| [1]刘梦桃,贾安琦.镍铬合金烤瓷修复体对局部牙龋组织损伤的机制[J].国外医学:口腔医学分册,2004,31(1): 44-45.[2]张荣和,宋琦,张勇.镍铬合金烤瓷冠组织面离子析出的研究[J].国际口腔医学杂志, 2008,35(6):611-614.[3]Imirzalioglu P,Alaaddinoglu E,Yilmaz Z,et al.Influence of recasting different types of dental alloys on gingival fibroblast cytotoxicity. J Prosthet Dent.2012;107(1):24-33.[4]Muyzer G,de Waal EC,Uitterlinden AG.Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA.Appl Environ Microbiol.1993;59(3):695-700.[5]Su C,Lei L,Duan Y,et al.Culture-independent methods for studying environmental microorganisms: methods, application, and perspective.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol.2012;93(3): 993-1003.[6]Mikesková H,Novotný C,Svobodová K.Interspecific interactions in mixed microbial cultures in a biodegradation perspective. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol.2012;95(4):861-870.[7]Cocolin L,Dolci P,Rantsiou K.Biodiversity and dynamics of meat fermentations: the contribution of molecular methods for a better comprehension of a complex ecosystem.Meat Sci. 2011;89(3):296-302.[8]Zheng L,Gao N,Deng Y.Evaluation of DNA extraction methods for the analysis of microbial community in biological activated carbon. Environ Technol.2012; 33(4-6):437-444.[9]Minas K,McEwan NR,Newbold CJ,et al.Optimization of a high-throughput CTAB-based protocol for the extraction of qPCR-grade DNAfrom rumen fluid, plant and bacterial pure cultures.FEMS Microbiol Lett.2011;325(2):162-169.[10]Gillan DC,Speksnijder AG,Zwart G,et al.Genetic diversity of the biofilm covering Montacuta ferruginosa (Mollusca, bivalvia) as evaluated by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis and cloning of PCR-amplified gene fragments coding for 16S rRNA.Appl Environ Microbiol. 1998;64(9):3464-3472.[11]Zijnge V,Harmsen HJ,Kleinfelder JW,et al.Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis to study bacterial community structure in pockets of periodontitis patients.Oral Microbiol Immunol.2003;18(1):59-65.[12]Bulgari D,Casati P,Brusetti L,et al.Endophytic bacterial diversity in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) leaves described by 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis and length heterogeneity- PCR.J Microbiol.2009;47(4):393-401.[13]Neonakis IK,Gitti Z,Kontos F,et al.Mycobacterium arupense pulmonary infection: antibiotic resistance and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis.Indian J Med Microbiol. 2010;28(2):173-176.[14]Ong SH,Kukkillaya VU,Wilm A,et al.Species Identification and Profiling of Complex Microbial Communities Using Shotgun Illumina Sequencing of 16S rRNA Amplicon Sequences.PLoS One.2013;8(4):e60811.[15]Rudi K,Sekelja M.High or low correlation between co-occuring gene clusters and 16S rRNA gene phylogeny.FEMS Microbiol Lett.2013;339(1):23-29.[16]Wulff NA,Eveillard S,Foissac X,et al.rRNA operons and genome size of 'Candidatus Liberibacter americanus', a bacterium associated with citrus huanglongbing in Brazil.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol.2009;59(8):1984-1991.[17]Caselli M,Cassol F,Gentili V,et al.Genome sequences of segmented filamentous bacteria in animals: implications for human research.Gut Microbes.2012;3(5):401-405. [18]Korobeinikova AV,Garber MB,Gongadze GM.Ribosomal proteins: structure, function, and evolution. Biochemistry (Mosc).2012;77(6):562-574. [19]Schrenzel MD,Witte CL,Bahl J,et al.Genetic characterization and epidemiology of Helicobacters in non-domestic animals. Helicobacter.2010; 15(2):126-142.