| [1] 王行予,常建英.移植肾失功后的血液透析患者发生肾反应并发症的临床观察[J].透析与人工器官,2000,11(4):3.[2] 陆石,吕振裕. 38例移植肾失功能后恢复血液透析的体会[J].临床泌尿外科杂志,1992,7(4):222-223.[3] 马潞林.慢性移植肾失功的原因和影响因素[J].中国血液净化, 2003,2(11):593,转617.[4] 王珏,张炜.慢性移植肾失功的危险因素及预测指标[J].国际泌尿系统杂志,2006,26(4):476-478.[5] 邹和群.移植肾失功分类诊断和治疗[J].器官移植内科学杂志, 2010,5(2):70-82.[6] 徐恩五,于立新,曾伟生,等.肾移植术后早期移植肾失功的危险因素分析[J].器官移植,2010,1(5):295-299.[7] 李晏强,罗皓,邹和群,等. MCP-1、RANTES在慢性移植肾失功肾组织中的表达及意义[J].浙江临床医学,2012,14(8):897-900.[8] 郭义峰.肾移植术后急性排斥反应的治疗和预防[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版, 2013,7(1):10-11. [9] 徐卫波,张广伟,杜信毅,等.肾移植术后肾功能恢复延迟原因分析及预防[J].山东医药,2010,50(7): 98-99.[10] 万有贵,陈博,徐志强,等.肾移植后早期监测环孢素A血药浓度峰值的临床意义[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(5): 843-846.[11] 裴向克,白玉梅.群体反应性抗体阳性对移植肾功能影响的临床研究[J].中国综合临床, 2013,29(4):399-402.[12] El-Shafey EM, EI-Nagar GF, Selim MF, et al. Is serum cystatin C an accurate endogenous marker of glomerular fiheration rate for detection of early renal impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus? Ren Fail. 2009;31(5):355-359.[13] 林开颜,张晋,蒙喻,等.人体表面积计算方法对内生肌酐清除率测定结果的影响[J].贵阳医学院学报,2012,37(4):397-398.[14] United States Renal Data System (USRDS). The USRDS Dialysis Morbidity and Mortality Study: Wave 2. Am J Kidney Dis. 1997;30: S67-85.[15] 殷苏燕.中药口服辅以灌肠治疗早中期慢性肾衰临床观察[J].中国民间疗法,2008,16(2): 34-35.[16] 农振勇.中西医结合治疗慢性肾功能衰竭40例临床观察[J].实用中西医结合临床,2011,11(3): 29-30.[17] Schulman G, Hakim RM. Improving outcomes in chronic hemodialysis patients: should dialysis be initiated earlier? Semin Dial. 1996;9:225-228.[18] 林家谊.维持性血液透析患者生活质量影响因素及健康教育研究进展[J].中华现代护理杂志,2012,18(16):1980-1981.[19] 王莉君,袁伟杰,谷立杰,等.终末期肾脏病维持性透析患者生活质量状态及α酮酸对其影响[J].中国血液净化, 2013, 12(3): 121-125.[20] 程宗华.维持性血液透析患者生活质量状况的调查[J].中国医疗前沿,2012,7(21):96.[21] Wu F, Cui L, Gao X,et al. Quality of Life in Peritoneal and Hemodialysis Patients in China. Ren Fail. 2013;35(4): 456-459.[22] 季大玺.浅谈透析时机对患者长期生存的影响[J].医学研究生学报, 2011,24(12): 1233-1235.[23] 殷俊,袁伟杰.终末期肾脏病患者透析时机的选择[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2012,28(7):575-578.