中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (16): 2526-2530.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2244
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
α-氰基丙烯酸正丁酯医用黏合剂修复大鼠口腔黏膜创口
胡开维1,聂 玲1,张 赫2,李雨舟2,3,4,杨 生2,3,4
- 1重庆医科大学口腔医学院,重庆市 401147;2重庆医科大学附属口腔医院,重庆市 401147;3口腔疾病与生物医学重庆市重点实验室,重庆市 401147;4重庆市高校市级口腔生物医学工程重点实验室,重庆市 401147
Application of α-n-butyl 2-cyanoacrylate medical adhesive for repair of oral mucosal wound of rats
Hu Kaiwei1, Nie Ling1, Zhang He2, Li Yuzhou2, 3, 4, Yang Sheng2, 3, 4
- 1College of Stomatology, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 401147, China; 2Stomatological Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 401147, China; 3Chongqing Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases and Biomedical Sciences, Chongqing 401147, China; 4Chongqing Municipal Key Laboratory of Oral Biomedical Engineering of Higher Education, Chongqing 401147, China
摘要:

文题释义:
α-氰基丙烯酸正丁酯医用黏合剂:俗称504医用胶,是美国 FDA和欧洲各国批准用于人体组织内的唯一医用胶产品,具有良好的生物相容性、生物降解性、抗菌性,在室温下能快速黏合机体组织,目前作为组织黏接剂已被应用于整形美容外科、儿科手术、眼科外伤的简单、快速修补等领域。
α-氰基丙烯酸酯正丁酯黏合剂黏合切口的作用原理:该类黏合剂的α-位碳原子上含有极强吸电性的基团如-CN和-COOR,产生诱导效应,使β-位的碳原子有很强的吸电性,在遇到黏膜表面水分或者血液时能产生瞬间聚合反应,固化成膜,同时形成多极性中心,此膜通过电镜观察为直径2.0-3.0 μm的网状结构,与创面组织镶嵌,其结合力大于黏膜的张力,使创面保持对合。
背景:α-氰基丙烯酸正丁酯医用黏合剂(504医用胶)具有良好的生物相容性、抗菌性等,是一种简单有效的粘接剂,但其在口腔领域手术切口闭合中的应用少有报道。
目的:探讨α-氰基丙烯酸正丁酯医用黏合剂在大鼠口腔黏膜创口愈合中的应用效果。
方法:取15只雌性SD大鼠(重庆医科大学实验动物中心提供),建立口腔黏膜切开创口模型,分3组:自然愈合组不做任何处理,缝线组采用可吸收性外科缝线间断缝合1针闭合创口,504黏合组采用α-氰基丙烯酸正丁酯医用黏合剂封闭创口,术后7 d进行创口大体与组织学观察。取20只雌性SD大鼠,建立口腔黏膜 1 cm×1 cm的正方形缺损模型,分2组:自然愈合组不做任何处理,504封闭组采用α-氰基丙烯酸正丁酯医用黏合剂涂布缺损区,术后10 d进行缺损部位大体与组织学观察。实验方案经重庆医科大学实验动物伦理委员会批准。
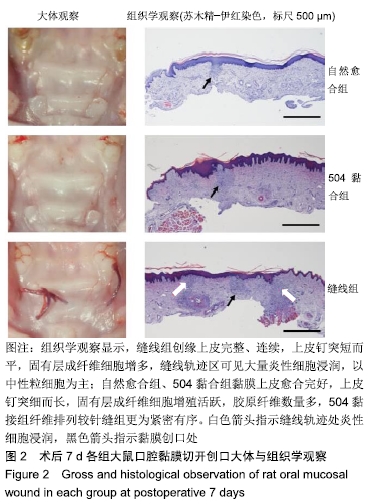
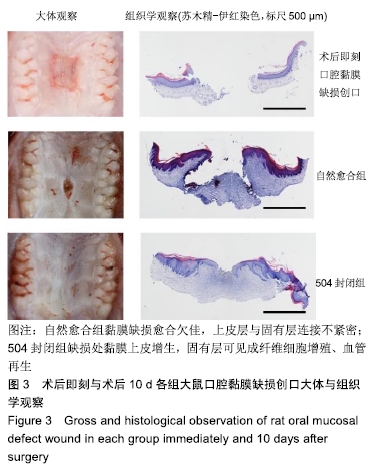
结果与结论:①口腔黏膜切开创口模型:大体观察显示3组创口愈合良好,未见红肿流脓等炎性反应;组织学观察显示,缝线组创缘上皮完整、连续,上皮钉突短而平,固有层成纤维细胞增多,缝线轨迹区可见大量炎性细胞浸润;自然愈合组、504黏合组黏膜上皮愈合完好,上皮钉突细而长,固有层成纤维细胞增殖活跃,胶原纤维数量多,504黏合组纤维排列较针缝组更为紧密有序;②口腔黏膜缺损模型:大体观察显示,自然愈合组创口愈合不全,未见肿胀、坏死溃烂等感染情况,504封闭组创面基本愈合;组织学观察显示,自然愈合组黏膜缺损明显,上皮层与固有层连接不紧密,可见坏死组织、少量成纤维细胞及大量炎性细胞浸润;504封闭组黏膜缺损创缘长度显著减小,固有层可见成纤维细胞增殖、血管再生,纤维排列一致有序;③结果表明,α-氰基丙烯酸正丁酯医用黏合剂的异物反应小,可促进黏膜组织再生,为封闭口腔黏膜创口的一种潜在方法。
ORCID: 0000-0002-5986-5231(胡开维)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: