Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (16): 4105-4114.doi: 10.12307/2026.714
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of swimming exercise combined with probiotic intervention on anti-inflammatory and apoptotic gene expression in renal tissue of type 2 diabetic rats
Niu Qi1, Chen Junji2, Tu Haining2, Mo Weibin3, 4, Zhong Yujin3, Li Mingliang3
- 1Hunan University of Information Technology, Changsha 410151, Hunan Province, China; 2Guilin University of Physical Education and Health, Guilin 541006, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3College of Physical Education and Health, Guangxi Normal University, Guilin 541006, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 4State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Resources Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Guilin 541004, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2025-04-22Accepted:2025-08-25Online:2026-06-08Published:2025-11-27 -
Contact:Chen Junji, MS, Associate professor, Guilin University of Physical Education and Health, Guilin 541006, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China Co-corresponding author: Mo Weibin, PhD, Professor, College of Physical Education and Health, Guangxi Normal University, Guilin 541006, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Resources Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Guilin 541004, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Niu Qi, PhD, Hunan University of Information Technology, Changsha 410151, Hunan Province, China -
Supported by:Guangxi Department of Education Research Project, No. 2021KY1596 (to CJJ); Education Development Foundation of Guangxi Normal University - “Teacher Growth Fund,” No. EDF2016005 (to MWB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Niu Qi, Chen Junji, Tu Haining, Mo Weibin, Zhong Yujin, Li Mingliang. Effect of swimming exercise combined with probiotic intervention on anti-inflammatory and apoptotic gene expression in renal tissue of type 2 diabetic rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4105-4114.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
