Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (30): 4777-4782.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.30.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Three-dimensional finite element analysis of severe wedge-shaped defective premolar restored with fiber post and composite resin
Shen Qing-yi1, Wang Dong-mei2, Zhong Qun1, Chen Dong1
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Shanghai Stomatological Disease Center, Shanghai 200031, China
2School of Mechanical Power, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
-
Revised:2014-06-06Online:2014-07-16Published:2014-08-08 -
Contact:Chen Dong, Chief physician, Department of Prosthodontics, Shanghai Stomatological Disease Center, Shanghai 200031, China -
About author:Shen Qing-yi, M.D., Associate chief physician, Department of Prosthodontics, Shanghai Stomatological Disease Center, Shanghai 200031, China -
Supported by:Project of Shanghai Health Bureau, No. 20114136
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shen Qing-yi, Wang Dong-mei, Zhong Qun, Chen Dong. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of severe wedge-shaped defective premolar restored with fiber post and composite resin[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(30): 4777-4782.
share this article

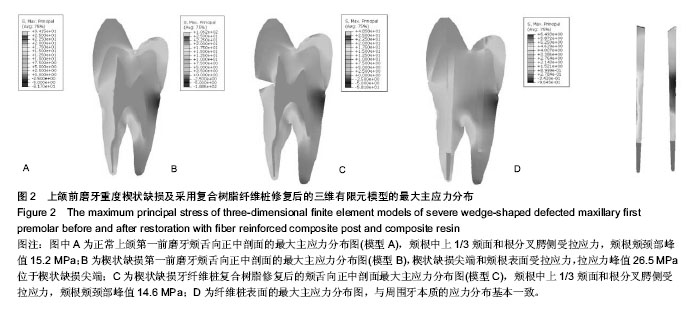
2.1 上颌前磨牙重度楔状缺损及采用复合树脂纤维桩修复后的三维有限元模型的最大主应力分布 通过颊舌向正中剖面图,观察各模型的最大主应力分布云图(图2A-C)。模型A正常前磨牙与模型C纤维桩复合树脂修复重度楔状缺损前磨牙的牙本质最大主应力分布趋势基本一致,拉应力主要分布于颊颈部和颊、腭根中上1/3的颊表面,且拉应力峰值均位于颊根颊颈部,分别为15.2 MPa和14.6 MPa。而模型B重度楔状缺损前磨牙的最大主应力除了分布于上述两个部位外,尤以楔状缺损尖端最为集中,拉应力峰值位于楔状缺损尖端位高达26.5 MPa。而模型C中,经复合树脂修复后的楔缺尖端牙本质的拉应力仅为4.1 MPa,与无楔缺的正常牙基本相当。纤维桩表面的最大主应力分布与其周边的根方牙本质应力分布云图基本一致(图2D)。"
| [1] Litonjua LA, Andreana S, Bush PJ, et al. Non carious cervical lesions and Abfractions: A Re-evalution. J Am Dent Assoc. 2003;134(7):845-850. [2] 刘彦,牛忠英,石馨,等.2038例中老年人健康体检中牙齿楔形缺损的调查和分析[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2010,20(11): 645-647. [3] Bergstrom J, Eliasson S. Cervical abrasion to relation to tooth brushing and periodontal health. Scand J Pent Res. 1988;96 (5): 405-411. [4] Rees JS. The biomechanics of abfraction. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2006;220(1):69-80. [5] Shetty SM, Shetty RG, Mattigatti S. No carious cervical lesion: abfraction. J Int Oral Health. 2013;5(5):143-146 [6] 杨文丽,林雪峰,朱娟芳,等.人工楔状缺损对牙颈部硬组织应力分布的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2011,29(2):118-123. [7] Senna P, Edl Bel Cruy A, Rösing C. Non-carious cervical lesions and occlusion: a systematic review of clinical studies. J Oral Rehabil. 2012;39(6):450-462. [8] Murakami N, Wakabayashi N. Finite element contact analysis as a critical technique in dental biomechanics. J Prosthodont Res. 2014;58(2):92-101. [9] 杨文丽,林雪峰,李相如,等.人工楔状缺损牙颈部硬组织应力分布的有限元接触分析[J].上海口腔医学,2012,21(4)407-411. [10] Ma H, Wang Q, Liu Z, et al. The influence of lateral occlusal forces to the stress distribution of restorative material of wedge-shaped defect.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011; 29(5):550-554. [11] Rees JS, Hammadeh M. Undermining of enamel as a mechanism of abfraction lesion formation: a finite element study. Eur J Oral Sci. 2004;112(4):347-352. [12] 杨文丽,林雪峰,刘耀鹏.釉牙本质界潜行性破坏对牙颈部硬组织应力分布的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(7):1015-1020. [13] Dietschi D, Duc O, Krejci I, et al. Biomechanical considerations for the restoration of endodontically treated teeth: a systematic review of the literature, PartⅡ (Evaluation of fatigue behavior, interfaces, and in vivo studies). Quintessence Int. 2008;39(2):117-129. [14] 许琳,朱文军,程绍华,等.