Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (16): 4229-4239.doi: 10.12307/2026.724
Previous Articles Next Articles
Postmenopausal osteoporosis: visualization analysis of related signaling pathways
Zou Shunyi1, Yi Jin2, Zeng Hao1, Li Jianqi1, Wu Zhongping1
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Spinal Surgery, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2025-06-06Accepted:2025-08-21Online:2026-06-08Published:2025-11-29 -
Contact:Yi Jin, MS, Attending physician, Lecturer, Department of Spinal Surgery, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zou Shunyi, MS candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Guangxi Famous Traditional Chinese Medicine Inheritance Studio Construction Project, No. (2024)30 (to YJ [project participant]); Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine Student Innovation Training Program, No. 202310600040 (to WZP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zou Shunyi, Yi Jin, Zeng Hao, Li Jianqi, Wu Zhongping. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: visualization analysis of related signaling pathways[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4229-4239.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
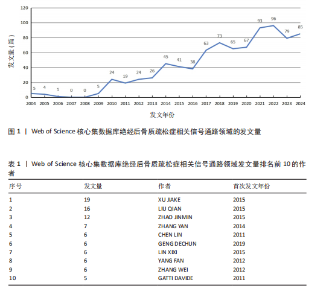
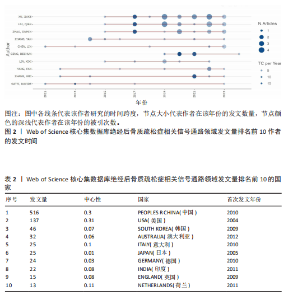
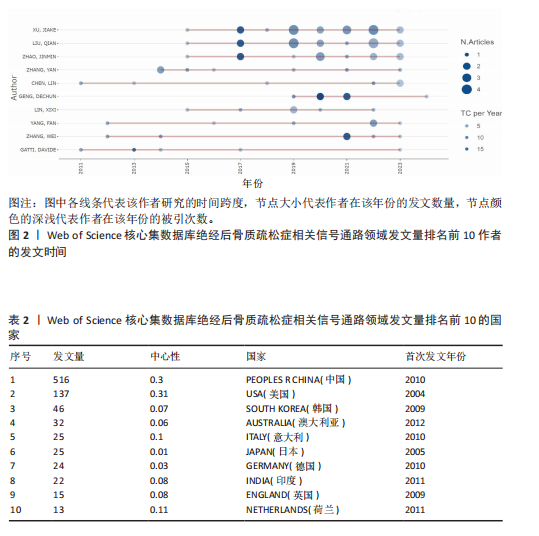
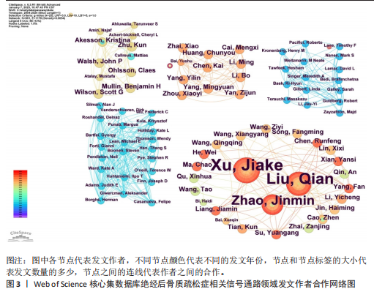
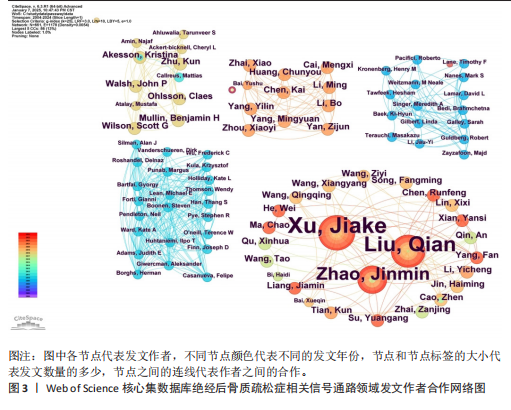
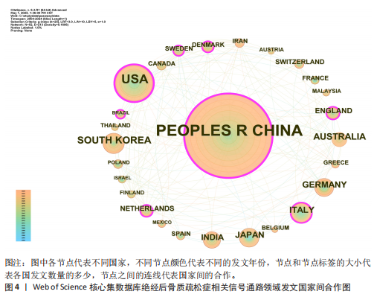
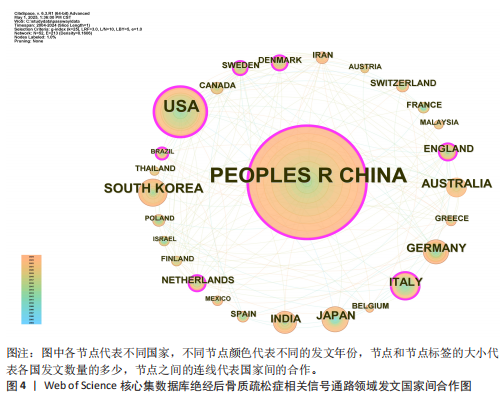
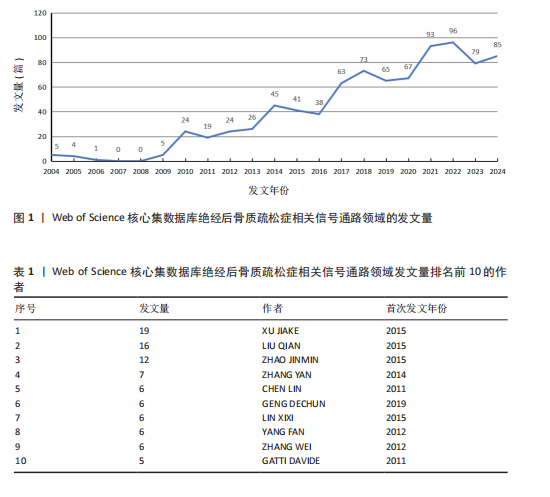
2.1 绝经后骨质疏松症相关信号通路领域文献检索结果 从Web of Science核心集数据库共检索到相关文献1 055篇,根据文献纳入标准和排除标准,最终纳入文献853篇,其中论著类文献684篇、综述类文献169篇。 2.2 绝经后骨质疏松症相关信号通路领域发文的年份特征 绝经后骨质疏松症相关信号通路领域发文趋势可大致分为2个阶段,第一阶段为2004-2007年,这一阶段发文量总体较低且增长停滞;第二阶段为2008-2024年,该阶段发文量较为规律,呈阶段上升趋势,见图1。该领域近20年发文量年平均增长率为15.22%,总体增长较迅速,并于2017年年均发文量超过50篇,有较高的发文水平。由此可见,信号通路在绝经后骨质疏松症中的研究受到越来越多研究者的重视。 2.3 绝经后骨质疏松症相关信号通路领域发文作者分析 纳入的853篇文献共包含5 083位发文作者,表1为绝经后骨质疏松症相关信号通路研究中发文量前10的作者。