Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (7): 1026-1031.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0112
Previous Articles Next Articles
Related factors for dysphagia after single-level anterior cervical descectomy and fusion
Lu Ying-jie, Bao Wei-guo, Zou Jun, Zhou Feng, Jiang Wei-min, Yang Hui-lin, Zhang Zhi-ming, Zhu Xue-song
- Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Online:2018-03-08Published:2018-03-08 -
Contact:Zhang Zhi-ming, M.D., Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China Zhu Xue-song, M.D., Researcher, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Lu Ying-jie, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81772358; the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program), No. 2015AA020316
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lu Ying-jie, Bao Wei-guo, Zou Jun, Zhou Feng, Jiang Wei-min, Yang Hui-lin, Zhang Zhi-ming, Zhu Xue-song. Related factors for dysphagia after single-level anterior cervical descectomy and fusion[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(7): 1026-1031.
share this article
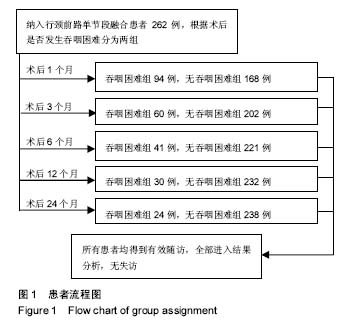
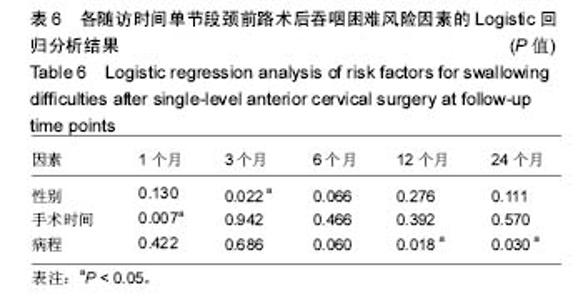
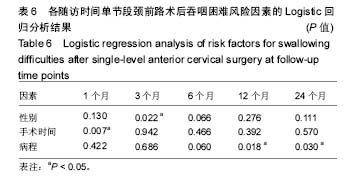
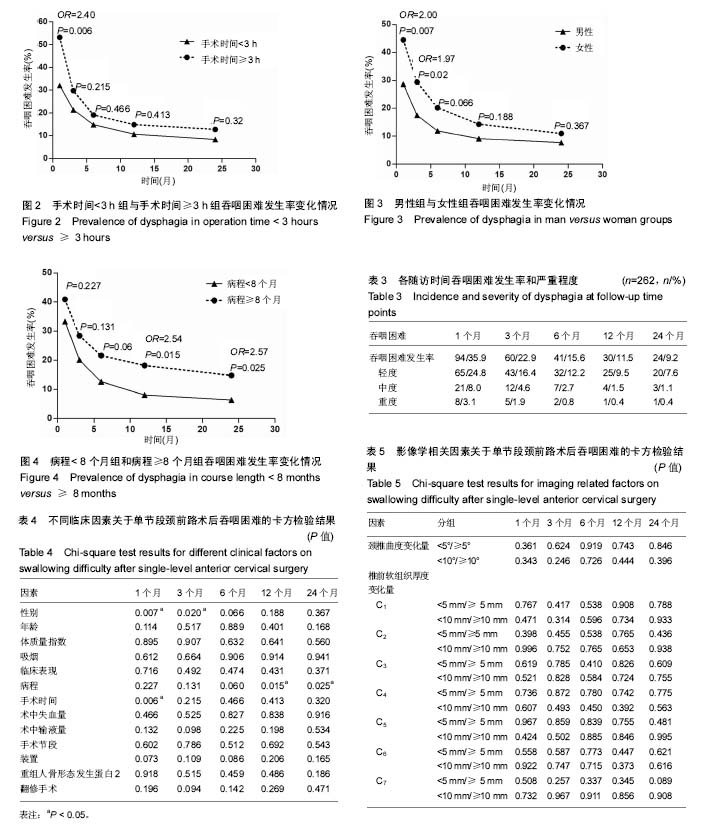
2.2 吞咽困难发生率 吞咽困难的总体发生率在术后1,3,6,12和24个月分别为35.9%,22.9%,15.6%,11.5%和9.2%。在术后1个月,出现轻度、中度和重度吞咽困难的发生率分别是24.8%,8.0%和3.1%;而在术后6个月,轻度、中度和重度吞咽困难的发生率分别是12.2%,2.7%和0.8%;术后24个月,各发生率分别是7.6%,1.1%和0.4%。吞咽困难发生率随时间呈下降趋势,且在术后的前6个月降低最为明显(表3)。 2.3 吞咽困难相关因素分析 统计分析显示,术后第1,3,6,12,24个月有吞咽障碍患者较无吞咽困难患者有相似的年龄、体质量指数、临床表现、失血量和输液量、手术节段分布、装置和rhBMP-2的使用、翻修手术、颈椎曲度和椎前软组织厚度变化量,见表4,5。 根据手术时间长短将患者分成< 3 h和≥3 h两组,在术后第1个月≥3 h组较<3 h组患者有明显较高的吞咽困难率(53.2% vs 32.1%;OR=2.40;95%CI:1.27-4.56;P=0.006),见图2和表4。女性患者术后吞咽困难的发生率均高于男性患者,其中术后1个月(44.5% vs 28.7%;OR= 2.00;95%CI:1.20-3.33;P=0.007)和3个月(29.4% vs 17.5%;OR=1.97;95%CI:1.10-3.53;P=0.02)差异具有统计学意义,见图3和表4。此外,首次发现术前病程≥8个月组与< 8个月组相比,其吞咽困难率在术后12个月(18.2% vs 8.0%;OR=2.54;95%CI,1.18-5.48;P=0.015)和24个月(14.8% vs 6.3%;OR=2.57;95% CI:1.10-6.00;P=0.025)均明显较高,且差异有显著性意义(图4和表4)。 Logistic回归分析显示:在术后1个月,手术时间≥3 h与术后吞咽困难的发生相关;术后3个月,女性与术后吞咽困难的发生相关;术后12个月和24个月,病程≥8个月与术后吞咽困难的发生相关(表6)。"
| [1] Riley LR, Vaccaro AR, Dettori JR, et al. Postoperative dysphagia in anterior cervical spine surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010; 35(9 Suppl):S76-S85.[2] Cho SK, Lu Y, Lee DH. Dysphagia following anterior cervical spinal surgery: a systematic review. Bone Joint J.2013;95-B(7):868-873.[3] Ratnaraj J, Todorov A, McHugh T, et al. Effects of decreasing endotracheal tube cuff pressures during neck retraction for anterior cervical spine surgery. J Neurosurg.2002;97(2 Suppl): 176-179.