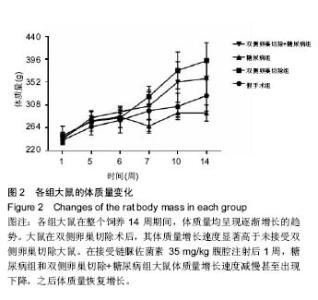
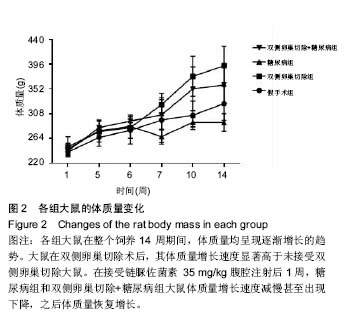
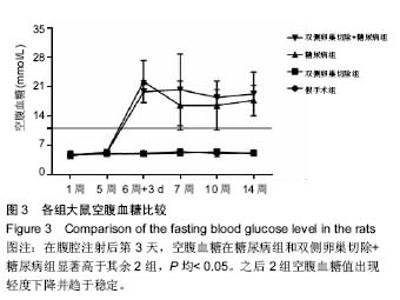
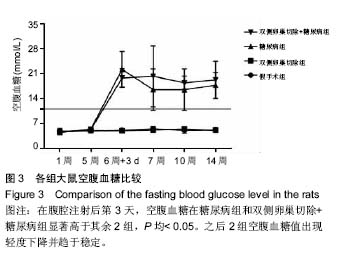
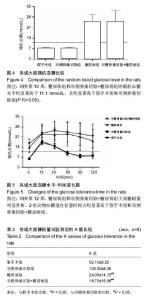
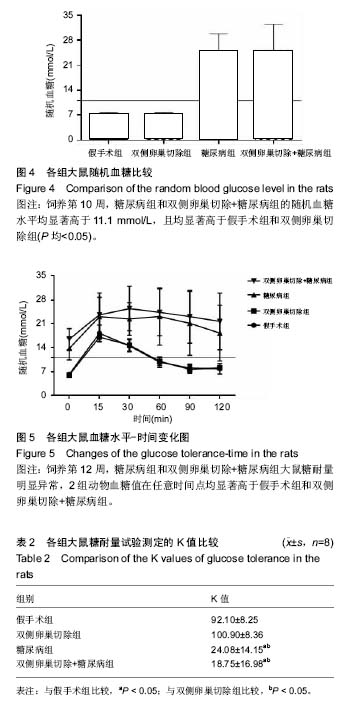
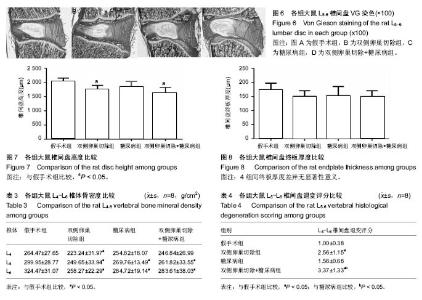
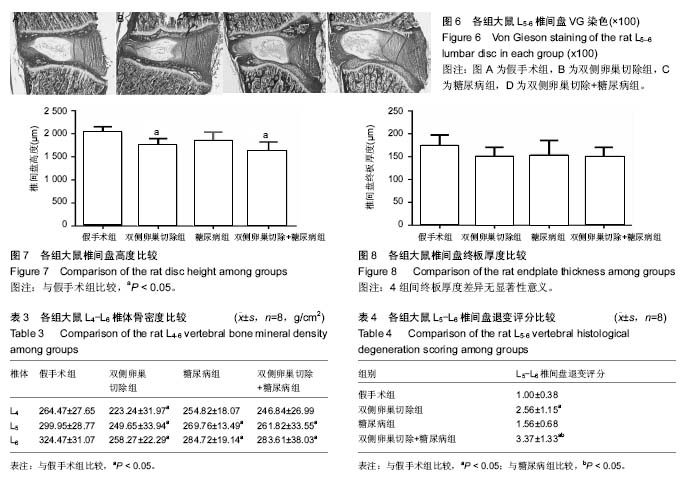
| [1] Robinson D, Mirovsky Y, Halperin N, et al. Changes in proteoglycans of intervertebral disc in diabetic patients. A possible cause of increased back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998;23(8): 849-855; discussion 856.[2] Licciardone JC, Kearns CM, Hodge LM, et al. Osteopathic manual treatment in patients with diabetes mellitus and comorbid chronic low back pain: subgroup results from the OSTEOPATHIC Trial. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2013;113(6): 468-478.[3] Takahashi S, Suzuki A, Toyoda H, et al. Characteristics of diabetes associated with poor improvements in clinical outcomes after lumbar spine surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38(6): 516-522.[4] Luoma K, Riihimaki H, Luukkonen R, et al. Low back pain in relation to lumbar disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(4): 487-492.[5] Park JB, Byun CH, Park EY. Rat Notochordal Cells Undergo Premature Stress-Induced Senescence by High Glucose. Asian Spine J. 2015;9(4): 495-502.[6] 陈森,徐振华,贾吉光,等.糖尿病大鼠终板微血管改变与髓核细胞凋亡的关系[J]. 武汉大学学报(医学版), 2008, 29(5): 584-586.[7] Gorth DJ, Shapiro IM, Risbud MV. Discovery of the drivers of inflammation induced chronic low back pain: from bacteria to diabetes. Discov Med. 2015;20(110): 177-184.[8] He J, Lian C, Fang Y, et al. Effect of CXCL10 receptor antagonist on islet cell apoptosis in a type I diabetes rat model. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(11): 14542-14548.[9] Srinivasan K, Viswanad B, Asrat L, et al. Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose streptozotocin-treated rat: a model for type 2 diabetes and pharmacological screening. Pharmacol Res. 2005;52(4): 313-320.[10] Hu H, Xu M, Qi R, et al. Sitagliptin downregulates retinol-binding protein 4 and upregulates glucose transporter type 4 expression in a type 2 diabetes mellitus rat model. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(10): 17902-17911.