Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (27): 4345-4354.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.27.014
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanical embolectomy using Penumbra system for acute cerebral embolism: model establishment and finite element analysis in one case
Liu Bo1, Xie Peng2, Li Zhi-wei1
- 1 Department of Neurology, Yongchuan Hospital, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 402160, China; 2 Department of Neurology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400016, China
-
Online:2014-06-30Published:2014-06-30 -
Contact:Li Zhi-wei, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Neurology, Yongchuan Hospital, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 402160, China -
About author:Liu Bo, Studying for doctorate, Attending physician, Department of Neurology, Yongchuan Hospital, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 402160, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Yongchuan District of Chongqing City, No. Ycstc, 2013nc8031; the Foundation of Chongqing Municipal Health Bureau, No. 2010-2-250; the Soft Science Foundation of Yongchuan District of Chongqing City, No. Ycstc, 2011BE5004.
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Bo, Xie Peng, Li Zhi-wei. Mechanical embolectomy using Penumbra system for acute cerebral embolism: model establishment and finite element analysis in one case[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(27): 4345-4354.
share this article
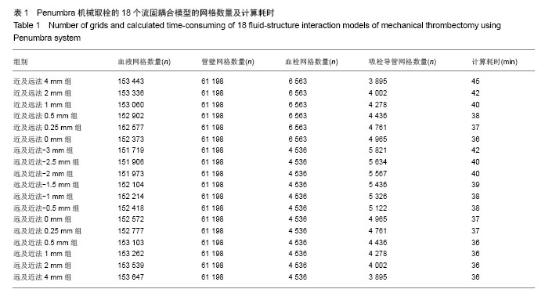
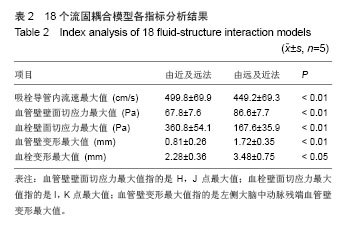
2.1 Penumbra机械取栓的18个流固耦合模型的网格数量和计算耗时 每个流固耦合模型包括4部分,即血液、血管壁、血栓、吸栓导管。由于18个流固耦合模型具有相同的血管壁,故划分的血管壁网格数量均为61 198个。“由近及远吸栓法”的6个模型具有相同的完整的血栓模型,其血栓网格数量均为6 563个;而“由远及近吸栓法”的12个模型亦具有相同的血栓模型,但由于血栓被吸栓导管戳了个洞,网格数量减少,其血栓网格数量均为4 536个。由于18个模型具有相同的血管内腔,意味着吸栓导管深入模型越多,血液的体积将越少。因此,“由近及远吸栓法”的6个模型从4 mm组至0 mm组吸栓导管网格数量逐渐增多,从3 895个增至4 965个,而血液网格数量逐渐减少,从153 443个减至152 373个;同样,“由远及近吸栓法”的12个模型从-3 mm组至4 mm组吸栓导管网格数量逐渐减,从5 821个减至 3 895个,而血液网格数量逐渐增多,从151 719个增至 153 647个。18个模型总的计算耗时相当,为36-45 min (表1)。"
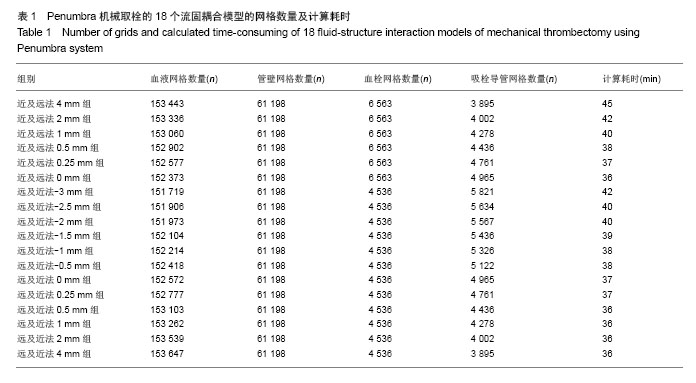
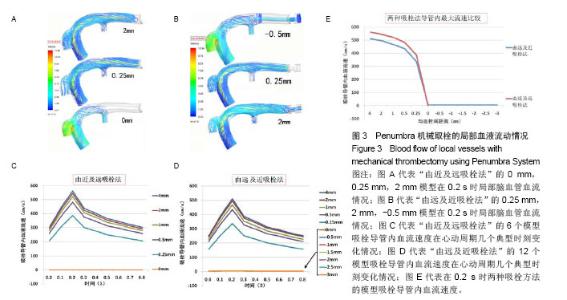
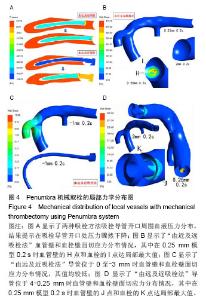
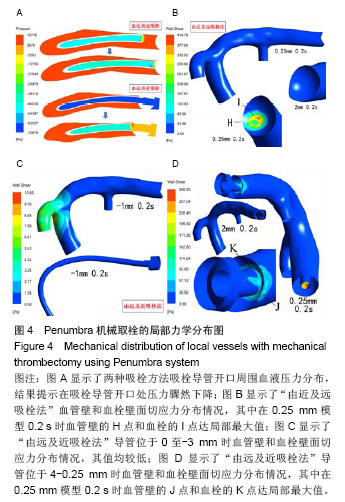
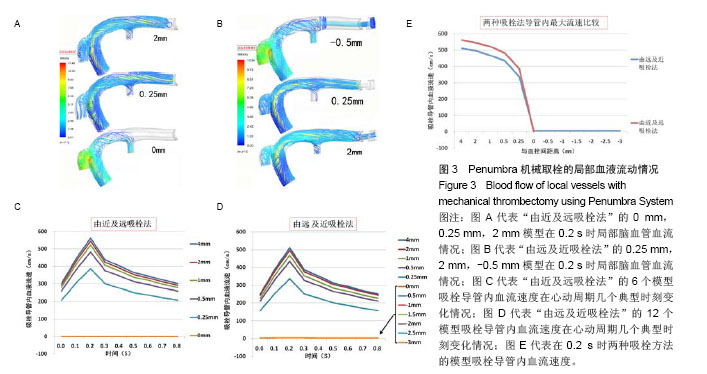
