Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (49): 7930-7937.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.49.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
Establishing myocardial infarction animal models by the median sternotomy versus the left intercostal thoracotomy
Yang Shao-ling1, Tang Ke-qiang2, Tao Jun-jia1, Gu Fang-fang1, Guo Qing-kui3
- 1Department of Ultrasound, South Branch of Shanghai Sixth People’s Hospital/Fengxian District Central Hospital, Shanghai 201499, China; 2ICU, 3Department of Thoracic Surgery, Central Hospital of Songjiang District, Shanghai 201600, China
-
Revised:2014-08-30Online:2014-11-30Published:2014-11-30 -
Contact:Yang Shao-ling, Department of Ultrasound, South Branch of Shanghai Sixth People’s Hospital/Fengxian District Central Hospital, Shanghai 201499, China -
About author:Yang Shao-ling, M.D., Associate chief physician, Department of Ultrasound, South Branch of Shanghai Sixth People’s Hospital/Fengxian District Central Hospital, Shanghai 201499, China -
Supported by:a grant from the Science and Technology Commission of Feng Xian District in Shanghai, No. 20111003
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Shao-ling, Tang Ke-qiang, Tao Jun-jia, Gu Fang-fang, Guo Qing-kui. Establishing myocardial infarction animal models by the median sternotomy versus the left intercostal thoracotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(49): 7930-7937.
share this article
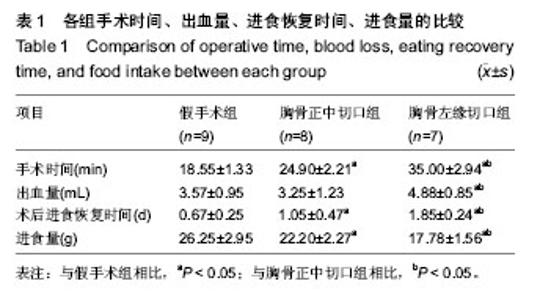
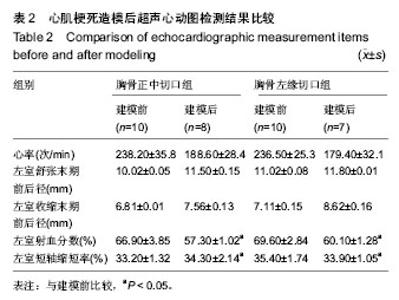
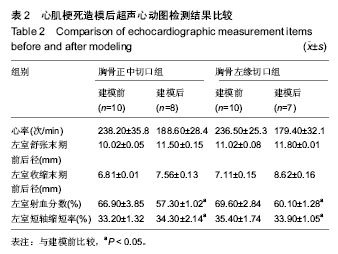
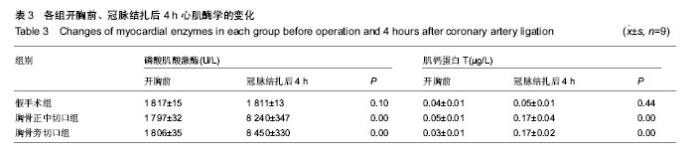
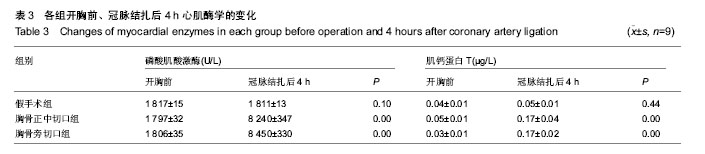
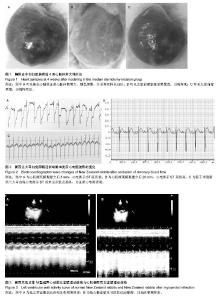
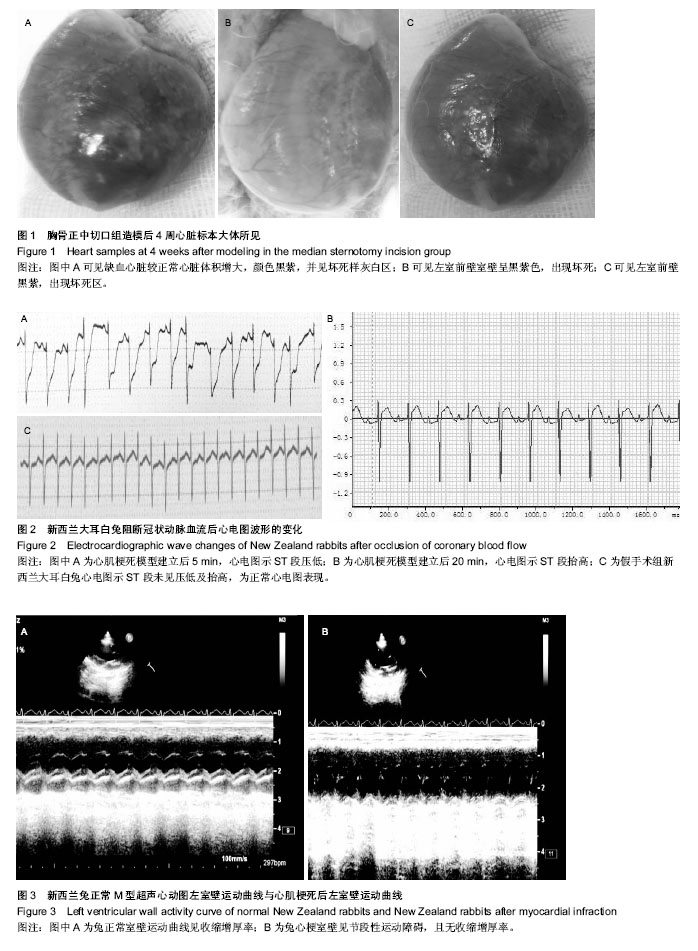
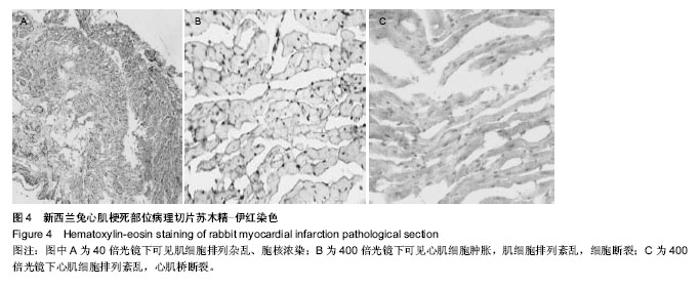
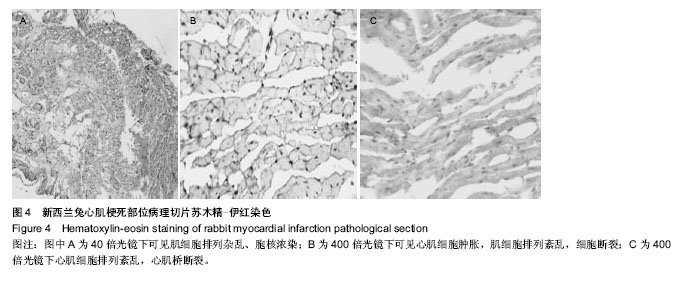
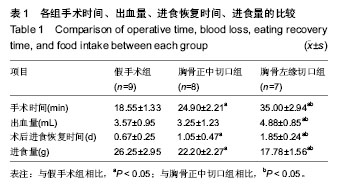
2.1 实验兔成活率 假手术组(10只)1只死于麻醉意外,9只成活。围手术期胸骨正中切口组(10只)和胸骨左缘切口组(10只)各死亡1只,死亡率10%(1/10)。4周后胸骨左缘切口组死于心包填塞2只,总死亡率30%(3/10),成活率70%(7/10);胸骨正中切口组死于术后切口感染1只,总死亡率20%(2/10),存活率80%(8/10)。 胸骨正中切口组与胸骨左缘切口组造模成功后,心脏大体观察,梗死灶主要在左室前壁及心尖部(图1),且均为透壁性坏死。 2.2 手术时间、进食恢复时间、进食量 假手术组所用的手术时间最短,胸骨正中切口组所需的手术时间较胸骨左缘切口组短,差异有显著性意义。而胸骨正中切口组和胸骨左缘切口组所需的手术时间与假手术组相比差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05,表1)。胸骨正中切口组术中出血量与假手术组相比差异无显著性意义,胸骨左缘切口组与胸骨正中切口组及假手术组相比出血量多且差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05,表1)。假手术组术后进食恢复时间最短,其次是胸骨正中切口组,而胸骨左缘切口组术后进食恢复时间最长,3组间比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05,表1)。进食量比较亦存在假手术组最多,其次是胸骨正中切口组,胸骨左缘切口组最少,3组间比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05,表1)。 