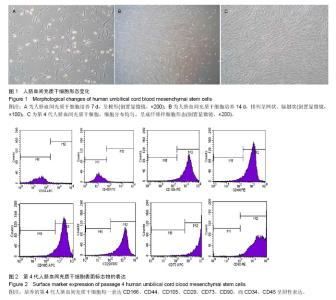
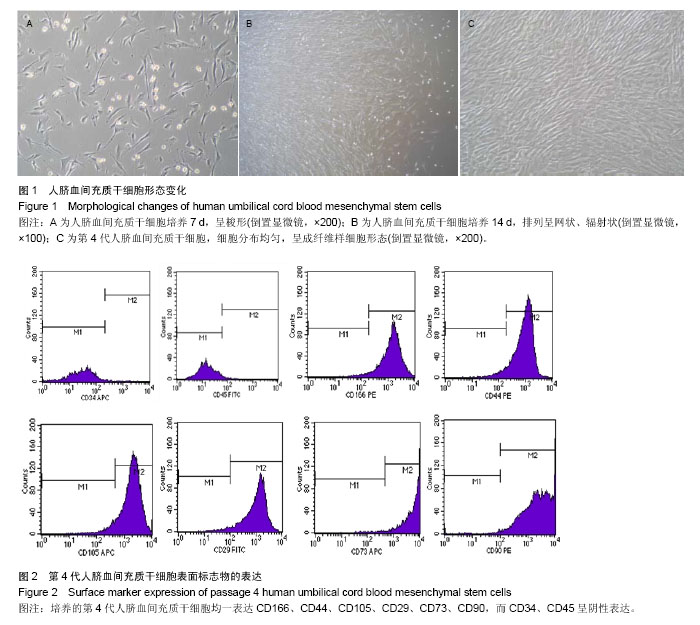
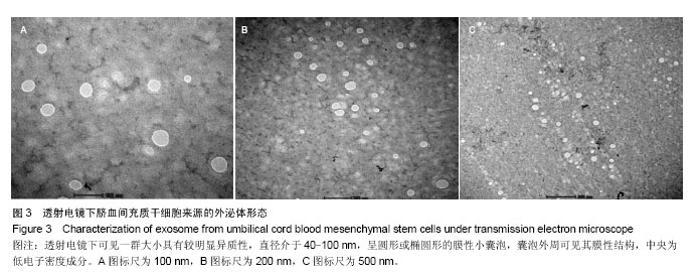
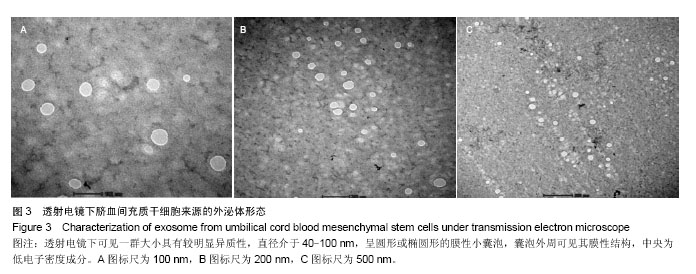
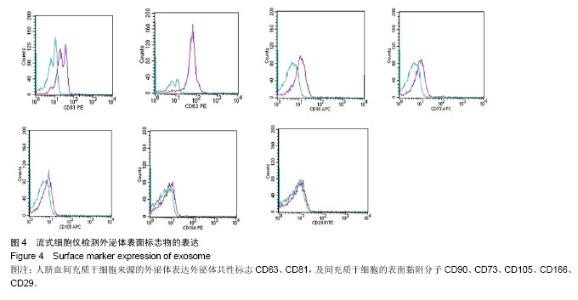
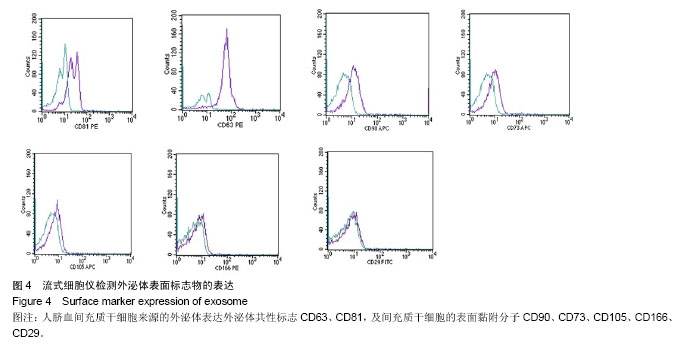
| [1] De Bari C, Dell'Accio F, Tylzanowski P,et al.Multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from adult human synovial membrane. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(8):1928-1942.
[2] 曲鑫,王新超,韩璐,等.不同来源间质干细胞移植治疗大鼠肝纤维化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(6):926-931.
[3] 王艳,赵新利,张军艳,等.脐带间充质干细胞治疗帕金森病的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(6):932-937.
[4] Gnecchi M, Zhang Z, Ni A, et al.Paracrine mechanisms in adult stem cell signaling and therapy.Circ Res. 2008;103(11): 1204-1219.
[5] Sun D, Zhuang X, Zhang S,et al. Exosomes are endogenous nanoparticles that can deliver biological information between cells.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(3):342-347.
[6] Lee Y, El Andaloussi S, Wood MJ.Exosomes and microvesicles: extracellular vesicles for genetic information transfer and gene therapy.Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21(R1): R125-134.
