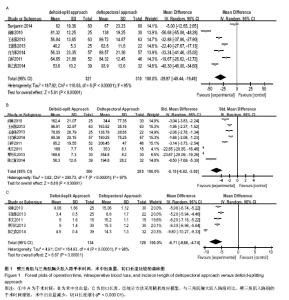
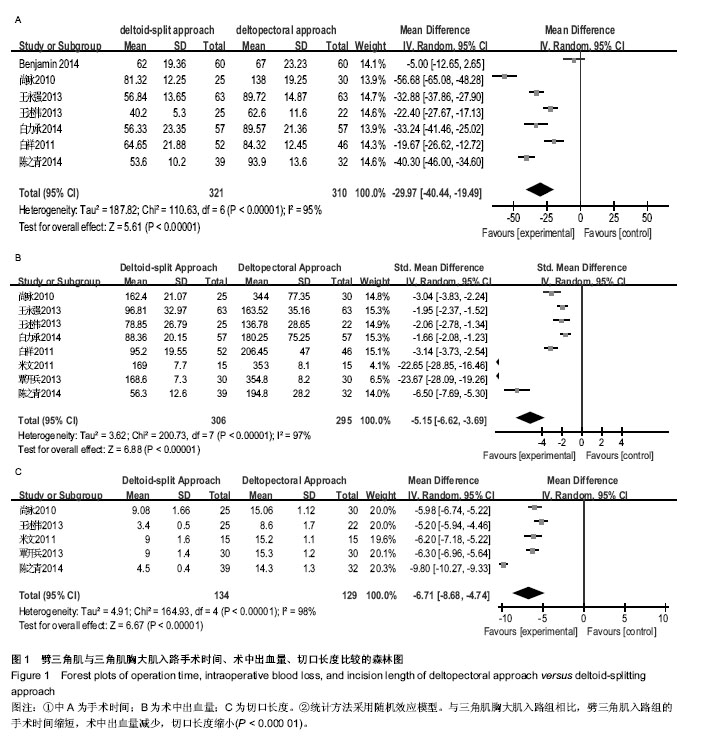
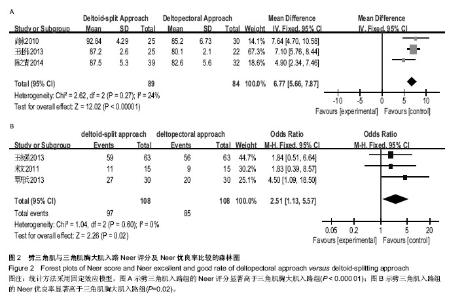
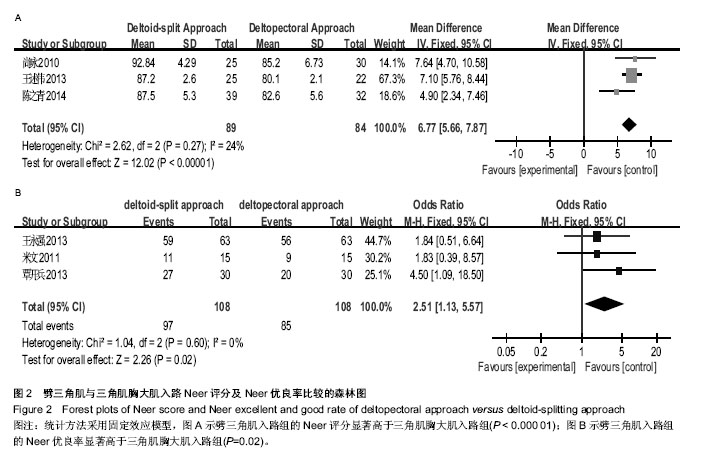
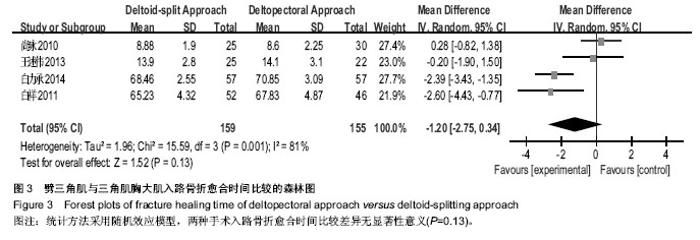
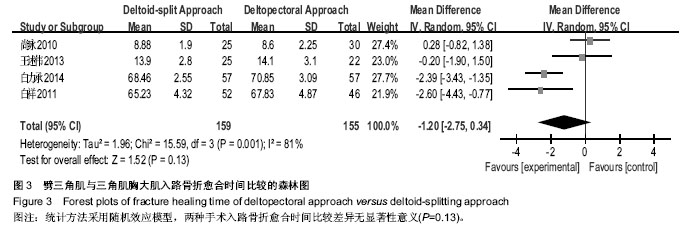
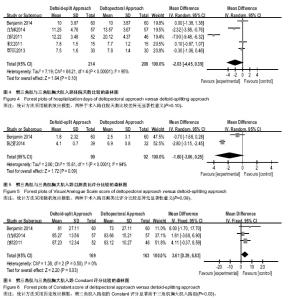
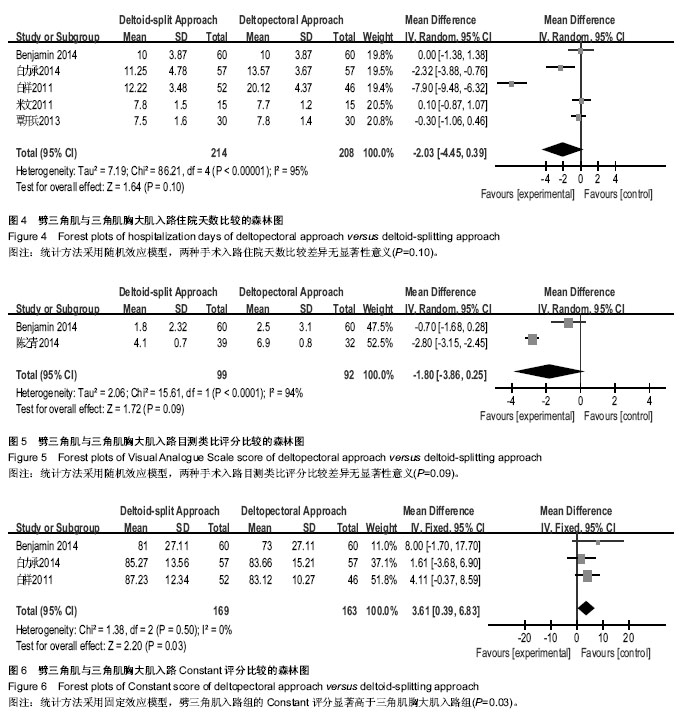
| [1] Helmy N, Hintermann B. New trends in the treatment of proximal humerus fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006; 442:100-108.
[2] Buecking B, Mohr J, Bockmann B,et al. Deltoid-split or Deltopectoral Approaches for the Treatment of Displaced Proximal Humeral Fractures? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014; 472:1576-1585.
[3] 曲志国,崔玉玲,崔正宏.肱骨近端锁定钢板与传统钢板及交叉针治疗老年肱骨近端骨折的疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2008,22(2):248-250.
[4] Alderson P, Green S, Higgins JPT, et al. Cochrane Reviews’ Handbook4.2.1//the Cochrane Library. UK: John Wiley &Sons, Ltd,2004.
[5] Smith AM,Mardones RM,Sperling JW, et al. Early complications Of operatively treated proximal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16:14-24.
