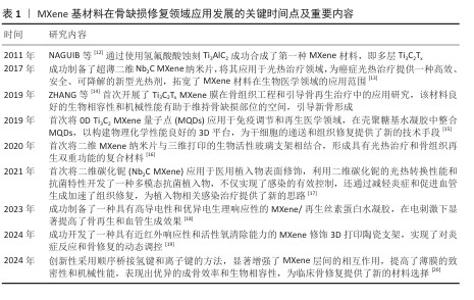
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (20): 5282-5294.doi: 10.12307/2026.328
Previous Articles Next Articles
Clinical application and prospects of MXene-based materials for the repair of bone defects
Wang Liang1, Zhang Xin1, He Wei2, Wang Jian1
- 1State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China; 2Chengdu Institute for Drug Control; Key Laboratory for Quality Research and Control of Chemical Medicine of SiChuan Medical Products Administration, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Accepted:2025-07-28Online:2026-07-18Published:2025-12-02 -
Contact:Wang Jian, MD, Professor, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Wang Liang, Master candidate, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82271034 (to WJ); Innovative Research Group of Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province, No. 2023NSFSC2000 (to WJ); National Natural Science Foundation Youth Science Fund Project, No. 82201128 (to ZX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Liang, Zhang Xin, He Wei, Wang Jian. Clinical application and prospects of MXene-based materials for the repair of bone defects[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(20): 5282-5294.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

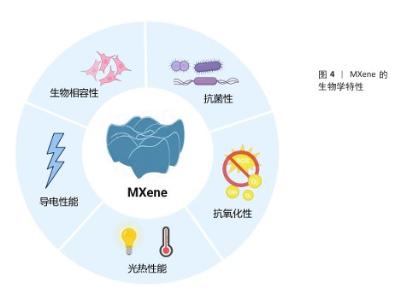
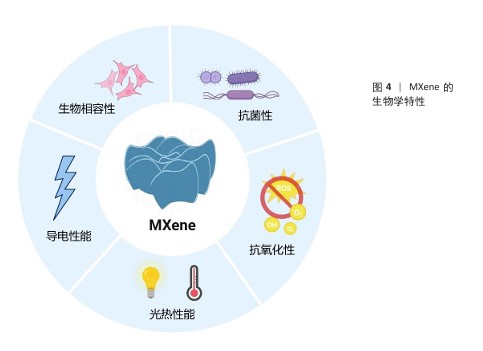
2.2.1 生物相容性 MXene的主要组成元素(如C、N、H和O)与生物体的基本元素高度一致;此外,MXene中包含的过渡金属(如钛、钒和钼)也在生理过程中发挥着重要作用,并且MXene表面丰富的官能团呈现亲水性,因此,MXene能够为细胞提供适宜的生长微环境。例如,添加了Ti3C2 MXene纳米片的明胶水凝胶对前成骨细胞MC3T3-E1细胞无毒,还能促进细胞的增殖、黏附和成骨分化[21]。有研究者对Ti2NTx MXene纳米片的多种细胞毒性进行了评估,发现0-500 mg/L Ti2NTx MXene纳米片对正常细胞(如人类永生化角质形成细胞、正常人乳腺上皮细胞)活性无明显影响;相比之下,250 mg/L Ti2NTx MXene纳米片可显著降低癌细胞(如人类皮肤恶性黑色素瘤细胞和人类乳腺癌细胞)活性,癌细胞生存率低于70%,并且细胞活性下降与纳米片质量浓度呈剂量依赖性关系[22]。这种差异化作用可能是由于癌细胞通常具有更活跃的代谢和增殖能力,更容易摄取MXene纳米片,从而诱导癌细胞内的活性氧水平上升,同时癌细胞的抗氧化系统可能调控异常,不能及时清除活性氧[23]。然而,目前关于MXene诱导活性氧产生的具体机制尚不清楚,仍待进一步研究。CUI等[24]研究了超薄二维Ti3C2Tx纳米片的生物相容性及对人牙周膜细胞的影响,体内外实验结果表明,Ti3C2Tx纳米片在30-90 mg/L质量浓度范围内对人牙周膜细胞无明显的细胞毒性,并且能够显著促进牙周膜细胞的成骨分化。ZHANG等[25]采用两种质量浓度(100,500 mg/L)的MXene处理人脐静脉内皮细胞,细胞增殖和凋亡实验结果均未观察到明显的细胞毒性;但代谢组学数据得出结论,高质量浓度(500 mg/L)的MXene可引起人脐静脉内皮细胞能量代谢变化,表现出对三羧酸循环的明显抑制、糖酵解增强及脂肪酸生物合成和脂质积累,这与线粒体功能障碍密切相关。MXene对红细胞表现出良好的生物相容性,即使在高达200 μg/mL的质量浓度下仅引起0.8%的溶血率,相比之下,同样质量浓度的石墨烯可引起50.8%的溶血率[26]。另外,NASRALLAH等[27]利用斑马鱼胚胎模型分析评价碳化钛的潜在体内毒性和生物相容性,结果显示碳化钛的最高不可观测效应质量浓度(死亡率< 20%)为50 μg/mL,最低可观测效应质量浓度(死亡率≥20%)为100 μg/mL。SZUPLEWSKA等[28]系统证明了经大豆磷脂改性的MnOx/MXene具有良好的体外体内生物安全性。多维度实验结果共同证实了MXene具有良好的可控的生物安全性。 在体内的长期应用中,研究适当的生物降解行为将有助于评估MXene在体内的安全性以及MXene作为组织再生材料的适用性。目前,Nb2C MXene是MXene纳米材料中被证实具有生物可降解性的主要材料。LIN等[13]探索了N2C-聚乙烯吡咯烷酮纳米片的生物降解性,并开发了一种创新的酶触发方法来启动它们的生物降解,这种方法可以使纳米片在完成治疗功能后在合理时间范围内进行无害降解,将Nb2C-聚乙烯吡咯烷酮注入血液后对器官进行组织切片染色,发现Nb2C-聚乙烯吡咯烷酮在所有组织中都能被高效代谢[29]。与Nb2C MXene相比,有关Ti3C2 MXene的降解性能研究较少,表面修饰可以显著影响MXene的降解性能[30]。 "


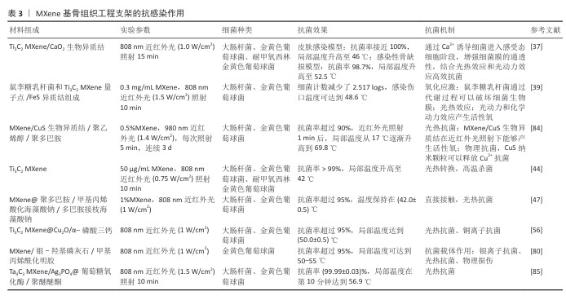
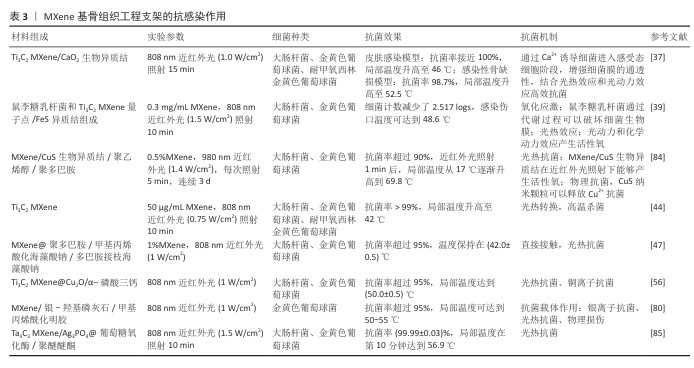
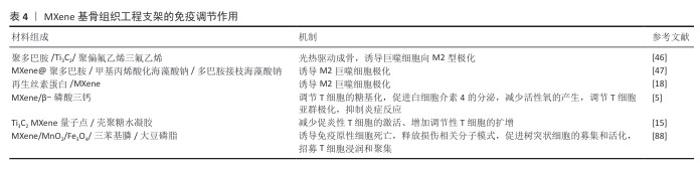
2.2.2 抗菌性 MXene对包括耐药菌株在内的多种病原体表现出强大的抗菌作用,在对抗细菌感方面具有重要价值[31]。MXene的显著特点,如大的表面积、可调的表面化学和优异的导电性,有利于与细菌膜的有效相互作用。RASOOL等[32]的研究表明,单层MXene(Ti3C2Tx)薄片相较于多层MXene展现出更强的抑菌能力,并且抗菌效率优于氧化石墨烯。ARABI SHAMSABADI等[33]进一步指出MXene的抗菌性能与其暴露时间和纳米片尺寸密切相关,小尺寸MXene纳米片表现出更高的抗菌活性。值得注意的是,老化的Ti3C2Tx膜(在室温和空气中存放30 d以上)对枯草芽孢杆菌和大肠杆菌的生长抑制超过99%,显著高于新鲜Ti3C2Tx膜的抑菌效果,这可能得益于膜表面TiO2纳米晶体的存在,增强了杀菌活性[34]。因此,除了MXene纳米片的尺寸和结构,材料的长期稳定性也会影响抗菌效果。 MXene 的抗菌机制主要集中在以下几个方面(图5):①物理损伤:MXene纳米片具有锋利的边缘,可以切割细菌的细胞膜导致细胞内容物泄漏,从而杀死细菌[35]。这种机制类似于其他二维材料(如石墨烯)的纳米刀抗菌作用。一般来说,基于切割效应的纳米刀抗菌效果由其原子结构、尺寸和厚度、电导率和孵育时间决定。PANDEY等[36]探索了单层Nb2CTX MXene和Nb4C3TX MXene的抗菌作用,结果表明原子结构在杀菌功能中起着至关重要的作用,其中Nb2CTX MXene和Nb4C3TX MXene表现出显著的细菌生长抑制作用,对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制率分别为94.2%和96.1%、91.6%和93.7%。②光热抗菌:MXene具有光热性能,在近红外光照射下可以产生局部高温,利用热效应杀灭细菌[37-38]。通常来说,MXene的浓度越高,近红外光功率越大,照射时间越长,产生的热量就越多,杀菌效果越好。但局部过高的温度有可能对周围细胞和组织造成损伤,因此,需要通过材料设计将局部温度控制在合理范围内,大多数研究将温度控制在40-60 ℃内,在这个范围内既可以实现有效杀菌又可以不伤害周围组织。③氧化应激:MXene可以通过光催化或化学反应诱导细菌产生氧化应激,破坏细菌的氧化还原平衡。例如,MXene表面丰富的羟基(-OH)和氧基(-O-)官能团可以与环境中的氧分子和水分子相互作用,产生超氧阴离子自由基(O2?-)和羟基自由基(?OH);此外,MXene在光照条件下导致局部温度升高,进而加速水分子的分解,从而促进过氧化氢的生成,这些活性氧能够有效破坏细菌的细胞结构,最终导致细菌死亡[39]。④抗菌载体作用:MXene可以释放金属离子或作为抗菌药物的载体增强抗菌效果[40]。例如,Cu2O纳米球可以均匀地锚定在MXene表面构建异质结,对金黄色葡萄球菌和铜绿假单胞菌的抗菌效率分别为97.04%和95.59%,优于单独的MXene和Cu2O及其混合物,这种增强的性能归因于它们的协同抗菌机制[41]。 传统骨修复材料(如钛合金、生物陶瓷和聚合物等)可通过以下方式抗菌:①添加抗生素、抗菌剂或抗菌涂层来实现抗菌效果;②某些材料可以结合光敏剂在光照下产生活性氧,进而杀死细菌;③部分金属材料可以释放抗菌离子。在骨感染的临床管理中,抗生素治疗是必不可少的,但抗生素治疗治疗失败率约为20%[42],并且长期的抗生素治疗可损害免疫系统、增加细菌耐药性[43]。未添加抗菌剂的传统骨修复材料抗菌性能较差,细菌容易在材料表面黏附、繁殖,形成生物膜,进而引发感染;即使材料中添加抗菌剂的抗菌效果也往往不如MXene理想,并且抗菌剂的释放量和释放时间难以精确控制,可能会出现早期释放量不足、后期释放过量等问题。与传统骨修复材料相比,MXene不仅能够在较短时间内显著降低细菌存活率,抗菌率可达90%以上[44],而且其多种机制协同抗菌减少了对单一抗生素的依赖,有效对抗多重耐药菌,同时具有多功能整合的独特优势,在抗菌的同时协同骨修复作用。 "


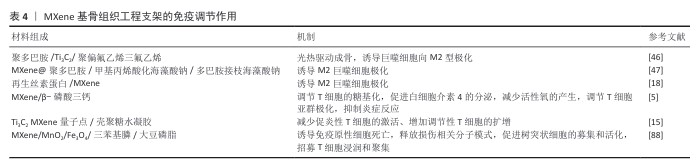