2.2 Penumbra机械取栓的18个流固耦合模型的计算结果总体情况 由于颈内动脉的灌注压和血流速度随着心跳周期性变化着,故每个流固耦合模型入出口边界条件也周期性变化着。在心动周期每个时刻血液流线图、血液压力降图、血管壁和血栓壁面切应力图、血管壁和血栓变形情况分布图的ANSYS染色均无明显变化,只是色彩代表的值随时在变(图3-5)。因此,在每个模型任选一时刻的ANSYS染色图均能代表该模型各时刻对应分布图的整体情况。 2.3 Penumbra机械取栓的18个流固耦合模型的血液流动情况 患者心率为75次/min,故每个心动周期为0.8 s,设患者左侧颈内动脉C5段灌注压某最低值(8 kPa)处为0 s,下一个最低值处时间应为0.8 s。观察两种吸栓方法的每个模型在0-0.8 s的整个心动周期各时刻血液流线图发现:①在“由近及远吸栓法”的4 mm模型中在吸栓导管抽吸前,闭塞大脑中动脉近端无血液流动,血流仅流向大脑中动脉分支,当吸栓导管使用-70 kPa抽吸时,大量血液通过血管残端流入吸栓导管,在2 mm,1 mm,0.5 mm,0.25 mm模型中有与之相同的表现;在“由近及远吸栓法”的0 mm模型中吸栓导管已直接接触血栓,血管残端和吸栓导管内无血液流动(图3A)。②在“由远及近吸栓法”的0 mm,-0.5 mm,-1 mm,-1.5 mm,-2 mm,-2.5 mm,-3 mm模型中血管残端无血液流动,吸栓导管有少许血流,血流来自闭塞远端血管,在0.25 mm模型中有少许血液通过血管残端流向远端血管,另大量血液通过残端流入吸栓导管;在“由远及近吸栓法”的4 mm,2 mm,1 mm,0.5 mm模型中既有大量血液流入吸栓导管,又有较多血液流向远端血管(图3B)。 测量两种吸栓方法的每个模型吸栓导管内血流速度发现:①如图3C所示,在“由近及远吸栓法”的4 mm,2 mm,1 mm,0.5 mm,0.25 mm模型中吸栓导管内血流速度随心跳周期性变化着,在0 s,0.8 s处位于最低值,在0.2 s时均达最大值,其值依次为563 cm/s,545 cm/s,522 cm/s,482 cm/s,387 cm/s;但0 mm模型导管内血流速度不随时间变化,始终为0 cm/s。②如图3D所示,在“由远及近吸栓法”的0 mm,-0.5 mm,-1 mm,-1.5 mm,-2 mm,-2.5 mm,-3 mm模型导管内血流速度不随时间变化,始终为4-6 cm/s;在4 mm,2 mm,1 mm,0.5 mm,0.25 mm 模型中吸栓导管内血流速度也随心跳周期性变化着,在0 s,0.8 s处均位于最低值,在0.2 s时均达最大值,其值依次为511 cm/s,496 cm/s,468 cm/s,434 cm/s,337 cm/s。假定在0.2 s时刻的血管状态下分别使用两种方法实施取栓,如图3E所示,“由近及远吸栓法” 的吸栓导管随着慢慢靠近血栓,其管腔内血液流速逐渐降低,直至停止。“由远及近吸栓法” 的吸栓导管送入到血栓远端后,边退边吸,开始导管内有少许血流,血流较慢,当导管退到0 mm处后,其管腔内血流速度逐渐增高。在4-0.25 mm的5个模型中比较两种吸栓方法的导管内血流速度最大值,统计方法采用配对t检验,结果提示差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01,表2),显示在4-0.25 mm范围内“由近及远吸栓法” 导管内血流速度最大值较“由远及近吸栓法”更大。 2.4 Penumbra机械取栓的18个流固耦合模型的血流压力降分布情况 如图4所示,观察每个模型在心动周期不同时刻血液压力降分布情况发现:①“由近及远吸栓法”的各模型大脑中动脉血管残端腔内压力均较高,接近于颈内动脉;吸栓导管颅内段腔内压力为-40-50 kPa,而血液压力陡然下降的部位为吸栓导管开口。②“由远及近吸栓法” 的各模型大脑中动脉血管残端腔内压力也接近于颈内动脉,但吸栓导管位于-3-0 mm时,导管腔内压力很低,接近-70 kPa,当导管退回到大脑中动脉血管残端腔内时,导管内压力有所上升,远端血管血压亦有所上升,但血液压力下降最迅速的部位仍为吸栓导管开口。 2.5 Penumbra机械取栓的18个流固耦合模型的血管壁和血栓壁面切应力分布 2.5.1 左侧大脑中动脉血管壁壁面切应力分布 观察18个流固耦合模型的血管壁壁面切应力分布图发现,每个模型左侧大脑中动脉血管壁壁面切应力均不高,其值为 1-60 Pa(图4B,C,D)。其中“由近及远吸栓法”0.25 mm模型在0.2 s时血栓近端附近的血管壁的H点局部达最大值(图4B);“由远及近吸栓法”0.25 mm模型在0.2 s时血栓近端附近的血管壁的J点局部达最大值(图4D),该吸栓法的0至-3 mm模型血栓远端血管管壁壁面切应力极低,为 1-5 Pa(图4C下图)。由于两种吸栓法的0.25 mm模型均计算了5个周期,H点和J点每个周期均在0.2 s时达局部最大值,计算5个周期H点和J点最大值的均值,比较2个模型均值之间差异,经过t 检验提示差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01,表2),显示J点最大值高于H点最大值。 2.5.2 血栓壁面切应力分布 观察18个流固耦合模型的血栓壁面切应力分布图发现,其值范围较大,为1-420 Pa (图4B,D)。在“由近及远吸栓法”的4 mm,2 mm,1 mm,0 mm模型中血栓壁面切应力较小,整体小于10 Pa,但在0.5 mm,0.25 mm模型中血栓壁面切应力明显增高,甚至高于400 Pa,其中0.25 mm模型在0.2 s时在I点达到局部最大值(图4B)。在“由远及近吸栓法”的4-1 mm,0至-3 mm模型中血栓壁面切应力也较小,整体也小于10 Pa, 在 0.5 mm,0.25 mm模型中血栓壁面切应力也明显增高,其中0.25 mm模型在0.2 s时在K点达到局部最大值(图4D)。由于两种吸栓法的0.25 mm模型均计算了5个周期,I点和K点每个周期均在0.2 s时达局部最大值,计算5个周期I点和K点最大值的均值,比较2个模型均值之间差异,经过t检验提示差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01),见表2,显示I点最大值明显高于K点最大值。 "
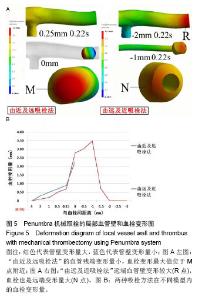
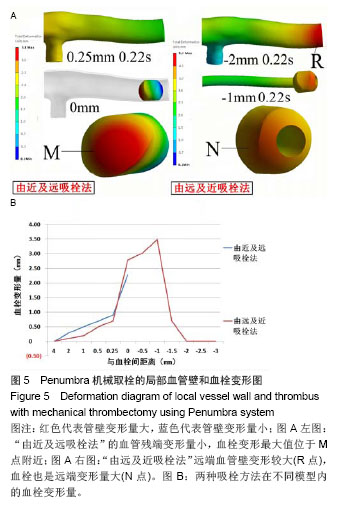