纤维桩对复合树脂修复根管治疗后磨牙影响的有限元研究[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志, 2014,8(1): 18-22. [15] 李向荣,邱建平,郭爱军.玻璃纤维桩复合树脂核在楔状缺损露髓基牙中应用的临床观察[J].北京口腔医学,2012,20(1):48-49. [16] 王惠芸.我国人牙的测量与统计[J].中华口腔科杂志, 1959,3(2): 149-155. [17] Guimarães JC, Guimarães Soella G, Brandão Durand L, et al. Stress amplifications in dental non-carious cervical lesions. J Biomech. 2014;47(2):410-416. [18] 庄茁,由小川,廖剑晖,等.基于ABAQUS的有限元分析和应力[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2009. [19] Borcic J, Anic I, Urek MM, et al. The prevalence of non-carious cervical lesions in permanent dentition. J Oral Rehabil. 2004;31(2):117-123. [20] Soares PV, Souza LV, Verissimo C, et al. Effect of root morphology on biomechanical behavior of premolars associated with abfraction lesion and different loading types. J Oral Rehabil. 2014;41(2):108-114. [21] Salameh Z, Ounsi HF, Aboushelib MN, et al. Effect of different onlay systems on fracture resistance and failure pattern of endodontically treated mandibular molars restored with and without glass fiber posts. Am J Dent. 2010;23(2):81-86. [22] 徐娟,刘洪臣,王延荣,等.下颌前磨牙创伤咬合点加载的三维有限元应力分析[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2001,2(1):8-10. [23] 李苏伶,付钢,王璐.不同载荷角度下后牙残根核桩冠修复后三维有限元应力分析[J].重庆医科大学学报,2009,34(3):342-345. [24] 皮昕.口腔解剖生理学(第6版)[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2007. [25] 王惠芸,陈一怀,刘继光,等.生理牙合咬合接触点的计算机图像分析[J].实用口腔医学杂志,1997,13(1):37-40. [26] Okada D, Miura H, Suzuki C, et al. Stress distribution in roots restored with different types of post systems with composite resin. Dent Mater J. 2008;27(4):605-611. [27] Pegoretti A, Fambri L, Zappini G, et al. Finite element analysis of a glass fibre reinforced composite endodontic post. Biomaterials. 2002;23(13):2667-2682 [28] Cheng ZJ, Wang XM, Ge J, et al. The mechanical anisotropy on a longitudinal section of human enamel studied by nanoindentation. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21(6): 1811-1816. [29] 徐韵,陆卫青.牙合力与深度对楔状缺损修复疗效影响的有限元分析[J].同济大学学报(医学版)2011,32(5):57-60. [30] Costa A, Xavier T, Noritomi P, et al. The influence of elastic modulus of inlay materials on stress distribution and fracture of premolars. Oper Dent. 2014;39(4):E160-E170. [31] Oyar P, Ulusoy M, Eskita?ç?o?lu G. Finite element analysis of stress distribution in ceramic crowns fabricated with different tooth preparation designs. J Prosthet Dent. 2014. [32] Murakami K, Yamamoto K, Tsuyuki M, et al. Theoretical efficacy of preventive measures for pathologic fracture after surgical removal of mandibular lesions based on a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;72(4):833. [33] Durmu? G, Oyar P. Effects of post core materials on stress distribution in the restoration of mandibular second premolars: A finite element analysis. J Prosthet Dent. 2014 . [34] Cui C, Sun J. Optimizing the design of bio-inspired functionally graded material (FGM) layer in all-ceramic dental restorations. Dent Mater J. 2014;33(2):173-178. [35] Oyar P. The effects of post-core and crown material and luting agents on stress distribution in tooth restorations. J Prosthet Dent. 2014. [36] O'Brien S, Shaw J, Zhao X, et al. Size dependent elastic modulus and mechanical resilience of dental enamel. J Biomech. 2014;47(5):1060-1066. [37] Belli S, Eraslan O, Eraslan O, et al. Effects of NaOCl, EDTA and MTAD when applied to dentine on stress distribution in post-restored roots with flared canals. Int Endod J. 2014. [38] Costa A, Xavier T, Noritomi P, et al. The Influence of Elastic Modulus of Inlay Materials on Stress Distribution and Fracture of Premolars. Oper Dent. 2014. [39] Lazari PC, Oliveira RC, Anchieta RB, et al. Stress distribution on dentin-cement-post interface varying root canal and glass fiber post diameters. A three-dimensional finite element analysis based on micro-CT data. J Appl Oral Sci. 2013;21(6): 511-517. [40] Zhao L, Li LJ, Zhao K, et al. Finite element analysis of first maxillary molars restored with different post and core materials. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2013;22(6):607-12. [41] Park JW, Ferracane JL. Water aging reverses residual stresses in hydrophilic dental composites. J Dent Res. 2014;93(2):195-200. [42] Bicalho AA, Valdívia AD, Barreto BC, et al. Incremental filling technique and composite material--part II: shrinkage and shrinkage stresses. Oper Dent. 2014;39(2):E83-92. [43] Belli S, Eraslan Ö, Eraslan O, et al. Effect of restoration technique on stress distribution in roots with flared canals: an FEA study. J Adhes Dent. 2014;16(2):185-191. [44] Petcu CM, Ni?oi D, Mercu? V, et al. Masticatory tensile developed in upper anterior teeth with chronic apical periodontitis. A finite-element analysis study. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2013;54(3):587-592. [45] Feitosa SA, Corazza PH, Cesar PF, et al. Pressable feldspathic inlays in premolars: effect of cementation strategy and mechanical cycling on the adhesive bond between dentin and restoration. J Adhes Dent. 2014;16(2):147-154. [46] He L, Liu L, Gao B, et al. Finite element analysis of the stress distribution of two-piece post crown with different adhesives. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013;31(4):348-352. [47] Su KC, Chuang SF, Ng EY, et al. An investigation of dentinal fluid flow in dental pulp during food mastication: simulation of fluid-structure interaction. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2014; 13(3):527-535. [48] Lü LW, Meng GW, Liu ZH. Finite element analysis of multi-piece post-crown restoration using different types of adhesives. Int J Oral Sci. 2013;5(3):162-166. [49] Afroz S, Tripathi A, Chand P, et al. Stress pattern generated by different post and core material combinations: a photoelastic study. Indian J Dent Res. 2013;24(1):93-97. [50] 缪羽,于蕴之,李婧,等.桩核对牙冠完整的上颌第一前磨牙的应力影响[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2012,13(1):30-33. [51] Ona M, Wakabayashi N, Yamazaki T,et al. The influence of elastic modulus mismatch between tooth and post and core restorations on root fracture. Int Endod J. 2013;46(1):47-52. |
| [1] | Peng Zhixin, Yan Wengang, Wang Kun, Zhang Zhenjiang. Finite element analysis and structural optimization design of 3D printed forearm braces [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1340-1345. |
| [2] | Wu Tianliang, Tao Xiuxia, Xu Hongguang. Influence of different bone mineral densities on cage subsidence after stand-alone oblique lateral interbody fusion: three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1352-1358. |
| [3] | Liu Jinyu, Zhang Hanshuo, Cui Hongpeng, Pan Lingzhi, Zhao Boran, Li Fei, Ding Yu. Finite element biomechanical analysis of minimally invasive treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy and accurate exercise rehabilitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1359-1364. |
