Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (37): 5961-5966.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.37.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparison of methods for culturing the mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord blood
Huang Hong-yu1, Liu Guo-ping2, Duan Li2, 3, Chen Yun-fang2, 3, Xiong Jian-yi2, 3, Wang Da-ping2, 3
- 1Shantou University Medical College, Shantou 515000, Guangdong Province, China
2Second People’s Hospital of Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518035, Guangdong Province, China
3Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Tissue Engineering, Shenzhen 518035, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2014-07-12Online:2014-09-03Published:2014-09-03 -
Contact:Wang Da-ping, M.D., Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Second People’s Hospital of Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518035, Guangdong Province, China; Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Tissue Engineering, Shenzhen 518035, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Huang Hong-yu, Studying for master’s degree, Shantou University Medical College, Shantou 515000, Guangdong Province -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. S2012010008129; the Funds of Science and Technology Commission of Shenzhen Municipality, No. ZDSY20120614154551201, GJHZ20130412153906739, CXZZ20120614160234842, JSGG20140519105550503
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Hong-yu, Liu Guo-ping, Duan Li, Chen Yun-fang, Xiong Jian-yi, Wang Da-ping. Comparison of methods for culturing the mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord blood[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(37): 5961-5966.
share this article
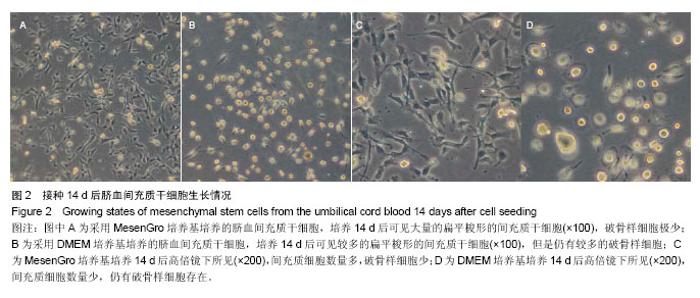
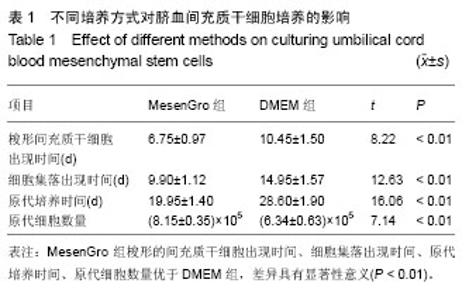
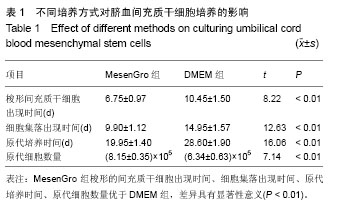
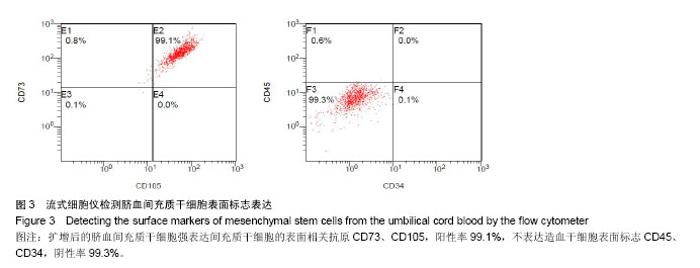
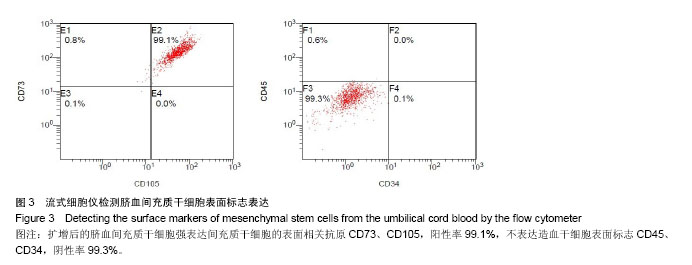
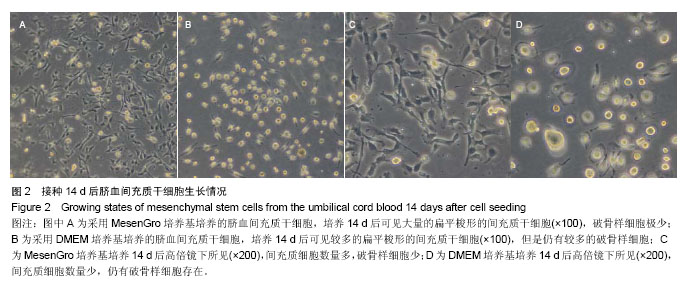
2.1 不同培养方法对脐血间充质干细胞的影响 MesenGro组细胞接种于MesenGro人间充质干细胞培养基后,漂浮于培养液中,多为圆形或不规则形,接种平均24 h后出现贴壁细胞,更换培养基后细胞继续生长。接种平均7 d后,细胞胞体逐渐长大,出现零散的成纤维样的扁平梭形的间充质干细胞,单个核,剩下部分为破骨样细胞,胞体大,呈圆形,多个核,以间充质干细胞居多。接种平均10 d后,细胞迅速增殖,破骨样细胞逐渐减少,间充质干细胞呈片状生长,出现大量的扁平梭形的间充质干细胞。接种平均14 d后,破骨样细胞进一步减少,扁平梭形细胞进一步增多(图2)。接种平均21 d后,细胞生长达80%-90%贴壁,呈形态均一的扁平梭形的间充质干细胞,形态类似于骨髓间充质干细胞,较骨髓间充质干细胞稍小。DMEM组接种于DMEM培养基,梭形的间充质干细胞出现时间、细胞集落出现时间、原代细胞培养时间、原代细胞数量与MesenGro组相比差异有显著性意义(表1)。"
| [1] Kim SM, Lim JY, Park SI,et al.Gene therapy using TRAIL-secreting human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells against intracranial glioma.Cancer Res. 2008;68(23):9614-9623. [2] Bieback K, Kern S, Kocaömer A,et al. Comparing mesenchymal stromal cells from different human tissues: bone marrow, adipose tissue and umbilical cord blood. Biomed Mater Eng. 2008;18(1 Suppl):S71-76. [3] Zhao F, Qu Y, Liu H,et al.Umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells co-modified by TERT and BDNF: A novel neuroprotective therapy for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2014. [Epub ahead of print] [4] Jaing TH.Umbilical cord blood: a trustworthy source of multipotent stem cells for regenerative medicine.Cell Transplant. 2014;23(4-5):493-496. [5] Phuoc Thi-My Nguyen, Anh Thai-Quynh Nguyen, Nhung Thi Nguyen,et al. Human umbilical cord blood derived mesenchymal stem cells were differentiated into pancreatic endocrine cell by Pdx-1 electrotransfer. Biomedical Research and Therapy. 2014;1(2): 50-56. [6] Zhu Y, Guan YM, Huang HL,et al.Human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cell transplantation suppresses inflammatory responses and neuronal apoptosis during early stage of focal cerebral ischemia in rabbits.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014;35(5):585-591. [7] Lee M, Jeong SY, Ha J,et al.Low immunogenicity of allogeneic human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and in vivo.