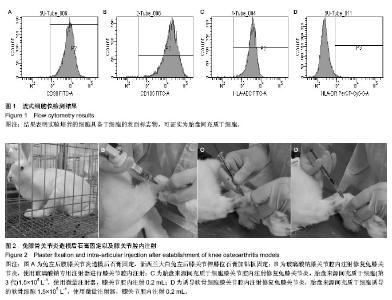
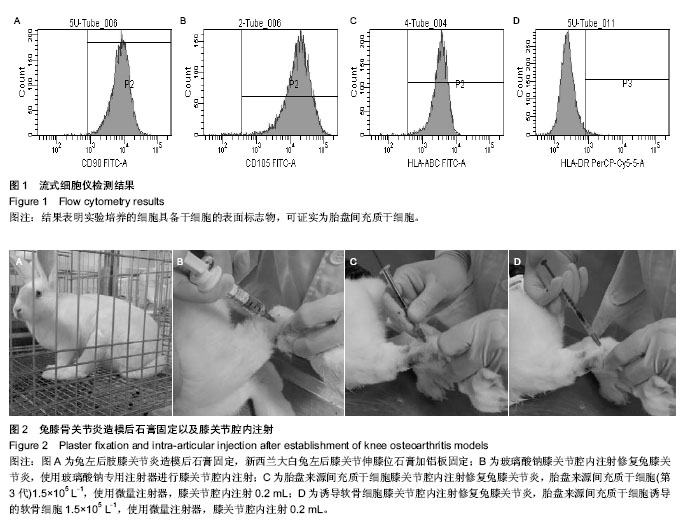
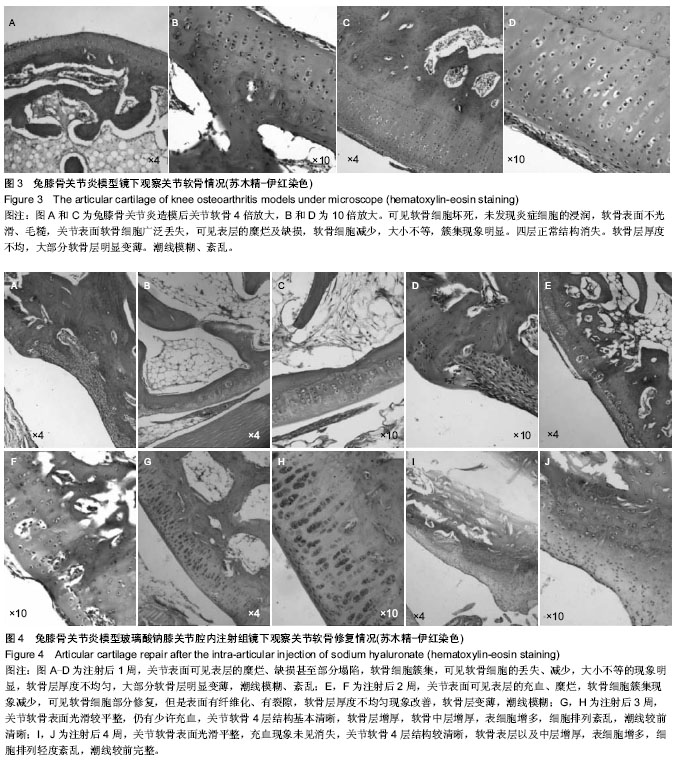
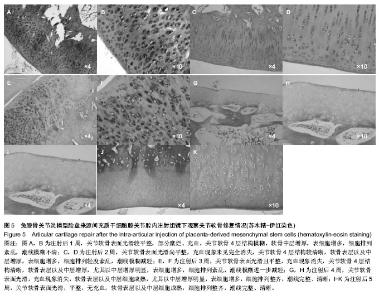
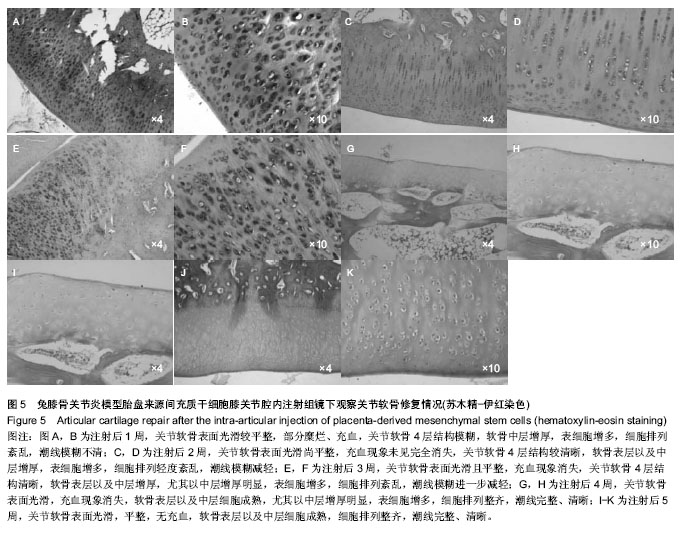
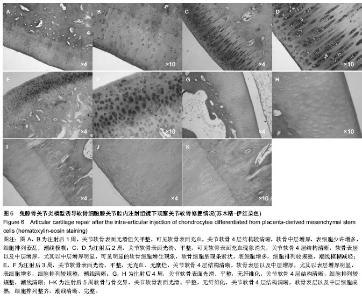
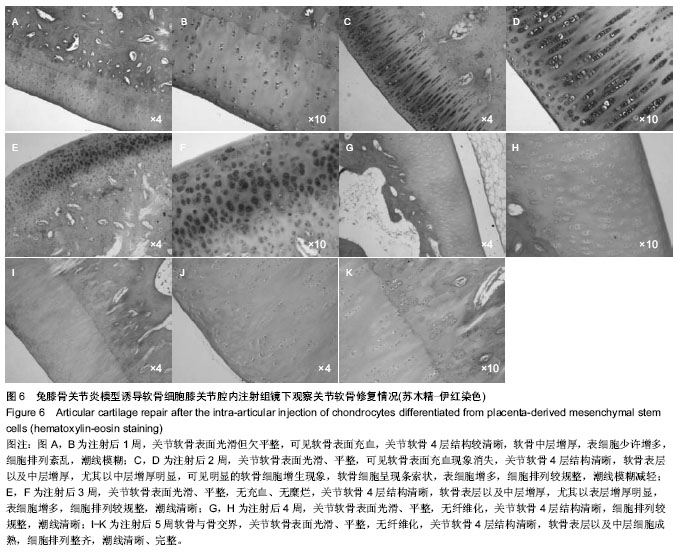
| [1] Frizziero A, Maffulli N, Masiero S, et al. Six-months pain relief and functional recovery after intra-articular injections with hyaluronic acid (mw 500-730 KDa) in trapeziometacarpal osteoarthritis. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2014;4(2):256-261.
[2] Ishijima M, Nakamura T, Shimizu K, et al. Intra-articular hyaluronic acid injection versus oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a multi-center, randomized, open-label, non-inferiority trial. Arthritis Res Ther.2014;16(1):R18.
[3] Wexler SA, Donaldson C, Denning-Kendall P. Adult bone marrow is a rich source of human mesenchymal “stem” cells but umbilical cord and mobilized adult blood are not. Br J Haematol.2003;121(2):368-374.
[4] Rao MS, Mattson MP. Stem cells and aging: expanding the possibilities. Mech Ageing Dev.2001;122(7):713-734.
[5] Giuliani N, Mangoni M, Rizzoli V. Osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in multiple myeloma: identification of potential therapeutic targets. Exp Hematol.2009;37(8): 879-886.
[6] Banas A. Purification of adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells and differentiation toward hepatic-like cells. Methods Mol Biol.2012;826:61-72.