2.3 心电图检查结果 术中实验组新西兰大耳白兔在结扎1-20 min后出现不同程度的心电图改变,胸骨正中切口组与胸骨左缘切口组中各有1只ST段压低(图2A),其余18只均表现在ST段抬高(图2B),成功率为84%。R波明显减小。假手术组心电图无明显改变(图2C)。 2.4 超声心动图检查结果 结扎成功后存活4周,M型超声心动图显示,结扎前降支前各组左室前壁局部心肌运动幅度及增厚率均正常(图3A),结扎前降支后胸骨正中切口组和胸骨左缘切口组左室前壁可见节段性运动障碍,收缩增厚率较结扎前均明显减低(图3B)。 实验兔术后左室射血分数及左室短轴缩短率较术前相比均明显减低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05,表2)。结扎冠脉后,胸骨正中切口组:术后4周存活的8只兔中,7只均提示节段性室壁运动障碍并有5只有室壁瘤形成,2只提示心包少量积液(其中1只见胸腔积液)。胸骨左缘切口组:术后4周存活的7只兔中,其中5只提示节段性室壁运动障碍,其中1只合并室壁瘤形成,3只提示心包积液。 2.5 病理切片 结扎成功后兔心梗部位病理切片显示,40倍光学显微镜下可见心肌细胞排列紊乱(图4A),400倍光学显微镜下见心肌细胞排列紊乱,细胞肿胀,肌细胞断裂(图4B,C),说明心梗模型制做成功。 2.6 心肌酶学指标 胸骨正中切口组与胸骨左缘切口组制作心肌梗死模型成功后4 h心肌酶学指标磷酸肌酸激酶与肌钙蛋白较术前明显升高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05,表3),而假手术组术前术后无显著变化(P > 0.05)。"
| [1] Zhao XJ, Liu XL, He GX,et al. Effects of single-dose atorvastatin on interleukin-6, interferon gamma, and myocardial no-reflow in a rabbit model of acute myocardial infarction and reperfusion.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2014;47(3): 245-251. [2] Kren L, Meluzin J, Pavlovsky Z,et al.Experimental model of myocardial infarction: Histopathology and reperfusion damage revisited.Pathol Res Pract. 2010;206(9):647-650. [3] Chou CC, Wen MS, Lee HL,et al. Dantrolene suppresses ventricular ectopy and arrhythmogenicity with acute myocardial infarction in a langendorff-perfused pacing-induced heart failure rabbit model.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2014;25(4):431-439. [4] Chou CC, Chang PC, Wen MS,et al. Effects of SEA0400 on arrhythmogenicity in a Langendorff-perfused 1-month myocardial infarction rabbit model.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2013;36(5):596-606. [5] Mitsos S, Koletsis EN, Katsanos K,et al. Intramyocardial thrombin promotes angiogenesis and improves cardiac function in an experimental rabbit model of acute myocardial infarction. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;147(4):1376-1383. [6] Cona MM, Feng Y, Li Y,et al.Comparative study of iodine-123-labeled hypericin and (99m)Tc-labeled hexakis [2-methoxy isobutyl isonitrile] in a rabbit model of myocardial infarction.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2013; 62(3):304-311. [7] Piccirillo G, Moscucci F, D'Alessandro G,et al.Myocardial repolarization dispersion and autonomic nerve activity in a canine experimental acute myocardial infarction model.Heart Rhythm. 2014;11(1):110-118. [8] Glukhov AV, Hage LT, Hansen BJ,et al.Sinoatrial node reentry in a canine chronic left ventricular infarct model: role of intranodal fibrosis and heterogeneity of refractoriness.Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2013;6(5):984-994. [9] Park N, Kim J, Lee M,et al. Echocardiographic assessment of coronary artery flow in normal canines and model dogs with myocardial infarction.J Vet Sci. 2014;15(1):149-155. [10] Welt FG, Gallegos R, Connell J,et al. Effect of cardiac stem cells on left-ventricular remodeling in a canine model of chronic myocardial infarction.Circ Heart Fail. 2013;6(1):99-106.. [11] Peukert D, Laule M, Kaufels N,et al.A minimally invasive method for induction of myocardial infarction in an animal model using tungsten spirals.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2009; 25(5):529-535. [12] Munz MR, Faria MA, Monteiro JR,et al.Surgical porcine myocardial infarction model through permanent coronary occlusion.Comp Med. 2011;61(5):445-452. [13] Saeed M, Martin AJ, Saloner D,et al.Noninvasive MR characterization of structural and functional components of reperfused infarct.Acta Radiol. 2010;51(10):1093-1102. [14] Lukács E, Magyari B, Tóth L,et al. Evaluation of experimental myocardial infarction models via electromechanical mapping and magnetic resonance imaging.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013;91(8):617-624. [15] Houtgraaf JH, de Jong R, Kazemi K,et al. Intracoronary infusion of allogeneic mesenchymal precursor cells directly after experimental acute myocardial infarction reduces infarct size, abrogates adverse remodeling, and improves cardiac function.Circ Res. 2013;113(2):153-166. [16] Chandrakala AN, Kwiatkowski P, Sai-Sudhakar CB,et al. Induction of early biomarkers in a thrombus-induced sheep model of ischemic heart failure.Tex Heart Inst J. 2013;40(5): 511-520. [17] Spata T, Bobek D, Whitson BA,et al. A nonthoracotomy myocardial infarction model in an ovine using autologous platelets.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:938047. [18] Hofmann U, Beyersdorf N, Weirather J,et al.Activation of CD4+ T lymphocytes improves wound healing and survival after experimental myocardial infarction in mice.Circulation. 2012;125(13):1652-1663. [19] Noyan-Ashraf MH, Momen MA, Ban K,et al. GLP-1R agonist liraglutide activates cytoprotective pathways and improves outcomes after experimental myocardial infarction in mice. Diabetes. 2009;58(4):975-983. [20] Zhang Y, Elsik M, Edgley AJ,et al. A new anti-fibrotic drug attenuates cardiac remodeling and systolic dysfunction following experimental myocardial infarction.Int J Cardiol. 