2.6 Penumbra机械取栓的18个流固耦合模型的血管壁和血栓变形情况 2.6.1 左侧大脑中动脉残端血管壁变形情况 观察每个模型整个心动周期左侧大脑中动脉残端管壁变形图,每个模型均在0.22 s时刻管壁变形量最大。比较每个模型在0.22 s时刻的左侧大脑中动脉残端管壁变形量最大值发现:①在“由近及远吸栓法”的4-0 mm模型残端管壁变形量最大值均较小,不超过1.5 mm(图5A左图);在“由远及近吸栓法”的4-0.25 mm模型残端管壁变形量最大值也较小,而在-3-0 mm模型中血栓远端的血管壁变形量较大(图5A右图的R点)。②其中“由近及远吸栓法”的0.25 mm模型在0.22 s时局部最大值是该方法所有模型的管壁变形量最大值;“由远及近吸栓法”的-2 mm模型在0.22 s时血栓远端的血管壁变形量是本法所有模型的管壁变形量最大值;这两个最大值均计算了5个周期,分别取均值,两最大值的均值之间经过t检验提示差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01) (表2),显示“由远及近吸栓法”的血管壁变形量明显大于“由近及远吸栓法”。 2.6.2 血栓变形情况 观察每个模型整个心动周期血栓变形图,每个模型血栓变形量受心跳影响较小,整个心动周期其值几乎不变。如图5B图所示,“由近及远吸栓法”的4-0.25 mm模型血栓变形量较小,小于1.0 mm,在0 mm 模型达最大值,最大值位于血栓近心段M点附近(图5A);“由远及近吸栓法”的4-0.25 mm,-1.5至-3 mm模型血栓变形量也较小,小于1.0 mm,但在0 mm,-0.5 mm,-1 mm模型血栓变形量值均较大,其中-1 mm模型达本法的最大值,最大值位于血栓远心段N点附近(图5A)。比较两种吸栓方法所得血栓变形量最大值,均计算了5个周期,分别取均值,两最大值的均值之间经过t检验提示差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表2,显示“由远及近吸栓法”的血栓变形量明显大于“由近及远吸栓法”。 "
| [1]Uesaka Y.Cerebral embolism and atrial fibrillation.Brain Nerve. 2013;65(7):761-769. [2]Avrahami I, Dilmoney B, Azuri A,et al.Investigation of risks for cerebral embolism associated with the hemodynamics of cardiopulmonary bypass cannula: a numerical model.Artif Organs. 2013;37(10):857-865. [3]Merchant FM, Delurgio DB.Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation and risk of asymptomatic cerebral embolism.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2014;37(3):389-397. [4]Haines DE.ERACEing the risk of cerebral embolism from atrial fibrillation ablation.Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2013; 6(5):827-829. [5]Verma A, Debruyne P, Nardi S,et al.Evaluation and reduction of asymptomatic cerebral embolism in ablation of atrial fibrillation, but high prevalence of chronic silent infarction: results of the evaluation of reduction of asymptomatic cerebral embolism trial.Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2013;6(5):835-842. [6]Ito A, Ii Y, Higashigawa T,et al.A case of spectacular shrinking deficit caused by paradoxical cerebral embolism secondary to pulmonary arteriovenous fistula.Brain Nerve. 2013;65(12): 1509-1513. [7]Gasparovic H, Borojevic M, Malojcic B,et al.Single aortic clamping in coronary artery bypass surgery reduces cerebral embolism and improves neurocognitive outcomes.Vasc Med. 2013;18(5):275-281. [8]Montavont A, Nighoghossian N, Derex L,et al.Intravenous r-TPA in vertebrobasilar acute infarcts.Neurology. 2004;62(10): 1854-1856. [9]Baltacio?lu F, Af?ar N, Ekinci G,et al.Intraarterial Thrombolysis with r-tPA for Treatment of Anterior Circulation Acute Ischemic Stroke. Technical and Clinical Results.Interv Neuroradiol. 