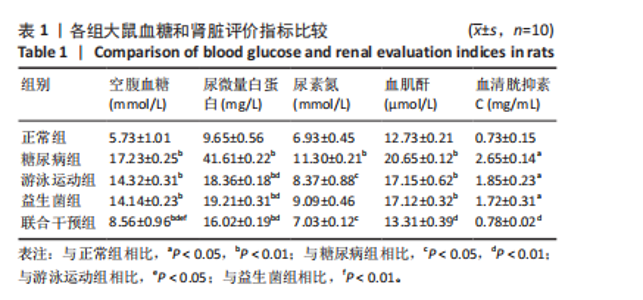
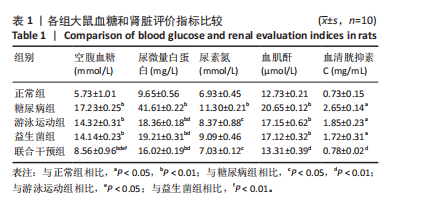
糖尿病组、游泳运动组、益生菌组、联合干预组大鼠尿微量白蛋白水平高于正常组(P < 0.01),大鼠分别进行游泳运动、益生菌及游泳运动联合益生菌干预后,尿微量白蛋白水平均较糖尿病组有所下降(P < 0.01)。 糖尿病组大鼠血清尿素氮水平高于正常组(P < 0.01),大鼠分别进行游泳运动、益生菌及游泳运动联合益生菌干预后,游泳运动组和联合干预组大鼠血清尿素氮水平低于糖尿病组(P < 0.05)。 糖尿病组、游泳运动组、益生菌组大鼠血清血肌酐水平均高于正常组(P < 0.01),大鼠分别进行游泳运动、益生菌及游泳运动联合益生菌干预后,血肌酐水平均有所下降,其中联合干预组血肌酐水平与糖尿病组比较有显著性差异(P < 0.01)。 糖尿病组、游泳运动组、益生菌组大鼠血清胱抑素C水平均高于正常组(P < 0.05),大鼠分别进行游泳运动、益生菌及游泳运动联合益生菌干预后,血清胱抑素C水平均有所下降,其中联合干预组血清胱抑素C水平与糖尿病组比较有显著性差异(P < 0.01)。 2.3 各组大鼠血清炎症因子水平比较 见表2。糖尿病组大鼠血清肿瘤坏死因子α水平高于正常组(P < 0.01),大鼠分别进行游泳运动、益生菌干预、游泳"
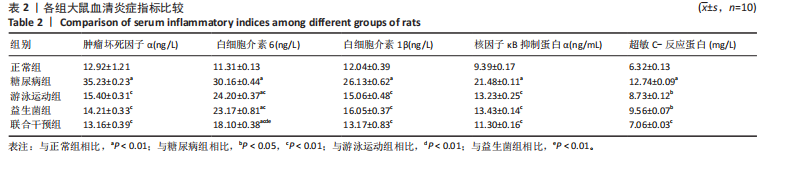
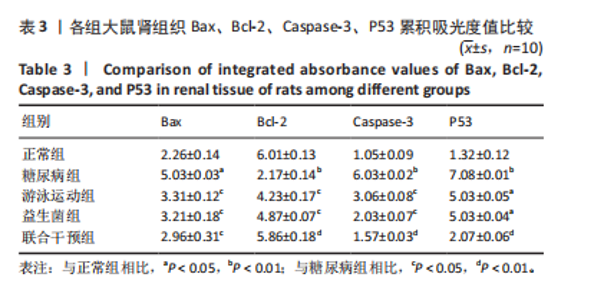
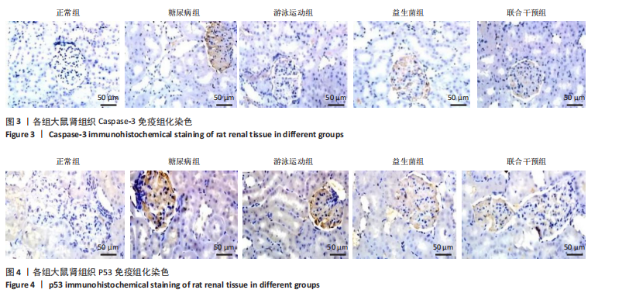
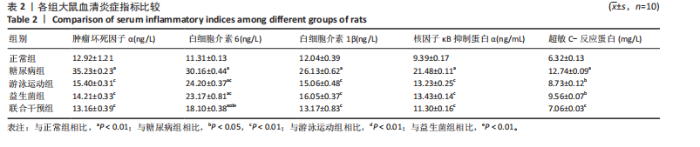
运动联合益生菌干预后,游泳运动组、益生菌组、联合干预组大鼠血清肿瘤坏死因子α水平均有所下降,与糖尿病组比较有显著性差异(P < 0.01),尤其是联合干预组大鼠血清肿瘤坏死因子α水平基本上恢复到正常组水平。 糖尿病组、游泳运动组、益生菌组、联合干预组大鼠血清白细胞介素6水平均高于正常组(P < 0.01),大鼠分别进行游泳运动、益生菌干预、游泳运动联合益生菌干预后,游泳运动组、益生菌组、联合干预组大鼠血清白细胞介素6水平均有所下降,与糖尿病组比较有显著性差异(P < 0.01),其中联合干预组大鼠血清白细胞介素6水平下降较明显,与游泳运动组、益生菌组比较有显著性差异(P < 0.01)。 糖尿病组大鼠血清白细胞介素1β水平高于正常组(P < 0.01),大鼠分别进行游泳运动、益生菌干预、游泳运动联合益生菌干预后,游泳运动组、益生菌组、联合干预组大鼠血清白细胞介素1β水平均有所下降,与糖尿病组比较有显著性差异(P < 0.01),尤其是联合干预组大鼠血清白细胞介素1β水平基本上恢复到正常组水平。 糖尿病组大鼠血清核因子κB抑制蛋白α水平高于正常组(P < 0.01),大鼠分别进行游泳运动、益生菌干预、游泳运动联合益生菌干预后,游泳运动组、益生菌组、联合干预组大鼠血清核因子κB抑制蛋白α水平均有所下降,与糖尿病组比较有显著性差异(P < 0.01)。 糖尿病组大鼠血清超敏C-反应蛋白水平高于正常组(P < 0.01),大鼠分别进行游泳运动、益生菌干预、游泳运动联合益生菌干预后,游泳运动组、益生菌组、联合干预组大鼠血清超敏C-反应蛋白水平均有所下降,其中游泳运动组、益生菌组与糖尿病组比较有差异性(P < 0.05),联合干预组与糖尿病组比较有显著性差异(P < 0.01)。 2.4 各组大鼠肾组织 Bax、Bcl-2、Caspase-3、P53表达比较 见图1-4,表3。糖尿病组大鼠肾组织Bax"
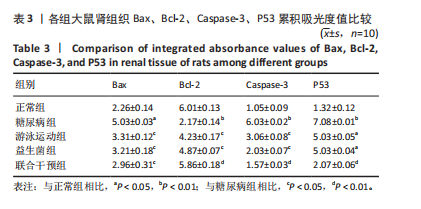
