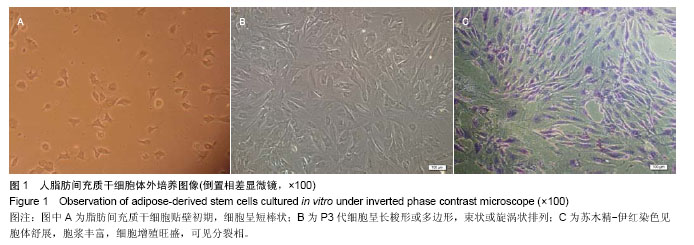
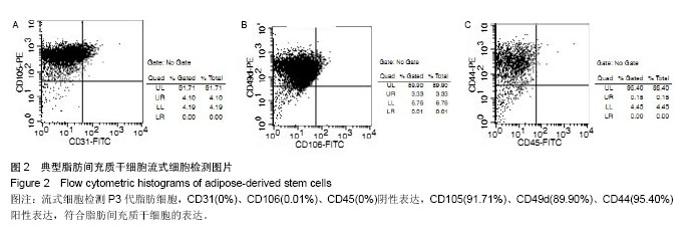
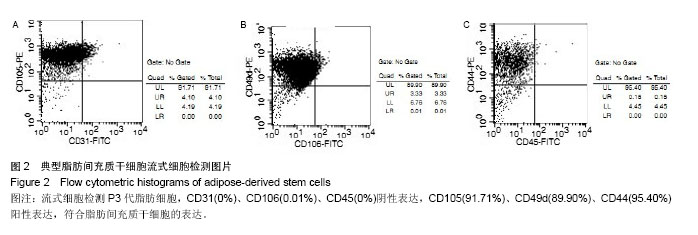
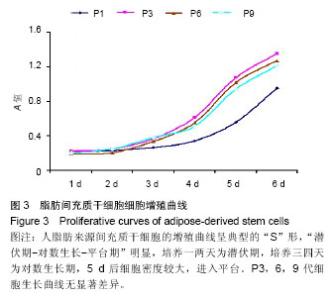
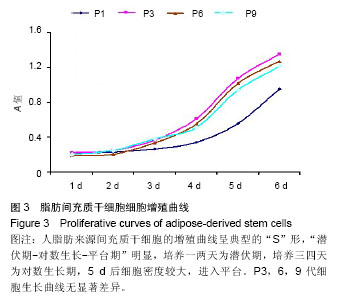
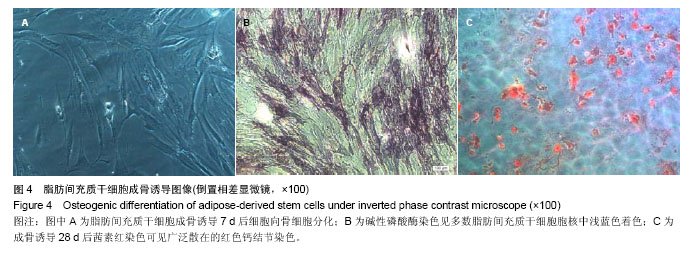
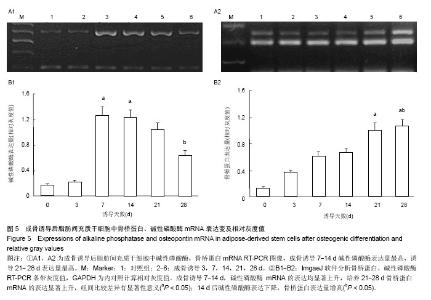
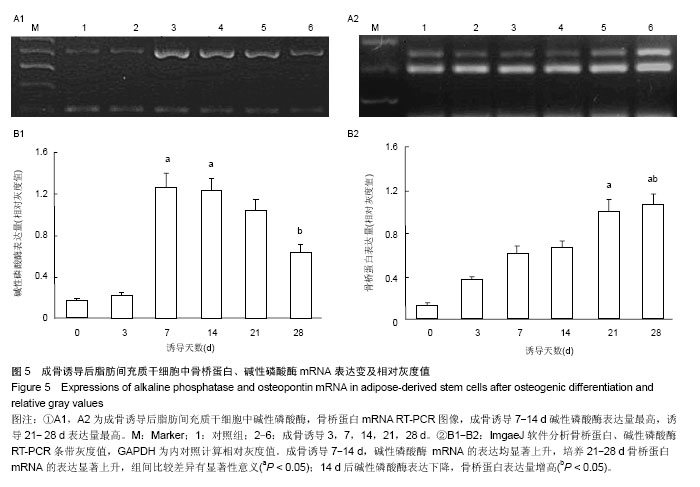
| [1] 孙宝谦,兑振华,王增良等.颅骨修补与颅骨保存研究进展[J].中国医药导刊,2009,12(1):9-10.
[2] 张贺,张蔷,王锡亮.颅骨缺损修补的研究与进展[J].中华现代外科学杂志,2005,2(18):1679-1681.
[3] 于明琨,王永谦.自体骨移植修补颅骨缺损的材料与方法[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(41):126-129.
[4] 李景峰,郑启新.异种,异体骨材料的研究进展[J].国际生物医学工程杂志,2008,31(4):249-253.
[5] 张永光,王志强.骨移植替代材料研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2008,22(10):1264-1268.