[7] Sacchetti B, Funari A, Michienzi S, et al. Self-renewing osteoprogenitors in bone marrow sinusoids can organize a hematopoietic microenvironment. Cell.2007;131(2):324-336.
[8] Aziz Aly LA, Menoufy HE, Ragae A, et al. Adipose stem cells as alternatives for bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in oral ulcer healing. Int J Stem Cells.2012;5(2):104-114.
[9] Sun NZ, Ji H. In vitro differentiation of osteocytes and adipocytes from human placenta-derived cells. J Int Med Res.2012;40(2):761-767.
[10] Hayati AR, Nur Fariha MM, Tan GC, et al. Potential of human decidua stem cells for angiogenesis and neurogenesis. Arch Med Res.2011;42(4):291-300.
[11] Brooke G, Tong H, Levesque JP, et al. Molecular trafficking mechanisms of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells derived from human bone marrow and placenta. Stem Cells Dev.2008; 17(5):929-940.
[12] Abumaree MH, Al Jumah MA, Kalionis B, et al. Phenotypic and functional characterization of mesenchymal stem cells from chorionic villi of human term placenta. Stem Cell Rev. 2013;9(1):16-31.
[13] 费倩怡,刘春丽,朱振威,等.人胎盘来源间充质干细胞和大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的生物学特征比较[J].吉林大学学报:医学版,2013, 39(3):467-471.
[14] 李治,赵伟,刘伟,等.胎盘来源间充质干细胞的体外诱导成软骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(32):5203-5208.
[15] Sakaguchi Y, Sekiya I, Yagishita K, et al. Comparison of human stem cells derived from various mesenchymal tissues: superiority of synovium as a cell source. Arthritis Rheum.2005; 52(8):2521-2529.
[16] Dicker A, Le Blanc K, Aström G, et al. Functional studies of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult human adipose tissue. Exp Cell Res.2005;308(2):283-290.
[17] Kadam S, Muthyala S, Nair P, et al. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and islet-like cell clusters generated from these cells as a novel source for stem cell therapy in diabetes. Rev Diabet Stud.2010;7(2):168-182.
[18] Sabapathy V, Ravi S, Srivastava V, et al. Long-term cultured human term placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells of maternal origin displays plasticity. Stem Cells Int.2012;2012: 174328.
[19] Lu GH, Zhang SZ, Chen Q, et al. Isolation and multipotent differentiation of human decidua basalis-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.2011;1(2):262-265.
[20] Ringden O, Keating A. Mesenchymal stromal cells as treatment for chronic GVHD. Bone Marrow Transplant.2011;46(2):163-164.
[21] Jin J, Wang J, Huang J, et al. Transplantation of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a silk fibroin/hydroxyapatite scaffold improves bone repair in rabbits. J Biosci Bioeng. 2014;118(5):593-598.
[22] 卢遥,王静成,顾加祥,等.兔胎盘来源间充质干细胞修复兔桡骨骨缺损的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(11):1060-1065.
[23] 钱寒光,苗宗宁,赵基栋,等.丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石材料复合人胎盘间充质干细胞修复桡骨节段性骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(51):9507-9511.
[24] Richardson SM, Hoyland JA, Mobasheri R, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative medicine: opportunities and challenges for articular cartilage and intervertebral disc tissue engineering. J Cell Physiol.2010; 222(1):23-32.
[25] Mobasheri A, Csaki C, Clutterbuck AL, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in connective tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: applications in cartilage repair and osteoarthritis therapy. Histol Histopathol.2009;24(3):347-366.
[26] Onyekwelu I, Goldring MB, Hidaka C.Chondrogenesis, joint formation, and articular cartilage regeneration.J Cell Biochem. 2009;107(3):383-392.
[27] Shimomura K, Ando W, Tateishi K,et al.The influence of skeletal maturity on allogenic synovial mesenchymal stem cell-based repair of cartilage in a large animal model. Biomaterials. 2010;31(31):8004-8011 |