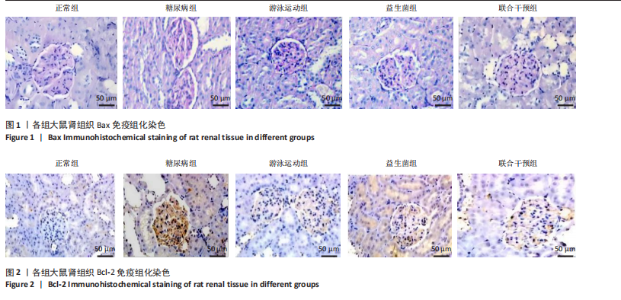
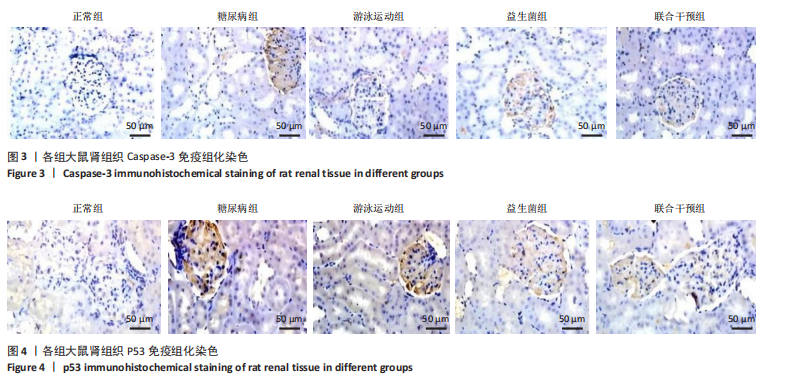
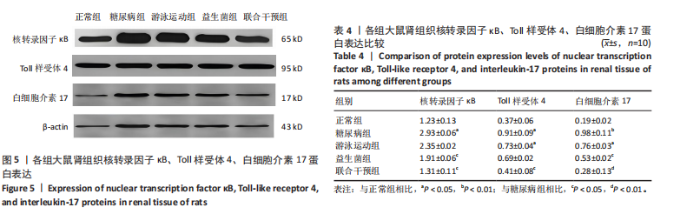
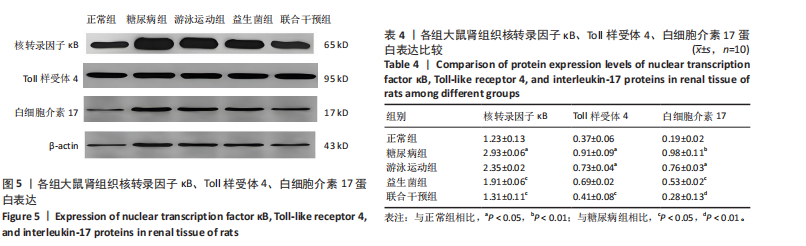
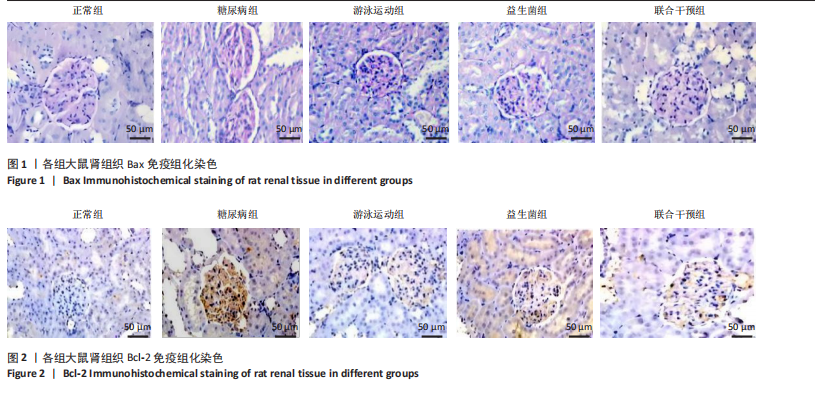
表达高于正常组(P < 0.05),大鼠分别进行游泳运动、益生菌干预、游泳运动联合益生菌干预后,游泳运动组、益生菌组、联合干预组大鼠肾组织Bax表达均低于糖尿病组(P < 0.05)。 糖尿病组大鼠肾组织Bcl-2表达低于正常组(P < 0.01),大鼠分别进行游泳运动、益生菌干预、游泳运动联合益生菌干预后,游泳运动组、益生菌组、联合干预组大鼠肾组织Bcl-2表达均高于糖尿病组(P < 0.05或P < 0.01)。 糖尿病组大鼠肾组织Caspase-3表达高于正常组(P < 0.01),大鼠分别进行游泳运动、益生菌干预、游泳运动联合益生菌干预后,游泳运动组、益生菌组、联合干预组大鼠肾组织Caspase-3表达均低于糖尿病组(P < 0.05或P < 0.01)。 糖尿病组大鼠肾组织P53表达高于正常组(P < 0.01),大鼠分别进行游泳运动、益生菌干预、游泳运动联合益生菌干预后,游泳运动组、益生菌组、联合干预组大鼠P53表达均低于糖尿病组,游泳运动组、益生菌组与正常组比较有差异性(P < 0.05),而联合干预组大鼠P53表达下降较明显,与糖尿病组比较有显著性差异(P < 0.01)。 2.5 大鼠肾组织核转录因子κB 、Toll样受体4、白细胞介素17蛋白表达比较 见图5和表4。糖尿病组大鼠肾组织核转录因子κB蛋白表达高于正常组(P < 0.05),大鼠分别进行游泳运动、益生菌干预、游泳运动联合益生菌干预后,游泳运动组、益生菌组、"

联合干预组大鼠肾组织核转录因子κB蛋白表达均低于糖尿病组,其中益生菌组、联合干预组大鼠肾组织核转录因子κB蛋白表达与糖尿病组比较有差异性(P < 0.05)。 糖尿病组大鼠肾组织Toll样受体4蛋白表达高于正常组(P < 0.05),大鼠分别进行游泳运动、益生菌干预、游泳运动联合益生菌干预后,游泳运动组、益生菌组、联合干预组大鼠肾组织Toll样受体4蛋白表达均低于糖尿病组,其中游泳运动组大鼠肾组织Toll样受体4蛋白表达与正常组比较有差异性(P < 0.05),联合干预组大鼠肾组织Toll样受体4蛋白表达与糖尿病组比较有差异性(P < 0.05)。 糖尿病组大鼠肾组织白细胞介素17蛋白表达高于正常组(P < 0.01),大鼠分别进行游泳运动、益生菌干预、游泳运动联合益生菌干预后,游泳运动组、益生菌组、联合干预组大鼠肾组织白细胞介素17蛋白表达均低于糖尿病组,尤其是联合干预组下降较明显,游泳运动组大鼠肾组织白细胞介素17蛋白表达与正常组比较有差异性(P < 0.05),益生菌组大鼠肾组织白细胞介素17蛋白表达与糖尿病组比较有差异性(P < 0.05),而联合干预组大鼠肾组织白细胞介素17蛋白表达与糖尿病组比较有显著性差异(P < 0.01)。"

| COHEN RV, AZEVEDO MA, LE ROUX CW, et al. Metabolic/Bariatric Surgery is Safe and Effective in People with Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Obes Surg. 2024;34(11): 4097-4105. [2] CHAI J, WANG Y, GUO S, et al. Proteomics exploration of metformin hydrochloride for diabetic kidney disease treatment via the butanoate metabolism pathway. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2025;254:116584. [3] YOU L, HONG X, FENG Q, et al. Glucose Metabolism Indices and the Development of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Cohort Study of Middle-Aged and Elderly Chinese Persons. Int J Endocrinol. 