[11] Gopalakrishnan V, Iyyam Pillai S, Subramanian SP. Synthesis, Spectral Characterization, and Biochemical Evaluation of Antidiabetic Properties of a New Zinc-Diosmin Complex Studied in High Fat Diet Fed-Low Dose Streptozotocin Induced Experimental Type 2 Diabetes in Rats. Biochem Res Int. 2015;2015: 350829.[12] Tajbakhsh S, Aliakbari K, Hussey DJ, et al. Differential Telomere Shortening in Blood versus Arteries in an Animal Model of Type 2 Diabetes. J Diabetes Res. 2015;2015:153829.[13] Wang T, Zhang L, Huang C, et al. Relationship between osteopenia and lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration in ovariectomized rats. Calcif Tissue Int. 2004;75(3):205-213.[14] Hofbauer LC, Brueck CC, Singh SK, et al. Osteoporosis in patients with diabetes mellitus. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22(9): 1317-1328.[15] Schwartz AV. Diabetes Mellitus: Does it Affect Bone? Calcif Tissue Int. 2003;73(6): 515-519.[16] Pan H, Wu N, Yang T, et al. Association between bone mineral density and type 1 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2014; 30(7): 531-542.[17] Nakashima A, Nakashima R, Ito T, et al. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors prevent bone loss in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 2004;21(9): 1020-1024.[18] Hou K, Lin C, Wu B, et al. Exogenetic insulin increased bone mineral densityin middle-aged male patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2015;28(6 Suppl): 2227-2230.[19] Luo Y, Zhang L, Wang WY, et al. The inhibitory effect of salmon calcitonin on intervertebral disc degeneration in an ovariectomized rat model. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(8): 1691-1701.[20] Zhang W, Shen X, Wan C, et al. Effects of insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation: differential signalling via Akt and ERK. Cell Biochem Funct. 2012;30(4): 297-302.[21] Clemens TL, Karsenty G. The osteoblast: an insulin target cell controlling glucose homeostasis. J Bone Miner Res. 2011; 26(4): 677-680.[22] Fields AJ, Berg-Johansen B, Metz LN, et al. Alterations in intervertebral disc composition, matrix homeostasis and biomechanical behavior in the UCD-T2DM rat model of type 2 diabetes. J Orthop Res. 2015;33(5): 738-746. |