Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (19): 2966-2972.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.19.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Analgesic effect of femoral and sciatic nerve block under multimodal analgesia in total knee arthroplasty
Gao Wei-lu1, Li Hong1, Liu Bi-quan1, Hu Yong1, Liu Jing-jun1, Yin Li1, Liu Hu2, Mei Bin2, Yin Zong-sheng1
- 1Department of Joint and Bone Tumor Surgery, 2Department of Anesthesiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230022, Anhui Province, China
-
Online:2017-07-08Published:2017-08-10 -
Contact:Yin Zong-sheng, M.D., Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Joint and Bone Tumor Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230022, Anhui Province, China -
About author:Gao Wei-lu, M.D., Attending physician, Department of Joint and Bone Tumor Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230022, Anhui Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gao Wei-lu, Li Hong, Liu Bi-quan, Hu Yong, Liu Jing-jun, Yin Li, Liu Hu, Mei Bin, Yin Zong-sheng. Analgesic effect of femoral and sciatic nerve block under multimodal analgesia in total knee arthroplasty
share this article
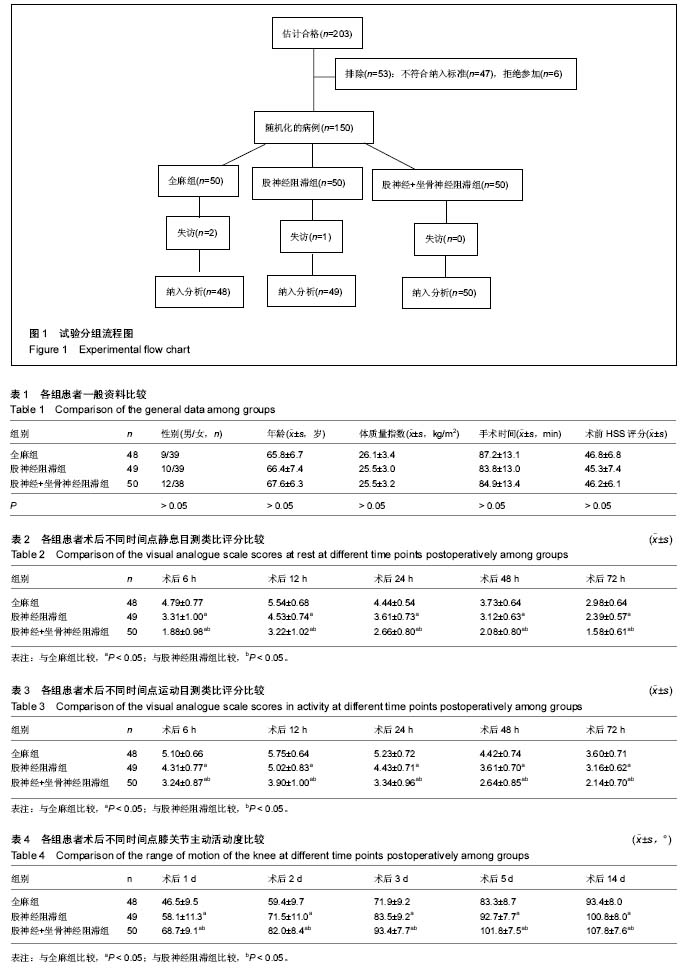
2.1 参与者数量分析 纳入拟行单侧全膝关节置换的患者150例,随机分为3组,每组50例。全麻组术后3个月时失访1例,术后6个月时失访1例;术后6个月时股神经阻滞组失访1例,其余病例均得到随访。最终对全麻组48例、股神经阻滞组49例、股神经+坐骨神经阻滞组50例,共147例患者的数据资料进行整理和分析,见图1。 2.2 基线资料比较 3组患者在性别、年龄、体质量指数、手术时间、术前HSS评分方面的差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表1。 2.3 术后疼痛程度的比较 股神经阻滞组、股神经+坐骨神经阻滞组术后各时间点静息目测类比评分、运动目测类比评分均低于全麻组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);股神经+坐骨神经阻滞组术后各时间点静息目测类比评分、运动目测类比评分均低于股神经阻滞组,差异有显著性意义 (P < 0.05),见表2,3。 2.4 术后膝关节主动活动度的比较 股神经阻滞组、股神经+坐骨神经阻滞组术后各时间点膝关节主动活动度均大于全麻组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);股神经+坐骨神经阻滞组术后各时间点膝关节主动活动度均大于股神经阻滞组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表4。"
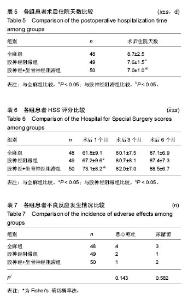
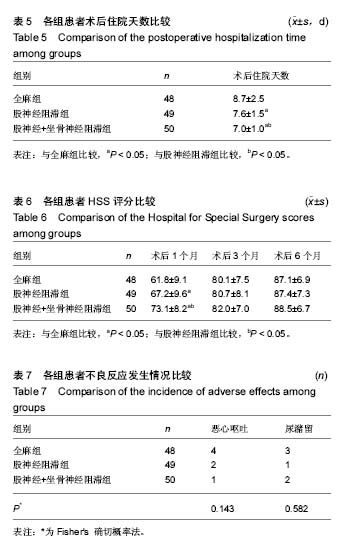
2.5 术后住院天数的比较 股神经阻滞组、股神经+坐骨神经阻滞组术后住院天数均少于全麻组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);股神经+坐骨神经阻滞组术后住院天数少于股神经阻滞组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表5。 2.6 HSS评分的比较 术后1个月时,股神经阻滞组、股神经+坐骨神经阻滞组的HSS评分均高于全麻组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);股神经+坐骨神经阻滞组的HSS评分高于股神经阻滞组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。术后3个月和6个月时,3组间HSS评分的差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表6。 2.7 不良反应 全麻组4例患者出现恶心呕吐,股神经阻滞组2例,股神经+坐骨神经阻滞组1例,恶心呕吐发生率的差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。全麻组3例患者出现尿潴留,股神经阻滞组1例,股神经+坐骨神经阻滞组2例,尿潴留发生率的差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表7。 股神经阻滞组未出现股神经损伤,股神经+坐骨神经阻滞组未出现股神经、坐骨神经损伤。3组患者均未出现嗜睡、精神障碍、跌倒、穿刺部位感染等并发症。"
| [1] Lungu E, Vendittoli PA, Desmeules F. Preoperative Determinants of Patient-reported Pain and Physical Function Levels Following Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review. Open Orthop J. 2016;10: 213-231.[2] Shin HJ, Soh JS, Lim HH, et al. In-plane three-step needle insertion technique for ultrasound-guided continuous femoral nerve block after total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective review of 488 cases. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2016; 69(6): 587-591.