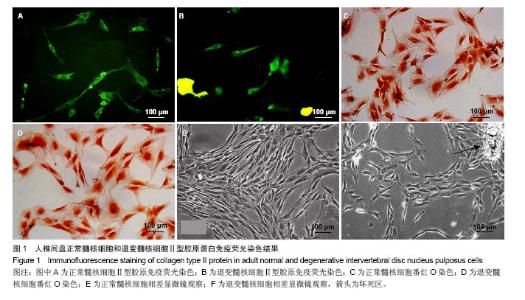
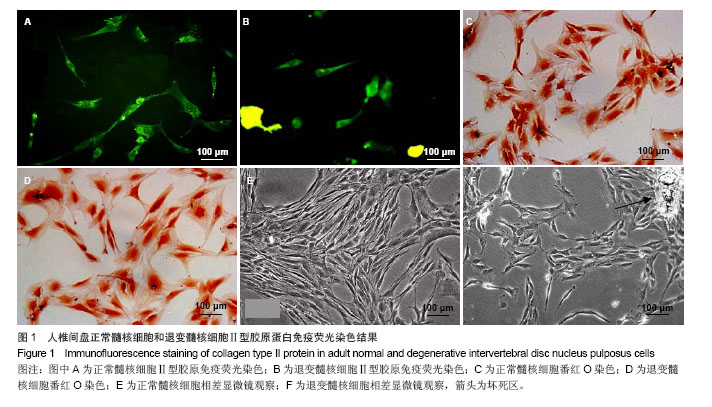
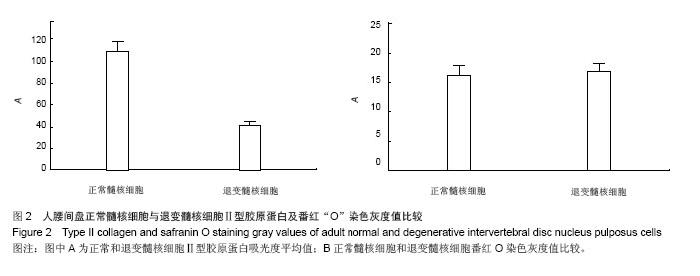
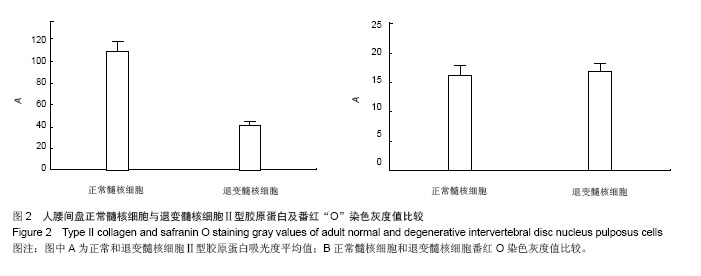
| [1]李锋生,梁伟国,叶冬平,等. 体外培养人退变髓核细胞的生物学性状[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(28): 5141-5144.
[2]林曦,叶君健. 骨形态发生蛋白2对退变椎间盘组织学和Ⅰ,Ⅱ型胶原的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(43):7501-7506.
[3]李树文,武海军,银和平,等. Ⅱ型胶原酶消化结合组织块贴壁法分离培养兔髓核细胞[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(39): 6861-6866.
[4]王海,黄博,周跃,等. 改良简易法获取人退变椎间盘髓核细胞及生物学特点[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(28):5139-5144.
[5]张子言,佟珅,颜华东,等. 人类髓核细胞分离培养方法的优化选择[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013:17(28):5151-5156.
[6]武海军,银和平,李树文,等.不同代次兔髓核细胞的形态学特征和生物学性状[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(11): 901-1908.
[7]沈皆亮,胡侦明,钟小明,等. 白藜芦醇恢复去分化正常髓核细胞表型的实验研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2013,27(5): 547-553.
[8]周小锐,刘世清,贺斌,等. 地塞米松可影响兔髓核细胞增殖及Ⅱ型胶原的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,(11):1915-1919.
[9]张涛,贠喆,蔡承魁,等.大鼠髓核细胞原代培养及表型鉴定[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2012,12(3):430-434.
[10]王祺,王祺,何君仁,等. 正常与退变髓核细胞Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和番红染色的研究[J]. 中国医疗前沿,2012,7(1):4-5.
[11]张丽,马迅,关晓明,等. 应用流式细胞术测定CD24表达鉴定人髓核细胞[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(46): 8583-8586.
[12]Aaron RK,Jolly G, Ciombor DM, et al. Histochemical Method for the Demonstration of Calcifying Cartilage. Calcif Tissue Int. 1988; 43(4):244-249.
[13]Rosenbeg L.Chemical basis for the histological use of safranin O in the study of articular cartilage.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1971; 53(1): 69-82.
[14]Hunter CJ, Matyas JR, Duncan NA. The threedimensional architecture of the notochordal nucleus pulposus : novel observations on cell structures in the canine intervertebral disc.JAnat.2003;202(3): 279-292. [15]Kim KW, Lim TH, Kim JC, et al. The origin of chondrocytes in the nucleus pulposus and histologic findings associated with the transition of a notochordal nucleus pulposus to a fibrocartilaginous nucleus pulposus in intact rabbit intervertebral discs. Spine.2003;28(10) :982-990.
