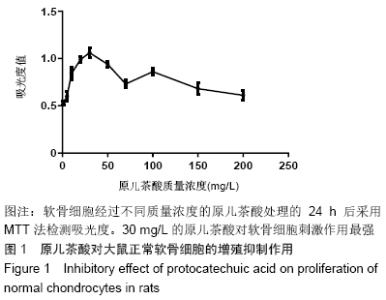
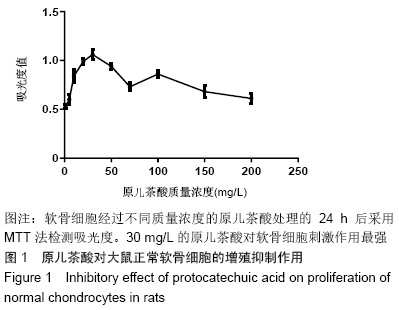
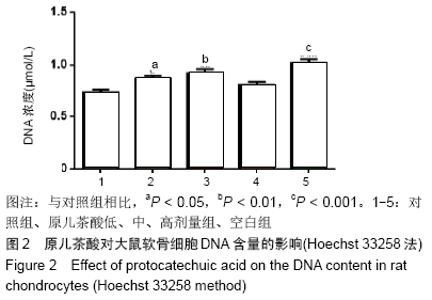
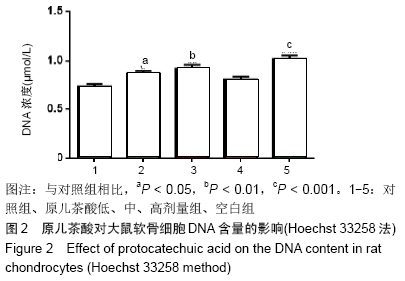
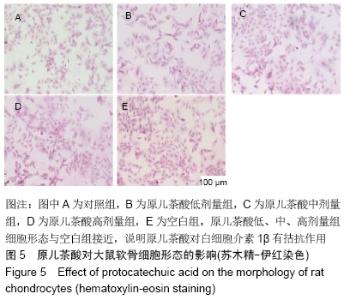
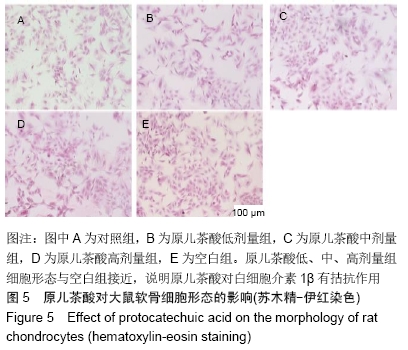
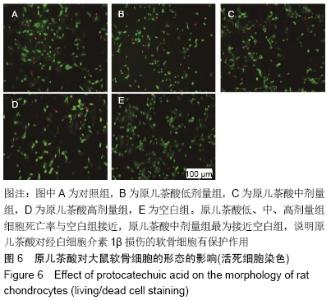
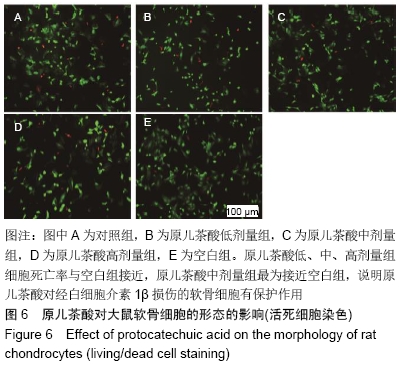
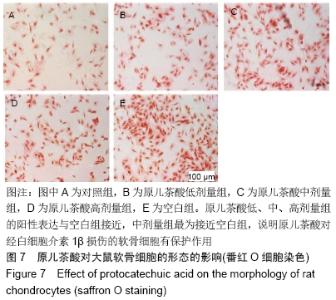
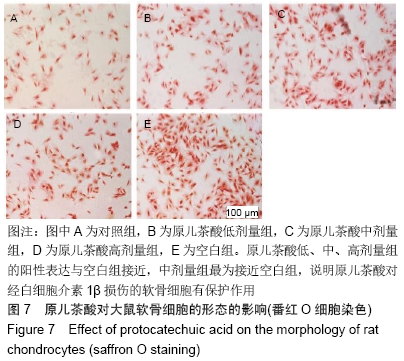
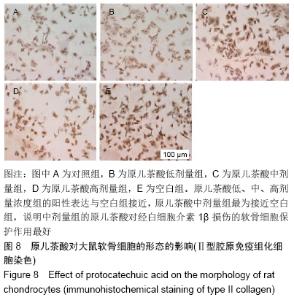
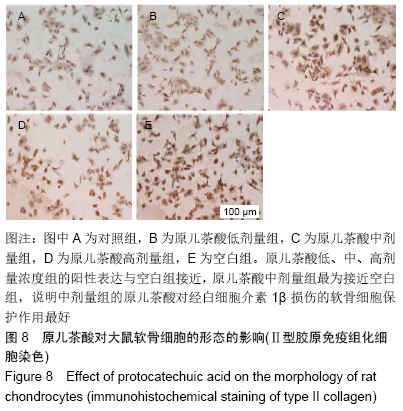
[1] GOLDRING MB. Update on the biology of the chondrocyte and new approaches to treating cartilage diseases. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2006;20(5):1003-1025.
[2] MOLLON B, KANDEL R, CHAHAL J, et al. The clinical status of cartilage tissue regeneration in humans. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(12):1824-1833.
[3] GARGIULO S, GAMBA P, POLI G, et al. Metalloproteinases and metalloproteinase inhibitors in age-related diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(18):2993-3018.
[4] NELSON FRT. The value of phenotypes in knee osteoarthritis research. Open Orthop J. 2018;12:105-114.
[5] ZHOU PH, QIU B, DENG RH, et al. Chondroprotective Effects of Hyaluronic Acid-Chitosan Nanoparticles Containing Plasmid DNA Encoding Cytokine Response Modifier A in a Rat Knee Osteoarthritis Model. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018; 47(3):1207-1216.
[6] MASELLA R, SANTANGELO C, D'ARCHIVIO M, et al. Protocatechuic acid and human disease prevention: biological activities and molecular mechanisms. Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(18):2901-2917.
[7] LIN HH, CHEN JH, CHOU FP, et al. Protocatechuic acid inhibits cancer cell metastasis involving the down-regulation of Ras/Akt/NF-κB pathway and MMP-2 production by targeting RhoB activation. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;162(1): 237-254.
[8] 陈颖娟,黄慈波,牛素平,等.骨关节炎患者关节软骨细胞合成和分解基因的表达研究[J].风湿病与关节炎,2016,5(5):5-8,31.
[9] 刘庆珍,吴尽,邳晓盟,等.软骨发育过程中负调控Sox9基因表达机制研究进展[J].农业科学与技术(英文版),2017,18(6): 1038-1041.
[10] 陈克明,葛宝丰,刘兴炎,等.骨软骨组织中Ⅰ、Ⅱ型胶原基因表达的检测[J].西北国防医学杂志,2000,21(3):216-218.
[11] PFANDER D, SWOBODA B, KIRSCH T. Expression of early and late differentiation markers (proliferating cell nuclear antigen, syndecan-3, annexin VI, and alkaline phosphatase) by human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Am J Pathol. 2001; 159(5):1777-1783.
[12] WU J, TAO Y, SHANG A, et al. Effect of the interaction between MiR-200b-3p and DNMT3A on cartilage cells of osteoarthritis patients. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(10): 2308-2316.
[13] TSUCHIYA H, KITOH H, SUGIURA F, et al. Chondrogenesis enhanced by overexpression of sox9 gene in mouse bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;301(2):338-343.
[14] MA B, LEIJTEN JC, WU L, et al. Gene expression profiling of dedifferentiated human articular chondrocytes in monolayer culture. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(4):599-603.
[15] 张加雄,屈巧玲,王凌.高效液相色谱法同时测定四季青中4种酚酸类成分的含量[J].西南国防医药,2010,20(6):611-613.
[16] WANG HY, WANG H, WANG JH, et al. Protocatechuic Acid Inhibits Inflammatory Responses in LPS-Stimulated BV2 Microglia via NF-κB and MAPKs Signaling Pathways. Neurochem Res. 2015;40(8):1655-1660.
[17] GUAN S, GE D, LIU TQ, et al. Protocatechuic acid promotes cell proliferation and reduces basal apoptosis in cultured neural stem cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 2009;23(2):201-208.
[18] FOSANG AJ, BEIER F. Emerging Frontiers in cartilage and chondrocyte biology. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2011; 25(6):751-766.
[19] GAN L, KANDEL RA. In vitro cartilage tissue formation by Co-culture of primary and passaged chondrocytes. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(4):831-842.
[20] CHOI WS, YANG JI, KIM W, et al. Critical role for arginase II in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(3): 421-428.
[21] HU ZC, GONG LF, LI XB, et al. Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling with leonurine for ameliorating the progression of osteoarthritis: In vitro and in vivo studies. J Cell Physiol. 2019; 234(5):6940-6950.
[22] MURAHASHI Y, YANO F, KOBAYASHI H, et al. Intra-articular administration of IκBα kinase inhibitor suppresses mouse knee osteoarthritis via downregulation of the NF-κB/HIF-2α axis. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):16475.
|