[3] Albrecht E, Morfey D, Chan V, et al. Single-injection or continuous femoral nerve block for total knee arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014; 472(5): 1384-1393.[4] Jakobsen TL, Kehlet H, Husted H, et al. Early progressive strength training to enhance recovery after fast-track total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2014; 66(12): 1856-1866.[5] Grosu I, Thienpont E, De Kock M, et al. Dynamic view of postoperative pain evolution after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective observational study. Minerva Anestesiol. 2016; 82(3): 274-283.[6] Baratta JL, Gandhi K, Viscusi ER. Perioperative pain management for total knee arthroplasty. J Surg Orthop Adv. 2014; 23(1): 22-36.[7] Burns LC, Ritvo SE, Ferguson MK, et al. Pain catastrophizing as a risk factor for chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. J Pain Res. 2015; 8: 21-32.[8] Aveline C, Roux AL, Hetet HL, et al. Pain and recovery after total knee arthroplasty: a 12-month follow-up after a prospective randomized study evaluating Nefopam and Ketamine for early rehabilitation. Clin J Pain. 2014; 30(9): 749-754.[9] Lewis GN, Rice DA, McNair PJ, et al. Predictors of persistent pain after total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2015; 114(4): 551-561.[10] 杨礼庆,马超,杜帅. 人工全膝关节置换术围手术期疼痛管理现状[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(3): 247-250.[11] Lewis C, Gunta K, Mitchell K, et al. Effectiveness of multimodal pain management protocol in total knee arthroplasty patients. Orthop Nurs. 2012;31(3):153-159.[12] Lamplot JD, Wagner ER, Manning DW. Multimodal pain management in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled trial. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29(2): 329-334.[13] Moore A, Makinson G, Li C. Patient-level pooled analysis of adjudicated gastrointestinal outcomes in celecoxib clinical trials: meta-analysis of 51,000 patients enrolled in 52 randomized trials. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013; 15(1): R6.[14] Leese PT, Hubbard RC, Karim A, et al. Effects of celecoxib, a novel cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, on platelet function in healthy adults:a randomized, controlled trial.J Clin Pharmacol. 2000;40:124-132.[15] Huang YM, Wang CM, Wang CT, et al. Perioperative celecoxib administration for pain management after total knee arthroplasty-a randomized, controlled study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2008; 9: 77.[16] Mammoto T, Fujie K, Mamizuka N, et al. Effects of postoperative administration of celecoxib on pain management in patients after total knee arthroplasty: study protocol for an open-label randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2016; 17: 45-51.[17] Chloropoulou P, Iatrou C, Vogiatzaki T, et al. Epidural anesthesia followed by epidural analgesia produces less inflammatory response than spinal anesthesia followed by intravenous morphine analgesia in patients with total knee arthroplasty. Med Sci Monit. 2013; 19: 73-80.[18] 刘艳,刘海林.连续股神经阻滞与静脉自控对全膝关节置换的镇痛效果比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(48): 7736-7740.[19] Tang Q, Li X, Yu L, et al. Preoperative ropivacaine with or without tramadol for femoral nerve block in total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2016; 24(2): 183-187.