2013;168(2):1174-1185. [21] Yannarelli G, Tsoporis JN, Desjardins JF,et al. Donor mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) undergo variable cardiac reprogramming in vivo and predominantly co-express cardiac and stromal determinants after experimental acute myocardial infarction.Stem Cell Rev. 2014;10(2):304-315. [22] Liehn EA, Tuchscheerer N, Kanzler I,et al. Double-edged role of the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis in experimental myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58(23):2415-2423. [23] 孙帅,郭涛.冠状动脉堵闭法与栓塞法制备小型猪心肌梗死模型的对比[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,13(50):9913- 9916. [24] Lukács E, Magyari B, Tóth L, et al. Overview of large animal myocardial infarction models (review).Acta Physiol Hung. 2012;99(4):365-381. [25] Unis A, Abdelbary A, Hamza M.Comparison of the effects of escitalopram and atorvastatin on diet-induced atherosclerosis in rats.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014;92(3):226-233. [26] Zhou BR, Pan Y, Zhai ZM. Fibrinogen and P-selectin expression in atherosclerosis model of Sprague Dawley rat. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011;124(22):3768-3772. [27] Dillard A, Matthan NR, Lichtenstein AH.Use of hamster as a model to study diet-induced atherosclerosis.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2010;7:89. [28] Floyd JS, Maynard C, Weston P,et al.Effects of ischemic preconditioning and arterial collateral flow on ST-segment elevation and QRS complex prolongation in a canine model of acute coronary occlusion.J Electrocardiol. 2009;42(1):19-26. [29] 靳激扬.心肌梗死的动物模型制作[J].中国CT和MRI杂志, 2008, 6(4):73-75. [30] Popovsky J.Gradual occlusion of mesenteric vessels with ameroid clamp.Arch Surg. 1966;92(2):202-205. [31] 屈正,安春雷,党海明,等.中国实验小型猪慢性心肌缺血模型的制备与研究田[J].中国实验外科学杂志,2001,18(3):281. [32] Akiyama M, Akasaka T, Fujimoto K,et al. Heterogeneity of myocardial perfusion in distal coronary embolism with different particle sizes.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2006;19(1): 55-63. [33] 赵慧强,韩雅玲,王守力,等.置入铜丝缠绕型支架制作猪急性心肌梗死模型[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2008,16(3):189-192. [34] Mewton N, Rapacchi S, Augeul L,et al. Determination of the myocardial area at risk with pre- versus post-reperfusion imaging techniques in the pig model.Basic Res Cardiol. 2011;106(6):1247-1257. [35] 红梅.丹蒌片对大鼠心肌梗死面积和心室重构的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2011,17(10):208 -210. [36] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30. [37] 蒋清安,何国祥,刘建平,等.一种新的非人工通气兔心肌梗死模型的制作[J].第三军医学学报,2008, 30(5):406-409. [38] 孙林,李易,光雪峰,等.开胸结扎兔冠状动脉致急性心肌梗塞实验模型的研究[J].昆明医学院学报,2001,22(1): 39-41. [39] Suzuki Y, Oyane A, Ikeno F,et al. Development of animal model for calcified chronic total occlusion.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2009;74(3):468-475. [40] 徐军,张红明.结扎兔冠状动脉左前降支制作急性心肌梗死模型的价值[J].