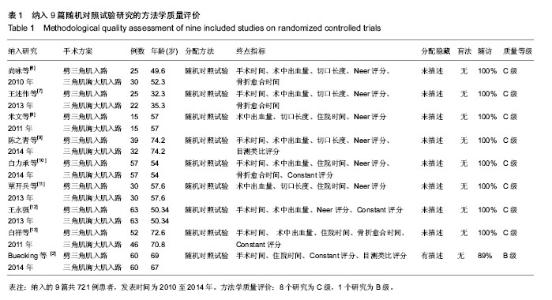
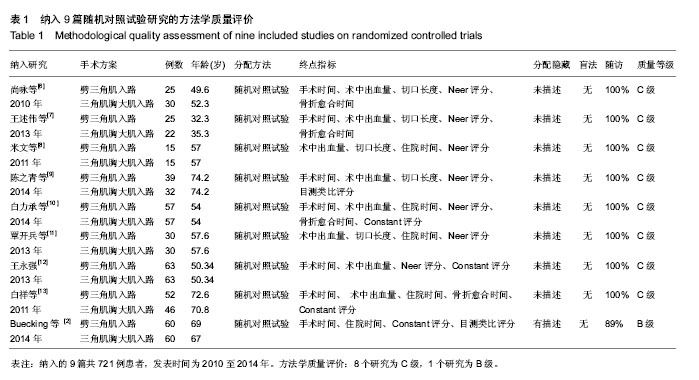
[6] 尚咏,伍骥,赵旭红,等.小切口与传统术式治疗肱骨外科颈骨折疗效比较[J].山西医科大学学报,2010,41(3):265-267.
[7] 王述伟,苏山林,马象武,等. 两种手术入路空心螺钉固定治疗肱骨大结节撕脱骨折比较[J].中国民间疗法,2013,21(10):60-61.
[8] 米文,徐微.小切口入路与传统术式治疗肱骨外科颈骨折疗效比较[J].中国现代医生,2011,49(15):35-36.
[9] 陈之青,谢金兔,李坚.微创切口与经典大切口结合锁定钢板内固定治疗老年人肱骨近端骨折疗效比较[J].中国医师杂志, 2014, 16(3): 386-388.
[10] 白力承,顾邵,熊鹰,等.锁定加压钢板置入肱骨近端骨折的最理想位置:选择肩外侧三角肌劈开入路[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(9):1453-1458.
[11] 覃开兵,周树权.小切口入路与传统术式治疗肱骨外科颈骨折疗效观察[J].现代诊断与治疗,2013,24(5):1042-1043.
[12] 王永强.两种不同手术入路治疗肱骨近端骨折的疗效比较[J].中外健康文摘,2013,10(15):67-68.
[13] 白祥,黄建明,吴金平.不同手术入路治疗老年肱骨近端骨折[J]. 临床骨科杂志, 2011,14(6):671-673.
[14] 孙惠清,任亚军,张云庆,等. 锁定加压钢板治疗肱骨近端骨折[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(11):1082-1083.
[15] Gardner MJ, Voos JE, Wanich T, et al. Vascular implications of minimally invasive plating of proximal humerus fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20:602-607.
[16] 许林东,廖前德.MIPPO技术结合锁定加压钢板和传统内固定法治疗肱骨近端骨折的疗效比较[J].中国医师杂志,2011,13(7): 956-958.
[17] Wu CH, Ma CH, Yeh JJ, et al. Locked Plating for Proximal Humeral Fractures: Differences Between the Deltopectoral and Deltoid-Splitting Approaches. J Trauma.2011;71: 1364-1370.
[18] 蔡俊丰,尹峰,祝建光,等.微创经皮钢板内固定治疗肱骨近端骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2010,26(7):606-610.
[19] Gardner MJ, Griffith MH, Dines JS, et al.The extended anterolateral acromial approach allows minimally invasive access to the proximal humerus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005; (434):123-129.
[20] 王俊生,武志兵.腋神经、桡神经与肱骨关系的应用解剖[J].创伤外科杂志,2003,5(1):64.
[21] 刘德荣,梁加利,陆耀刚.微创技术植入锁定加压钢板治疗肱骨干近端骨折[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2009,23(11):1282-1284.
[22] Chou YC, Tseng IC, Chiang CW, et al. Shoulder hemiarthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures: comparisons between the deltopectoral and anterolateral deltoid-splitting approaches. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22: e1-e7.
[23] Hepp P, Theopold J, Voigt C, et al. The surgical approach for locking plate osteosynthesis of displaced proximal humeral fractures influences the functional outcome.J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2008;17:21-28. |