2.2.3 抗氧化和免疫调节 MXene通过清除活性氧和调控免疫微环境有效抑制炎症反应。 清除活性氧:MXene本身具有清除多种活性氧的能力,包括超氧自由基、羟基自由基、过氧化氢等[21]。MXene的抗氧化机制可能与其表面的金属中心和官能团有关,可以发生氧化还原反应,将活性氧转化为无毒物质。MXene也可以通过调节细胞行为减轻炎症反应,间接降低氧化应激水平[45];此外,MXene还可以作为抗氧化酶的载体提高酶的稳定性和活性,增强抗氧化效果。将MXene与其他抗氧化剂(例如维生素C、谷胱甘肽等协同作用)可获得增强的抗氧化效果。 调控巨噬细胞极化:MXene通过表面化学特性和物理刺激(如光热效应)调控巨噬细胞从促炎的M1表型向抗炎的M2表型极化[46-47]。例如,光活化的MXene纳米片可清除促炎因子(活性氧/活性氮),抑制炎症反应,诱导M2巨噬细胞极化,促进组织修复和骨再生。 MXene的抗氧化和免疫调节特性使它在骨修复领域具有重要的应用价值。MXene通过清除骨缺损部位过量的活性氧保护细胞免受氧化损伤,并且可以调节巨噬细胞极化,抑制炎症因子如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β的表达,同时促进抗炎细胞因子如白细胞介素10的分泌[47],从而减轻局部炎症反应、改善骨组织修复微环境、加速骨缺损的愈合。传统骨修复材料大多不会主动调节免疫细胞,例如聚己内酯和聚乳酸-羟基乙酸复合物主要是通过材料本身的物理和化学性质来影响免疫细胞的黏附、增殖和分化,或者通过控制药物释放来调节巨噬细胞的极化状态,但调控效果依赖于药物的种类和释放速率[48]。也有部分材料可以通过释放Ca2+、SiO32-和Na+等离子来影响免疫细胞的活性,但效果因离子释放的动态变化而异[49]。另外,传统材料在植入后还可能会引起一定的炎症反应,如β-磷酸三钙陶瓷虽然具有良好的生物相容性和骨传导性,然而其物理化学特性如结晶度、溶解度和化学计量比等容易诱导炎症反应[50-51],分泌炎症因子(肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β),诱导活性氧产生[52]。 "


2.2.4 光热性能 MXene在近红外光的第一、二生物窗口展现出显著的光吸收和高效光热转换能力,这使它在光热治疗领域具有巨大的应用潜力[13]。MXene由于独特的电子结构和表面等离子体共振效应具有优异的光热转换效率,转换效率可高达100%[53]。MXene的电子结构在很大程度上决定了其光吸收和热转换效率,通过调整化学组成、晶体结构、尺寸、表面化学基团等因素可以改变电子结构,调控光吸收和转换性能。例如,SHIN研究团队[54]开发了一种具有MXene和有机层交替排列超晶格结构MXene超材料,通过降低折射率并诱导产生多重光反射增加了光吸收,实现了90%的光热转换效率。MXene的光吸收峰主要集中在近红外区,而近红外光具有良好的组织穿透性,能够深入组织内部到达病灶部位,因此,利用MXene的近红外光光响应特性可以实现深部组织的光热治疗。通过调节激光功率、照射时间和MXene浓度等参数可以精确控制光热治疗温度,实现温和热疗或高强度热疗,满足不同的治疗需求。例如,低强度热疗可以用于调控细胞行为,促进组织再生;高强度热疗可以用于杀灭细菌或肿瘤细胞。另外,MXene表现出良好的光热稳定性和可重复性[55]。WAN等[20]制备的可扩展顺序桥接MXene薄膜,可以在超过100次的激光开关循环中反复加热和冷却到固定值。 MXene的光热性能为骨修复领域带来了新的机遇。利用MXene的光热抗菌特性可以有效治疗感染性骨缺损,避免传统抗生素治疗的弊端[56]。另外,MXene在骨肿瘤治疗中具有独特优势。有研究人员开发了一种由纳米羟基磷灰石、MXene纳米片和石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4)组成的多功能支架材料,该支架在近红外照射下可同时产生光热和光动力效应,快速消除骨肿瘤细胞,同时诱导骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,促进新骨形成[55]。"


2.2.5 导电性能 MXene中的自由电子使其具有优异的金属导电性[57],电导率通常在1 000-10 000 S/cm之间。LI等[58]合成的Ti3C2Tx MXene气凝胶纤维显示出高达10 000 S/cm的电导率,甚至一种由改性的高质量Al-Ti3C2纳米片制成的自支撑薄膜的电导率可高达20 000 S/cm。与其他常见导电材料(如碳纳米管、石墨烯等)相比,MXene的电导率相当,但MXene具有更好的可调性和稳定性,可以通过表面功能化实现特定应用的优化,而其他常见导电材料的导电性能主要取决于其结构完整性和制备质量[59-60]。 MXene的导电性与其表面官能团有很强的相关性[61]。例如,儿茶酚官能团可以通过氢键和π-π相互作用与MXene表面结合,形成强的相互作用,从而保持MXene的高导电性。KO等[62]的研究显示,使用3,4-二羟基-L-苯丙氨酸处理的,其导电性为6 404 S/cm,接近未处理MXene的导电性。另一些官能团(如磷酸盐)可通过形成共价键显著提高MXene在非极性溶剂中的分散性,但可能会降低MXene的导电性。官能团的密度也会影响MXene的导电性能,例如,增加接枝到MXene表面的4-硝基苯基浓度,改性MXene的导电性降低,同时使MXene场效应晶体管的开关电流比从1.46提升至3.56[63]。 将MXene的导电性能应用于骨修复材料的构建,有望提高骨修复效果,主要体现在以下几个方面:①模拟骨组织的电生理环境:天然骨组织是一种电活性组织,存在内源性电场。MXene的导电性可以赋予骨修复材料导电性,为骨细胞的生长和功能发挥提供更自然的电生理微环境[64]。②促进成骨细胞的增殖和分化:MXene基导电骨修复材料可以通过自身的导电性或在外加电场的刺激下传递电信号,通过Ca2+/钙调蛋白信号通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,加速骨缺损的修复[18,65]。③促进血管生成和神经再生:MXene基导电骨修复材料可能通过导电性促进血管内皮细胞和神经细胞的生长和功能发挥,增强骨组织的血管化和神经支配,从而促进骨修复[23]。NAN等[66]开发了一种导电的MXene-聚己内酯神经引导管,在体外实验中,该导管不仅能够促进施万细胞的增殖和分化,还能增强血管生成相关基因(如血管内皮生长因子A、血管内皮生长因子B和成纤维细胞生长因子2)的表达,促进内皮细胞的增殖、迁移和管状结构的形成,加速血管网络的形成;在大鼠坐骨神经缺损模型中,该导管移植表现出与自体神经移植组相似的神经再生效果。 "

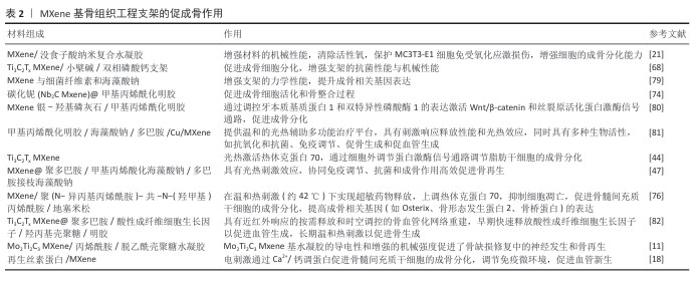
2.3 MXene基材料修复骨缺损中的应用 2.3.1 MXene基骨组织工程支架 骨组织工程作为一种极具潜力的骨缺损修复策略,旨在通过生物材料、细胞和生长因子等要素的优化组合,构建具有生物活性和结构功能的骨替代物,从而诱导和促进受损骨组织的再生与修复。该文从力学增强、促进成骨、免疫调节和抗感染4个方面进行深入阐述,旨在全面展现MXene在骨组织工程领域的应用潜力。 (1)力学增强支架:生物聚合物和生物陶瓷因良好的生物降解性和可加工性被广泛应用于骨组织工程支架的制备,但材料的力学性能常有不足,如聚合物强度低、生物陶瓷脆性大,难以满足骨组织修复对力学强度的要求[67]。MXene具有高强度、高模量和生物活性,将它作为增强相添加到聚合物基体中可显著提升复合支架的力学性能和促骨再生能力[68]。例如,与未改性的没食子酸接枝明胶水凝胶相比,添加了Ti3C2 MXene纳米片的没食子酸接枝明胶水凝胶具有更高的压缩强度(44.0-75.6 kPa)和模量(24.0-44.5 kPa)[21]。通过3D打印技术制备的MXene复合水凝胶支架具有适宜的孔隙率和孔径,机械强度和稳定性良好,可为骨组织生长提供有力支撑,支架的多孔结构也利于细胞附着和生长[10]。徐志民[69]制备了3D打印MXene/聚己内酯复合支架,利用MXene增强聚己内酯支架的力学性能,开发用于原位骨组织工程的高性能支架。DIEDKOVA等[70]通过MXene改性聚己内酯纳米纤维支架,发现MXene不仅赋予支架导电性,还能改善支架的力学性能。 (2)促进成骨:在骨缺损修复中诸多因素会影响骨再生,而核心问题在于如何促使前成骨细胞迁移到损伤部位并分化为成骨细胞,同时保障其活性和生长分化能力。基于此,研究者们从MXene的二维片层结构特性出发,探索材料对成骨相关细胞的潜在影响。例如,JIANG等[71]制备了多层Ti3C2 MXene薄膜,发现该膜不仅生物相容性良好,还能显著促进MC3T3细胞的成骨分化,提升碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素和骨桥蛋白蛋白的mRNA表达。有研究使用质量浓度0-100 μg/mL的MXene 处理人间充质干细胞7 d,发现当MXene质量浓度> 50 μg/mL具有细胞毒性,而质量浓度< 20 μg/mL促进细胞的成骨分化。MXene促进成骨细胞分化的通路可能涉及Wnt/β-catenin和骨形态发生蛋白/Smad[72-73]。CUI等[24]制备的Ti3C2Tx纳米片通过Wnt/缺氧诱导因子1α介导的代谢途径促进人牙周膜细胞的成骨分化,加速大鼠牙周缺损模型中的新骨再生。XU等[74]开发了由二维碳化铌MXene(2D Nb2C)和甲基丙烯酰化明胶组成的骨水泥,在骨修复中不仅促进成骨细胞活化,还可促进体内骨整合过程。WANG等[11]将Mo2Ti2C3 MXene引入水凝胶后不仅提升了水凝胶的机械强度和导电性,还促进了神经生长因子和脑源性神经营养因子的表达,通过免疫荧光染色证实该水凝胶在骨缺损修复过程中促进了神经元和感觉神经元的生成。YIN等[75]制备了整合Nb2C MXene纳米片的3D打印生物活性玻璃支架,体外实验显示该支架增强了人脐静脉内皮细胞的迁移能力和成管能力,促进血管生成因子和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子的表达,同时在体内也表现出优异的促血管生成性能。 光热刺激成骨:温度是影响骨生长发育的重要因素,温和的热刺激可有效促进细胞分化和骨再生[76]。MXene是一种高效的近红外光热转换器,可在近红外辐射下快速、时空控制地产生热量,这种光热效应可用于调控细胞行为,激活热休克蛋白70,从而抑制细胞凋亡,为成骨细胞的增殖和分化提供有利环境,并通过 细胞外调节蛋白激酶信号通路调节脂肪干细胞的成骨分化[44]。研究显示,局部高温通过激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路增强骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化和矿化能力[77]。LIN等[13]首次报道了Nb2C MXene在近红外光Ⅰ和近红外光Ⅱ生物窗口中的光热性能,尽管该研究聚焦于肿瘤治疗,但结果为光热刺激成骨提供了理论基础。WU等[47]开发的MXene@聚多巴胺/甲基丙烯酸化海藻酸钠/多巴胺接枝海藻酸钠水凝胶平台,利用MXene的光热效应实现温和的热刺激协同免疫调节和成骨作用,从而高效促进骨再生。当MXene与温度敏感聚合物结合形成水凝胶并负载促骨药物(如地塞米松)时,近红外光照射会使MXene产热导致水凝胶在特定温度下急剧收缩,从而超敏释放药物,这种药物与光热作用的协同机制可在早期抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的凋亡,在后期促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化,实现优异的成骨效果[78]。 电刺激成骨:骨组织具有压电效应,并且电刺激已被证实可有效促进骨再生。MXene因优异的导电性成为构建电刺激骨组织工程支架的理想选择。DIEDKOVA等[70]制备的MXene涂层聚己内酯纳米纤维膜具备导电性,为电刺激骨组织工程支架的构建奠定了材料基础。未来,通过优化MXene基导电支架的设计有望实现对细胞的电刺激,从而更高效地促进骨再生。HU等[18]基于再生丝素蛋白和生物包埋的MXene开发了一种多功能水凝胶,用于探索导电材料在电刺激下骨再生的细胞机制,发现电刺激可增加细胞内Ca2+浓度、激活钙调蛋白,进而促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。 MXene基骨组织工程支架促成骨应用,见表2。 "