发文量最多的作者是XU JIAKE,发文量为19篇,其次是LIU QIAN和ZHAO JINMIN,发文量分别为16篇和12篇,他们在该领域研究开始于2015年,是近年较为活跃的研究者,共同形成了以XU JIAKE为代表的学术团体,团队中合作紧密;除此之外,其他作者合作网络较为松散,这就需要各研究团队之间进一步加强合作,优势互补;CHEN LIN和GATTI DAVIDE在该领域的研究从2011年持续至2023年,是时间跨度最长的研究者,具体见图2,3。 2.4 绝经后骨质疏松症相关信号通路领域发文国家与机构分析 通过该领域发文国家的分析发现,近20年绝经后骨质疏松症相关信号通路领域发文量最多的国家是中国(516篇),其次是美国(137篇)和韩国(46篇),发文量排名前10的国家具体如表2所示。美国首次发文在2004年,在该领域起步最早,同时也有最高的中心性(0.31)。中国首次发文在2010年,虽起步较晚但近10年增长迅速,总发文量远高于其他国家。从国家合作图(图4)中可以看出,各节点间连线较多,说明国家间的合作较为紧密。 发文量排名前10的机构如表3所示,该领域发文量最多的机构是上"
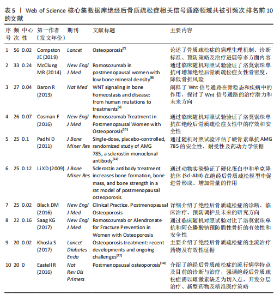
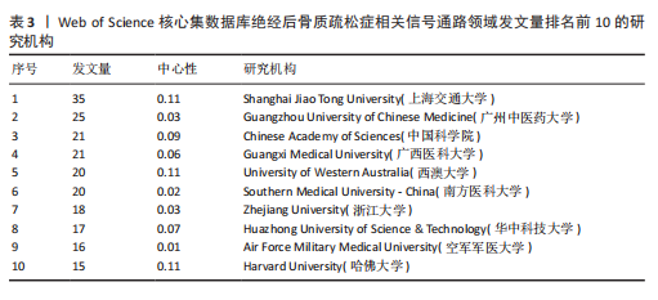
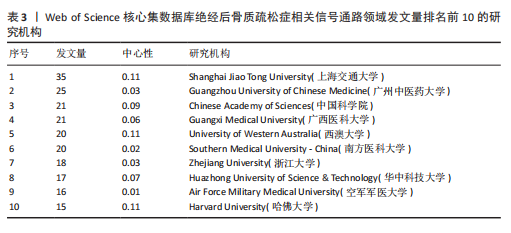
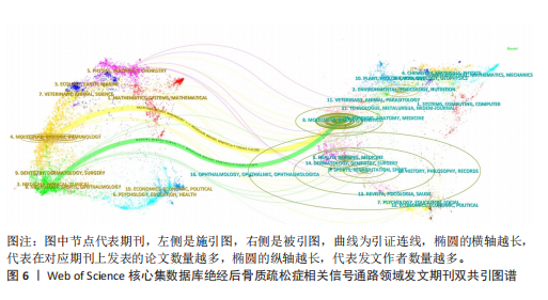
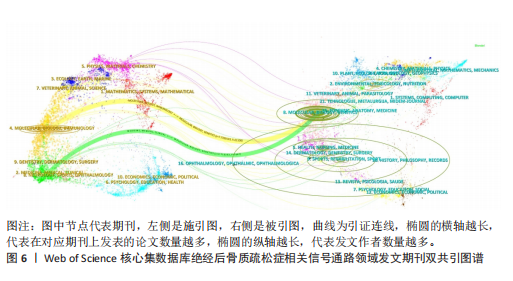
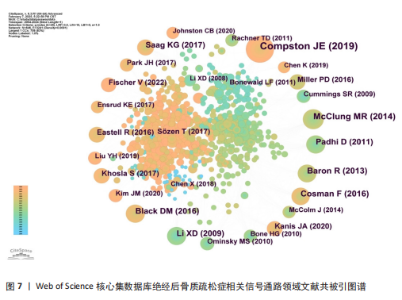
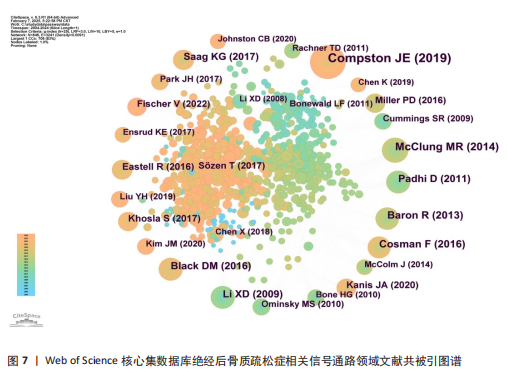
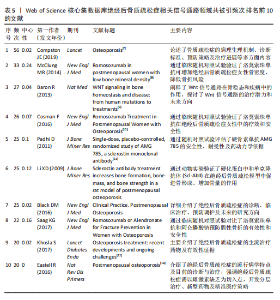
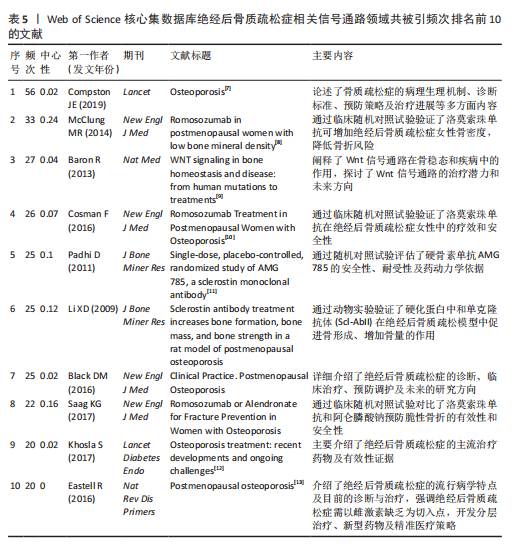
海交通大学,发文量为35篇,其次是广州中医药大学和中国科学院,发文量分别为25篇和21篇。中心性最高的机构是上海交通大学、西澳大学和哈佛大学,中心性均为0.11,同时发文量≥15篇,这3所高校兼具较高的发文量与中心性,是该领域各机构的重要合作中心。发文量排名前10的机构中高校占绝大多数,这与高校浓厚的学术氛围密不可分,具体见图5。 2.5 绝经后骨质疏松症相关信号通路领域发文期刊分析 纳入的853篇文献共发表在326种期刊上,其中收录文献数量最多的期刊是《Frontiers In Pharmacology》,收录文献40篇,其次是《Bone》和《International Journal Of Molecular Sciences》分别收录文献35篇和26篇。被引期刊中被引频次最多的是《Journal of Bone and Mineral Research》,被引频次为697次,其次是《Bone》和《Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry》,被引频次分别为629次和488次。绝经后骨质疏松症相关信号通路领域发文量和被引量排名前10的期刊具体如表4所示。期刊双图叠加反应了施引期刊和被引期刊之间的引用关系,从期刊双图叠加(图6)中可以发现,绝经后骨质疏松症相关信号通路领域知识流动最频繁的是学科是molecular(分子科学)、biology(生物学)、genetics(遗传学)、immunology(免疫学)。 2.6 绝经后骨质疏松症相关信号通路领域共被引文献分析 绝经后骨质疏松症相关信号通路领域共被引文献共现图,如图7所示。在被引频次前10的文献中,5篇文献通过不同方式验证了硬骨素单克隆抗体的安全性和有效性,4篇文献综述了骨质疏松症或绝经后骨折疏松症的诊断与治疗,1篇文献探讨了Wnt信号在骨稳态和骨相关疾病中的作用机制。其中文献共被引频次最多的是Compston JE于2019年发表在期刊《LANCET》上的综述类文章,共被引次数为56次,中心性为0.02,文章主要介绍了骨质疏松症的流行病学、临床表现、治疗"
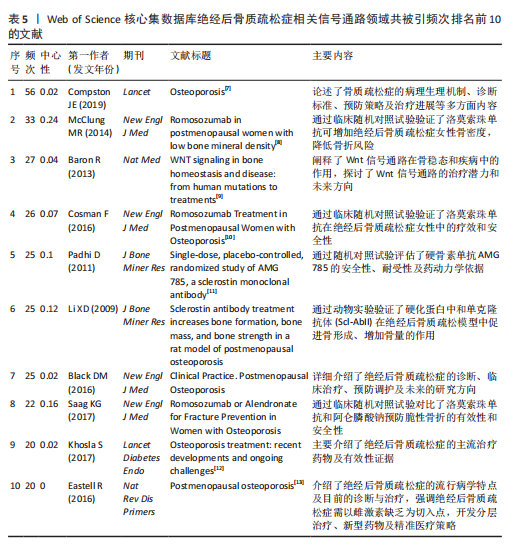

方法等,是骨质疏松症的基础文献,为临床上骨质疏松症的诊断与治疗提供了重要的指导作用[7];发文文献共被引中心性最高的文献是McClung MR于2014年发表在《NEW ENGL J MED》的随机对照试验,共被引次数为33次,中心性为0.24,该文通过随机对照试验比较了洛莫索珠单抗与阿仑膦酸盐类及特立帕肽的治疗作用,证明了洛莫索珠单抗的有效性和安全性,为洛莫索珠单抗的使用提供了一定的循证医学证据[8]。这些文献的高被引频次说明相关研究被广泛认可,是该领域较为重要的文献,具体见表5[7-13]。 2.7 绝经后骨质疏松症相关信号通路领域文献的关键词分析 2.7.1 关键词共现分析 关键词是文章主要内容的精炼与核心,通过对文章关键词进行统计分析,可以很好地把握某一领域的研究热点和发展势态。通过CiteSpace软件分析得到节点数为 497、连线为1 028、网络密度为0.008 3的关键词共现网络图,见图8。 绝经后骨质疏松症相关信号通路领域共现频次及中心性排名前10的关键词如表6所示。共现频次最高的是postmenopausal women(绝经后女性),其次是postmenopausal osteoporosis(绝经后骨质疏松症)和gene expression(基因表达);中心性最高的关键词是growth factor(生长因子),其次是bone loss(骨质流失)和mechanism(作用机制),由此可知,揭示绝经后骨质疏松症的作用机制及关键调控基因是目前研究的主要方向。 2.7.2 关键词聚类分析 通过对数自然似算法对关键词进行聚类,如图9所示。关键词聚类以聚类模块值(Q)及聚类平局轮廓值(S)为评判标准,该聚类Q=0.726 6、S=0.874 4,说明该聚类社团结构显著,聚类结果合理。聚类标签反映该聚类研究的主要内容,聚类序号反应该聚类的规模,聚类序号越小则聚类规模越大,所包含的关键词越多。聚类规模前10的聚类"

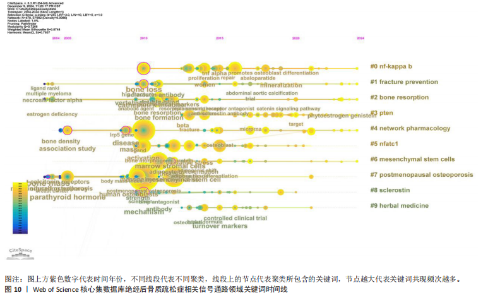
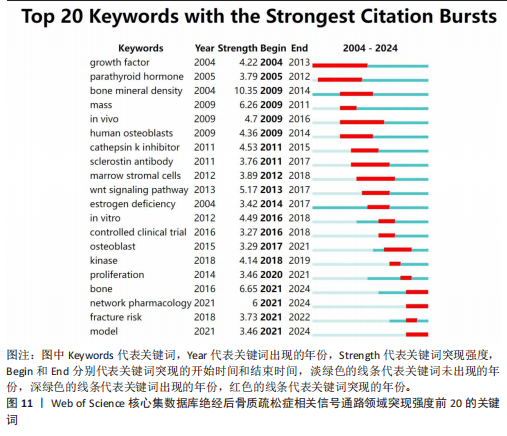
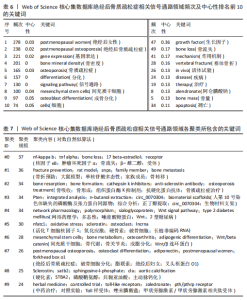
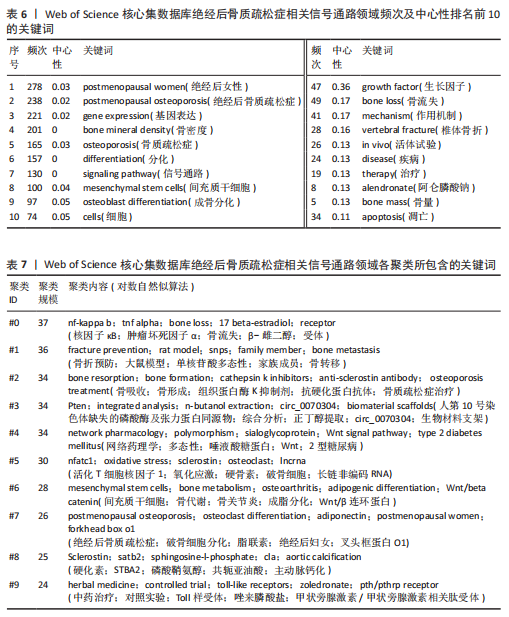
分别为#0 nf-kappa b(核因子κB)、#1 facture prevent(骨折预防)、#2 bone resorption(骨吸收)、#3 pten(人第10号染色体缺失的磷酸酶及张力蛋白同源物)、#4 network pharmacology (网络药理学)、#5 nfatc1(活化T细胞核因子1)、#6 mesenchymal stem cells (间充质干细胞)、#7 postmenopausal osteoporosis(绝经后骨质疏松症)、#8 sclerostin(骨硬化蛋白)、#9 herbal medicine(中药治疗)。见表7。 2.7.3 关键词时间线分析 关键词时间线基于关键词聚类,用于探究各聚类发展的起始,见图10。由图可知,#2 骨折预防和#3 骨吸收的研究始于2004年,热度持续至今,说明它们是绝经后骨质疏松相关信号通路领域较为稳定的研究方向。#1 核因子κB的研究虽起始于2010年,较其他聚类起步较晚,但已发展为目前研究规模最大的聚类,说明近年来有较多研究投入。 2.7.4 关键词突现分析 关键词突现反映的是某一时间段关键词出现频次的突然增加,可以折射该时间段研究者们的共同关注情况。图11展示了绝经后骨质疏松症相关信号通路领域突现强度前20的关键词。由图可知,growth factor(生长因子)突现出现时间较早,开始于2005年且有较长的突现时间,说明它是该领域最早受关注的研究热点。bone(骨)和network pharmacology(网络药理学)和model(模型)突现年份起始于2021年并持续至今,是近年研究的热点内容。"

| [1] GREGSON CL, ARMSTRONG DJ, BOWDEN J, et al. UK clinical guideline for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Arch Osteoporos. 2022;17(1):58. [2] 中国骨质疏松症流行病学调查及“健康骨骼”专项行动结果发布[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2019,12(4):317-318. [3] KIM JM, LIN C, STAVRE Z, et al. Osteoblast-Osteoclast Communication and Bone Homeostasis. Cells. 2020;9(9):2037. [4] ONO T, HAYASHI M, SASAKI F, et al. RANKL biology: bone metabolism, the immune system, and beyond. Inflamm Regen. 2020;40:2. [5] NINKOV A, FRANK JR, MAGGIO LA. Bibliometrics: Methods for studying academic publishing. Perspect Med Educ. 2022;11(3):173-176. [6] KOKOL P, BLAUN VH, ZAVRNIK J. Application of bibliometrics in medicine: a historical bibliometrics analysis. Health Info Libr J. 2021;38(2):125-138. [7] COMPSTON JE, MCCLUNG MR, LESLIE WD. Osteoporosis. Lancet. 2019;393(10169): 364-376. [8] MCCLUNG MR, GRAUER A, BOONEN S, et al. Romosozumab in postmenopausal women with low bone mineral density. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(5):412-420. [9] BARON R, KNEISSEL M. WNT signaling in bone homeostasis and disease: from human mutations to treatments. Nat Med. 2013;19(2):179-192. [10] COSMAN F, CRITTENDEN DB, ADACHI JD, et al. Romosozumab Treatment in Postmenopausal Women with Osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(16):1532-1543. [11] PADHI D, JANG G, STOUCH B, et al. Single-dose, placebo-controlled, randomized study of AMG 785, a sclerostin monoclonal antibody. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(1):19-26. [12] KHOSLA S, HOFBAUER LC. Osteoporosis treatment: recent developments and ongoing challenges. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5(11):898-907. [13] EASTELL R, O’NEILL TW, HOFBAUER LC, et al. Postmenopausal osteoporosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:6069. [14] LU L, TIAN L. Postmenopausal osteoporosis coexisting with sarcopenia: the role and mechanisms of estrogen. J Endocrinol. 2023;259(1):e230116. [15] WANG T, LIU Q, ZHOU L, et al. Andrographolide Inhibits Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss via the Suppression of RANKL Signaling Pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(11):27470-27481. [16] YANG X, LIANG J, WANG Z, et al. Sesamolin Protects Mice From Ovariectomized Bone Loss by Inhibiting Osteoclastogenesis and RANKL-Mediated NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:664697. [17] ZHANG L, SUN Y, XU W, et al. Baicalin inhibits Salmonella typhimurium-induced inflammation and mediates autophagy through TLR4/MAPK/NF-κB signalling pathway. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021;128(2):241-255. [18] CAPECE D, VERZELLA D, FLATI I, et al. NF-κB: blending metabolism, immunity, and inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2022; 43(9):757-775. [19] WAJANT H, PFIZENMAIER K, SCHEURICH P. Tumor necrosis factor signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2003;10(1):45-65. [20] BAUD V, KARIN M. Is NF-kappaB a good target for cancer therapy? Hopes and pitfalls. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8(1):33-40. [21] HOESEL B, SCHMID JA. The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer. 2013;12:86. [22] YAMASHITA T, YAO Z, LI F, et al. NF-kappaB p50 and p52 regulate receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) and tumor necrosis factor-induced osteoclast precursor differentiation by activating c-Fos and NFATc1. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(25): 18245-18253. [23] ZHENG LW, WANG WC, MAO XZ, et al. TNF-α regulates the early development of avascular necrosis of the femoral head by mediating osteoblast autophagy and apoptosis via the p38 MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Biol Int. 2020;44(9): 1881-1889. [24] ZUO Q, LIU J, HUANG L, et al. AXL/AKT axis mediated-resistance to BRAF inhibitor depends on PTEN status in melanoma. Oncogene. 2018;37(24):3275-3289. [25] WHANG YE, WU X, SUZUKI H, et al. Inactivation of the tumor suppressor PTEN/MMAC1 in advanced human prostate cancer through loss of expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(9):5246-5250. [26] GAO X, QIN T, MAO J, et al. PTENP1/miR-20a/PTEN axis contributes to breast cancer progression by regulating PTEN via PI3K/AKT pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1): 256. [27] LI X, MIAO C, WANG L, et al. Estrogen promotes Epithelial ovarian cancer cells proliferation via down-regulating expression and activating phosphorylation of PTEN. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2023;743:109662. [28] SUGATANI T, ALVAREZ U, HRUSKA KA. PTEN regulates RANKL- and osteopontin-stimulated signal transduction during osteoclast differentiation and cell motility. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(7):5001-5008. [29] 叶恒,张卫华,韩俊,等.miR-26a-5p靶向PTEN基因影响成骨细胞分化及基质矿化[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(8):1126-1130+1138. [30] LORENZ J, RICHTER S, KIRSTEIN AS, et al. Pten knockout in mouse preosteoblasts leads to changes in bone turnover and strength. JBMR Plus. 2024;8(3):ziad16. [31] SATO Y, HABARA M, HANAKI S, et al. Calcineurin/NFATc1 pathway represses cellular cytotoxicity by modulating histone H3 expression. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):14732. [32] NEGISHI-KOGA T, TAKAYANAGI H. Ca2+-NFATc1 signaling is an essential axis of osteoclast differentiation. Immunol Rev. 2009;231(1):241-256. [33] LEE JU, KIM LK, CHOI JM. Revisiting the Concept of Targeting NFAT to Control T Cell Immunity and Autoimmune Diseases. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2747. [34] OMATA Y, TACHIBANA H, AIZAKI Y, et al. Essentiality of Nfatc1 short isoform in osteoclast differentiation and its self-regulation. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):18797. [35] TAKAYANAGI H, KIM S, KOGA T, et al. Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 2002;3(6):889-901. [36] LI X, YANG L, GUO Z. miR-193-3p ameliorates bone resorption in ovariectomized mice by blocking NFATc1 signaling. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019;12(11):4077-4086. [37] LIU L, WU S, WEI L, et al. Romosozumab adverse event profile: a pharmacovigilance analysis based on the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) from 2019 to 2023. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2025;37(1):23. [38] MILLER SA, ST OE, WHALEN KL. Romosozumab: A Novel Agent in the Treatment for Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. J Pharm Technol. 2021; 37(1):45-52. [39] 彭越,岳梦圆,邹佳盈,等.传统中药与激素治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的有效性和安全性比较[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2023,25(1):46-55. [40] CHEN Y, LI X, TANG X, et al. Combined Extracts of Herba Epimedii and Fructus Ligustri Lucidi Rebalance Bone Remodeling in Ovariectomized Rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019;2019:1596951. [41] LUO Y, XIA H, WANG J, et al. Jiawei Yanghe Decoction Regulates Bone-Lipid Balance through the BMP-SMAD Signaling Pathway to Promote Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:2885419. [42] ZHANG R, ZHU X, BAI H, et al. Network Pharmacology Databases for Traditional Chinese Medicine: Review and Assessment. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:123. [43] ZHOU Z, CHEN B, CHEN S, et al. Applications of Network Pharmacology in Traditional Chinese Medicine Research. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:1646905. |
| [1] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Yuping, Ba Yinying, Chi Li, Wang Wenjuan, Wang Jiajia. Research context and trend of TBK1 in autoimmunity, signaling pathways, gene expression, tumor prevention and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [2] | Zhu Xiaolong, Zhang Wei, Yang Yang. Visualization analysis of research hotspots and cutting-edge information in the field of intervertebral disc regeneration and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2391-2402. |
| [3] | Wen Fayan, Li Yan, Qiang Tianming, Yang Chen, Shen Linming, Li Yadong, Liu Yongming. Unilateral biportal endoscopic technology for treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases: global research status and changing trends [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2380-2390. |
| [4] | Chen Haojie, Wang Dai, Shen Shan. Immune inflammatory microenvironment mechanisms in peri-implantitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2054-2062. |
| [5] | Hu Xiongke, Liu Shaohua, Tan Qian, Liu Kun, Zhu Guanghui. Shikonin intervention with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves microstructure of femur in aged mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1609-1615. |
| [6] | Han Nianrong, Huang Yifei, Akram · Osman, Liu Yanlu, Hu Wei . Programmed cell death receptor-1 suppresses osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a high-glucose microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1649-1657. |
| [7] | Liu Anting, Lu Jiangtao, Zhang Wenjie, He Ling, Tang Zongsheng, Chen Xiaoling. Regulation of AMP-activated protein kinase by platelet lysate inhibits cadmium-induced neuronal apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1800-1807. |
| [8] | Peng Zhiwei, Chen Lei, Tong Lei. Luteolin promotes wound healing in diabetic mice: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [9] | Zhu Kuicheng, Du Chunyan, Zhang Jintao. Mechanism by which hairless gene mutation promotes white adipose tissue browning in hairless mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1424-1430. |
| [10] | Li Hao, Tao Hongcheng, Zeng Ping, Liu Jinfu, Ding Qiang, Niu Chicheng, Huang Kai, Kang Hongyu. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway regulates the development of osteoarthritis: guiding targeted therapy with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1476-1485. |
| [11] | Huang Jie, Zeng Hao, Wang Wenchi, Lyu Zhucheng, Cui Wei. Visualization analysis of literature on the effect of lipid metabolism on osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1558-1568. |
| [12] | Chen Ju, Zheng Jinchang, Liang Zhen, Huang Chengshuo, Lin Hao, Zeng Li. Effect and mechanism of beta-caryophyllene in mice with osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1341-1347. |
| [13] | Lyu Guoqing, Aizimaitijiang·Rouzi, Xiong Daohai. Irisin inhibits ferroptosis in human articular chondrocytes: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1359-1367. |
| [14] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [15] | Chen Yixian, Chen Chen, Lu Liheng, Tang Jinpeng, Yu Xiaowei. Triptolide in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 805-815. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||