[24] Rosansky S, Glassock RJ, Clark WF. Early start of dialysis:A critical review. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;6:1222-1228.[25] 李红,高继宁,行延霞,等.老年慢性肾衰竭患者开始血液透析时机的观察[J].中华保健医学杂志, 2013,15(2):177-178.[26] Hemodialysis Adequacy 2006 Work Group. Clinical practice guidelines for hemodialysis adequacy,update 2006. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;48 Suppl 1: S2- 90.[27] 王苏娅,陈江华,王逸民,等.乙、丙型肝炎病毒感染对肾移植患者长期存活的影响[J].中华器官移植杂志,2000,21(1):8-10.[28] 严春寅,王晖,陈卫国,等.丙型肝炎病毒感染对肾移植患者免疫功能的影响[J].中华器官移植杂志,2000,21(5):296-297.[29] 于立新,王志鹏,付绍杰,等.丙型肝炎病毒感染对肾移植术后影响的临床研究[J].第一军医大学学报,2004, 24(6):682-684.[30] 谢续标,蓝恭斌,彭龙开,等.乙肝/丙肝阳性供肾移植临床观察[J].中南大学学报:医学版, 2009,34(3):259-263.[31] 毕文浩,陈正,马俊杰,等.丙型肝炎病毒阳性受者肾移植后的安全13性分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(31): 5789- 5792.[32] 兰天猋,任星峰,彭隽.乙、丙型肝炎病毒感染的肾移植受者肝损害临床观察[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志, 2011, 12(9): 785-787, 后插3.[33] 陈小勇,李斌华,闫雪华.失代偿期丙肝肝硬化患者并发症消除后的抗病毒治疗[J].中华实验和临床病毒学杂志,2012,26(3): 229-231.[34] 黄英,杨颜茹.丙型肝炎后肝硬化与骨质疏松的临床研究[J].吉林医学,2012,33(23): 4938-4939. [35] 庄桂凤,张杰伟,曾仕平.肝源性糖尿病临床分析[J].中国医药, 2012,7(9):1105-1106. [36] Philpneri M, Bastani B. Kidney disease in patients with chronic hepatitis. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2001;3:79-83.[37] Daghestani L, Pomeroy C. Renal manifestations of hepatitis Cinfection. Am J Med. 1999;106:347-354. [38] Korevaar JC, Jansen MA, Dekker FW, et al. Evaluat ion of DOQI guidelines: early start of dialysis treatment is not associated with better healthrelated quality of life. National Kidney Foundation Dialysis Out come Quality Initiative. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;39(1):108-115.[39] 陈灏珠.实用内科学[M].12版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2006:2104.[40] 傅芳婷.把握慢性肾衰竭患者的透析时机[J].中国全科医学杂志, 2010,13(12):22. |
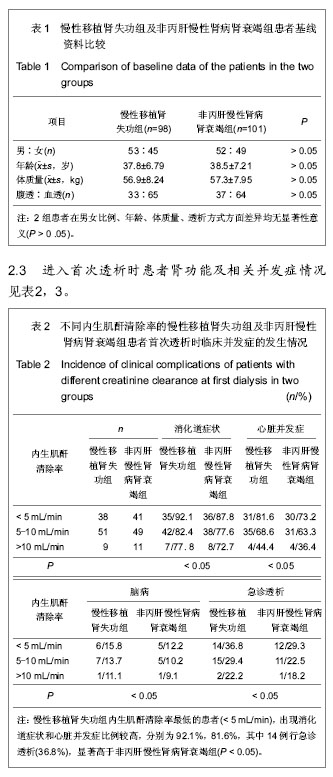
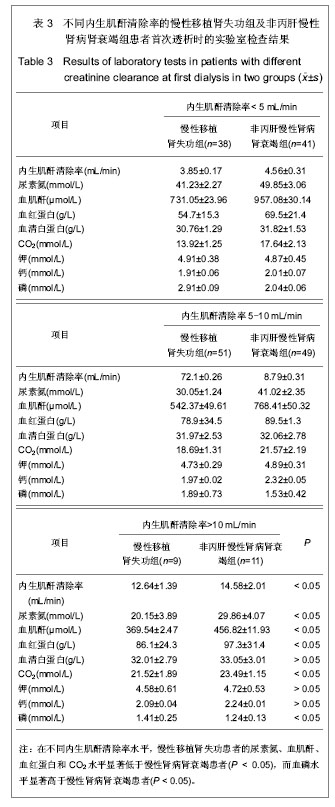


.jpg)