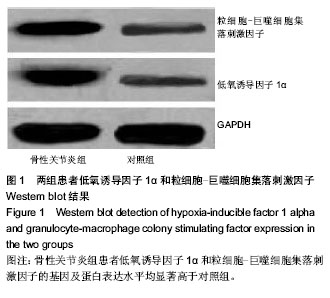
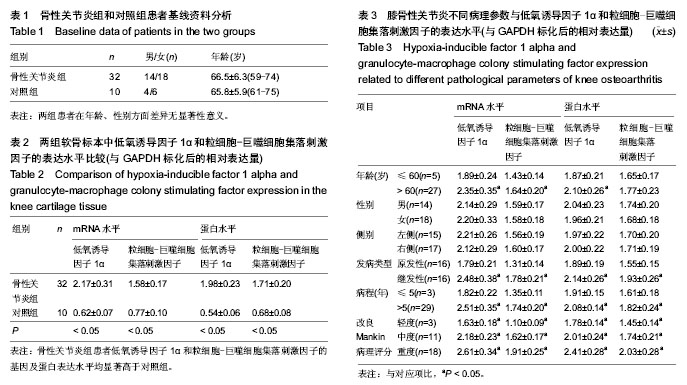
| [1] Wu L, Huang X, Li L,et al.Insights on biology and pathology of hif-1alpha/-2alpha, tgfbeta/bmp, wnt/beta-catenin, and nf-kappab pathways in osteoarthritis. Curr Pharm Des. 2012; 18(22):3293-3312.
[2] 李笑颜,赵建,曾文,等.晚期骨关节炎患者关节软骨细胞中HIF-1α和VEGF的表达[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版,2010,30(7): 812-816.
[3] Pfander D, Swoboda B, Cramer T. The role of hif-1alpha in maintaining cartilage homeostasis and during the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Arthritis research & therapy.2006;8:104.
[4] van der Sluijs JA, Geesink RG, van der Linden AJ,et al. The reliability of the Mankin score for osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 1992;10(1):58-61.
[5] Pfander D, Gelse K.Hypoxia and osteoarthritis: How chondrocytes survive hypoxic environments. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2007;19(5):457-462.
[6] Murab S, Chameettachal S, Bhattacharjee M,et al. Matrix-embedded cytokines to simulate osteoarthritis-like cartilage microenvironments. Tissue engineering Part A. 2013;19(15-16):1733-1753.
[7] Hoff P, Buttgereit F, Burmester GR,et al.Osteoarthritis synovial fluid activates pro-inflammatory cytokines in primary human chondrocytes. Int Orthop. 2013;37(1):145-151.
[8] Zhang SL, Liu HQ, Xu XZ,et al. Effects of exercise therapy on knee joint function and synovial fluid cytokine levels in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Molecular medicine reports. 2013; 7(1):183-186.
[9] Cook AD, Pobjoy J, Steidl S, et al. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor is a key mediator in experimental osteoarthritis pain and disease development. Arthritis Res Therapy.2012;14:R199.
[10] Loeser RF. Osteoarthritis year in review 2013: biology. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(10):1436-1442.
[11] Wenham CY, Conaghan PG. New horizons in osteoarthritis. Age and ageing. 2013;42(3):272-278.
[12] 彭勇,陈勇,邬秀娣,等. HIF-1α及VEGF 在类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞中的表达及意义[J]. 浙江医学,2013,35(18): 1628-1631.
[13] Ryu JH, Chae CS, Kwak JS,et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha is an essential catabolic regulator of inflammatory rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS biology. 2014;12(6):e1001881.
[14] Mendes SO, dos Santos M, Peterle GT,et al. HIF-1alpha expression profile in intratumoral and peritumoral inflammatory cells as a prognostic marker for squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. PLoS One.2014;9(1):e84923.
[15] Rathnasamy G, Ling EA, Kaur C. Hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha mediates iron uptake which induces inflammatory response in amoeboid microglial cells in developing periventricular white matter through MAP kinase pathway. Neuropharmacology.2014;77:428-440.
[16] Hirohata S, Nagai T, Asako K, et al. Induction of type b synoviocyte-like cells from plasmacytoid dendritic cells of the bone marrow in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Clin Immunol.2011;140:276-283.
[17] Atawia RT, Mosli HH, Tadros MG,et al. Modulatory effect of silymarin on inflammatory mediators in experimentally induced benign prostatic hyperplasia: emphasis on PTEN, HIF-1alpha, and NF-kappaB. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2014; 387(12):1131-1140.
[18] 吴振彪,卢宁,王彦宏,等.GM-CSF对类风湿性关节炎患者单核细胞合成MMP的影响[J].现代免疫学,2005, 25(5):394-397.
[19] 张延辉,高春阳,李少华.骨性关节炎患者退变软骨及滑膜组织中细胞因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(37): 6671-6675.
[20] Yudoh K, Nakamura H, Masuko-Hongo K, et al.Catabolic stress induces expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (hif)-1 alpha in articular chondrocytes: Involvement of hif-1 alpha in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Arthritis research & therapy. 2005;7:R904-914.
[21] Pfander D, Cramer T, Swoboda B. Hypoxia and hif-1alpha in osteoarthritis. Int Orthop.2005;29:6-9.
[22] Schipani E, Ryan HE, Didrickson S,et al. Hypoxia in cartilage: HIF-1alpha is essential for chondrocyte growth arrest and survival. Genes & development.2001; 15(21):2865-2876.
[23] Nakao K, Kubota S, Doi H, et al. Collaborative action of m-csf and ctgf/ccn2 in articular chondrocytes: Possible regenerative roles in articular cartilage metabolism. Bone.2005;36:884-892.
[24] Yoshimatsu T, Saitoh A, Ryu JN,et al.Characterization of immortalized human chondrocytes originated from osteoarthritis cartilage. Int J Mol Med. 2001;8(4):345-351.
[25] 徐苏洋,陈永强.低氧诱导因子与骨关节炎[J].国际骨科学杂志,2011,32(6):384-385. |