[6] 王呈,曾炳芳.骨移植替代材料在创伤骨科的应用[J].国际骨科学杂志,2012,33(1):37-38.
[7] De Peppo GM, Thomsen P, Karlsson C,et al, Human progenitor cells for bone engineering applications.curr mol med.2013;13(5):723-734.
[8] Yuan J,Cui L,Zhang WJ,et al.Repair of canine mandibular bone defets with marrow stromal cells and porous beta-tricalcium phosphate.Biomaterials.2007;28(6): 1005-1013.
[9] 王宇玫,张浩,李君,等.不同年龄人群骨髓间充质干细胞的生长变化[J].中华老年多器官疾病杂志,2008,9(3):223-226.
[10] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P,et al. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell.2002;13(12): 4279-4295.
[11] Tapp H,Hanley EN Jr,Patt JC,et al.Adipose-derived stem cells:characterization and current application in orthopaedic tissue repair.Exp Biol Med(Maywood).2009;234(1):1-9.
[12] Zaminy A, Ragerdi Kashani I, Barbarestani M, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of rat mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue in comparison with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: melatonin as a differentiation factor. Iran Biomed J. 2008;12(3):133-141.
[13] Mahmoudifar N, Doran PM.Osteogenic Differentiation and Osteochondral Tissue Engineering Using Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells.Biotechnol Prog. 2013;29(1): 176-185.
[14] Hamid AA, Idrus RB, Saim AB, Sathappan S,et al. Characterization of human adipose-derived stem cells and expression of chondrogenic genes during induction of cartilage differentiation.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2012;67(2): 99-106.
[15] Moioli EK, Chen M, Yang R, et al.Hybrid adipogenic implants from adipose stem cells for soft tissue reconstruction in vivo. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(11):3299-3307.
[16] Palpant NJ, Metzger JM.Aesthetic cardiology: adipose-derived stem cells for myocardial repair.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther.2010;5(2):145-152.
[17] 张钦,马真胜,刘建,等.成骨诱导自体脂肪源干细胞用于修复兔颅骨缺损[J].中国骨肿瘤病,2009,8(2):104-107.
[18] 鲍慧婧,邹俊,尹烁,等.兔脂肪间充质干细胞复合PLGA支架的生物相容性研究[J].中华实验眼科杂志,2001,29(6):511-516.
[19] 李强,陶常波,张爱君,等.EGF刺激对脂肪间充质干细胞促血管生成作用的影响[J].中华医学美学杂志,2012,18(6):440-442.
[20] Bose S, Roy M, Bandyopadhyay A.Recent advances in bone tissue engineering scaffolds.Trends Biotechnol. 2012;30(10): 546-554.
[21] Khan WS, Hardingham TE.Mesenchymal stem cells, sources of cells and differentiation potential.J Stem Cells. 2012;7(2): 75-85.
[22] Amini AR, Laurencin CT, Nukavarapu SP.Bone tissue engineering: recent advances and challenges.Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2012;40(5):363-408.
[23] Han J, Koh YJ, Moon HR,et al.Adipose tissue is an extramedullary reservoir for functional hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.Blood. 2010 ;115(5):957-964.
[24] Nakao N, Nakayama T, Yahata T,et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells facilitate hematopoiesis in vitro and in vivo:advantages over bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Pathol.2010;177(2):547-554.
[25] 黄宏,朱方强,孙宏振,等.脂肪来源干细胞体外成骨诱导和成脂分化[J].第三军医大学学报,2008,30(13):1219-1222.
[26] Datta P, Ghosh P, Ghosh K, et al .In vitro ALP and osteocalcin gene expression analysis and in vivo biocompatibility of N-methylene phosphonic chitosan nanofibers for bone regeneration. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2013;9(5):870-879.
[27] McKee MD, Pedraza CE, Kaartinen MT. Osteopontin and wound healing in bone.Cells Tissues Organs. 2011;194(2-4): 313-319.
[28] 柳向东,唐朝晖,白祥军,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞定向成骨诱导中碱性磷酸酶对成骨能力的影响[J].中华创伤杂志,2009,25(10): 945-948.
[29] Strem BM, Hicok KC, Zhu M,et al. Multipotential differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Keio J Med. 2005;54(3): 132-141.
[30] Jurgens WJ, Oedayrajsingh-Varma MJ, Helder MN,et al. Effect of tissue-harvesting site on yield of stem cells derived from adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies.Cell Tissue Res. 2008;332(3):415-426.
[31] Arthur A, Zannettino A, Gronthos S.The therapeutic applications of multipotential mesenchymal/stromal stem cells in skeletal tissue repair.J Cell Physiol. 2009;218(2):237-245.
[32] Sen A, Lea-Currie YR, Sujkowska D, et al.Adipogenic potential of human adipose derived stromal cells from multiple donors is heterogeneous. J Cell Biochem.2001;81(2): 312-319.
[33] Tchkonia T, Giorgadze N, Pirtskhalava T,et al.Fat depot origin affects adipogenesis in primary cultured and cloned human preadipocytes.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2002; 282(5):R1286-1296.
[34] Strong AL, Strong TA, Rhodes LV, et al.Obesity associated alterations in the biology of adipose stem cells mediate enhanced tumorigenesis by estrogen dependent pathways. Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(5):R102. |