| [4] | He Yujie, Kang Zhijie, Xue Mingming, Jin Feng, Li Zhijun, Wang Xing, Xu Yangyang, Gao Mingjie, Li Jiawei, Li Xiaohe, Wang Haiyan. Finite element analysis of transarticular screw fixation of adolescent thoracic vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1365-1370. |
| [5] | Wen Xinghua, Ding Huanwen, Cheng Kai, Yan Xiaonan, Peng Yuanhao, Wang Yuning, Liu Kang, Zhang Huiwu. Three-dimensional finite element model analysis of intramedullary nailing fixation design for large femoral defects in Beagle dogs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1371-1376. |
| [6] | Zhu Lin, Gu Weiping, Wang Can, Chen Gang. Biomechanical analysis of All-on-Four and pterygomaxillary implants under different maxillary bone conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 985-991. |
| [7] | Sun Jiangwei, Wang Junxiang, Baibujiafu·Yellisi, Dai Huijuan, Nijati·Turson. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution in different smooth collar implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1004-1011. |
| [8] | Jiang Yifang, Cai Qimin, Chu Zhengyi, Qin Min, Shen Yurong, Gu Yuanping. Simulation analysis of stress distribution of NRT FILES in curved root canals [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1038-1042. |
| [9] | Li Huiqin, Wang Chunjuan, Wang Yu, Wang Weifeng, Chen Dinggen, Li Na. Clear aligner orthodontic therapy of rotated mandibular teeth with different shapes: a three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1050-1054. |
| [10] | Liu Qinghua, Cai Yongqiang, Jin Feng, Yu Jinghong, Wang Haiyan, Zhang Yunfeng, Wang Lidong, Li Jiawei, Wang Xing, He Yujie, Dai Lina, Wang Jianzhong, Wu Chao, Tong Ling, Kang Zhijie, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe. Finite element model of the 12-year-old child whole cervical spine: establishment and validity verification based on CT data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 500-504. |
| [11] | Lu Hui, Wu Qimei, Liu Rong. Finite element analysis and application of unilateral and bilateral bone-filling mesh container in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 391-397. |
| [12] | Liu Baijie, Zhou Honghai, He Xinyu, Qin Hongtu, Chen Longhao, Tian Junming, Lu Qingwang. Three-dimensional finite element method to analyze biomechanical characteristics of spinal manipulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4385-4392. |
| [13] | Li Jie, Cao Shuai, Guo Dong, Zhang Qiongchi, He Xijing, Li Haopeng, Lu Teng. Finite element analysis of polyetheretherketone and titanium rods in posterior lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(22): 3445-3450. |
| [14] | Gao Hongliang, Li Xusheng, Wang Zhenhu, Zhang Xiaomin, Li Peng, Zhang Tao, Liu Hua, Li Songkai. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the treatment of lumbar spondylolysis with cannulated lag screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(22): 3451-3456. |
| [15] | Chen Jianquan, Chen Maoshui, Lyu Zhouming, Chen Rongbin, Yu Zhaoyu, Liu Wanpeng, Lin Xinyuan, Lin Dingkun. Biomechanical properties of cortical bone trajectory combined with pedicle screw fixation on vertebral body motion unit: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(22): 3457-3462. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||