(3)抗感染作用:骨感染是最具破坏性的骨科结局之一,而抗生素的过度使用可能会引起耐药性问题。光热治疗是一种很有前途的治疗感染性骨缺损的无抗生素策略。MXene因优异的光热性能可作为光热治疗剂。ZHANG等[83]构建了一种基于MXene的光热纳米抗菌材料,先利用聚多巴胺修饰MXene使材料表面带负电,进而利用静电作用固定带正电的溶菌酶,在光照下,MXene@聚多巴胺的局部温度升高导致细菌蛋白质变性和DNA损伤,从而杀死细菌。ZHAO等[56]利用3D打印技术制备了内外夹心的多功能Cu2O@MXene/α-磷酸三钙支架,其中MXene能响应近红外光刺激产热,实现短期高温杀菌和长期温热促骨形成的效果,而Cu2O的加入增强了杀菌效果、改善了感染微环境,从而促进骨缺损修复。然而,耐药致病菌的致密细胞膜显著降低了热传导效率,阻碍活性氧进入细菌细胞,导致杀菌效果不理想。HUANG等[37]受感受态细菌细胞膜特性的启发设计了一种MXene/CaO2生物异质结,通过激活感受态细胞样抗菌策略增强致病菌细胞膜的通透性,在近红外光照射下MXene/CaO2生物异质结产生的热量和活性氧很容易通过细菌膜,极大干扰细菌新陈代谢,从而实现快速杀菌,促进感染组织再生。QIN等[39]设计了一种益生菌生物异质结,结合鼠李糖乳杆菌与MXene量子点/FeS异质结用于治疗生物膜相关感染、促进伤口组织再生。MXene的抗感染作用,见表3。 "
(4)免疫调节作用:骨组织修复是一个复杂的生物学过程,免疫反应在其中扮演着至关重要角色。MXene材料及其复合材料在免疫调节方面表现出一定的潜力,可通过调控免疫细胞行为优化骨组织修复的免疫微环境,从而促进骨再生。 巨噬细胞驱动的免疫反应在骨组织再生中发挥重要作用,众所周知,巨噬细胞可根据周围微环境变化极化为2种不同表型,M1型巨噬细胞可通过分泌促炎细胞因子损伤宿主骨组织,M2型巨噬细胞可通过分泌抗炎细胞因子加速新骨的形成[86]。赵月鑫等[87]综述了巨噬细胞极化在骨组织工程免疫研究中的进展,强调了通过调节巨噬细胞极化比例来调控免疫微环境,是促进骨组织工程成骨的关键手段。MXene的光热效应可抑制炎症因子的产生,下调促炎基因表达(肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、诱导型一氧化氮合成酶、CD86),上调抗炎基因表达(转化生长因子β、白细胞介素10、精氨酸酶1、CD206),减少炎症反应。MXene 可协同减少活性氧和氮物质,同时促进M2巨噬细胞极化,进一步减轻炎症,为成骨创造有利条件[47]。 YU等[5]将Ti3C2 MXene掺入到β-磷酸三钙陶瓷纳米材料中,发现复合材料能够激活T细胞的N-糖基化并调节白细胞介素4的产生,从而产生抗炎和抗氧化作用,促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,最终促进骨再生。RAFIEERAD等[15]将Ti3C2 MXene量子点掺入到壳聚糖水凝胶中制备了Ti3C2 MXene量子点/壳聚糖复合水凝胶,发现Ti3C2 MXene量子点不仅赋予复合水凝胶良好的导电性和优异的理化性能,更重要的是,Ti3C2 MXene量子点展现出内在的免疫调节特性,能够选择性地降低人CD4+干扰素γ+ T淋巴细胞的活化,同时促进免疫抑制性CD4+CD25+FoxP3+调节性T细胞的扩增。该研究首次报道了Ti3C2 MXene量子点在免疫调节方面的应用。MXene还能够调节树突状细胞的成熟,影响树突状细表面共刺激分子如 CD80、CD86等的表达,进而影响树突状细胞的抗原呈递能力,调节T细胞的激活和免疫反应启动[88]。这些研究表明,基于MXene的纳米复合材料在骨免疫调节方面具有独特的功能。MXene基骨组织工程支架的免疫调节作用,见表4。 "

2.3.2 MXene基引导骨再生膜 将MXene与高分子材料复合制备成薄膜,可以用于引导骨再生膜。MXene的加入可以赋予膜材料导电性、抗菌性、增强力学性能等。目前关于MXene基引导骨再生膜的研究相对较少,但基于MXene在骨修复领域的巨大潜力,MXene基引导骨再生膜有望成为未来研究的热点方向。对于引导骨再生膜的构建,通常要求具备以下要点:①生物相容性:MXene具有良好生物相容性。②足够的强度,防止膜在组织愈合过程中塌陷,从而为骨再生保留充足的空间,维持骨缺损区域的形态。WAN等[20]通过集成顺序桥接的卷对卷辅助刀片涂层制备了高性能MXene薄膜,该薄膜展现出强大的力学自支撑性能,弹性模量高达(32.9±1.9) GPa,拉伸强度为(755±22) MPa,在近红外光照射下具备良好的光热转换和成骨效率,将它作为引导骨再生膜植入大鼠颅骨缺损处8周后仍能保持完整的结构,有效阻挡非骨形成组织的侵入,为骨缺损处提供稳定的生长空间,证明了MXene薄膜用作引导骨再生膜的巨大潜力。③细胞屏障作用与多孔性:ZHOU等[89]开发了具有双层结构的Janus细菌纤维素/MXene膜用作引导骨再生膜,致密的表面充当了可靠的物理屏障,L929细胞在致密层表面表现出典型的成纤维细胞形态,呈延伸的纺锤状;多孔层有利于成骨和空间保留,大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞在疏松层表面具有更大的细胞铺展面积,呈扁平的多边形形态。两面结构都提供了良好的细胞黏附表面,并且不论体外还是体内都表现出优异的骨诱导性能。④适当的降解速率:材料的降解速度应与骨再生速度相匹配,一般应能稳定维持骨再生空间至少达4-6周,材料降解过快会导致骨再生空间过早丧失,影响骨再生效果;材料降解过慢则可能增加膜暴露、感染等风险,甚至可能对新形成的骨组织造成压迫或干扰。运用静电纺丝技术合成的多功能Ti3C2 Tx Mxene/β-磷酸三钙/聚乳酸-碳酸酯骨再生膜具有良好的生物可降解性,在12周时的质量损失率在17%-22%之间,降解速率适中,能够在骨再生过程中提供足够的支撑时间,同时不会引起周围环境的显著变化,避免二次手术移除膜的风险[90]。⑤促进骨细胞生长和分化:MXene具有一定的促成骨活性,能够诱导或促进骨祖细胞的增殖、分化以及成骨细胞的活性,加速新骨形成[14]。ZHANG等[90]将具有导电功能的MXene二维纳米材料和β-磷酸三钙颗粒原位掺杂到聚乳酸-碳酸酯复合纳米可吸收膜中,开发了一种集柔性弹性、电刺激和骨诱导活性于一体的多功能骨再生膜,体外实验表明,在电刺激下该膜有效促进了骨髓间充质干细胞在的募集和成骨分化、增强了内皮细胞的血管生成能力,促进骨再生;此外,该膜还具有良好的柔韧性和弹性记忆能力,便于临床操作,能够适应复杂的骨缺损部位。⑥预防感染:在口腔环境中,理想的引导骨再生膜应具备一定的抗菌活性,能够有效抑制细菌的生长和繁殖,减少术后感染的风险,保护骨缺损区域的血凝块,为骨再生提供一个相对无菌的环境。MXene基引导骨再生膜的特点,见表5。 综上所述,MXene具有适宜做引导骨再生膜的多种特性,有望在未来作为一种新型的引导骨再生膜,发挥有广阔的应用潜力。 "


2.3.3 MXene基植入物/涂层 骨科植入物,如钛合金、不锈钢等,是临床上常用的骨缺损修复材料,然而,传统金属植入物存在生物惰性、骨整合不良以及术后感染风险等问题[92]。在植入物表面构建生物活性涂层可以改善植入物的表面生物学性能,促进成骨细胞的黏附、增殖和分化,加速骨整合,同时抑制细菌生长,降低感染风险[93]。MXene因优异的生物活性和抗菌性能成为构建高性能植入物涂层的理想选择。例如,HUANG等[37]创新性地通过激活感受态细胞样抗菌策略成功制备了一种新型的MXene/CaO2生物异质结,将此生物异质结应用于骨科植入物涂层后可有效促进感染骨缺损的骨整合。 为了解决植入物相关感染问题,YANG等[17]开发了一种基于Nb2C MXene的钛板(Nb2C@TP)植入物,该植入物具有多模式抗感染功能,一方面能够直接破坏已形成的生物膜对细菌起到直接杀灭作用,从源头上抑制生物膜的形成;另一方面,借助激活辅助基因调节器促使已生成的生物膜加速脱落,抗菌机制主要与下调细菌能量代谢途径有关;此外,还能清除感染微环境中的活性氧,减轻炎症反应,促进组织重建。 MXene的光热特性赋予植入物涂层独特的抗菌和骨修复双重功效。在近红外光照射下,MXene涂层能够产生局部高温进而高效灭菌,同时激活成骨细胞,促进骨组织再生。在骨肉瘤切除术后骨修复研究中,YIN等[94]构建了磺化聚醚醚酮@MXene/甲基丙烯酰化明胶多功能植入物,凭借独特的光热效应,该植入物能够有效杀灭肿瘤细胞,在负载妥布霉素后的抗菌性能尤为突出,可显著抑制术后感染;展现出良好的生物性能,能够促进细胞增殖、铺展,提升碱性磷酸酶活性,加速钙基质矿化,并且可促进体内骨整合。此研究极大地拓宽了MXene植入物涂层的应用范围,将它引入骨肿瘤治疗与感染控制领域可实现肿瘤治疗、感染预防及促进骨再生的多重目标。顽固性种植体相关感染是植入物失败的主要原因,特别是在糖尿病情况下,对此,GONG等[85]开发了一种多功能的MXene/Ag3PO4@葡萄糖氧化酶生物异质结涂层,该生物涂层的应用不仅促进了成骨细胞在植入体上的黏附和增殖,还可通过生物催化反应和光热/光动力过程产生的局部高温和活性氧,发挥优异的抗菌效果,最终形成一个具有级联放大治疗能力的新平台。 MXene涂层还具有免疫调节功能。XIA等[46]设计的聚多巴胺/Ti3C2/聚(偏氟乙烯三氟乙烯)纳米复合涂层,通过近红外光触发的温和热刺激促进了骨髓间充质干细胞的铺展和生长,激活了整合素介导的MEK/细胞外调节蛋白激酶成骨分化信号通路,同时促进了抗炎性精氨酸酶1和白细胞介素10细胞因子的表达,调节巨噬细胞向M2表型极化,为加速骨再生创造有利微环境。 综上所述,MXene涂层显著提升了金属植入物的表面生物活性和抗菌性能,通过光热效应实现了抗菌和促骨修复的双重功能。通过合理设计涂层的成分和结构可以开发出高性能的植入物涂层,提高骨科植入物的长期疗效和安全性。 "


