Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (27): 4355-4361.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.27.015
Previous Articles Next Articles
Analgesic effect of intrathecal injection of dexmedetomidine on selective damage of sciatic nerve branch in a rat model
Deng Hai-hong, Ma Song-mei, Xiao Xiao-shan
- Department of Anesthesiology, Guangdong Provincial Second People’s Hospital, Guangzhou 510317, Guangdong Province, China
-
Online:2014-06-30Published:2014-06-30 -
Contact:Xiao Xiao-shan, Master, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Anesthesiology, Guangdong Provincial Second People’s Hospital, Guangzhou 510317, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Deng Hai-hong, Studying for master’s degree, Associate chief physician, Department of Anesthesiology, Guangdong Provincial Second People’s Hospital, Guangzhou 510317, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Medical Scientific Research Project of Guangdong Province, No. A2012146
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Deng Hai-hong, Ma Song-mei, Xiao Xiao-shan. Analgesic effect of intrathecal injection of dexmedetomidine on selective damage of sciatic nerve branch in a rat model[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(27): 4355-4361.
share this article
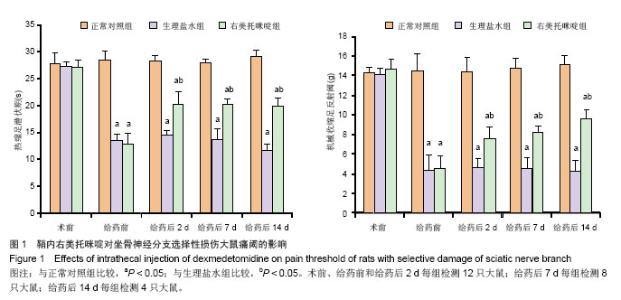
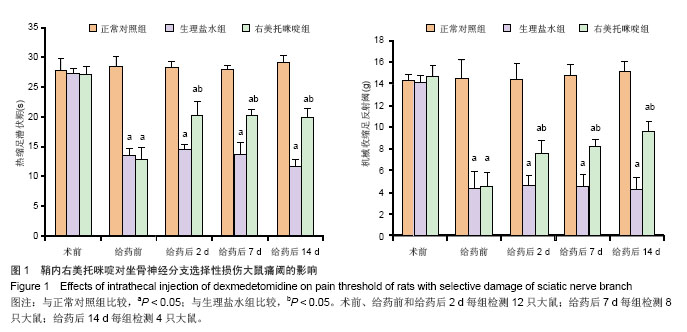
2.1 实验动物数量分析 总共饲养53只SD大鼠,36只纳入实验,17只不纳入实验统计:鞘内置管后死亡4例,出现神经病理性损伤感觉和运动丧失12例,导管脱落1例。 2.2 一般行为学变化 纳入实验大鼠实验过程中健康状况良好,体质量无明显减轻,觅食和饮水基本正常。坐骨神经分支选择性损伤麻醉清醒后即出现疼痛表现,损伤侧足趾并拢并轻度内收,伴有舔足、踮地行走及自发甩腿等反应,损伤侧足趾承重能力下降,术侧足翘起不着地,没有出现自噬现象。右美托咪啶组大鼠注药后2 d左足疼痛较生理盐水组明显改善,舔足、踮地行走明显减少,左足翘起不着地或着地不负重的次数也减少。正常对照组活动如常,未出现舔足、踮地行走及自发甩腿反应,双后爪着地且负重。 2.3 鞘内右美托咪啶对坐骨神经分支选择性损伤大鼠痛阈影响 3组大鼠在坐骨神经分支选择性损伤前机械性缩足反射阈值与热缩足潜伏期无显著性差异。坐骨神经分支选择性损伤术后,手术组与正常对照组比较,机械性缩足反射阈值及热缩足潜伏期明显降低(P < 0.05);与生理盐水组比较,右美托咪啶组在给药后2,7,14 d机械性缩足反射阈值与热缩足潜伏期显著性升高(P < 0.05);见图1。 "
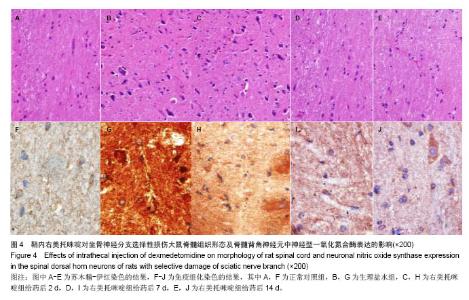
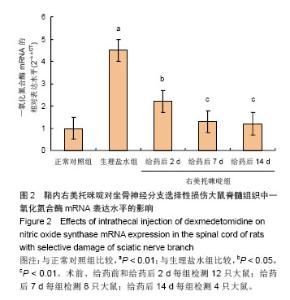
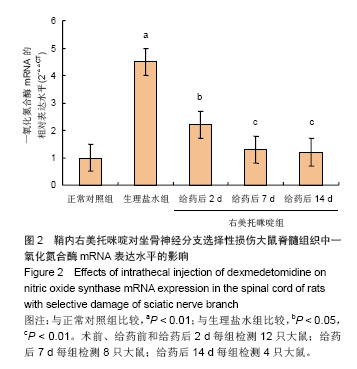
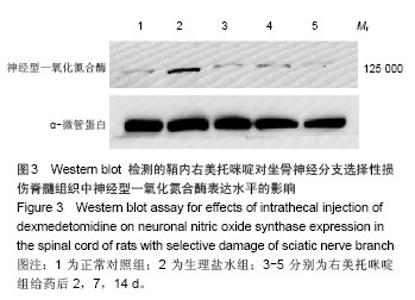
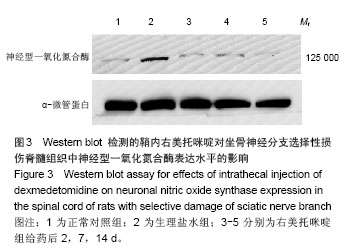
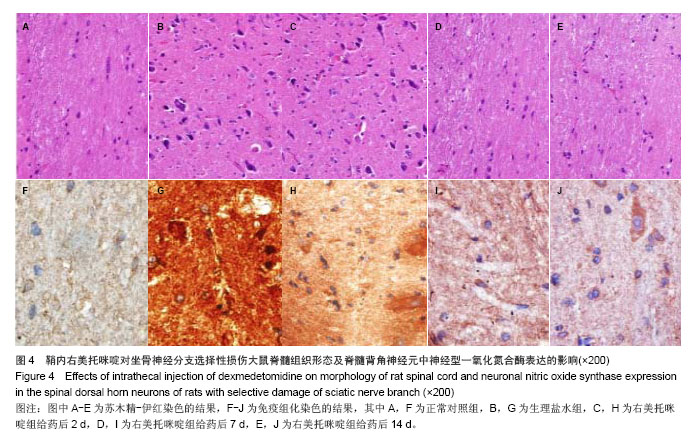
2.6 鞘内右美托咪啶对坐骨神经分支选择性损伤大鼠脊髓组织形态及脊髓背角神经元中神经型一氧化氮合酶表达的影响 光镜下观察可见,正常对照组大鼠脊髓组织中神经元细胞未见明显病理改变;生理盐水组大鼠脊髓背角神经元数目明显减少,部分细胞出现皱缩、胞核轮廓不清, 甚至变性坏死,细胞内尼氏体聚集成团块状或溶解消失;右美托咪啶组大鼠在给药前脊髓背角神经元变性坏死及尼氏体凝固、溶解情况与生理盐水组相似,但随着给药天数的增加逐渐减轻直至14 d接近正常(图4)。 同时,免疫组化染色结果也显示,各组一氧化氮合酶蛋白表达比较正常对照组脊髓背角神经型一氧化氮合酶蛋白表达为阴性或弱阳性;生理盐水组脊髓背角中神经型一氧化氮合酶表达为强阳性;右美托咪啶组神经元在给药后神经型一氧化氮合酶表达为强阳性,随着给药天数的增加,其表达逐渐降低,到14 d表达接近阴性(图4)。"