[20]Silva CC,Jesus EC,Torres AP,et al.Investigation of bacterial diversity in membrane bioreactor and conventional activated sludge processes from petroleum refineries using phylogenetic and statistical approaches.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010;20(3):447-459.[21]Wieland M,Berschneider B,Erlacher MD,et al. Aptazyme-mediated regulation of 16S ribosomal RNA. Chem Biol.2010;17(3):236-242.[22]Větrovský T,Baldrian P.The variability of the 16S rRNA gene in bacterial genomes and its consequences for bacterial community analyses.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57923.[23]Fischer SG,Lerman LS.Length-independent separation of DNA restriction fragments in two-dimensional gel electrophoresis.Cell.1979; 16(1):191-200. [24]周彦玢,束蓉,刘大力.应用变性梯度凝胶电泳分析牙周基础治疗前后龈下菌群的变化[J].上海口腔医学,2012,21(1):73-78.[25]刘彩霞,胡燕,周东蕊,等.聚合酶链反应-变性梯度凝胶电泳技术动态分析不同分娩方式对新生儿早期肠道菌群的影响[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2012, 27(19):1491-1494.[26]孟庆伟,赵尔扬.牙周炎致病菌的变性梯度凝胶电泳检测[J].国际口腔医学杂志, 2009,36(5): 547-549.[27]Sato K,Azama Y,Nogawa M,et al.Analysis of a change in bacterial community in different environments with addition of chitin or chitosan.J Biosci Bioeng. 2010;109(5): 472-478. [28]江泳,陈智滨,冯海兰.镍铬合金烤瓷冠修复上颌切牙对牙周组织的影响[J].口腔医学,2004,24(5): 279-280.[29]赵彤,高平.镍铬合金烤瓷冠对龈沟液中IL-1β及AST水平的影响[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2007,8(3): 172-174.[30]Li RQ,Kan HX,Zheng ZF.Effects of Ni-Cr based porcelain-fused-to-metal crown on periodontal tissue. J Clin Rehabil Tissue Eng Res.2009;13(25):4989-4992. [31]Ozen J,Atay A,Beydemir B,et al.In vitro IL-1beta release from gingival fibroblasts in response to pure metals, dental alloys and ceramic.J Oral Rehabil.2005;32(7):511-517.[32]Barnes VM,Teles R,Trivedi HM,et al.Acceleration of purine degradation by periodontal diseases.J Dent Res.2009; 88(9): 851-855.[33]Darany DG,Beck FM,Walters JD.The relationship of gingival fluid leukocyte elastase activity to gingival fluid flow rate.J Periodontol.1992; 63(9):743-747.[34]Haffajee AD,Yaskell T,Torresyap G,et al.Comparison between polymerase chain reaction-based and checkerboard DNA hybridization techniques for microbial assessment of subgingival plaque samples.J Clin Periodontol.2009; 36(8): 642-649.[35]Surna A,Kubilius R,Sakalauskiene J,et al.Lysozyme and microbiota in relation to gingivitis and periodontitis.Med Sci Monit.2009;15(2):66-73.[36]D'Ercole S,Catamo G,Tripodi D,et al.Comparison of culture methods and multiplex PCR for the detection of periodontopathogenic bacteria in biofilm associated with severe forms of periodontitis.New Microbiol.2008; 31(3): 383-391.[37]Miyagawa J,Maeda H,Murauchi T,et al.Rapid and simple detection of eight major periodontal pathogens by the loop-mediated isothermal amplification method. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2008;53(3):314-321.[38]Fujimoto C,Maeda H,Kokeguchi S,et al.Application of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) to the analysis of microbial communities of subgingival plaque.J Periodontal Res.2003;38(4):440-445.[39]Zijnge V,Harmsen HJ,Kleinfelder JW,et al.Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis to study bacterial community structure in pockets of periodontitis patients.Oral Microbiol Immunol.2003;18(1):59-65.[40]郭大伟,滕敏华,陈正岗,等.镍铬合金烤瓷修复体拆除前后患者血清镍铬含量的检测与评估[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(34): 6457-6460. |

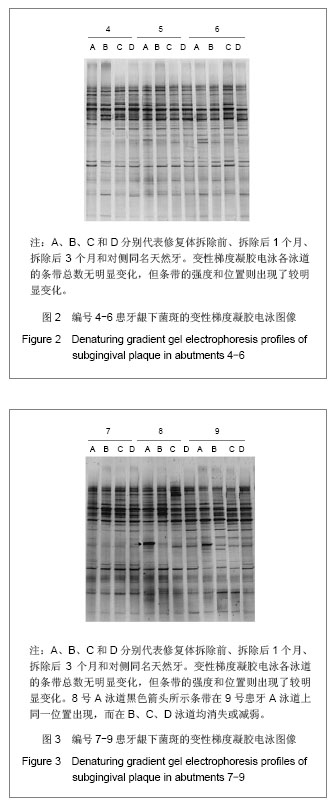

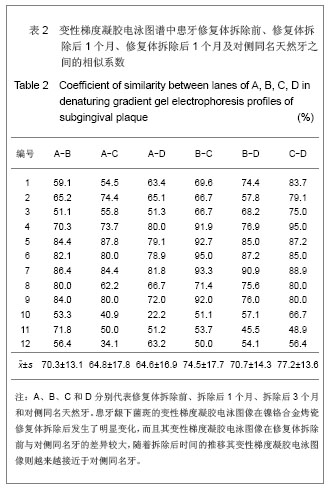
.jpg)
.jpg)