2.3.4 MXene基3D打印骨支架 3D打印技术可依据患者的CT或MRI影像数据精确构建个性化、结构复杂的骨支架,支架在形状匹配、孔隙结构可控、药物缓释等方面具有传统方法无法比拟的优势。MXene的良好分散性使它可以作为3D打印墨水的组分,它优异的力学性能、导电性和生物活性可以赋予3D打印骨支架更优异的性能;此外,作为光阻隔剂或光固化油墨,MXene增强了3D打印结构的精度和分辨率[95]。 制备适合3D打印的MXene基墨水,是构建MXene基3D打印骨支架的关键。MXene纳米片的分散性、稳定性及与基体材料的相容性,是影响墨水打印性能和支架最终性能的重要因素。通过对墨水材料进行合理设计,可以打印出生物相容性良好、机械性能佳的多功能支架。NIE等[10]制备了甲基丙烯酰化明胶/β-磷酸三钙/海藻酸锶/MXene复合生物支架,在近红外光照射下,该支架于体内外均可杀灭革兰阳性菌和革兰阴性菌,在抗菌和成骨作用中发挥协同作用,最终促进骨再生。ZHAO等[56]开发了Cu2O@MXene/α-磷酸三钙复合生物墨水,成功制备了Cu2O@Ti3C2/磷酸三钙多功能支架,该支架具有一定的韧性和机械稳定性,能够满足松质骨力学的基本要求,还具有抗菌、成骨和促血管生成性能,为感染性骨缺损的治疗提供了新思路。利用Ti3C2 MXene与羟基磷灰石和海藻酸钠复合制备的3D打印墨水,可打印出具有均匀的多孔结构的支架,并且随着Ti3C2 MXene浓度的增加,支架颜色逐渐变深,支架平均孔隙率为60%,有利于营养物质和代谢废物的循环以及组织修复和重建[96]。总之,MXene作为3D打印墨水组分具有极大的可行性和潜力。 MXene基3D打印骨支架不仅具有形状可控、孔隙结构可调等3D打印支架的共性优势,还具备独特的功能,如电刺激成骨、药物缓释、光热治疗等。WANG等[11]开发的Mo2Ti2C3 MXene复合水凝胶不仅可以作为注射水凝胶,也可以用于3D打印。通过将MXene与药物缓释系统结合可以实现药物的控制释放和靶向治疗,提高骨缺损修复的疗效。例如,ZHAO等[97]开发的一种近红外响应聚乳酸/MXene支架可负载药物微球,在近红外光照射下实现药物的控制释放和靶向治疗,增强抗肿瘤效果并促进骨形成。MXene的光热性能不仅赋予支架光热抗菌功能,还能通过调控免疫微环境进一步促进骨缺损愈合[19];此外,还可与骨再生功能结合,为感染性骨缺损修复提供新策略。一项研究将二维MXene纳米片与3D打印生物活性玻璃支架相结合开发了一种多功能支架,该支架显著增强了成骨细胞相关基因的表达、促进了胞质钙结节的沉积,在大鼠颅骨缺损模型中显著促进了新骨生成[16]。 综上所述,MXene基3D打印骨支架融合了3D打印的个性化定制优势和MXene的优异性能,在骨缺损修复领域展现出巨大潜力。 "

| [1] HABIBOVIC P. Strategic Directions in Osteoinduction and Biomimetics. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(23-24):1295-1296. [2] BEZ M, SHEYN D, TAWACKOLI W, et al. In situ bone tissue engineering via ultrasound-mediated gene delivery to endogenous progenitor cells in mini-pigs. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9(390):eaal3128. [3] BAROLI B. From natural bone grafts to tissue engineering therapeutics: Brainstorming on pharmaceutical formulative requirements and challenges. J Pharm Sci. 2009;98(4):1317-1375. [4] BHUMIRATANA S, BERNHARD JC, ALFI DM, et al. Tissue-engineered autologous grafts for facial bone reconstruction. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8(343):343ra83-343ra83. [5] YU F, ZHAO X, ZHANG S, et al. Regulation of T cell glycosylation by MXene/β-TCP nanocomposite for enhanced mandibular bone regeneration. Adv Healthcare Mater. 2025;14(6):e2404015. [6] ALAGARSAMY KN, SALETH LR, SEKARAN S, et al. MXenes as emerging materials to repair electroactive tissues and organs. Bioact Mater. 2025;48:583-608. [7] NAGUIB M, BARSOUM MW, GOGOTSI Y. Ten Years of Progress in the Synthesis and Development of MXenes. Adv Mater. 2021;33(39):2103393. [8] PARK H, KIM S, KIM S, et al. Bioactive inorganic compound MXene and its application in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. J Ind Eng Chem. 2023;117:38-53. [9] LI T, QIANG W, LEI B. Bioactive surface-functionalized MXenes for biomedicine. Nanoscale. 2025;17(9):4854-4891. [10] NIE R, SUN Y, LV H, et al. 3D printing of MXene composite hydrogel scaffolds for photothermal antibacterial activity and bone regeneration in infected bone defect models. Nanoscale. 2022;14(22):8112-8129. [11] WANG H, HSU YC, WANG C, et al. Conductive and enhanced mechanical strength of Mo2Ti2C3 MXene-based hydrogel promotes neurogenesis and bone regeneration in bone defect repair. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(14):17208-17218. [12] NAGUIB M, KURTOGLU M, PRESSER V, et al. Two-Dimensional Nanocrystals Produced by Exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Adv Mater. 2011; 23(37):4248-4253. [13] LIN H, GAO S, DAI C, et al. A two-dimensional biodegradable niobium carbide (MXene) for photothermal tumor eradication in NIR-I and NIR-II biowindows. J Am Chem Soc. 2017;139(45):16235-16247. [14] ZHANG J, FU Y, MO A. Multilayered Titanium Carbide MXene Film for Guided Bone Regeneration. Int J Nanomed. 2019; 14:10091-10103. [15] RAFIEERAD A, YAN W, SEQUIERA GL, et al. Application of Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots for immunomodulation and regenerative medicine. Adv Healthcare Mater. 2019; 8(16):e1900569. [16] PAN S, YIN J, YU L, et al. 2D MXene-integrated 3D-printing scaffolds for augmented osteosarcoma phototherapy and accelerated tissue reconstruction. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7(2):1901511. [17] YANG C, LUO Y, LIN H, et al. Niobium carbide MXene augmented medical implant elicits bacterial infection elimination and tissue regeneration. ACS Nano. 2021;15(1): 1086-1099. [18] HU ZC, LU JQ, ZHANG TW, et al. Piezoresistive MXene/silk fibroin nanocomposite hydrogel for accelerating bone regeneration by Re-establishing electrical microenvironment. Bioact Mater. 2023;22:1-17. [19] HUANG B, LI S, DAI S, et al. Ti3C2Tx MXene-decorated 3D-printed ceramic scaffolds for enhancing osteogenesis by spatiotemporally orchestrating inflammatory and bone repair responses. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024; 11(34):e2400229. [20] WAN S, CHEN Y, HUANG C, et al. Scalable ultrastrong MXene films with superior osteogenesis. Nature. 2024;634(8036):1103-1110. [21] ZHAO J, WANG T, ZHU Y, et al. Enhanced osteogenic and ROS-scavenging MXene nanosheets incorporated gelatin-based nanocomposite hydrogels for critical-sized calvarial defect repair. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;269(Pt 1):131914. [22] SZUPLEWSKA A, WOJCIECHOWSKA A, POŹNIAK S, et al. Multilayered stable 2D nano-sheets of Ti2NTx MXene: synthesis, characterization, and anticancer activity. J Nanobiotechnology. 2019;17:114 [23] SZUPLEWSKA A, KULPIŃSKA D, DYBKO A, et al. 2D Ti2C (MXene) as a novel highly efficient and selective agent for photothermal therapy. Mater Sci Eng C. 2019;98:874-886. [24] CUI D, KONG N, DING L, et al. Ultrathin 2D Titanium Carbide MXene (Ti3C2Tx ) Nanoflakes Activate WNT/HIF-1α-Mediated Metabolism Reprogramming for Periodontal Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021; 10(22):e2101215. [25] ZHANG D, ZHENG W, LI X, et al. Investigating the effect of Ti3C2 (MXene) nanosheet on human umbilical vein endothelial cells via a combined untargeted and targeted metabolomics approach. Carbon. 2021;178:810-821. [26] HUANG J, SU J, HOU Z, et al. Cytocompatibility of Ti3C2Tx MXene with Red Blood Cells and Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells and the Underlying Mechanisms. Chem Res Toxicol. 2023; 36(3):347-359. [27] NASRALLAH GK, AL-ASMAKH M, RASOOL K, et al. Ecotoxicological assessment of Ti3C2Tx (MXene) using a zebrafish embryo model. Environ Sci Nano. 2018;5(4): 1002-1011. [28] SZUPLEWSKA A, KULPIŃSKA D, JAKUBCZAK M, et al. The 10th anniversary of MXenes: Challenges and prospects for their surface modification toward future biotechnological applications. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2022; 182:114099. [29] REN X, HUO M, WANG M, et al. Highly catalytic niobium carbide (MXene) promotes hematopoietic recovery after radiation by free radical scavenging. ACS Nano. 2019;13(6):6438-6454. [30] LI G, ZHONG X, WANG X, et al. Titanium carbide nanosheets with defect structure for photothermal-enhanced sonodynamic therapy. Bioact Mater. 2022;8:409-419. [31] SEIDI F, ARABI SHAMSABADI A, DADASHI FIROUZJAEI M, et al. MXenes antibacterial properties and applications: a review and perspective. Small. 2023;19(14):2206716. [32] RASOOL K, HELAL M, ALI A, et al. Antibacterial activity of Ti3C2Tx MXene. ACS Nano. 2016;10(3):3674-3684. [33] ARABI SHAMSABADI A, SHARIFIAN GH. M, ANASORI B, et al. Antimicrobial Mode-of-Action of Colloidal Ti3C2Tx MXene Nanosheets. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng. 2018;6(12):16586-16596. [34] RASOOL K, MAHMOUD KA, JOHNSON DJ, et al. Efficient antibacterial membrane based on two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx (MXene) nanosheets. Sci Rep0 2017;7(1):1598. [35] GUO H, CHU X, GUO Y, et al. A water transfer printing method for contact lenses surface 2D MXene modification to resist bacterial infection and inflammation. Sci Adv. 2024;10(15):eadl3262. [36] RASHEED PA, PANDEY RP, GOMEZ T, et al. Large interlayer spacing Nb4C3Tx (MXene) promotes the ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of Pb2+ on glassy carbon electrodes. RSC Adv. 2020;10(41):24697-24704. [37] HUANG Y, LI J, YU Z, et al. Elaborated bio-heterojunction with robust sterilization effect for infected tissue regeneration via activating competent cell-like antibacterial tactic[J]. Adv Mater. 2024;36(48):e2414111. [38] CAI Z, MA Y, YUN M, et al. Multifunctional MXene/holey graphene films for electromagnetic interference shielding, joule heating, and photothermal conversion. Compos Part B Eng. 2023;251:110477. [39] QIN M, ZHANG X, DING H, et al. Engineered probiotic bio-heterojunction with robust antibiofilm modality via “eating” extracellular polymeric substances for wound regeneration. Adv Mater. 2024;36(35):2402530. [40] SHIFRINA ZB, MATVEEVA VG, BRONSTEIN LM. Role of Polymer Structures in Catalysis by Transition Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticle Composites. Chem Rev. 2020; 120(2):1350-1396. [41] WANG W, FENG H, LIU J, et al. A photo catalyst of cuprous oxide anchored MXene nanosheet for dramatic enhancement of synergistic antibacterial ability. Chem Eng J. 2020;386:124116. [42] ALDER KD, LEE I, MUNGER AM, et al. Intracellular Staphylococcus aureus in bone and joint infections: A mechanism of disease recurrence, inflammation, and bone and cartilage destruction. Bone. 2020; 141:115568. [43] MASTERS EA, RICCIARDI BF, BENTLEY KLM, et al. Skeletal infections: microbial pathogenesis, immunity and clinical management. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2022;20(7):385-400. [44] QU X, GUO Y, XIE C, et al. Photoactivated MXene nanosheets for integrated bone–soft tissue therapy: effect and potential mechanism. ACS Nano. 2023;17(8): 7229-7240. [45] YU Y, YOU Z, LI X, et al. Injectable Nanocomposite Hydrogels with Strong Antibacterial, Osteoinductive, and ROS-Scavenging Capabilities for Periodontitis Treatment. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(12):14421-14433. [46] XIA S, LIU D, JIANG K, et al. Photothermal driven BMSCs osteogenesis and M2 macrophage polarization on polydopamine-coated Ti3C2 nanosheets/poly(vinylidene fluoride trifluoroethylene) nanocomposite coatings. Mater Today Bio. 2024;27:101156. [47] WU M, LIU H, ZHU Y, et al. Mild photothermal-stimulation based on injectable and photocurable hydrogels orchestrates immunomodulation and osteogenesis for high-performance bone regeneration. Small. 2023;19(28):e2300111. [48] DONG C, TAN G, ZHANG G, et al. The function of immunomodulation and biomaterials for scaffold in the process of bone defect repair: a review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1133995. [49] LI S, ZHANG L, LIU C, et al. Spontaneous immunomodulation and regulation of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by Sr/Cu-borosilicate glass (BSG) bone cement to repair critical bone defects. Bioact Mater.2023;23:101-117. [50] VELARD F, BRAUX J, AMEDEE J, et al. Inflammatory cell response to calcium phosphate biomaterial particles: an overview. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(2): 4956-4963. [51] MALARD O, BOULER JM, GUICHEUX J, et al. Influence of biphasic calcium phosphate granulometry on bone ingrowth, ceramic resorption, and inflammatory reactions: preliminary in vitro and in vivo study. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999;46(1):103-111. [52] ZHAO Z, ZHANG J, YANG Z, et al. Biodegradation of HA and β-TCP Ceramics Regulated by T-Cells. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(9):1962. [53] LI Q, WANG W, FENG H, et al. NIR-triggered photocatalytic and photothermal performance for sterilization based on copper sulfide nanoparticles anchored on Ti3C2Tx MXene. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2021;604:810-822. [54] SHIN H, JEONG W, HAN TH. Maximizing light-to-heat conversion of Ti3C2Tx MXene metamaterials with wrinkled surfaces for artificial actuators. Nat Commun. 2024; 15(1):10507. [55] ZHANG G, LU Y, SONG J, et al. A multifunctional nano-hydroxyapatite/MXene scaffold for the photothermal/dynamic treatment of bone tumours and simultaneous tissue regeneration. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2023;652(Pt B):1673-1684. [56] ZHAO Y, KANG H, XIA Y, et al. 3D printed photothermal scaffold sandwiching bacteria inside and outside improves the infected microenvironment and repairs bone defects. Adv Healthcare Mater. 2024; 13(6):e2302879. [57] ZHANG YZ, WANG Y, JIANG Q, et al. MXene Printing and Patterned Coating for Device Applications. Adv Mater. 2020; 32(21):e1908486. [58] LI Y, ZHANG X. Electrically Conductive, Optically Responsive, and Highly Orientated Ti3C2T MXene Aerogel Fibers. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;32(4):2107767. [59] MATHIS TS, MALESKI K, GOAD A, et al. Modified MAX phase synthesis for environmentally stable and highly conductive Ti3C2 MXene. ACS Nano. 2021; 15(4):6420-6429. [60] 郭妙才,黑艳伟,李斌太,等.石墨烯/碳纳米管共改性碳纤维复合材料的结构、力学、导电和雷击性能[J].复合材料学报, 2022,39(9):4354-4365. [61] JUNG S, BALOCH U, ACHARY L, et al. Ligand chemistry for surface functionalization in MXenes :A review. Ecomat. 2023;5(10).doi:10.1002/eom2.12395. [62] KO TY, KIM D, KIM SJ, et al. Universal ligands for dispersion of two-dimensional MXene in organic solvents. ACS Nano. 2023;17(2): 1112-1119. [63] JING H, YEO H, LYU B, et al. Modulation of the Electronic Properties of MXene (Ti3C2Tx) via Surface-Covalent Functionalization with Diazonium. ACS Nano. 2021;15(1):1388-1396. [64] FU Y, HUANG S, FENG Z, et al. MXene-functionalized ferroelectric nanocomposite membranes with modulating surface potential enhance bone regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(2):900-917. [65] BOULARAOUI S, SHANTI A, LANOTTE M, et al. Nanocomposite Conductive Bioinks Based on Low-Concentration GelMA and MXene Nanosheets/Gold Nanoparticles Providing Enhanced Printability of Functional Skeletal Muscle Tissues. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(12):5810-5822. [66] NAN LP, LIN Z, WANG F, et al. Ti3C2Tx MXene-Coated Electrospun PCL Conduits for Enhancing Neurite Regeneration and Angiogenesis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:850650. [67] CUI ZK, KIM S, BALJON JJ, et al. Microporous methacrylated glycol chitosan-montmorillonite nanocomposite hydrogel for bone tissue engineering. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):3523. [68] TAN Y, SUN H, LAN Y, et al. Study on 3D printed MXene-berberine-integrated scaffold for photo-activated antibacterial activity and bone regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2024;12(8): 2158-2179. [69] 徐志民.3D打印MXene/PCL原位骨组织工程支架及其成骨分子机制的研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2022. [70] DIEDKOVA K, POGREBNJAK AD, KYRYLENKO S, et al. Polycaprolactone–MXene Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023;15(11):14033-14047. [71] JIANG JH, LEE EJ. Influence of MXene Particles with a Stacked-Lamellar Structure on Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(16):4453. [72] SONG D, HE G, SHI Y, et al. Functional interaction between wnt and bmp signaling in periosteal bone growth. Sci Rep. 2021; 11(1):10782. [73] MAJIDINIA M, SADEGHPOUR A, YOUSEFI B. The roles of signaling pathways in bone repair and regeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(4):2937-2948. [74] XU D, LI Y, YE Y, et al. Super-assembled niobium-MXene integrated frameworks for accelerated bone repair and osseointegration. Nano Today. 2024;59:102471. [75] YIN J, PAN S, GUO X, et al. Nb2C MXene-functionalized scaffolds enables osteosarcoma phototherapy and angiogenesis/osteogenesis of bone defects. Nano Micro Lett. 2021;13(1):30. [76] ZHANG X, CHENG G, XING X, et al. Near-Infrared Light-Triggered Porous AuPd Alloy Nanoparticles To Produce Mild Localized Heat To Accelerate Bone Regeneration. J Phys Chem Lett. 2019;10(15):4185-4191. [77] ZHANG J, TANG S, DING N, et al. Surface-modified Ti3C2 MXene nanosheets for mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation via photothermal conversion. Nanoscale Adv. 2023;5(11):2921-2932. [78] CHEN Y, LIU W, WAN S, et al. Superior synergistic osteogenesis of MXene‐based hydrogel through supersensitive drug release at mild heat. Adv Funct Mater. 2024;34(2):2309191. [79] HU T, CAI P, XIA C. MXene reinforced microporous bacterial cellulose/sodium alginate dual crosslinked cryogel for bone tissue engineering. Biomed Mater. 2024;19(5):55022. [80] LI J, FAN Z, GUAN Z, et al. Injectable MXene/Ag-HA composite hydrogel for enhanced alveolar bone healing and mechanistic study. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1485437. [81] ZHU Y, LIU H, WU P, et al. Multifunctional injectable hydrogel system as a mild photothermal-assisted therapeutic platform for programmed regulation of inflammation and osteo-microenvironment for enhanced healing of diabetic bone defects in situ. Theranostics. 2024;14(18):7140-7198. [82] WU M, ZHANG Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Photoactivated hydrogel therapeutic system with MXene-based nanoarchitectonics potentiates endogenous bone repair through reshaping the osteo-vascularization network. Small. 2024;20(51):e2403003. [83] ZHANG D, HUANG L, SUN DW, et al. Bio-interface engineering of MXene nanosheets with immobilized lysozyme for light-enhanced enzymatic inactivation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Chem Eng J. 2023;452:139078. [84] SU Y, ZHANG X, WEI Y, et al. Nanocatalytic Hydrogel with Rapid Photodisinfection and Robust Adhesion for Fortified Cutaneous Regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023;15(5):6354-6370. [85] GONG J, LAI S, ZHANG S, et al. Multi‐Functional Bio‐HJzyme Engineered Polyetheretherketone Implant with Cascade‐Amplification Therapeutic Capabilities Toward Intractable Implant‐Associated Infections. Small. 2024;21(7):e2409437. [86] 杨雨晴,陈志宇.早期短暂M1巨噬细胞在骨组织工程中的作用及应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(4):594-601. [87] 赵月鑫,陈滨.巨噬细胞极化在骨组织工程免疫研究中的进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(13):2120-2126. [88] YU X, PAN H, HE Q, et al. MXene-based dual-gated multifunctional nanodrug induced ferroptosis and modulated tumor microenvironment to treat pancreatic cancer. Chem Eng J. 2024;500:157233. [89] ZHOU H, ZHAO Y, ZHA X, et al. A Janus, robust, biodegradable bacterial cellulose/Ti3C2Tx MXene bilayer membranes for guided bone regeneration. Biomater Adv. 2024;161:213892. [90] ZHANG S, HUANG L, BIAN M, et al. Multifunctional bone regeneration membrane with flexibility, electrical stimulation activity and osteoinductive activity. Small (Weinh Bergstr Ger). 2024; 20(47):e2405311. [91] YANG K, LEI S, QIN X, et al. Biodegradable polyvinyl alcohol/nano-hydroxyapatite composite membrane enhanced by MXene nanosheets for guided bone regeneration. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2024;155:106540. [92] YU Y, JIN G, XUE Y, et al. Multifunctions of dual Zn/Mg ion co-implanted titanium on osteogenesis, angiogenesis and bacteria inhibition for dental implants. Acta Biomater. 