临床军医杂志,2008,36(2):3-5. [41] Romero D, Ringborn M, Demidova M,et al. Characterization of ventricular depolarization and repolarization changes in a porcine model of myocardial infarction.Physiol Meas. 2012; 3(12):1975-1991. [42] Kobayashi T, Ito T, Yamada S,et al. Electrocardiograms corresponding to the development of myocardial infarction in anesthetized WHHLMI rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus), an animal model for familial hypercholesterolemia.Comp Med. 2012;62(5):409-418. [43] Chrastina A, Pokreisz P, Schnitzer JE.Experimental model of transthoracic, vascular-targeted, photodynamically induced myocardial infarction.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014; 306(2):H270-278. [44] Lim BK, Shin JO, Choe SC,et al. Myocardial injury occurs earlier than myocardial inflammation in acute experimental viral myocarditis.Exp Mol Med. 2005;37(1):51-57. [45] Guo J, Li HZ, Wang LC,et al. Increased expression of calcium-sensing receptors in atherosclerosis confers hypersensitivity to acute myocardial infarction in rats.Mol Cell Biochem. 2012;366(1-2):345-354. [46] Cimino S, Canali E, Petronilli V,et al.Global and regional longitudinal strain assessed by two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography identifies early myocardial dysfunction and transmural extent of myocardial scar in patients with acute ST elevation myocardial infarction and relatively preserved LV function.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013;14(8):805-811. [47] Havakuk O, Entin-Meer M, Ben-Shoshan J,et al. Effect of vitamin D analogues on acute cardiorenal syndrome: a laboratory rat model.Isr Med Assoc J. 2013;15(11):693-697. [48] 董安平,韩克,马爱群,等.心肌梗死模型的建立及心功能的超声评价[J].中国医学影像技术,2003,19(8): 964-966. [49] 张蕊,王健,薛继平,等.猪心肌梗死模型的建立以及心功能的超声评价[J].山西医药杂志,2008,37(11) : 994-995. |
| [1] | Liu Wei, Huang Jian. Applied research and progress of three-dimensional printing technology in joint replacement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1123-1130. |
| [2] | Yang Bao-jia, Yang Kai-shun, Yao Ru-bin. Correlation of nicotine dose and lumbar posterolateral fusion rate: imaging and biomechanical testing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(48): 7251-7260. |
| [3] | Wu Xiao-guang, Qiu Zhi-fu, Meng Jie, Zu Bing-xue, Li Meng-meng, Miao Hui. Effects of Buyanghuanwu decoction on the protein expression of PI3K, Akt, Bcl-2 and BAX in brain tissue of a rat model of cerebral hemorrhage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 5933-5938. |
| [4] | Zhang Jian-jun, Shi Huan-chang. Immunosuppressed rat model of cerebral hemorrhage: construction and assessment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 5939-5945. |