[20] Cip J, Erb-Linzmeier H, Stadlbauer P,et al. Continuous intra-articular local anesthetic drug instillation versus discontinuous sciatic nerve block after total knee arthroplasty. J Clin Anesth. 2016; 35: 543-550.[21] Nader A, Kendall MC, Manning DW, et al. Single-dose adductor canal block with local infiltrative analgesia compared with local infiltrate analgesia after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2016; 41(6): 678-684.[22] Macrinici G, Drescher M, Ascan J, et al. Poster 391 Prospective, Double-blind, Randomized Clinical Trial to Compare Single Shot Adductor Canal Nerve Block Versus Femoral Nerve Block Combined with Local Infiltration Analgesia: Postoperative Functional Outcomes After Total Knee Arthroplasty. PM R. 2016; 8(9S): S288-S289.[23] 康鹏德,王浩洋,沈彬,等. 加入局部浸润镇痛的多模式镇痛在全膝关节置换中的应用[J].中华骨科杂志, 2013,33(3):246-251.[24] Schinsky MF, McCune C, Bonomi J. Multifaceted comparison of two cryotherapy devices used after total knee arthroplasty: cryotherapy device comparison. Orthop Nurs. 2016; 35(5): 309-316. [25] Wang F, Zhou Y, Sun J, et al. Influences of continuous femoral nerve block on knee function and quality of life in patients following total knee arthroplasty. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015; 8(10): 19120-19125.[26] Peng L, Ren L, Qin P, et al. Continuous femoral nerve block versus intravenous patient controlled analgesia for knee mobility and long-term pain in patients receiving total knee replacement: a randomized controlled trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014; 2014: 569107.[27] Kinjo S, Lim E, Sands LP, et al. Does using a femoral nerve block for total knee replacement decrease postoperative delirium? BMC Anesthesiol. 2012; 12: 4.[28] Wegener JT, van Ooij B, van Dijk CN, et al. Long-term pain and functional disability after total knee arthroplasty with and without single-injection or continuous sciatic nerve block in addition to continuous femoral nerve block: a prospective, 1-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2013; 38(1): 58-63.[29] Sato K, Adachi T, Shirai N, et al. Continuous versus single-injection sciatic nerve block added to continuous femoral nerve block for analgesia after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, double-blind study. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2014; 39(3): 225-229.[30] Akkaya A, Tekelioglu UY, Demirhan A, et al. Ultrasound- guided femoral and sciatic nerve blocks combined with sedoanalgesia versus spinal anesthesia in total knee arthroplasty. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2014; 67(2): 90-95.[31] Carvalho Júnior LH, Temponi EF, Paganini VO, et al. Reducing the length of hospital stay after total knee arthroplasty: influence of femoral and sciatic nerve block. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2015; 61(1): 40-43.[32] Jules-Elysee KM, Wilfred SE, Memtsoudis SG, et al. Steroid modulation of cytokine release and desmosine levels in bilateral total knee replacement: a prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94(23): 2120-2127.[33] Jianda X, Yuxing Q, Yi G, et al. Impact of preemptive analgesia on inflammatory responses and rehabilitation after primary total knee arthroplasty: a controlled clinical study. Sci Rep. 2016; 6: 30354.