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;446(4):983-989. [8] Berg L, Koch T, Heerkens T,et al.Chondrogenic potential of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from equine bone marrow and umbilical cord blood.Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2009; 22(5):363-370. [9] Chang YS, Oh W, Choi SJ,et al.Human umbilical cord blood- derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate hyperoxia-induced lung injury in neonatal rats.Cell Transplant. 2009;18(8):869-886. [10] Toupadakis CA, Wong A, Genetos DC,et al.Comparison of the osteogenic potential of equine mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, adipose tissue, umbilical cord blood, and umbilical cord tissue.Am J Vet Res. 2010;71(10):1237-1245. [11] Jung KH, Shin HP, Lee S,et al.Effect of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a cirrhotic rat model. Liver Int. 2009;29(6):898-909. [12] Malgieri A, Kantzari E, Patrizi MP, et al.Bone marrow and umbilical cord blood human mesenchymal stem cells: state of the art.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2010;3(4):248-269. [13] Wang M, Yang Y, Yang D,et al. The immunomodulatory activity of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro.Immunology. 2009;126(2):220-232. [14] Campagnoli C, Roberts IA, Kumar S,et al.Identification of mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells in human first-trimester fetal blood, liver, and bone marrow.Blood. 2001;98(8): 2396-2402. [15] Kern S, Eichler H, Stoeve J,et al.Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, or adipose tissue.Stem Cells. 2006;24(5):1294-1301. [16] Wagner W, Wein F, Seckinger A,et al.Comparative characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord blood.Exp Hematol. 2005;33(11):1402-1416. [17] Liu G, Li Y, Sun J,et al.In vitro and in vivo evaluation of osteogenesis of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells on partially demineralized bone matrix.Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(3):971-982. [18] Rebelatto CK, Aguiar AM, Moretão MP,et al.Dissimilar differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, and adipose tissue.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2008;233(7):901-913. [19] Horn P, Bork S, Diehlmann A,et al.Isolation of human mesenchymal stromal cells is more efficient by red blood cell lysis.Cytotherapy. 2008;10(7):676-685. [20] Phuc PV, Nhung TH, Loan DT,et al.Differentiating of banked human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells into insulin-secreting cells.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2011; 47(1):54-63. [21] Avanzini MA, Bernardo ME, Cometa AM,et al.Generation of mesenchymal stromal cells in the presence of platelet lysate: a phenotypic and functional comparison of umbilical cord blood- and bone marrow-derived progenitors.Haematologica. 2009;94(12):1649-1660. [22] Rodrigues JP, Paraguassú-Braga FH, Carvalho L, et al. Evaluation of trehalose and sucrose as cryoprotectants for hematopoietic stem cells of umbilical cord blood.Cryobiology. 2008;56(2):144-151. [23] Rubinstein P.Cord blood banking for clinical transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009;44(10):635-642. [24] Pesce M, Orlandi A, Iachininoto MG,et al.Myoendothelial differentiation of human umbilical cord blood-derived stem cells in ischemic limb tissues.Circ Res. 2003;93(5):e51-62. [25] Hogan CJ, Shpall EJ, McNulty O,et al.Engraftment and development of human CD34(+)-enriched cells from umbilical cord blood in NOD/LtSz-scid/scid mice.Blood. 1997;90(1): 85-96. [26] Murohara T, Ikeda H, Duan J,et al.Transplanted cord blood-derived endothelial precursor cells augment postnatal neovascularization.J Clin Invest. 