| [5] | Fu Feng, Zhao Ming-liang, Li Xiao-hong, Chen Chong, Wang Li-na, Sun Hong-tao, Tu Yue, Zhang Sai . Dynamic changes of brain cavity in rats after traumatic brain injury detected by MRI-based three-dimensional reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 5946-5952. |
| [6] | Yu Yu-qin, Hu Nian-chun, Duan Ji-an, Li Da-peng, Liu Chang. Neuroprotective effects of sufentanil preconditioning on spinal cord injury in mouse models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 5966-5972. |
| [7] | Wang Zhan, Li Hao-peng, He Xi-jing, Hao Ding-jun, Zhang Kun, Chen Ming-xia, Lei Ting. Pathological changes in the spinal cord of a model of acute cauda equina compression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 5973-5978. |
| [8] | Zhao Yan-rui, Lv Wen-rui, Wang Dong, Zhou Jun-lin. Effects of carbonyl sulfide in a rat model of limb ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute lung injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 5994-6000. |
| [9] | Chen Wei-hua, Lv Guo-hua, Zhou Bin, Kang Yi-jun. Establishment of a dog model of pyogenic spinal infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 6014-6020. |
| [10] | Ge Run, Yang Lan. Protective effects of piperine on alveolar bone and collagen in a periodontitis model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 6034-6040. |
| [11] | Song Qiao-qiao, Zhou Hui-liang, Zhen Hai-tao, Wang Na, Deng Jing, Wang Jin-xiang, Pan Xing-hua . Establishment and evaluation of a rhesus monkey model of experimental type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 6048-6053. |
| [12] | Pan Lei, Zhang Jin-biao, Cui Rong-gang, Zhao Bao-hui, Li Hua, Zhang Zhong-yong, Wang Xu-chu. Establishment of nonalcoholic fatty liver C57BL/6 mouse models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 6054-6059. |
| [13] | Wang Shi-jun, Li Yu-ting, Li Chun-de. Establishment, application and progression of an animal model of cervical spondylosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 6067-6073. |
| [14] | Liu Ying-jie, Peng Jun, Liu Xiao-kang, Zhao Cheng, Yang Er-zhu, Xu Jian-guang. Experimental animal models of intervertebral fusion-induced adjacent segment degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(39): 5825-5833. |
| [15] | Zhang Meng, Wei Jun-qiang, Duan Jian-wei, Yan Shi. Relationship of quadriceps tendon and the stability of external fixator in rabbit femur fracture model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(39): 5834-5839. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||