2003; 9(3):273-282. [10]Zeumer H, Freitag HJ, Zanella F,et al.Local intra-arterial fibrinolytic therapy in patients with stroke: urokinase versus recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (r-TPA). Neuroradiology. 1993;35(2):159-162. [11]Aufderheide TP, Haselow WC, Hendley GE,et al.Feasibility of prehospital r-TPA therapy in chest pain patients.Ann Emerg Med. 1992;21(4):379-383. [12]Villwock MR, Singla A, Padalino DJ,et al.Acute ischaemic stroke outcomes following mechanical thrombectomy in the elderly versus their younger counterpart: a retrospective cohort study.BMJ Open. 2014;4(3):e004480. [13]Siu KL, Lee DG, Shim JH,et al.Mechanical Thrombectomy Using the Solitaire FR system for Occlusion of the Top of the Basilar Artery: Intentional Detachment of the Device after Partial Retrieval.Neurointervention. 2014;9(1):26-31. [14]Ahmad N, Nayak S, Jadun C,et al.Mechanical thrombectomy for ischaemic stroke: the first UK case series.PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e82218. [15]Friedrich B, Kertels O, Bach D,et al.Fate of the Penumbra after Mechanical Thrombectomy.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013. [Epub ahead of print] [16]Baek JM, Yoon W, Kim SK,et al.Acute Basilar Artery Occlusion: Outcome of Mechanical Thrombectomy with Solitaire Stent within 8 Hours of Stroke Onset.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013. [Epub ahead of print] [17]Hann S, Chalouhi N, Starke R,et al.Comparison of neurologic and radiographic outcomes with Solitaire versus Merci/Penumbra systems for acute stroke intervention. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:715170. [18]Akins PT, Amar AP, Pakbaz RS,et al.Complications of endovascular treatment for acute stroke in the SWIFT trial with solitaire and Merci devices.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014; 35(3):524-528. [19]Shaikh H, Pukenas BA, McIntosh A,et al.Combined use of Solitaire FR and Penumbra devices for endovascular treatment of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis in a child.BMJ Case Rep. 2014;2014. [20]Hann S, Chalouhi N, Starke R,et al.Comparison of neurologic and radiographic outcomes with Solitaire versus Merci/Penumbra systems for acute stroke intervention. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:715170. [21]Siu KL, Lee DG, Shim JH,et al.Mechanical Thrombectomy Using the Solitaire FR system for Occlusion of the Top of the Basilar Artery: Intentional Detachment of the Device after Partial Retrieval.Neurointervention. 