[7] Li T, Yan Y, Wang B,et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(6):845-854.
[8] Bruno S, Grange C, Deregibus MC,et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles protect against acute tubular injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20(5):1053-1067.
[9] Gatti S, Bruno S, Deregibus MC,et al. Microvesicles derived from human adult mesenchymal stem cells protect against ischaemia-reperfusion-induced acute and chronic kidney injury.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26(5):1474-1483.
[10] Bieback K, Kern S, Klüter H,et al. Critical parameters for the isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood. Stem Cells. 2004;22(4):625-634.
[11] Phuc PV, Ngoc VB, Lam DH,et al. Isolation of three important types of stem cells from the same samples of banked umbilical cord blood.Cell Tissue Bank. 2012;13(2):341-351.
[12] 赵霞,路希敬,刘国强,等.不同培养基培养人脐血间充质干细胞的差异[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(19):3449-3454.
[13] Johnstone RM, Adam M, Hammond JR,et al.Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes).J Biol Chem. 1987;262(19):9412-9420.
[14] Buschow SI, van Balkom BW, Aalberts M,et al. MHC class II-associated proteins in B-cell exosomes and potential functional implications for exosome biogenesis.Immunol Cell Biol. 2010;88(8):851-856.
[15] Andersson-Willman B, Gehrmann U, Cansu Z,et al. Effects of subtoxic concentrations of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles on human lymphocytes, dendritic cells and exosome production. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012;264(1):94-103.
[16] 余思,邓建中,李志澄,等.未成熟树突状细胞-胃癌细胞融合细胞来源的exosome诱导特异性抗肿瘤免疫[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2013,7(9):3897-3901.
[17] Masyuk AI, Huang BQ, Ward CJ,et al. Biliary exosomes influence cholangiocyte regulatory mechanisms and proliferation through interaction with primary cilia.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010;299(4):G990- 999.
[18] 张在云,李晓梅,王涓冬,等. IL-18 基因修饰对肺癌细胞来源 exosome 诱导杀伤肿瘤细胞作用的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2011,27(9):1758-1761.
[19] Février B, Raposo G. Exosomes: endosomal-derived vesicles shipping extracellular messages.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004; 16(4):415-421.
[20] 孙爱丽,胡晓燕,关广聚,等.尿胞外体亮氨酸氨基肽酶及二肽基肽酶在糖尿病肾病中的变化[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2011, 27(4): 775-778.
[21] Simpson RJ, Jensen SS, Lim JW. Proteomic profiling of exosomes: current perspectives. Proteomics. 2008;8(19): 4083-4099.
[22] Lässer C, Alikhani VS, Ekström K,et al. Human saliva, plasma and breast milk exosomes contain RNA: uptake by macrophages. J Transl Med. 2011;9:9.
[23] Michael A, Bajracharya SD, Yuen PS,et al. Exosomes from human saliva as a source of microRNA biomarkers.Oral Dis. 2010;16(1):34-38.
[24] Dai S, Wei D, Wu Z,et al. Phase I clinical trial of autologous ascites-derived exosomes combined with GM-CSF for colorectal cancer.Mol Ther. 2008;16(4):782-790.
[25] Blanchard N, Lankar D, Faure F,et al.TCR activation of human T cells induces the production of exosomes bearing the TCR/CD3/zeta complex.J Immunol. 2002;168(7):3235-3241.
[26] van Niel G, Raposo G, Candalh C,et al. Intestinal epithelial cells secrete exosome-like vesicles.Gastroenterology. 2001; 121(2):337-349.
[27] de Gassart A, Géminard C, Hoekstra D,et al. Exosome secretion: the art of reutilizing nonrecycled proteins. Traffic. 2004;5(11):896-903.
[28] 陈规划,杨扬,张琪,等.间充质干细胞应用现状及展望[J].中华肝脏外科手术学电子杂志,2013,2(4):210-212.
[29] 苏绍红,张俊峰,李倩如,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植小鼠免疫系统CD4+T细胞亚群的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(1): 106-111.
[30] 陶然,韩焱福, 柴家科.人脐带组织间充质干细胞研究进展及应用前景[J].军事医学科学院院刊,2010,34(3):293-296.
[31] 殷海斌,田新,杨春会,等.间充质干细胞的生物学特性及临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(14): 2282-2289.
[32] 张丹,王允野.骨髓间充质干细胞在肝纤维化中的研究进展[J].中国实用医药,2014,9(12):249-250.
[33] Camussi G, Deregibus MC, Tetta C. Paracrine/endocrine mechanism of stem cells on kidney repair: role of microvesicle-mediated transfer of genetic information.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2010;19(1):7-12.
[34] Lai RC, Arslan F, Lee MM,et al. Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.Stem Cell Res. 2010;4(3):214-222.
[35] Lai RC, Chen TS, Lim SK. Mesenchymal stem cell exosome: a novel stem cell-based therapy for cardiovascular disease. Regen Med. 2011;6(4):481-492.
[36] Timmers L, Lim SK, Arslan F, et al. Reduction of myocardial infarct size by human mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium.Stem Cell Res. 2007;1(2):129-137.
[37] Sibov TT, Severino P, Marti LC,et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood: parameters for isolation, characterization and adipogenic differentiation. Cytotechnology. 2012;64(5):511-521.
[38] 廖金卯,胡小宣,李灼日.人脐血间充质干细胞移植改善肝硬化大鼠的肝功能[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(27):5005-5011. |