[4] Bazaz R, Lee MJ, Yoo JU. Incidence of dysphagia after anterior cervical spine surgery: a prospective study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(22):2453-2458.[5] Frempong-Boadu A, Houten JK, Osborn B, et al. Swallowing and speech dysfunction in patients undergoing anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: a prospective, objective preoperative and postoperative assessment. J Spinal Disord Tech.2002;15(5):362-368.[6] Lee MJ, Bazaz R, Furey CG, et al. Risk factors for dysphagia after anterior cervical spine surgery: a two-year prospective cohort study. Spine J.2007;7(2):141-147.[7] Siska P A, Ponnappan RK, Hohl JB, et al. Dysphagia after anterior cervical spine surgery: a prospective study using the swallowing-quality of life questionnaire and analysis of patient comorbidities. Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2011;36(17):1387-1391.[8] 陈波,瞿霞,杨毅,等. 颈前路单节段融合钢板内固定后吞咽困难的危险因素分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(13):2028-2033.[9] Smith-Hammond CA, New KC, Pietrobon R, et al. Prospective analysis of incidence and risk factors of dysphagia in spine surgery patients: comparison of anterior cervical, posterior cervical, and lumbar procedures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2004;29(13):1441-1446.[10] Kalb S, Reis MT, Cowperthwaite MC, et al. Dysphagia after anterior cervical spine surgery: incidence and risk factors. World Neurosurg.2012;77(1):183-187.[11] Puvanesarajah V, Jain A, Shimer AL, et al. Complications and mortality following one to two-level anterior cervical fusion for cervical spondylosis in patients above 80 years of age. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2017;42(9):E509-E514.[12] Olsson EC, Jobson M, Lim MR. Risk factors for persistent dysphagia after anterior cervical spine surgery. Orthopedics. 2015;38(4):e319-e323.[13] Liu JM, Tong WL, Chen XY, et al. The incidences and risk factors related to early dysphagia after anterior cervical spine surgery: A prospective study. PLoS One.2017;12(3):e173364.[14] Lee MJ, Bazaz R, Furey CG, et al. Influence of anterior cervical plate design on Dysphagia: a 2-year prospective longitudinal follow-up study. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18(5):406-409.[15] Qi M, Chen H, Liu Y, et al. The use of a zero-profile device compared with an anterior plate and cage in the treatment of patients with symptomatic cervical spondylosis: A preliminary clinical investigation. Bone Joint J.2013;95-B(4):543-547.[16] Hofstetter CP, Kesavabhotla K, Boockvar JA. Zero-profile anchored spacer reduces rate of dysphagia compared with acdf with anterior plating. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015;28(5): E284-E290.[17] Khaki F, Zusman NL, Nemecek AN, et al. Postoperative prevertebral soft tissue swelling does not affect the development of chronic dysphagia following anterior cervical spine surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2013;38(9):E528-E532.[18] Riley LR, Skolasky RL, Albert TJ, et al. Dysphagia after anterior cervical decompression and fusion: prevalence and risk factors from a longitudinal cohort study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2005; 30(22):2564-2569.[19] Fengbin Y, Xinwei W, Haisong Y, et al. Dysphagia after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: a prospective study comparing two anterior surgical approaches. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(5): 1147-1151.[20] Rihn JA, Kane J, Albert TJ, et al. What is the incidence and severity of dysphagia after anterior cervical surgery? Clin Orthop Relat Res.2011;469(3):658-665.[21] Buttermann GR. Prospective nonrandomized comparison of an allograft with bone morphogenic protein versus an iliac-crest autograft in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. Spine J. 2008;8(3):426-435.[22] Lu DC, Tumialan LM, Chou D. Multilevel anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with and without rhBMP-2: a comparison of dysphagia rates and outcomes in 150 patients. J Neurosurg Spine.2013;18(1):43-49.[23] Shi S, Li XF, Zhao QT, et al. Risk factors for dysphagia after single-level anterior cervical decompression with arthroplasty or fusion: a prospective study comparing 2 zero-profile implants. World Neurosurg. 2016;95:148-155.[24] Suk KS, Kim KT, Lee SH, et al. Prevertebral soft tissue swelling after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with plate fixation. Int Orthop.2006;30(4):290-294.[25] Smith GW, Robinson RA. The treatment of certain cervical-spine disorders by anterior removal of the intervertebral disc and interbody fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1958;40-A(3):607-624.[26] Clave P, Shaker R. Dysphagia: current reality and scope of the problem[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;12(5):259-270.[27] Song KJ, Choi BW, Kim HY, et al. Efficacy of postoperative radiograph for evaluating the prevertebral soft tissue swelling after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. Clin Orthop Surg. 2012;4(1):77-82. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Tang Xiaokai, Li Weiming. Role and mechanism of Nel-like molecule-1 in promoting bone fusion after spinal fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3914-3920. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||