2000;105(11):1527-1536. [27] Fan CL, Li Y, Gao PJ,et al.Differentiation of endothelial progenitor cells from human umbilical cord blood CD 34+ cells in vitro.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2003;24(3):212-218. [28] 郭继强,刘爱兵,王东平,等. 密度梯度离心法分离脐血干细胞:分离介质的筛选[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(23): 4189-4195. [29] Kempuraj D, Saito H, Kaneko A,et al.Characterization of mast cell-committed progenitors present in human umbilical cord blood.Blood. 1999;93(10):3338-3346. [30] Leor J, Guetta E, Feinberg MS,et al.Human umbilical cord blood-derived CD133+ cells enhance function and repair of the infarcted myocardium.Stem Cells. 2006;24(3):772-780. [31] 赵霞,路希敬,刘国强,等.不同培养基培养人脐血间充质干细胞的差异[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(19): 3449-3454. [32] Baek EJ, Kim HS, Kim S,et al.In vitro clinical-grade generation of red blood cells from human umbilical cord blood CD34+ cells.Transfusion. 2008;48(10):2235-2245. [33] Koestenbauer S, Zisch A, Dohr G,et al.Protocols for hematopoietic stem cell expansion from umbilical cord blood.Cell Transplant. 2009;18(10):1059-1068. [34] Ratajczak J, Zuba-Surma E, Klich I,et al.Hematopoietic differentiation of umbilical cord blood-derived very small embryonic/epiblast-like stem cells.Leukemia. 2011;25(8): 1278-1285. [35] 赵春生,王更银,李俊峡,等.人脐血间充质干细胞体外分离培养条件的优化及其鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(27):5326-5330. [36] 马金本,单根法.以内皮细胞基础培养液复合不同方法培养犬脐血间充质干细胞的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008, 12(34): 6755-6758. [37] 王利培,姜红.脐血间充质干细胞培养体系的建立[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(3):502-504. [38] Lee OK, Kuo TK, Chen WM,et al.Isolation of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood.Blood. 2004;103(5):1669-1675. [39] Peters R, Wolf MJ, van den Broek M,et al.Efficient generation of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood in stroma-free liquid culture.PLoS One. 2010;5(12):e15689. [40] Lee CC, Lin SJ, Cheng PJ,et al.The regulatory function of umbilical cord blood CD4(+) CD25(+) T cells stimulated with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 and exogenous interleukin (IL)-2 or IL-15.Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2009;20(7):624-632. [41] Griffin DO, Holodick NE, Rothstein TL.Human B1 cells in umbilical cord and adult peripheral blood express the novel phenotype CD20+ CD27+ CD43+ CD70-.J Exp Med. 2011; 208(1):67-80. [42] Lee MW, Jang IK, Yoo KH,et al.Stem and progenitor cells in human umbilical cord blood.Int J Hematol. 2010;92(1):45-51. [43] Liu G, Li Y, Sun J,et al.In vitro and in vivo evaluation of osteogenesis of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells on partially demineralized bone matrix. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(3):971-982. [44] Seo MS, Jeong YH, Park JR,et al.Isolation and characterization of canine umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells.J Vet Sci. 2009;10(3):181-187. [45] Baek EJ, Kim HS, Kim S,et al.In vitro clinical-grade generation of red blood cells from human umbilical cord blood CD34+ cells.Transfusion. 2008;48(10):2235-2245. [46] 迟作华,张洹.脐带血间充质干细胞的研究进展[J].国际生物医学工程杂志,2006,29(1): 29-34. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [4] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [5] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [6] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [7] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [8] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [9] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [10] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [11] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [12] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [13] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [14] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [15] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||