2014;9(1):26-31. [22]Almekhlafi MA, Davalos A, Bonafe A,et al.Impact of Age and Baseline NIHSS Scores on Clinical Outcomes in the Mechanical Thrombectomy Using Solitaire FR in Acute Ischemic Stroke Study.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014. [Epub ahead of print] [23]Shaikh H, Pukenas BA, McIntosh A,et al.Combined use of Solitaire FR and Penumbra devices for endovascular treatment of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis in a child.BMJ Case Rep. 2014;2014. [24]Hussain SI, Zaidat OO, Fitzsimmons BF.The Penumbra system for mechanical thrombectomy in endovascular acute ischemic stroke therapy.Neurology. 2012;79(13 Suppl 1): S135-141. [25]Shrivastava M, Lahoti S, Sanghvi D,et al.Stand alone mechanical thrombectomy (with penumbra system) for acute ischemic stroke based on MR imaging: Single center experience. Neurol India. 2012;60(4):406-414. [26]Almekhlafi MA, Menon BK, Freiheit EA,et al.A meta-analysis of observational intra-arterial stroke therapy studies using the Merci device, Penumbra system, and retrievable stents.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34(1):140-145. [27]Kang DH, Kim YS, Park J,et al.Rescue forced-suction thrombectomy using the reperfusion catheter of the Penumbra System for thromboembolism during coil embolization of ruptured cerebral aneurysms.Neurosurgery. 2012;70(1 Suppl Operative):89-93. [28]Tarr R, Hsu D, Kulcsar Z,et al.The POST trial: initial post-market experience of the Penumbra system: revascularization of large vessel occlusion in acute ischemic stroke in the United States and Europe.J Neurointerv Surg. 2010;2(4):341-344. [29]Kang DH, Hwang YH, Kim YS,et al.Direct thrombus retrieval using the reperfusion catheter of the penumbra system: forced-suction thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32(2):283-287. [30]Kulcsár Z, Bonvin C, Pereira VM,et al.Penumbra system: a novel mechanical thrombectomy device for large-vessel occlusions in acute stroke.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010; 31(4):628-633. [31]Grunwald IQ, Walter S, Papanagiotou P,et al.Revascularization in acute ischaemic stroke using the penumbra system: the first single center experience.Eur J Neurol. 2009;16(11):1210-1216. [32]李震,焦征,马志刚.比较Penumbra系统取栓与SolitaireAB支架取栓治疗大脑中动脉血栓的疗效[J].临床合理用药杂志,2013, 6(36):89-90. [33]潘文龙,赵晓辉,王梅,等. 3例应用Penumbra系统介入治疗急性缺血性脑卒中患者的护理[J]. 