Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (15): 2442-2448.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.15.028
Previous Articles Next Articles
Osteogenesis effects and mechanisms of Kidney Chinese Herbs after fractures
Zeng Zhan-peng, Zhou Chi, Li Kang-huo, Wang Hai-bin, Tang Hong-yu
- Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2015-03-12Online:2015-04-09Published:2015-04-09 -
Contact:Zeng Zhan-peng, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zeng Zhan-peng, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Plan of Guangdong Province, No. 2013B021800167; the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81373665
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zeng Zhan-peng, Zhou Chi, Li Kang-huo, Wang Hai-bin, Tang Hong-yu . Osteogenesis effects and mechanisms of Kidney Chinese Herbs after fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(15): 2442-2448.
share this article
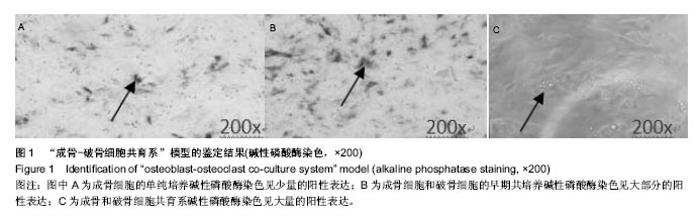
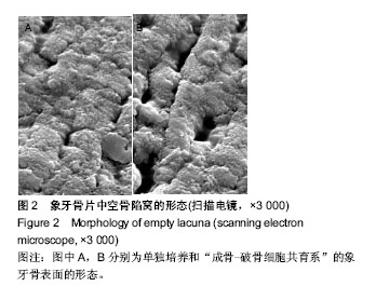
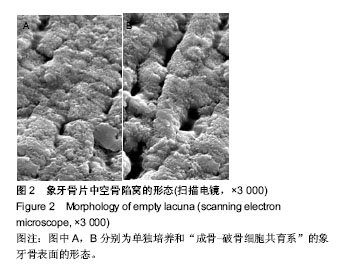
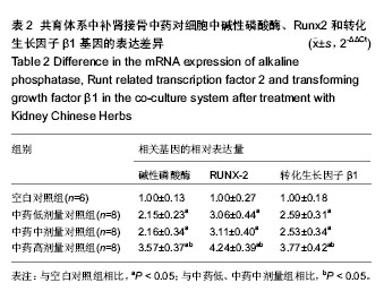
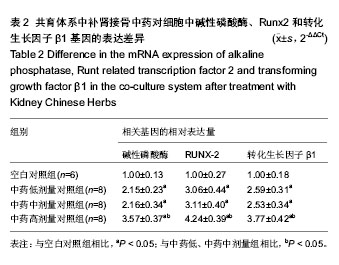
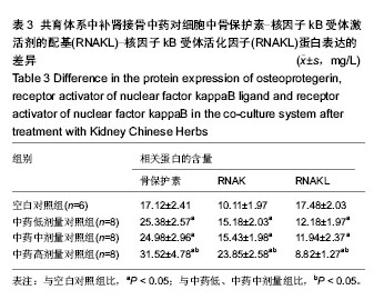
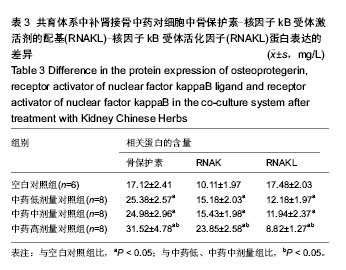
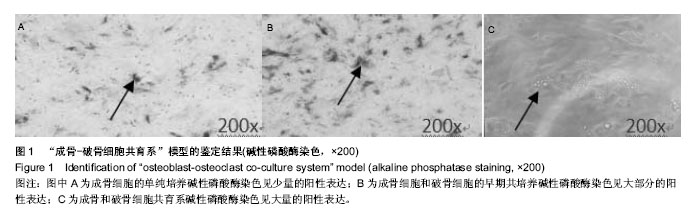
2.1 实验动物数量分析 纳入雌雄C57小鼠30只,进入结果分析25只,死亡4只和感染1只,均补充各组动物数量,最终计入结果分析的小鼠数量30只,用于细胞培养的小鼠不计入数量分析。 2.2 建立了稳定的“成骨-破骨细胞共育系”模型 培养3周,如图1A所示,单纯的成骨细胞培养,碱性磷酸酶染色仅有少量的阳性表达,说明只有很少的细胞分泌碱性磷酸酶;而如图1B所示,在将成骨细胞和破骨细胞共培养后,染色可见大量的阳性表达,说明有大量的细胞分泌碱性磷酸酶。与之相吻合的,对成骨细胞内碱性磷酸酶进行定量检测,如图1C所示,共育体系中的低、中、高剂量组碱性磷酸酶阳性细胞数分别为:2.15±0.23,2.16±0.34,3.57±0.37个,其各组表达均大于单纯培养的成骨细胞(1.00±0.13;P < 0.05)。"
| [1] Lewczuk E, Biatoszewski D. The level of physical activity in patients with osteoporosis in relation to the risk and prevention of falls. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2006;8(4): 412-421. [2] Ikeda K, Takeshita S. Factors and mechanisms involved in the coupling from bone resorption to formation: how osteoclasts talk to osteoblasts. J Bone Metab. 2014;21(3): 163-167. [3] 詹红生,赵咏芳等.用含药血清方法观察补肾接骨中药对成骨细胞功能的影响[J]中国骨伤,2001,3:54-56. [4] Jiang SD, Jiang LS, Dai LY. Effects of spinal cord injury on osteoblastogenesis,osteoclastogenesis and gene expression profiling in osteoblasts in young rats. Osteoporos Int. 2007; 18(3): 339-349. [5] Li CJ, Chang JK, Chou CH, et al. The PI3K/Akt/FOXO3a/ p27Kip1 signaling contributes to anti-inflammatory drug-suppressed proliferation of human osteoblasts. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010;79(6):926-937. [6] Itoh S, Udagawa N, Takahashi N, et al. A critical role for interleukin-6 family-mediated Stat3 activation in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Bone. 2006;39(3): 505-512. [7] Wu PH, Lin SK, Lee BS, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate diminishes cytokine-stimulated Cyr61 expression in human osteoblastic cells: a therapeutic potential for arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012;51(11):1953-1965. [8] Taketa T, Sakai A, Tanaka S, et al. Selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor prevents reduction of trabecular bone mass in collagen-induced arthritic mice in association with suppression of RANKL/OPG ratio and IL-6 mRNA expression in synovial tissues but not in bone marrow cells.. J Bone Miner Metab. 2008;26(2):143-151. [9] Hu JP, Nishishita K, Sakai E, et al. Berberine inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and survival through suppressing the NF-kappaB and Akt pathways . Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;580(1-2):70-79. [10] Von Knoch F, Heckelei A, Wedemeyer C, et al. Suppression of polyethylene particle-induced osteolysis by exogenous osteoprotegerin. J Biomed Mater Res. 2005;75(2):288-294. [11] Vandooren B, Cantaert T, Noordenbos T, et al. The abundant synovial expression of the RANK /RANKL/ Osteoprotegerin system in peripheral spondylarthritis is partially disconnected from inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(3):718-729. [12] 欧阳露,汪选斌.中药骨碎补调节骨代谢作用及机制研究进展[J].湖北医药学院学报,2013,32(2):187-190. [13] 赵亮,张晨.续断骨伤合剂在促进骨折愈合中对血生化指标的影响[J].湖北中医药大学学报,2011,13(1):11-13. [14] Kreja L, Liedert A, Hasni S, et al. Mechanical regulation of osteoclastic genes in human osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;368(3):582-587. [15] Taketa T, Sakai A, Tanaka S, et al. Selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor prevents reduction of trabecular bone mass in collagen-induced arthritic mice in association with suppression of RANKL/OPG ratio and IL-6 mRNA expression in synovial tissues but not in bone marrow cells. J Bone Miner Metab. 2008;26(2):143-151. [16] Suzuki N, Yoshimura Y, Deyama Y, et al. Mechanical stress directly suppresses osteoclast differentiation in RAW264.7 cells. Int J Mol Med. 2008;21(3):291-296. [17] Irie A, Takami M, Kubo H, et al. Heparin enhances osteoclastic bone resorption by inhibiting osteoprotegerin activity. Bone. 2007;41(2):165-174. [18] von Knoch F, Heckelei A, Wedemeyer C, et al. Suppression of polyethylene particle-induced osteolysis by exogenous osteoprotegerin. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2005;75(2):288-294. [19] Vandooren B, Cantaert T, Noordenbos T, et al. The abundant synovial expression of the RANK/ RANKL/ Osteoprotegerin system in peripheralspondylarthritis is partially disconnected from inflammation.Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(3):718-729. [20] Hu JP, Nishishita K, Sakai E, et al. Berberine inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and survival through suppressing the NF-kappaB and Akt pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;580(1-2):70-79. [21] Makihira S, Mine Y, Kosaka E, et al. Titanium surface roughness accelerates RANKL-dependent differentiation in the osteoclast precursor cell line, RAW264.7.Dent Mater J. 2007;26(5):739-745. [22] Poblenz AT, Jacoby JJ, Singh S, et al. Inhibition of RANKL-mediated osteoclast differentiation by selective TRAF6 decoy peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;359(3):510-515. [23] Funakoshi-Tago M, Tago K, Sonoda Y, et al. TRAF6 and C-SRC induce synergistic AP-1 activation via PI3-kinase- AKT-JNK pathway. Eur J Biochem. 2003; 270(6):1257-1268. [24] Chandrasekar B, Mummidi S, Valente AJ, et al. The pro-atherogenic cytokine interleukin-18 induces CXCL16 expression in rat aortic smooth muscle cells via MyD88, interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6, c-Src, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, Akt, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, andactivator protein-1 signaling. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(28):26263-26277. [25] Tsubaki M, Kato C, Manno M, et al. Macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha (MIP-1alpha) enhances a receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand (RANKL) expression in mouse bone marrow stromal cells 22/36 and osteoblasts through MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathways. Mol Cell Biochem. 