中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (4): 538-543.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1925
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
影响微种植体正畸治疗成功率的因素
吴也可1,郜然然2,左渝陵1,余剑锋1,赵立星3,聂汶涵1,郑 涛4,艾黄萍4,严 航4
- 1成都中医药大学附属医院,四川省成都市 610072;2河南省人民医院,河南省郑州市 450000;3四川大学华西口腔医院,四川省成都市 610041;4成都中医药大学临床医学院,四川省成都市 610072
Factors affecting the clinical success rate of miniscrew implants for orthodontic treatment
Wu Yeke1, Gao Ranran2, Zuo Yuling1, Yu Jianfeng1, Zhao Lixing3, Nie Wenhan1, Zheng Tao4, Ai Huangping4, Yan Hang4
- 1Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610072, Sichuan Province, China; 2Henan Provincial People's Hospital, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 3West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China; 4Clinical Medical College, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610072, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
支抗:正畸矫治中,任何施于被矫治牙使其移动的力必然产生一个反向、等大的反作用力,能抵抗该力的结构成为“支抗”。支抗控制对于正畸和颅颌面矫形的成败至关重要。多年来,正畸学者和临床医师设计了多种口外和口内支抗系统,但由于各种原因,实际临床应用不尽如人意。与传统支抗相比,微种植体具有体积小、植入移除简单、成本低、能行即刻或早期加载等明显优势,在正畸临床的应用越来越广泛。
骨整合&临床成功率:即显微镜下骨与种植体间的直接接触,是种植体生物学稳定性和临床成功率的决定因素。骨整合的程度主要由种植体自身设计、手术操作、应力载荷、临床用途及患者身体状况等多因素决定。影响微种植体骨整合乃至临床成功率的相关因素亟待进一步深入、系统的研究。
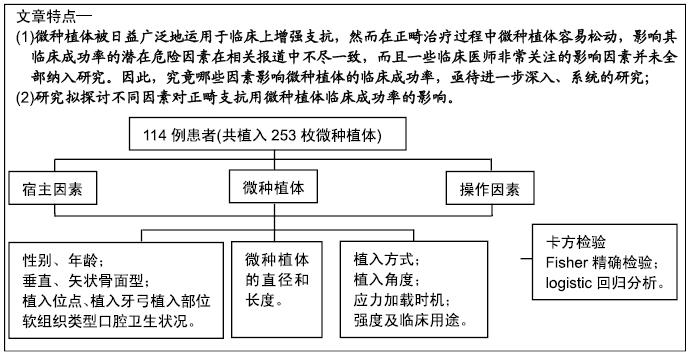
背景:在正畸治疗过程中,影响微种植体临床成功率的潜在危险因素的相关报道结果不尽一致,一些临床医师非常关注的影响因素未全部纳入研究,且动物实验所得结论难以直接运用于临床实践。因此,究竟哪些因素影响微种植体的临床成功率,亟待进一步深入、系统的研究。
目的:研究影响正畸支抗用微种植体临床成功率的相关因素。
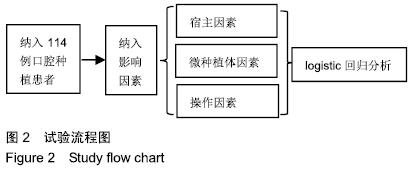
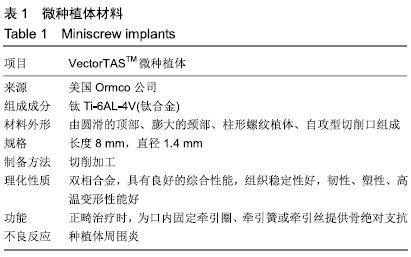
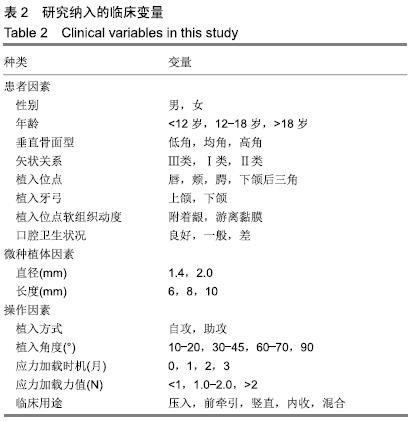
方法:试验纳入114例口腔种植患者,其中男42例,女72例,年龄(19.26±9.19)岁,共植入253枚微种植体作为正畸支抗。纳入以下影响因素:包括性别、年龄、垂直和矢状骨面型、植入位点、植入牙弓、植入部位软组织类型、口腔卫生状况、微种植体的直径和长度、植入方式、植入角度、应力加载时机和强度及临床用途,运用logistic回归分析研究成功率和所有变量间的相关性,方差分析检测各变量对成功率的影响。试验方案经过四川大学伦理委员会批准。
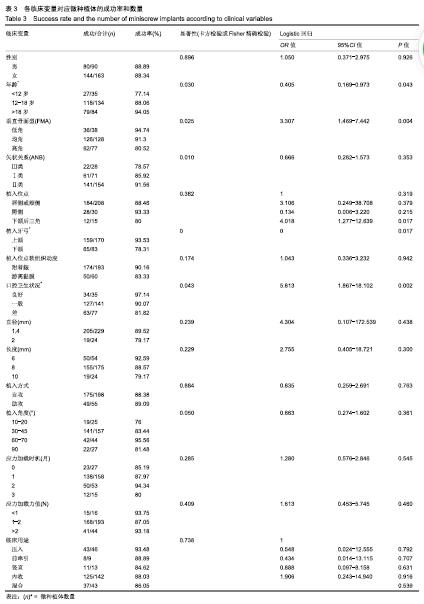
结果与结论:①253枚微种植体的总临床成功率为88.54%,平均应力加载时长为9.5个月,其中29枚植入失败,植入失败微种植体的平均加载时长为2.3个月;②在卡方检验、Fisher精确检验和logistic回归分析中,年龄、口腔卫生状况、垂直骨面型及植入位点与临床成功率显著相关(P < 0.05),而性别、矢状骨面型、植入牙弓、植入部位软组织类型、微种植体的直径和长度、植入方式、植入角度、应力加载时机和强度及临床用途11个变量与种植成功率无显著相关性(P > 0.05);③结果提示为了最大程度降低微种植体失败率,需给予患者正确的口腔卫生保健指导和有效监督,特别是年轻(<12岁)、高角、下颌骨植入微种植体的患者。ORCID: 0000-0003-2318-3199(吴也可)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: