|
[1] PIĄTEK J, KĘDZIORA A, KONSTANTY-KALANDYK J, et al. Coronary Artery Disease in Young Adults: Who Needs Surgical Revascularization? A Retrospective Cohort Study. Heart Surg Forum. 2016;19(4):E170-174.
[2] TAKAHASHI K, YAMANAKA S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126(4):663-676.
[3] ZHAO XY, LI W, LV Z, et al. iPS cells produce viable mice through tetraploid complementation. Nature. 2009;461(7260):86-90.
[4] TAKAHASHI K, TANABE K, OHNUKI M, et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 2007; 131(5):861-872.
[5] YU J, VODYANIK MA, SMUGA-OTTO K, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science. 2007; 318(5858):1917-1920.
[6] TAURA D, SONE M, HOMMA K, et al. Induction and isolation of vascular cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells--brief report. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009;29(7):1100-1103.
[7] CHOI KD, YU J, SMUGA-OTTO K, et al. Hematopoietic and endothelial differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells. 2009;27(3):559-567.
[8] NG ES, DAVIS R, STANLEY EG, et al. A protocol describing the use of a recombinant protein-based, animal product-free medium (APEL) for human embryonic stem cell differentiation as spin embryoid bodies. Nat Protoc. 2008;3(5):768-776.
[9] NOURSE MB, HALPIN DE, SCATENA M, et al. VEGF induces differentiation of functional endothelium from human embryonic stem cells: implications for tissue engineering. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010;30(1):80-89.
[10] LIPPMANN ES, AZARIN SM, KAY JE, et al. Derivation of blood-brain barrier endothelial cells from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2012;30(8):783-791.
[11] HARDING A, CORTEZ-TOLEDO E, MAGNER NL, et al. Highly Efficient Differentiation of Endothelial Cells from Pluripotent Stem Cells Requires the MAPK and the PI3K Pathways. Stem Cells. 2017;35(4): 909-919.
[12] LUNNEY JK. Advances in swine biomedical model genomics. Int J Biol Sci. 2007;3(3):179-184.
[13] WU Z, CHEN J, REN J, et al. Generation of pig induced pluripotent stem cells with a drug-inducible system. J Mol Cell Biol. 2009;1(1): 46-54.
[14] EZASHI T, TELUGU BP, ALEXENKO AP, et al. Derivation of induced pluripotent stem cells from pig somatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(27):10993-10998.
[15] CHENG D, GUO Y, LI Z, et al. Porcine induced pluripotent stem cells require LIF and maintain their developmental potential in early stage of embryos. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51778.
[16] WANG J, GU Q, HAO J, et al. Tbx3 and Nr5α2 play important roles in pig pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2013;9(5):700-708.
[17] LI X, SHAN ZY, WU YS, et al. Generation of neural progenitors from induced Bama miniature pig pluripotent cells. Reproduction. 2013; 147(1):65-72.
[18] GU M, NGUYEN PK, LEE AS, et al. Microfluidic single-cell analysis shows that porcine induced pluripotent stem cell-derived endothelial cells improve myocardial function by paracrine activation. Circ Res. 2012;111(7):882-893.
[19] ALMALKI SG, AGRAWAL DK. ERK signaling is required for VEGF-A/VEGFR2-induced differentiation of porcine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells into endothelial cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):113.
[20] ALMALKI SG, LLAMAS VALLE Y, et al. MMP-2 and MMP-14 Silencing Inhibits VEGFR2 Cleavage and Induces the Differentiation of Porcine Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Endothelial Cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(5):1385-1398.
[21] SCHLEGEL F, APPLER M, HALLING M, et al. Reprogramming Bone Marrow Stem Cells to Functional Endothelial Cells in a Mini Pig Animal Model. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2017;23:285-294.
[22] YUSUF S, HAWKEN S, OUNPUU S, et al. Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): case-control study. Lancet. 2004; 364(9438):937-952.
[23] HEIDENREICH PA, TROGDON JG, KHAVJOU OA, et al. Forecasting the future of cardiovascular disease in the United States: a policy statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2011; 123(8):933-944.
[24] WRITING GROUP MEMBERS, MOZAFFARIAN D, BENJAMIN EJ, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133(4):e38-360.
[25] BAI H, XIE YL, GAO YX, et al. The balance of positive and negative effects of TGF-β signaling regulates the development of hematopoietic and endothelial progenitors in human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(20):2765-2776.
[26] DROWLEY L, KOONCE C, PEEL S, et al. Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiac Progenitor Cells in Phenotypic Screening: A Transforming Growth Factor-β Type 1 Receptor Kinase Inhibitor Induces Efficient Cardiac Differentiation. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016; 5(2):164-174.
[27] COCHRANE A, KELAINI S, TSIFAKI M, et al. Quaking Is a Key Regulator of Endothelial Cell Differentiation, Neovascularization, and Angiogenesis. Stem Cells. 2017;35(4):952-966.
[28] WHITE MP, RUFAIHAH AJ, LIU L, et al. Limited gene expression variation in human embryonic stem cell and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived endothelial cells. Stem Cells. 2013;31(1):92-103.
[29] ORLOVA VV, VAN DEN HIL FE, PETRUS-REURER S, et al. Generation, expansion and functional analysis of endothelial cells and pericytes derived from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Protoc. 2014;9(6):1514-1531.
[30] YING QL, WRAY J, NICHOLS J, et al. The ground state of embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Nature. 2008;453(7194):519-523.
[31] BUEHR M, MEEK S, BLAIR K, et al. Capture of authentic embryonic stem cells from rat blastocysts. Cell. 2008;135(7):1287-1298.
[32] ZHANG P, LI J, TAN Z, et al. Short-term BMP-4 treatment initiates mesoderm induction in human embryonic stem cells. Blood. 2008; 111(4):1933-1941.
[33] LU TY, LIN B, KIM J, et al. Repopulation of decellularized mouse heart with human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiovascular progenitor cells. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2307.
[34] SIL S, PERIYASAMY P, THANGARAJ A, et al. PDGF/PDGFR axis in the neural systems. Mol Aspects Med. 2018;62:63-74.
[35] LEBLEU VS, TADURI G, O'CONNELL J, et al. Origin and function of myofibroblasts in kidney fibrosis. Nat Med. 2013;19(8):1047-1053.
[36] MIWA H, ERA T. Mesoderm Differentiation from hiPS Cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1357:403-413.
[37] IWAI K, ISHIKURA H, INOUE T, et al. A case of AFP-positive pancreas papillary carcinoma suggestive of a primitive endoderm phenotype. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1993;43(7-8):434-439.
[38] VIOTTI M, NOWOTSCHIN S, HADJANTONAKIS AK. Afp::mCherry, a red fluorescent transgenic reporter of the mouse visceral endoderm. Genesis. 2011;49(3):124-133.
[39] ABACI HE, GUO Z, COFFMAN A, et al. Human Skin Constructs with Spatially Controlled Vasculature Using Primary and iPSC-Derived Endothelial Cells. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(14):1800-1807.
[40] GIACOMELLI E, BELLIN M, SALA L, et al. Three-dimensional cardiac microtissues composed of cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells co-differentiated from human pluripotent stem cells. Development. 2017;144(6):1008-1017.
[41] HOMMA K, SONE M, TAURA D, et al. Sirt1 plays an important role in mediating greater functionality of human ES/iPS-derived vascular endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis. 2010;212(1):42-47.
[42] BAO X, LIAN X, PALECEK SP. Directed Endothelial Progenitor Differentiation from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Via Wnt Activation Under Defined Conditions.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1481:183-196.
[43] ZHANG F, WANG L, LI Y, et al. Optimizing mesoderm progenitor selection and three-dimensional microniche culture allows highly efficient endothelial differentiation and ischemic tissue repair from human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):6.
|

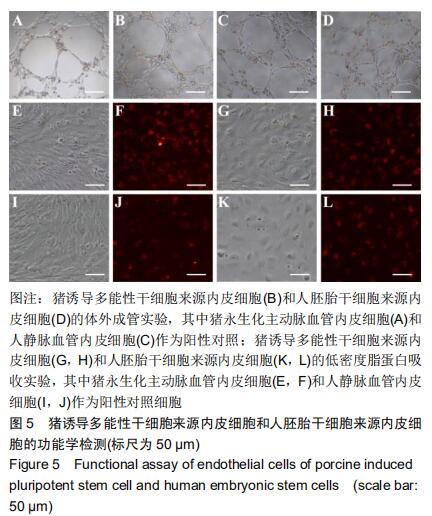


 #br#
#br#