.5%(117/120)。而且虚拟钉道安全核区可转换至X射线正侧位片上,表现为正位X射线片对应CT冠状面,即正位X射线片安全核区在双侧椎弓根中点连线与上下钩椎关节外缘连线交点周围(0.66±0.61) mm范围内;侧位X射线片对应CT矢状面,即侧位X射线片上安全核区在椎弓根中轴线与椎体后壁交点前方C3(2.08±0.41) mm或C4(2.34± 0.60) mm处。该法应用CT影像数据构建的虚拟“安全核区”转换至X射线正侧位片上,为二维影像寻找置钉参考提供了临床依据;但是该法样本量偏小,存在一定偏差,且目前还处于理论阶段,尚需要通过人体标本试验及临床应用进一步验证。 (3)自制导向器辅助置钉技术:赖必华等[51]利用钉道内壁探查法结合自制的导向器置钉,该导向器由导向杆、锚定杆、带角度仪的弧形手把,共计三部分组成。术前根据影像学测量出最佳的进钉点及进钉角度,术中利用导向器严格控制进钉角度。利用开路器钻探钉道,探针进至10 mm时透视确认外展角度,如阻力较大,则减小外展角度10°深入至 20 mm;如阻力仍大,则考虑钉道内壁阻挡。然后逐步向外探查深入至20 mm,明确钉道内外侧壁完整后置入螺钉;其报道置钉71枚,良好率91%。WANG等[52]利用类似的导向器于标本置钉50枚,准确率96%,该法以导向器作为角度控制,钉道内壁作为参考,起到了对内倾角控制的双重保障,提高了置钉准确性;但是该法同样学习曲线陡峭,且内壁更容易破裂,颈髓损伤的可能性也更大。"
| [1] ALSHAMI AM. Prevalence of spinal disorders and their relationships with age and gender. Saudi Med J. 2015;36(6):725-730. [2] KOLENKIEWICZ M, WŁODARCZYK A, WOJTKIEWICZ J. Diagnosis and Incidence of Spondylosis and Cervical Disc Disorders in the University Clinical Hospital in Olsztyn, in Years 2011–2015. BioMed Res Int. 2018; 2018:5643839. [3] ABUMI K, ITOH H, TANEICHI H, et al. Transpedicular Screw Fixation for Traumatic Lesions of the Middle and Lower Cervical Spine. J Spinal Disord. 1994;7(1):19-28. [4] KIM M, CHO H, KWAK D. A new anatomical approach of cervical lateral mass for cervical pedicle screw and paravertebral foramen screw insertion. PLOS ONE. 2019;14(7):e0219119. [5] WESTERMANN L, SPEMES C, EYSEL P, et al. Computer tomography-based morphometric analysis of the cervical spine pedicles C3-C7. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2018;160(4):863-871. [6] KIM M, CHO H, KWAK D, et al. Characteristics of regional bone quality in cervical vertebrae considering BMD: Determining a safe trajectory for cervical pedicle screw fixation. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(1):217-223. [7] HUH J, HYUN JH, PARK HG, et al. Three Dimensional Measurement of Ideal Trajectory of Pedicle Screws of Subaxial Cervical Spine Using the Algorithm Could Be Applied for Robotic Screw Insertion. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2019;62(4):376-381. [8] PAN Z, ZHONG J, XIE S, et al. Accuracy and Safety of Lateral Vertebral Notch-Referred Technique Used in Subaxial Cervical Pedicle Screw Placement. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown). 2019;17(1):52-60. [9] 李治国. 颈椎椎弓根形态个体化术前应用CT测量评价的临床意义[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志,2016,14(6):130-132. [10] 陈希,刘新宇,杨青,等. 颈椎椎间孔螺钉、椎弓根螺钉与侧块螺钉钉道的影像学测量比较[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020,40(19):1337-1347. [11] ZHOU Z, WEN C, SUN Q, et al. Morphometric measurement of the cervical spine for minimally invasive pedicle screw fixation using reverse engineering and three-dimensional reconstruction. Int J Med Robot. 2017;13(3):e1765. [12] Xu R,Kang A,ebraHein NA, et al. Anatomic Relation Between the Cervical Pedicle and the Adjacent Neural Structures. Spine. 1999;24(5): 451-454. [13] 周树成,张鹏.下颈椎椎弓根相邻解剖结构的应用研究[J]. 局解手术学杂志,2016,25(1):30-32. [14] 袁欣华,庞清江,许柯,等.下颈椎椎弓根通道穿透力及突破力的生物力学研究[J].现代实用医学,2012,24(10):1096-1098+1201. [15] 陈希,刘新宇,杨青,等. 颈椎椎间孔螺钉、侧块螺钉及椎弓根螺钉的生物力学强度比较[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020,40(4):236-243. [16] 薛晓北,王玉冰,纪经涛,等.区域法下颈椎椎弓根钉植入技术的临床应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(12):1515-1520. [17] WU C, HUANG Z, PAN Z, et al. Coronal Multiplane Reconstructed Computed Tomography Image Determining Lateral Vertebral Notch-Referred Pedicle Screw Entry Point in Subaxial Cervical Spine: A Preclinical Study. World Neurosurg. 2017;103:322-329. [18] LUO J, WU C, HUANG Z, et al. The accuracy of the lateral vertebral notch-referred pedicle screw insertion technique in subaxial cervical spine: a human cadaver study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017;137(4):517-522. [19] LIU J, LI Y, WU Y, et al. A novel method of cervical pedicle screw placement from C3 to C5 and its clinical applications. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(8):504-512. [20] LI Y, LIU J, LIU Y, et al. Cervical pedicle screw fixation at C6 and C7 A cadaveric study. Indian J Orthop. 2015;49(4):465-470. [21] 邹云龙,刘宇龙,李野,等. 颈椎椎弓根置钉精确度的临床研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2017,37(4):226-235. [22] LEE JH, CHOI BK, HAN IH, et al. Cervical Pedicle Screw Placement Using Medial Funnel Technique. Korean J Spine. 2017;14(3):84-88. [23] KARAIKOVIC EE, YINGSAKMONGKOL W, GAINES RW, et al. Accuracy of Cervical Pedicle Screw Placement Using the Funnel Technique. Spine. 2001;26(22):2456-2462. [24] LIU B, LIU X, SHEN X, et al. The “slide technique”-a novel free-hand method of subaxial cervical pedicle screw placement. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):399. [25] LEE S, SEO J, LEE MK, et al. Widening of the safe trajectory range during subaxial cervical pedicle screw placement: advantages of a curved pedicle probe and laterally located starting point without creating a funnel-shaped hole. J Neurosurg Spine. 2017;27(2):150-157. [26] BURCEV A, PAVLOVA O, DIACHKOV K, et al. Easy method to simplify “freehand” subaxial cervical pedicle screw insertion. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2017;8(4):390-395. [27] PARK J, LEE JY, LEE BH, et al. Free-Hand Cervical Pedicle Screw Placement by Using Para-articular Minilaminotomy: Its Feasibility and Novice Neurosurgeons’ Experience. Global Spine J. 2020: 2192568220919089. [28] 黄晓东,袁登荣,方弘伟,等. 经肌间隙入路椎弓根螺钉置入治疗下颈椎骨折脱位15例效果分析[J]. 中国乡村医药,2016,23(8):20-21. [29] 方弘伟,袁登荣,黄晓东,等. 经肌间隙入路行下颈椎椎弓根螺钉置入的应用解剖与初步临床应用[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2015,31(8):699-703. [30] 余伟,王蕾,何思峰,等. X射线透视辅助徒手法与CT三维图像导航下颈椎椎弓根置钉准确率的对比[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017, 21(11):1758-1763. [31] 刘亚军,乐晓峰,郑山,等. 计算机导航辅助颈椎椎弓根螺钉内固定技术[J]. 骨科临床与研究杂志,2018,3(3):182-187. [32] 姜廷华,李继斌,王自鸿,等. CT导航置钉与传统X线透视徒手置钉法在下颈椎椎弓根置钉的临床对比[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2018,39(4): 397-400. [33] SHIMOKAWA N, TAKAMI T. Surgical safety of cervical pedicle screw placement with computer navigation system. Neurosurg Rev. 2017; 40(2):251-258. [34] 黄圣斌,谢兆林,谭海涛,等. O型臂导航系统辅助颈椎椎弓根置钉的应用效果研究[J]. 广西医科大学学报,2018,35(7):976-979. [35] SOURABH C, RAHMATULLAH BARH, LIM LW, et al. Cervical pedicle screw instrumentation is more reliable with O-arm-based 3D navigation: analysis of cervical pedicle screw placement accuracy with O-arm-based 3D navigation. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(11):2729-2736. [36] WADA K, TAMAKI R, INOUE T, et al. Cervical Pedicle Screw Insertion Using O-Arm-Based 3D Navigation: Technical Advancement to Improve Accuracy of Screws. World Neurosurg. 2020;139:e182-e188. [37] 毛克政,王庆德,梅伟,等. 3D打印个体化导板辅助颈椎椎弓根螺钉置钉的可行性研究[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2016,32(1):47-50. [38] YU Z, ZHANG G, CHEN X, et al. Application of a novel 3D drill template for cervical pedicle screw tunnel design: a cadaveric study. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(9):2348-2356. [39] 郝申申,刘志斌,王飞,等. 3D打印个性化导航模板在后路下颈椎椎弓根螺钉置入中的应用价值[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(11): 1701-1706. [40] SUGAWARA T, KANEYAMA S, HIGASHIYAMA N, et al. Prospective Multicenter Study of a Multistep Screw Insertion Technique Using Patient-Specific Screw Guide Templates for the Cervical and Thoracic Spine. Spine. 2018;43(23):1685-1694. [41] 姜良海,谭明生,杨峰,等. 标杆型3D打印导板辅助颈椎椎弓根置钉的临床应用[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2016,36(5):257-264. [42] 张东升,王建华,李洪吉,等. 改良金属个性化导航模板辅助颈椎椎弓根置钉的准确性[J]. 脊柱外科杂志,2019,17(5):340-344. [43] LIEBERMAN IH, KISINDE S, HESSELBACHER S. Robotic-Assisted Pedicle Screw Placement During Spine Surgery. JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2020; 10(2):e0020. [44] 吕振东,陈智,韩应超,等. 机器人辅助颈椎后路椎弓根螺钉置入手术治疗颈椎病的置钉精确度与临床疗效[J]. 骨科临床与研究杂志,2020,5(3):131-137. [45] SU X, LV Z, CHEN Z, et al. Comparison of Accuracy and Clinical Outcomes of Robot-Assisted Versus Fluoroscopy-Guided Pedicle Screw Placement in Posterior Cervical Surgery. Global Spine J. 2020:2192568220960406. [46] ZHU S, ZHAO Z, PAN Y, et al. Markerless robotic pedicle screw placement based on structured light tracking. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2020;15(8):1347-1358. [47] 李绪辉. 后路微创经皮椎弓根钉内固定术治疗下颈椎骨折脱位的效果观察[J]. 广东医科大学学报,2020,38(4):417-420. [48] 郎昭,田伟,袁强,等. 术中即时三维导航引导经皮微创椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗颈椎骨折的临床研究[J]. 中华外科杂志,2015,53(10): 752-756. [49] KOMATSUBARA T, TOKIOKA T, SUGIMOTO Y, et al. Minimally Invasive Cervical Pedicle Screw Fixation by a Posterolateral Approach for Acute Cervical Injury. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(10):466-469. [50] 唐文,邱兴庭,赵凯. 基于CT影像的下颈椎椎弓根钉道虚拟构建法[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020,40(20):1409-1419. [51] 赖必华,吴建斌,叶宏,等. 导向器结合钉道内壁探查法在下颈椎椎弓根螺钉置入中应用研究[J]. 中国骨伤,2017,30(9):805-809. [52] WANG Q, XING R, ZENG Y. Design and application of subaxial cervical pedicle screw placement guide device. Exp Ther Med. 2019;17(6): 4357-4362. |
| [1] | Wang Jianping, Zhang Xiaohui, Yu Jinwei, Wei Shaoliang, Zhang Xinmin, Xu Xingxin, Qu Haijun. Application of knee joint motion analysis in machanism based on three-dimensional image registration and coordinate transformation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-5. |
| [2] | Zhang Yufang, Lü Meng, Mei Zhao. Construction and verification of a full spine biomechanical model of adolescent scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1351-1356. |
