| [1] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,许印坎.实用骨科学[M].3版.北京:人民军医出版社,2005:950-954. [2] 胡继红.分娩性臂丛神经损伤54例综合康复疗效观察[J].中国康复理论与实践,2006,12(7):633.[3] 贾文清.分娩引起臂丛神经损伤相关因素的分析[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2008,11(7):96-97.[4] Giuffre JL, Kakar S, Bishop AT,et al. Current concepts of the treatment of adult brachial plexus injuries.J Hand Surg Am. 2010;35(4):678-688.[5] 刘慧敏.电针加穴位注射治疗臂丛神经损伤疗效观察[J].现代诊断与治疗,2012,23(7):891-892.[6] 周俊明,徐晓君,张沈煜,等.臂丛神经损伤规范化康复治疗的临床研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2011,26(2):124-127.[7] 陈拓.臂丛神经损伤的诊断与治疗研究[J].亚太传统医药,2009, 5(2):69-70.[8] 崔庆元.48例臂丛神经损伤的疗效观察[J].中外健康文摘,2011,8(48):86-88.[9] 傅国,顾立强,秦本刚,等.臂丛损伤患者的生存质量调查分析[J].中华显微外科杂志,2010,33(2):125-128.[10] Kitajima I, Doi K, Hattori Y,et al. Evaluation of quality of life in brachial plexus injury patients after reconstructive surgery. Hand Surg. 2006;11(3):103-107.[11] Bailey R, Kaskutas V, Fox I,et al. Effect of upper extremity nerve damage on activity participation, pain, depression, and quality of life.J Hand Surg Am. 2009;34(9):1682-1688. [12] 沈杰,兰凤敏.臂丛神经损伤患者术后生活质量影响因素的研究进展[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2013,22(4):455-456.[13] 徐乐勤,丁道芳,李晓锋,等.胚胎干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2011,17(1):51-53.[14] 杨建华,李长德,翟饶生,等.胚胎干细胞移植修复脊髓损伤的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2007,21(5):487-491.[15] 韩发彬.诱导多能干细胞及其在神经退行性疾病研究中的应用[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2012,34(5):403-414.[16] 刘宁,扈佃磊,徐韬,等.神经干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(10):1809-1813.[17] 范广明,张文彬,张赛,等.神经生长因子联合神经干细胞移植治疗大鼠脊髓损伤[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(14): 2572-2578.[18] Ishii T, Ohsugi K, Nakamura S,et al. Gene expression of oligodendrocyte markers in human amniotic epithelial cells using neural cell-type-specific expression system.Neurosci Lett. 1999;268(3):131-134.[19] Miki T, Lehmann T, Cai H,et al. Stem cell characteristics of amniotic epithelial cells.Stem Cells. 2005;23(10):1549-1559. [20] Sakuragawa N, Thangavel R, Mizuguchi M,et al. Expression of markers for both neuronal and glial cells in human amniotic epithelial cells.Neurosci Lett. 1996;209(1):9-12.[21] Sakuragawa N, Kakinuma K, Kikuchi A,et al. Human amnion mesenchyme cells express phenotypes of neuroglial progenitor cells. J Neurosci Res. 2004;78(2):208-214.[22] Bertelli JA, Mira JC. Behavioral evaluating methods in the objective clinical assessment of motor function after experimental brachial plexus reconstruction in the rat.J Neurosci Methods. 1993;46(3):203-208.[23] 郑玲玲,肖波.大鼠臂丛神经损伤后脊髓运动神经元再生轴突的路径[J].中国康复医学杂志,2011,26(2):120-123.[24] 张豫庆.成人臂丛神经损伤的临床诊治探讨[J].中国实用神经疾病志,2012,15(16):47-48.[25] 杨飞,刘斌,田新良,等.羊膜细胞移植对帕金森病鼠纹状体中多巴胺神经元的促再生作用[J].中国老年学杂志,2001,21(5): 358-360.[26] 杨新新.人羊膜上皮细胞侧脑室移植对帕金森病大鼠模型行为、多巴胺能神经元、神经递质影响的实验研究[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2009,26(5):532-535.[27] Xue SR, Yang XX, Dong WL, et al. Monoamine alterations and rotational asymmetry in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease following lateral ventricle transplantation of human amniotic epithelial cells. Neural Regen Res. 2009;4(12): 1007-1012.[28] 吴智远,卢奕,惠国祯,等.人羊膜细胞移植治疗大鼠脊髓损伤的实验研究[J].中华神经外科杂志,2006,22(9):572-574.[29] Lu Y, Hui GZ, Wu ZY, et al. Transformation of human amniotic epithelial cells into neuron-like cells in the microenvironment of traumatic brain injury in vivo and in vitro. Neural Regen Res. 2011;6(10):744-749.[30] Okawa H, Okuda O, Arai H,et al. Amniotic epithelial cells transform into neuron-like cells in the ischemic brain. Neuroreport. 2001;12(18):4003-4007.[31] 郭兵,许家军.大鼠羊膜上皮细胞体外诱导可分化为类神经干细胞[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(19):3503-3507.[32] 陈旭东,华新宇,王晓兰.黄芪注射液对人羊膜上皮细胞向神经细胞分化作用及存活的影响[J].神经解剖学杂志,2012,28(4): 368-374.[33] 陈旭东,刘红敏,华新宇,等.人羊膜上皮细胞体外诱导分化为神经样细胞的研究[J].实用医学杂志,2011,27(8):1336-1338.[34] 夏剑,徐永丰,许永武,等.人羊膜上皮细胞移植修复尺经损伤的临床研究[J].实用临床医学,2011,12(12):44-45,51. [35] Wei JP, Zhang TS, Kawa S,et al. Human amnion-isolated cells normalize blood glucose in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice.Cell Transplant. 2003;12(5):545-552.[36] Takashima S, Ise H, Zhao P,et al. Human amniotic epithelial cells possess hepatocyte-like characteristics and functions. Cell Struct Funct. 2004;29(3):73-84.[37] 耿娟娟,崔勇,邱书奇.羊膜上皮细胞的体外培养及干细胞特性研究[J].实用医学杂志,2012,28(2):172-174.[38] Akle CA, Adinolfi M, Welsh KI,et al. Immunogenicity of human amniotic epithelial cells after transplantation into volunteers. Lancet. 1981;2(8254):1003-1005. |

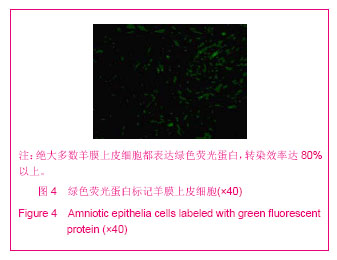
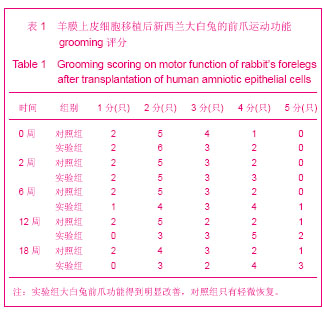

.jpg)