[34] Gwam CU, Mistry JB, Richards IV, et al. Does Addition of Adductor Canal Blockade to Multimodal Periarticular Analgesia Improve Discharge Status, Pain Levels, Opioid Use, and Length of Stay after Total Knee Arthroplasty? J Knee Surg. 2017. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1602131. [Epub ahead of print][35] Pinsornsak P, Nangnual S, Boontanapibul K. Multimodal infiltration of local anaesthetic in total knee arthroplasty; is posterior capsular infiltration worth the risk? a prospective, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(4):483-488. [36] Koh HJ, Koh IJ, Kim MS, et al. Does Patient Perception Differ Following Adductor Canal Block and Femoral Nerve Block in Total Knee Arthroplasty? A Simultaneous Bilateral Randomized Study. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(6):1856-1861.[37] Gwam CU, Mistry JB, Jha P, et al. Efficacy of Adductor Canal Blockade Compared to Multimodal Peri-Articular Analgesia Following Total Knee Arthroplasty. Surg Technol Int. 2017;30. pii: sti30/804. [Epub ahead of print][38] Gwam CU, Mistry JB, Khlopas A, et al. Does Addition of Multimodal Periarticular Analgesia to Adductor Canal Block Improve Lengths of Stay, Pain, Discharge Status, and Opioid Use After Total Knee Arthroplasty? J Arthroplasty. 2017; 32(5):1470-1473. |
| [1] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [2] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [3] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [4] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [5] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [6] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [7] | Sun Xiao-xin1, Zhou Wei2, Zuo Shu-ping3, Liu Hao1, Song Jing-feng1, Liang Chun-yu1. Morphological characteristics for the magnetic resonance imaging assessment of discoid lateral meniscal tears in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1104-1109. |
| [8] | Lin Han-wen, Wen Jun-mao, Huang Chao-yuan, Zhou Chi, Tang Hong-yu. Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1110-1114. |
| [9] | Zhang Yun-ge, Song Ke-guan. Periprosthetic osteolysis induced by wear particles: research progress of calcineurin/activated T cell nuclear factor signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1115-1122. |
| [10] | Liu Wei, Huang Jian. Applied research and progress of three-dimensional printing technology in joint replacement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1123-1130. |
| [11] | Liu Jian-kun, Deng Shu-cai. Status and role of three-dimensional printing technology in spine surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1131-1136. |
| [12] | Xi Li-cheng, Li Hong-yu. Research progress of the influence of alcohol on the local microenvironment of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1137-1142. |
| [13] | Ye Xiang-yang, Sun Xiang, Tang Li-xin, Zhen Ping, Geng Bin, Wang Hua-lei, Zhao Yu-guo. Acetabular liner wear of cross-linked versus conventional polyethylene for total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1143-1148. |
| [14] | Liang Xin, Wang Heng, Li Xian-rong. Preoperative application of alprazolam for patients with anxiety and depression and pain after total knee arthroplasty: its safety and effectiveness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 985-992. |
| [15] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||