| [3] | Bai Zixing, Cao Xuhan, Sun Chengyi, Yang Yanjun, Chen Si, Wen Jianmin, Lin Xinxiao, Sun Weidong. Construction and biomechanical analysis of ankle joint finite element model in gait cycle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1362-1366. |
| [4] | Liu Feng, Feng Yi. Finite element analysis of different Kirschner wire tension bands on transverse patella fractures during gait cycle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1367-1371. |
| [5] | Pan Baoshun, Fang Zhen, Gao Mingjie, Fang Guiming, Chen Jinshui. Design for posterior atlantoaxial internal fixation system with fusion cage based on imaging data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1372-1376. |
| [6] | Li Canhui, Wu Zhengjie, Zeng Yanhui, He Yinghao, Situ Xiaopeng, Du Xuelian, Hong Shi, He Jiaxiong. Advantage and disadvantage of robot-assisted sacroiliac screw placement and traditional fluoroscopy in orthopedic surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1434-1438. |
| [7] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [8] | Wen Mingtao, Liang Xuezhen, Li Jiacheng, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Mechanical stability of Sanders II type calcaneal fractures fixed by two internal fixation methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 838-842. |
| [9] | Huang Hao, Hong Song, Wa Qingde. Finite element analysis of the effect of femoral component rotation on patellofemoral joint contact pressure in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 848-852. |
| [10] | Zheng Yongze, Zheng Liqin, He Xingpeng, Chen Xinmin, Li Musheng, Li Pengfei, Lin Ziling. Extended finite element modeling analysis of femoral neck fracture based on ABAQUS software [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 853-857. |
| [11] | Wei Bing, Chang Shan. Finite element analysis of different angles of nail placement in sagittal plane of spinal fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 864-869. |
| [12] | Liu Yuhang, Zhou Jianqiang, Xu Xuebin, Qu Xingyue, Li Ziyu, Li Kun, Wang Xing, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe, Zhang Shaojie. Establishment and validation of finite element model of lower cervical spine in 6-year-old children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 870-874. |
| [13] | Song Yuxin, Zhang Tongtong, Niu Jianxiong, Wang Zengping, Wen Jie, Zhang Qunli, Xue Wen, Liu Lin. Precise screw placement of 3D printing model and orthopedic robot in spinal deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 904-907. |
| [14] | Yang Jun, Yang Qun, Zhang Rui, Jiang Chang. A novel slidable pedicle screw-rod system for lumbar tuberculosis: promoting bone graft fusion by producing stress stimulation to fused segment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 914-918. |
| [15] | Guo Xiaohui, Song Xizheng, Xiang Hanrui, Kang Zhaorong, Li Daming, Kang Yu, Hu Jun, Sheng Kai. External spinal fixation elastic stress in the treatment of jumping spinal fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 919-923. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||