[16]张闻力,刘浩,李坛珠.椎间盘退变动物模型的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2007,21(11):1259-1262.
[17]Dagenais S, Caro J, Haldeman S. A systematic review of low back pain cost of illness studies in the United States andinternationally. Spine J. 2008;8(1):8-20.
[18]Luoma K, Riihimaki H, Luukkonen R, et al. Low back pain in relation to lumbar disc degeneration.Spine. 2000;25(4): 487-492.
[19]Diwan AD, Parvataneni HK, Khan SN, et al. Current concepts in intervertebral disc restoration.Orthop Clin Nor Am. 2000; 31(3):453-464.
[20]Poiraudeau S,Monteiro I,Anract P,et al.Phenotypic characteristics of rabbit intervertebral disc cells: Comparison with cartilage cells from the same animals. Spine. 1999; 24: 837-844.
[21]Crean JK, Roberts S,Jaffray DC,et al.Matrix metalloproteinasesin the human intervertebral disc: role in disc degeneration and scoliosis. Spine. 1997;22:2877-2884.
[22]Goupille P, Jayson MI, Valat JP, et al. Matrixmetalloproteinases: the clue to intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine. 2008;23:1612-1626.
[23]赵勇,王文波,李吉友,等.骨形态发生蛋白-2与椎间盘细胞S ox9 和Ⅱ型胶原基因的调控关系[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2005,15(10):
612-615.
[24]钱忠来,高锋,倪莉,等.体外培养人退变髓核组织细胞的活力和表型变化[J].苏州大学学报:医学版,2010,30(5):951-954.
[25]Hansen HJ. Comparative views of the pathology of disk degeneration in animals. Lab Invest. 1959;8:1242-1265.
[26]Horner HA, Roberts S, Bielby RC,et al. Cells from different regions of the intervertebral disc: effect of culture system on matrix expression and cell phenotype. Spine.2002;27: 1018-1028.
[27]Moon SH, Gilbertson LG, Nishida K, et al. Human intervertebral disc cells aregenetically modifiable by adenovirus-mediated gene transfer. Spine.2000; 25: 2573-2579.
[28]Li S, Duance VC, Blain EJ. Zonal variations in cytoskeletal element organization, mRNA and protein expression in the intervertebral disc. J Anat. 2008; 213:725-732.
[29]Humzah MD,Soames RW.Human intervertebral disc:structure and function.Anat Rec.1988;220:337-356.
[30]Urban J,Disc biochemistry in relation to function.//Weinstein JN,Wiesel SW,eds.The lumbar spine.The International Society for the Study of the Lumbar Spine. Philadelphia:WB Saunders Co,1990:231-44.
[31]Chelberg MK, Banks GM, Geiger DF, et al. Identification of heterogeneous cell populations in normal human intervertebral disc. J Anat.1995;186:43-53.
[32]Roberts S, Caterson B, Menage J, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases and aggrecanase: their role in disorders of the human intervertebral disc.Spine.2000; 25(23): 3005-3013.
[33]Moskowitz RW, Ziv I, Denko CW, et al. Spondylosis in sand rats: a model of intervertebral disc degeneration and hyperostosis. J Orthop Res. 1990;8(3):401-411.
[34]胡有谷. 腰椎间盘突出症[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社, 1995: 47-89.
[35]郭世绂.椎间盘的解剖与理化性能[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 1995, 5(2):93
[36]Ebara S, Iatridis JC, Setton LA,et al. Tensile properties of nondegenerate human lumbar anulus fibrosus. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21(4):452-461.
[37]Takegami K, An HS, Kumano F, et al. Osteogenic protein-1 is most effective in stimulating nucleus pulposus an annulus fibrosus cells to repair their matrix after chondroitinase ABC-induced in vitro chemonucleolysis. Spine J. 2005; 5(3): 231-238.
[38]崔运能,周荣平,麦奇光,等.肌间隙入路腰椎间盘退变模型的构建[J].南方医科大学学报,2012,32(3):404-408.
[39]卢守亮,孙天威.椎间盘退变目的基因研究[J].国际骨科学杂志, 2011,32(2):116-118.
[40]胡新锋,王宸,芮云峰.纤维环穿刺法建立兔椎间盘退变模型[J].东南大学学报:医学版,2012,31(4) :441-446.
[41]胡明,马远征,黄凤山,等.成人退变性椎间盘髓核细胞体外培养及形态学观察[J].实用骨科杂志,2011,17(10):902-904.
[42]刘英杰.动态固定系统防治腰椎间盘退变的实验研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2011.
[43]任龙韬,卫陈刚,牛建鹏,等.正常与退变髓核细胞的变形能力[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(48):9030-9033.
[44]尹建石,芦健民.大鼠单侧椎板开窗及半椎板切除后椎间盘退变的实验研究[J].医学美学美容(中旬刊),2012,20(11):134-137.
[45]石志远,张超,阮狄克.椎间盘退变生物治疗进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2012,1(1):83-87.
[46]魏伟,于占革.椎间盘髓核组织工程研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(23):1987-1989
[47]王锋.水通道蛋白1在老化退变髓核中的表达及渗透压、氧分压影响其表达的实验研究[D].沈阳,中国医科大学,2011. |