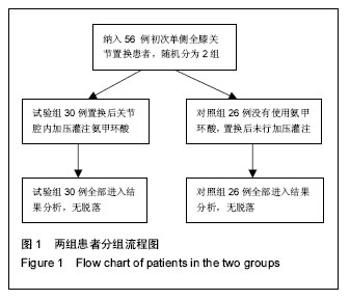
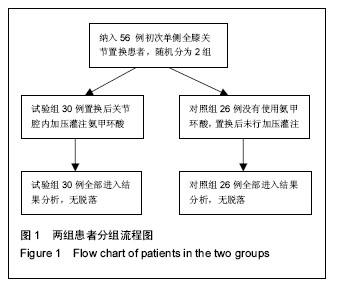
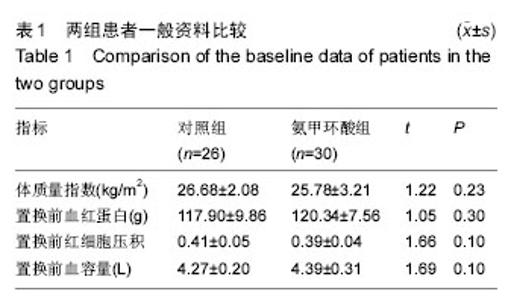
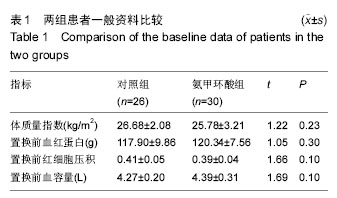
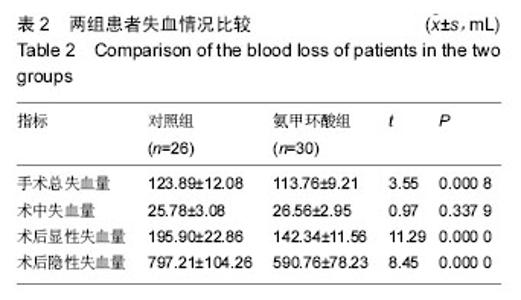
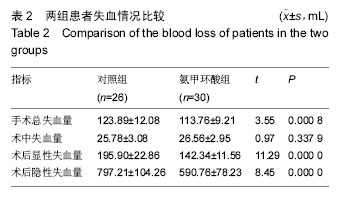
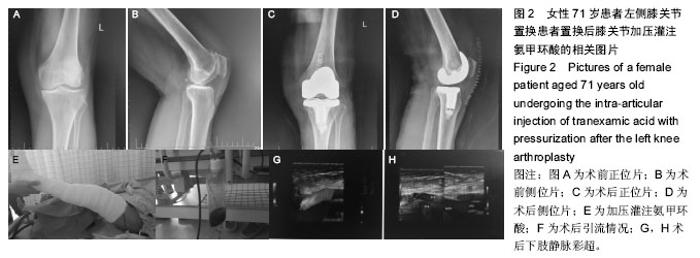
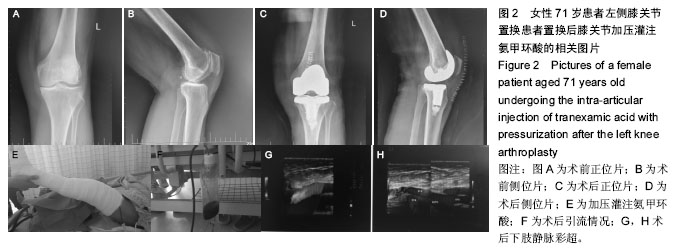
| [1] Ferraris VA,Brown JR,Despotis GJ, et al. 2011 update to theSociety of Thoracic Surgeons and the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists blood conservation clinicalpracticeguidelines.Ann Thorac Surg. 2011; 91(3):944-982.
[2] Lemaire R.Strategies for blood management in orthopaedicand trauma surgery.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(9):1128-1136.
[3] Roy SP, Tanki UF,Dutta A,et al.Efficacy of intra-articulartranexamic acid in blood loss reduction following primaryunilateral totaI knee arthroplasty.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2012;20(12): 2494-2501.
[4] 刘林,杨治,姚建锋,等.局部注射联合静脉滴注氨甲环酸对人工全膝关节置换术失血量的影响[J]. 川北医学院学报, 2015,30(5): 611-614.
[5] Mutsuzaki H,Ikeda K.Intra-articular injection of tranexamicacid via drain plus drain-clamping to reduce blood loss incementless total knee arthroplasty.J Orthop Surg Res.2012; 7:32.
[6] 高福强,李子剑,张克,等.人工关节置换术后隐性失血计算方法的初步探析[J].中华外科杂志,2011,49(12):1144- 1145.
[7] Li B,Wen Y,Wu H,et al.The effect of tourniquet use onhidden blood loss in total knee arthroplasty.Int Orthop.2009;33(5):1263-1268.
[8] Lotke PA,Faralli VJ,Orenstein EM,et al.Blood loss after total knee replacement:effects of tourniquet release and continuous passive motion.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1991;73(7):1037-1040.
[9] 闵令田,翁文杰,邱勇,等.关节腔内灌注氨甲环酸降低全膝关节置换手术出血的前瞻性随机对照研究[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2014,8(4):482-486.
[10] Tetro AM,Rudan JF. The effects of a pneumatic tourniquet on blood loss in total knee arthroplasty.Can J Surg. 2001;44:33-38.
[11] 陈德胜,金群华,李亚平,等. 隐性失血对双侧人工全膝关节同期置换手术的影响[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2007, 15(17):1290-1292.
[12] Panteli M,Papakostidis C,Dahabreh Z,et al. Topical tranexamic acid in total knee replacement: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee. 2013;20: 300-309.
[13] Hiippala S,Strid L,Wennerstrand M,et al. Tranexamic acid (Cyklokapron) reduces perioperative blood loss associated with total knee arthroplasty. Br J Anaesth. 1995;74:534-537.
[14] 王英明,孔荣,禹德万,等.氨甲环酸静脉滴注联合关节腔注射对初次全膝关节置换患者术后出血量的影响[J].安徽医学,2015,36(11):1350-1352.
[15] 杨朝君,孙智文,张爱民,等.氨甲环酸关节腔注射联合引流管夹闭3h在单侧全膝关节置换术中止血效果分析[J]. 中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2014,9(6):640-645.
[16] Akizuki S,Yasukawa Y,Takizawa T. A new method of hemostasis for cementless total knee arthroplasty.Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 1997;56:222-224.
[17] Kim TK,Chang CB, Koh IJ. Practical issues for the use of tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(8):1849-1858.
[18] Alshryda S, Mason J, Vaqhela M, et al. Topical(intra-articular)tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and transfusion rates following to-tal knee replacement:a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95:1961-1968.
[19] Sa-gasoongsong P,Channoom T,Kawinwonggowit V,et al. Postop-erative blood loss reduction in computer-assisted surgery total knee replacement by low dose intra-articular tranexamic acid injection together with 2-hour clamp drain: a prospective tripleblinded randomized controlled trial.Orthop Rev(Pavia). 2011;3(2):e12.
14:00 2016-11-9 |