2017;49:590-603. [93] GEULI O, METOKI N, ELIAZ N, et al. Electrochemically driven hydroxyapatite nanoparticles coating of medical implants. Adv Funct Mater. 2016;26(44):8003-8010. [94] YIN J, HAN Q, ZHANG J, et al. MXene-based hydrogels endow polyetheretherketone with effective osteogenicity and combined treatment of osteosarcoma and bacterial infection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020; 12(41):45891-45903. [95] DANANJAYA V, HANSIKA N, MARIMUTHU S, et al. MXenes and its composite structures: synthesis, properties, applications, 3D/4D printing, and artificial intelligence; machine learning integration. Prog Mater Sci. 2025; 152:101433. [96] MI X, SU Z, FU Y, et al. 3D printing of Ti3C2-MXene-incorporated composite scaffolds for accelerated bone regeneration. Biomed Mater. 2022;17(3):35002. [97] ZHAO Y, CHEN H, FU J, et al. Drug-loaded microspheres on NIR-responsive PLA/MXene scaffolds: controlled release and bone tissue regeneration. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2025;8(1):285-298. |
| [1] | Pan Zhiyi, Huang Jiawen, Xue Wenjun, Xu Jianda. Advantages of MXene-based flexible electronic sensors and their application in monitoring diabetic foot wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2023-2032. |
| [2] | Wu Yanting, Li Yu, Liao Jinfeng. Magnesium oxide nanoparticles regulate osteogenesis- and angiogenesis-related gene expressions to promote bone defect healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895. |
| [3] | Liu Dawei, Cui Yingying, Wang Fanghui, Wang Zixuan, Chen Yuhan, Li Yourui, Zhang Ronghe. Epigallocatechin gallate-mediated bidirectional regulation of reactive oxygen species and its application in nanomaterials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2101-2112. |
| [4] | Lai Yu, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun. Research hotspots and frontier trends of bioactive materials in treating bone infections [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2132-2144. |
| [5] | Lin Kejian, Chai Yinghong, Zou Jie, Huang Ruixin, Fang Yongchao, Huang Jing, Yang Qin, Luo Xia, Zhang Hong. Preparation of Cu2+-containing microarc oxidation functional coating on medical magnesium alloy and its anti-tumor and angiogenesis-promoting effects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(20): 5103-5114. |
| [6] | Zhou Xiaohui, Wang Siyi, Zhou Qiyun, He Zhao, Jia Yujuan, Wang Yuanbin, Ma Jianwu, Chen Gang, Zheng Feng, Chu Genglei. Nanohydroxyapatite-polyether carbonate urethane electrospinning membrane promotes bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(20): 5134-5142. |
| [7] | Chen Weifei, Mei Yuandong, Ju Jihui. Repair of infected bone defect with dual-ion time-sequenced release multifunctional hydrogels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(20): 5188-5200. |
| [8] | Xu Yawei, Meng Shilong, Zhang Xu, Wang Chengjie, Yuan Yifeng, Shi Xiaolin, Wang Jiao, Liu Kang . Repairing bone defects with active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine combined with hydrogels: successes and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(20): 5295-5303. |
| [9] | Tang Hao, Zhong Qian, Wu Honghan, Wu Hengpeng, Wu Xingkai, Wa Qingde. 3D-printed biodegradable polyester-based scaffolds in bone regeneration therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(20): 5304-5311. |
| [10] | He Zhenzhen, Huang Hanji, Wang Jiawei, Xie Qingtiao, Jiang Xianfang. Role of bioscaffolds in the repair of inflammation-driven bone and cartilage destruction and structural damage in temporomandibular joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(20): 5312-5320. |
| [11] | Wang Zhuo, Sun Panpan, Cheng Huanzhi, Cao Tingting. Application of chitosan in repair and regeneration of oral hard and soft tissues [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 459-468. |
| [12] | Wang Yu, Fan Minjie, Zheng Pengfei. Application of multistimuli-responsive hydrogels in bone damage repair: special responsiveness and diverse functions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 469-479. |
| [13] | Yan Qiquan, Yang Libin, Li Mengjun, Ni Yazhuo, Chen Keying, Xu Bo, Li Yaoyang, Ma Shiqing, Li Rui, Li Jianwen. Preparation and antibacterial properties of porcine small intestinal submucosal composite nanohydroxyapatite bioscaffold loaded with antimicrobial peptide KR-12-a5 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 384-394. |
| [14] | Yuan Qian, Zhang Hao, Pang Jie. Characterization and biological properties of naringin-loaded chitosan/beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 424-432. |
| [15] | Xu Wenhe, Li Xiaobing, Liu Fang. Functionalized biomimetic mineralized collagen modified orthopedic implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 516-527. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||