2007;304 (1-2):53-60. [26] Pang M, Martinez AF, Fernandez I, et al. AP-1 stimulates the cathepsin K promoter in RAW 264.7 cells. Gene. 2007;403 (1-2): 151-158. [27] Mohamed SG, Sugiyama E, Shinoda K, et al. Interleukin-10 inhibits RANKL-mediated expression of NFATc1 in part via suppression of c-Fos and c-Jun in RAW264.7 cells and mouse bone marrow cells. Bone. 2007;41(4):592-602. [28] Sandur SK, Ahn KS, Ichikawa H, et al. Zyflamend, a polyherbal preparation, inhibits invasion, suppresses osteoclastogenesis, and potentiates apoptosis through down-regulation of NF-kappa B activation and NF-kappa B-regulated gene products. Nutr Cancer. 2007;57(1):78-87. [29] Hirai F, Nakayamada S, Okada Y, et al. Small GTPase Rho signaling is involved in beta1 integrin-mediated up-regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand on osteoblasts and osteoclast maturation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;356(1): 279-285. [30] Fujita K, Janz S. Attenuation of WNT signaling by DKK-1 and -2 regulates BMP2-induced osteoblast differentiation and expression of OPG, RANKL and M-CSF. Mol Cancer. 2007; 6:71. [31] Li W, Zhu S, Hu J. Bone Regeneration Is Promoted by Orally Administered Bovine Lactoferrin in a Rabbit Tibial Distraction Osteogenesis Model. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015. [32] Wang Z, Ding L, Zhang S, et al. Effects of icariin on the regulation of the OPG-RANKL-RANK system are mediated through the MAPK pathways in IL-1β-stimulated human SW1353 chondrosarcoma cells. Int J Mol Med. 2014;34(6): 1720-1726. [33] Ju D, Liu M, Zhao H, et al. Mechanisms of "kidney governing bones" theory in traditional Chinese medicine. Front Med. 2014; 8(3):389-393. [34] Irtiuga OB, Zhiduleva EV, Dubrovskaia OB, et al. Concentration of osteoprotegerin and RANKL in blood serum of patients with aortic stenosis. Kardiologiia. 2014;54(6): 44-48. [35] Shimamura M, Nakagami H, Osako MK, et al. OPG/RANKL/RANK axis is a critical inflammatory signaling system in ischemic brain in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(22):8191-8196. [36] Liu CG, Luo QX, Ling TY, et al. Effect of Erigeron Breviscapus on the expression of OPG/RANKL/RANK in osteoblasts and pre-osteoclasts in vitro. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2013;33(12):1658-1664. [37] Zheng J, Liu JL, Lin MF, et al. Effect of modified sijunzi decoction on the bone metabolism of adriamycin induced nephropathy rats. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2013; 33(10):1376-1381. [38] Yasuda H. RANKL, a necessary chance for clinical application to osteoporosis and cancer-related bone diseases. World J Orthop. 2013;4(4):207-217. [39] Wang J, Chen TY, Qin S, et al. Inhibitory effect of metformin on bone metastasis of cancer via OPG/RANKL/RANK system. Med Hypotheses. 2013;81(5):805-806. [40] Szymczak J, Bohdanowicz-Pawlak A. Osteoprotegerin, RANKL, and bone turnover in primary hyperparathyroidism: the effect of parathyroidectomy and treatment with alendronate. Horm Metab Res. 2013;45(10):759-764. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Yang Caihui, Liu Qicheng, Dong Ming, Wang Lina, Zuo Meina, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Serine/threonine protein kinases can promote bone destruction in mouse models of chronic periapical periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3654-3659. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||