护理实践与研究,2013,10(22): 128-129. [34]Huang YM, Chou IC, Jiang CP,et al.Finite element analysis of dental implant neck effects on primary stability and osseointegration in a type IV bone mandible.Biomed Mater Eng. 2014;24(1):1407-1415. [35]Lu S, Li T, Zhang Y,et al.Biomechanical optimization of the diameter of distraction screw in distraction implant by three-dimensional finite element analysis.Comput Biol Med. 2013;43(11):1949-1954. [36]Cift H, Deniz S, Ek?io?lu F.Determination of the effect on the proximal femoral load distribution of diaphyseal cement support in femoral intertrochanteric fractures with calcar defect by finite element analysis.Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi. 2013;24(3):163-168. [37]Sende J, Jabre P, Leroux B,et al.Invasive arterial blood pressure monitoring in an out-of-hospital setting: an observational study.Emerg Med J. 2009;26(3):210-212. [38]Hager H, Mandadi G, Pulley D,et al.A comparison of noninvasive blood pressure measurement on the wrist with invasive arterial blood pressure monitoring in patients undergoing bariatric surgery.Obes Surg. 2009;19(6):717-724. [39]Cao H, Norris P, Ozdas A,et al.A simple non-physiological artifact filter for invasive arterial blood pressure monitoring: a study of 1852 trauma ICU patients.Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2006;1:1417-1420. [40]Cebral JR,Löhner R.From medical images to anatomically accurate finite element grids.Inter J Numer Method Eng. 2001; 51(8):985-1008. [41]Pedley TJ.The fluid mechanics of large blood vessels[M].UK: Cambridge University Press,1980. [42]Qiao A, Liu Y.Influence of graft-host diameter ratio on the hemodynamics of CABG.Biomed Mater Eng. 2006;16(3): 189-201. [43]Aenis M, Stancampiano AP, Wakhloo AK,et al.Modeling of flow in a straight stented and nonstented side wall aneurysm model.J Biomech Eng. 1997;119(2):206-212. [44]付文宇,乔爱科.基于个性化颈内动脉瘤模型的流固耦合分析[J].医用生物力学,2012,27(4):421-426. [45]伍悦滨.高等流体力学[M].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学出版社,2013. [46]王松岭.高等工程流体力学[M].北京:中国电力出版社,2011. [47]Kawaguchi T, Nishimura S, Kanamori M,et al.Distinctive flow pattern of wall shear stress and oscillatory shear index: similarity and dissimilarity in ruptured and unruptured cerebral aneurysm blebs.J Neurosurg. 2012;117(4):774-780. [48]Tanoue T, Tateshima S, Villablanca JP,et al.Wall shear stress distribution inside growing cerebral aneurysm.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32(9):1732-1737. [49]Hu Z, Lu P, Xie H,et al.The study of noninvasive ventilator impeller based on ANSYS.Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2011;28(3):456-459. [50]Liu B, Wang X, Zhu H,et al.ANSYS simulation of subcutaneous pustule electrical characteristics.Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2011;28(6):1110-1113. [51]吕晨光,陈龙,田书玲. 混合动网格方法研究[J]. 航空计算技术, 2012,42(2):81-83. [52]王坤,周建强,刘凯,等. 基于动网格的罗茨鼓风机内部流场数值模拟[J]. 现代制造技术与装备,2013,3:6-7. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [3] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [4] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [5] | Xu Yulin, Shen Shi, Zhuo Naiqiang, Yang Huilin, Yang Chao, Li Yang, Zhao Heng, Zhao Lu. Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 826-830. |
| [6] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [7] | Wang Jiangna, Zheng Huifen, Sun Wei. Changes in dynamic stability, motor coordination and joint mechanics of the lower extremity during stair descent and performing phone task [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 837-843. |
| [8] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [9] | Liu Zhao, Xu Xilin, Shen Yiwei, Zhang Xiaofeng, Lü Hang, Zhao Jun, Wang Zhengchun, Liu Xuzhuo, Wang Haitao. Guiding role and prospect of staging and classification combined collapse prediction method for osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 929-934. |
| [10] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [11] | Nie Shaobo, Li Jiantao, Sun Jien, Zhao Zhe, Zhao Yanpeng, Zhang Licheng, Tang Peifu. Mechanical stability of medial support nail in treatment of severe osteoporotic intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 329-333. |
| [12] | Tan Jiachang, Yuan Zhenchao, Wu Zhenjie, Liu Bin, Zhao Jinmin. Biomechanical analysis of elastic nail combined with end caps and wire fixation for long oblique femoral shaft fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 334-338. |
| [13] | Chen Lu, Zhang Jianguang, Deng Changgong, Yan Caiping, Zhang Wei, Zhang Yuan. Finite element analysis of locking screw assisted acetabular cup fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 356-361. |
| [14] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of multiple implants in treatment of traumatic dislocation of sternoclavicular joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 443-448. |
| [15] | Li Kun, Li Zhijun, Zhang Shaojie, Gao Shang, Sun Hao, Yang Xi, Wang Xing, Dai Lina . A 4-year-old child model of occipito-atlanto-axial joints established by finite element dynamic simulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3773-3778. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||