| [1]李琦,曾炳芳,王金武.神经病理性疼痛研究进展[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2007,13(4):244-246. [2]Bennett GJ. Neuropathic pain: new insights, new interventions. Hosp Pract (1995). 1998;33(10):95-98, 101-104, 107-10 passim. [3]Vallejo R, Tilley DM, Williams J, et al. Pulsed radiofrequency modulates pain regulatory gene expression along the nociceptive pathway. Pain Physician. 2013;16(5): E601-613. [4]Han G, Li L, Meng LX. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on pain-related behaviors and nitric oxide synthase in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Pain Res Manag. 2013;18(3): 137-141. [5]仲吉英,杨承祥,徐枫,等.鞘内注射右美托咪定对坐骨神经结扎损伤模型大鼠的镇痛作用[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2012,28(9): 916-918. [6]Szumita PM, Baroletti SA, Anger KE, et al. Sedation and analgesia in the intensive care unit: evaluating the role of dexmedetomidine. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007;64(1): 37-44. [7]陈章玲,曹德权,徐军美,等.右美托咪啶临床应用新进展[J].广东医学,2012,33(2):290-292. [8]苑进革,陈永学,赵森明,等.右美托咪啶注射液的临床应用进展[J].山东医药,2012,52(44):100-102. [9]Grewal A. Dexmedetomidine: New avenues. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2011;27(3):297-302. [10]Bhana N, Goa KL, McClellan KJ. Dexmedetomidine. Drugs. 2000;59(2):263-270. [11]周汾,李肇端,余剑波.右美托咪啶临床应用研究进展[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2013,19(2):215-217. [12]Kanazi GE, Aouad MT, Jabbour-Khoury SI, et al. Effect of low-dose dexmedetomidine or clonidine on the characteristics of bupivacaine spinal block. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2006; 50(2):222-227. [13]Shukla D, Verma A, Agarwal A, et al. Comparative study of intrathecal dexmedetomidine with intrathecal magnesium sulfate used as adjuvants to bupivacaine. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2011;27(4):495-499. [14]Ishii H, Kohno T, Yamakura T, et al. Action of dexmedetomidine on the substantia gelatinosa neurons of the rat spinal cord. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;27(12):3182-3190. [15]侯家保,肖兴鹏,夏中元,等.鞘内注射不同剂量右美托咪啶对大鼠的抗伤害效应和脊髓神经毒性[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2011,31(6): 710-713. [16]Yaksh TL, Rudy TA. Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav. 1976;17(6):1031-1036. [17]Bennett GJ, Xie YK. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain. 1988;33(1):87-107. [18]王一涵,冷玉芳,李娟,等.右美托咪啶对慢性神经病理性痛大鼠脊髓背角神经元凋亡的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2012,32(3): 353-357. [19]孙瑞卿,王韵,万有,等.神经源性痛的机制研究进展[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2003,9(2):105-110. [20]Civantos Calzada B, Aleixandre de Artiñano A. Alpha-adrenoceptor subtypes. Pharmacol Res. 2001;44(3): 195-208. [21]韩雪娜,冷玉芳,王一涵,等.右美托咪啶对神经病理性痛大鼠脊髓嘌呤受体P2X4mRNA和p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶mRNA表达的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2012,32(4):440-443. [22]邢艳红,冷玉芳,王殊秀,等.可乐定与右美托咪定对慢性神经病理性痛大鼠背根神经节生长相关蛋白-43 mRNA表达的影响[J].中华医学杂志,2012,92(7):444-447. [23]冯惠民,杜平,李廷坤,等.鞘内注射右美托咪啶对大鼠皮下蜜蜂毒诱导所致的持续性痛反应的抑制作用[J].上海医学,2011,34(12): 953-954. [24]张红星,曹学照,周芳鞘,等.鞘内注射右美托咪啶对小鼠急性炎性痛的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2011,31(12):1458-1460. [25]梁伟东,陈彦青.右美托咪定及舒芬太尼联合鞘内注射对CCI模型大鼠的镇痛效应[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2013,19(6): 336-340. [26]金小高,罗爱林,张广雄.三种大鼠神经病理性疼痛模型的制备和效果比较[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2005,21(5):338-340. [27]Decosterd I, Woolf CJ. Spared nerve injury: an animal model of persistent peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain. 2000;87(2): 149-158. [28]Pullen AH, Humphreys P, Baxter RG. Comparative analysis of nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivity in the sacral spinal cord of the cat, macaque and human. J Anat. 1997;191 (Pt 2): 161-175. [29]曾静波,李文斌,陈晓玲,等.大鼠甲醛炎症性痛过程中脊髓后角NOS的变化及其时间过程[J].中国病理生理杂志,2000,16(10): 1109-1113. [30]Woolf CJ, Salter MW. Neuronal plasticity: increasing the gain in pain. Science. 2000;288(5472):1765-1769. [31]郭建荣,贾东林,喻君,等.鞘内注射GDNF对神经病理性疼痛大鼠脊髓NO含量和NOS活性的影响[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2011, 17(13): 171-175. [32]Makuch W, Mika J, Rojewska E, et al. Effects of selective and non-selective inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase on morphine- and endomorphin-1-induced analgesia in acute and neuropathic pain in rats. Neuropharmacology. 2013;75: 445-457. [33]Bobadilla NA, Tapia E, Jiménez F, et al. Dexamethasone increases eNOS gene expression and prevents renal vasoconstriction induced by cyclosporin. Am J Physiol. 1999; 277(3 Pt 2):F464-471. [34]袁维秀,张宏,徐娟,等.鞘内注射氯胺酮对慢性神经痛大鼠脊髓背角一氧化氮合酶的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2004,24(5): 377-379. [35]Schulte D, Millar J. The effects of high- and low-intensity percutaneous stimulation on nitric oxide levels and spike activity in the superficial laminae of the spinal cord. Pain. 2003;103(1-2):139-150. [36]Yoon YW, Sung B, Chung JM. Nitric oxide mediates behavioral signs of neuropathic pain in an experimental rat model. Neuroreport. 1998;9(3):367-372. [37]Wong CS, Cherng CH, Tung CS. Intrathecal administration of excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists or nitric oxide synthase inhibitor reduced autotomy behavior in rats. Anesth Analg. 1998;87(3):605-608. [38]Knowles RG, Moncada S. Nitric oxide synthases in mammals. Biochem J. 1994;298 ( Pt 2):249-258. [39]Schmidt HH, Walter U. NO at work. Cell. 1994;78(6):919-925. [40]周初松,高建章,赵定麟,等. L-精氨酸对大鼠急性脊髓压迫损伤早期局部微循环的影响及其意义[J].中华创伤杂志,1997,13(2): 102-104 . [41]Micale V, Cristino L, Tamburella A, et al. Enhanced cognitive performance of dopamine D3 receptor "knock-out" mice in the step-through passive-avoidance test: assessing the role of the endocannabinoid/endovanilloid systems. Pharmacol Res. 2010;61(6):531-536. [42]Whiteside GT, Munglani R. Cell death in the superficial dorsal horn in a model of neuropathic pain. J Neurosci Res. 2001; 64(2): 168-173. [43]冷玉芳,金海燕.大鼠坐骨神经慢性压迫损伤后脊髓感觉神经元发生非凋亡性细胞程序性死亡[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2009, 15(1):23-26. [44]Appleby VJ, Corrêa SA, Duckworth JK, et al. LTP in hippocampal neurons is associated with a CaMKII-mediated increase in GluA1 surface expression. J Neurochem. 2011; 116(4):530-543. |
| [1] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [2] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [3] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [4] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [5] | Gao Yan, Zhao Licong, Zhao Hongzeng, Zhu Yuanyuan, Li Jie, Sang Deen. Alteration of low frequency fluctuation amplitude at brain-resting state in patients with chronic discogenic low back pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1160-1165. |
| [6] | Liu Zhengpeng, Wang Yahui, Zhang Yilong, Ming Ying, Sun Zhijie, Sun He. Application of 3D printed interbody fusion cage for cervical spondylosis of spinal cord type: half-year follow-up of recovery of cervical curvature and intervertebral height [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 849-853. |
| [7] | Zhao Zhongyi, Li Yongzhen, Chen Feng, Ji Aiyu. Comparison of total knee arthroplasty and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of traumatic osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
| [8] | Zhang Nianjun, Chen Ru. Analgesic effect of cocktail therapy combined with femoral nerve block on total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 866-872. |
| [9] | Wu Gang, Chen Jianwen, Wang Shilong, Duan Xiaoran, Liu Haijun, Dong Jianfeng. Simple HyProCure subtalar stabilization in treatment of adolescent flexible flatfoot combined with painful accessory navicular bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 901-905. |
| [10] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [11] | Li Quanxi, Shen Yu, Wan Wei, Sun Shanzhi. Changes of abdominal wall mechanics and pain after tension-free inguinal hernia repair with polypropylene mesh [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 548-552. |
| [12] | Wang Xiaofei, Teng Xueren, Cong Linyan, Zhou Xu, Ma Zhenhua. Herbert screw internal fixation for treating adult osteochondritis dissecans of the knees [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 397-402. |
| [13] | Yang Wei, Chen Zehua, Yi Zhiyong, Huang Xudong, Han Qingmin, Zhang Ronghua. Effectiveness of intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid versus placebo in the treatment of early and mid-stage knee osteoarthritis: a Meta-analysis based on randomized, double-blind, controlled, clinical trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3760-3766. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Jiang Hai, Yu Yu, Liu Zhicheng, Zhang Qiliang. Treatment of plantar fasciitis with extracorporeal shock wave and corticosteroid injection: comparison of plantar pressure and gait [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3286-3291. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||