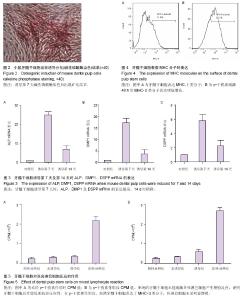
| [1] Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J,et al.Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630.
[2] Iohara K, Zheng L, Ito M,et al.Side population cells isolated from porcine dental pulp tissue with self-renewal and multipotency for dentinogenesis, chondrogenesis, adipogenesis, and neurogenesis.Stem Cells. 2006;24(11): 2493-2503.
[3] Luan X, Ito Y, Dangaria S,et al.Dental follicle progenitor cell heterogeneity in the developing mouse periodontium.Stem Cells Dev. 2006;15(4):595-608.
[4] Yang X, van den Dolder J, Walboomers XF,et al.The odontogenic potential of STRO-1 sorted rat dental pulp stem cells in vitro.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2007;1(1):66-73.
[5] Sloan AJ, Smith AJ.Stem cells and the dental pulp: potential roles in dentine regeneration and repair.Oral Dis. 2007; 13(2): 151-157.
[6] Harada H, Kettunen P, Jung HS,et al.Localization of putative stem cells in dental epithelium and their association with Notch and FGF signaling.J Cell Biol. 1999;147(1):105-120.
[7] Harada H, Kettunen P, Jung HS,et al.Localization of putative stem cells in dental epithelium and their association with Notch and FGF signaling.J Cell Biol. 1999;147(1):105-120.
[8] Téclès O, Laurent P, Zygouritsas S,et al.Activation of human dental pulp progenitor/stem cells in response to odontoblast injury.Arch Oral Biol. 2005;50(2):103-108.
[9] Shi S, Robey PG, Gronthos S.Comparison of human dental pulp and bone marrow stromal stem cells by cDNA microarray analysis.Bone. 2001;29(6):532-539.
[10] Ishizaka R, Iohara K, Murakami M,et al.Regeneration of dental pulp following pulpectomy by fractionated stem/progenitor cells from bone marrow and adipose tissue. Biomaterials. 2012;33(7):2109-2118.
[11] Miura M,Gronthos S,Zhao M,et al. stem cell from human exfoliated deciduous teeth.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003; 100(10):5807-5812.
[12] Chadipiralla K, Yochim JM, Bahuleyan B,et al.Osteogenic differentiation of stem cells derived from human periodontal ligaments and pulp of human exfoliated deciduous teeth.Cell Tissue Res. 2010;340(2):323-333.
[13] Nakamura S, Yamada Y, Katagiri W,et al.Stem cell proliferation pathways comparison between human exfoliated deciduous teeth and dental pulp stem cells by gene expression profile from promising dental pulp.J Endod. 2009; 35(11):1536-1542.
[14] 丁祥龙.人乳牙牙髓干细胞与骨髓间充质干细胞成骨能力的比较研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2011.
[15] 闫征斌,侯景秋,王天祥.人乳牙牙髓基质细胞的分离培养与牙再生能力[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(27): 5305-5308.
[16] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC,et al.Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells.Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.
[17] Bartholomew A, Sturgeon C, Siatskas M,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells suppress lymphocyte proliferation in vitro and prolong skin graft survival in vivo.Exp Hematol. 2002;30(1): 42-48.
[18] Bingaman AW, Waitze SY, Alexander DZ,et al.Transplantation of the bone marrow microenvironment leads to hematopoietic chimerism without cytoreductive conditioning.Transplantation. 2000;69(12):2491-2496.
[19] Nakashima M, Iohara K, Sugiyama M.Human dental pulp stem cells with highly angiogenic and neurogenic potential for possible use in pulp regeneration.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009;20(5-6):435-440.
[20] Horwitz EM, Prockop DJ, Fitzpatrick LA,et al.Transplantability and therapeutic effects of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal cells in children with osteogenesis imperfecta.Nat Med. 1999; 5(3):309-313.
[21] Niu LL, Zheng M, Cao F,et al.Migration and differentiation of exogenous rat mesenchymal stem cells engrafted into normal and injured hearts of rats.Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004; 84(1): 38-42.
[22] Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J,et al.Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630.
[23] Qin C, Brunn JC, Cadena E,et al. Dentin sialoprotein in bone and dentin sialophosphoprotein gene expressed by osteoblasts.Connect Tissue Res. 2003;44 Suppl 1:179-183.
[24] Shiba H, Mouri Y, Komatsuzawa H,et al.Enhancement of alkaline phosphatase synthesis in pulp cells co-cultured with epithelial cells derived from lower rabbit incisors.Cell Biol Int. 2003;27(10):815-823.
[25] Spoto G, Fioroni M, Rubini C,et al.Alkaline phosphatase activity in normal and inflamed dental pulps.J Endod. 2001; 27(3):180-182.
[26] 王志刚,刘兴容.牙髓干细胞及其表面特异标志物[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2010,37(1):56-58.
[27] Tsukamoto Y, Fukutani S, Shin-Ike T,et al.Mineralized nodule formation by cultures of human dental pulp-derived fibroblasts. Arch Oral Biol. 1992;37(12):1045-1055.
[28] MacDougall M, Simmons D, Luan X,et al.Dentin phosphoprotein and dentin sialoprotein are cleavage products expressed from a single transcript coded by a gene on human chromosome 4. Dentin phosphoprotein DNA sequence determination.J Biol Chem. 1997;272(2):835-842.
[29] Di Nicola M, Carlo-Stella C, Magni M,et al.Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T-lymphocyte proliferation induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli.Blood. 2002; 99(10):3838-3843. |