2023;2023: 1412424. [4] LIU PT, CHEN JD. The Associations Between Abdominal Obesity and Coronary Artery Calcification in Chronic Kidney Disease Population. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2024;17:39-45. [5] EPHRAIM RKD, AHORDZOR F, ASARE KK, et al. Abnormal Obesity Phenotype Is Associated with Reduced eGFR among Diabetes Mellitus and Hypertensive Patients in a Peri-Urban Community in Ghana. Int J Nephrol. 2022;2022:2739772. [6] FAN R, KONG J, ZHANG J, et al. Exercise as a therapeutic approach to alleviate diabetic kidney disease: mechanisms, clinical evidence and potential exercise prescriptions. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024;11: 1471642. [7] HOSHINO J, OHIGASHI T, TSUNODA R, et al. Physical activity and renal outcome in diabetic and non-diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease stage G3b to G5. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):26378. [8] SABERI S, ASKARIPOUR M, KHAKSARI M, et al. Exercise training improves diabetic renal injury by reducing fetuin-A, oxidative stress and inflammation in type 2 diabetic rats. Heliyon. 2024;10(6):e27749. [9] HSIEH MC, TSAI WH, JHENG YP, et al. Author Correction: The beneficial effects of Lactobacillus reuteri ADR-1 or ADR-3 consumption on type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):3872. [10] LI G, FENG H, MAO XL, et al. The effects of probiotics supplementation on glycaemic control among adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):442. [11] REED MJ, MESZAROS K, ENTES LJ, et al. A new rat model of type 2 diabetes: the fat-fed, streptozotocin-treated rat. Metabolism. 2000; 49(11):1390-1394. [12] 莫伟彬,杨衍滔,郭艳菊,等.益生菌干预对运动大鼠胃肠激素与AQP4表达的影响[J].中国实验动物学报,2018,26(4):411-417. [13] CHEN YM, WEI L, CHIU YS, et al. Lactobacillus plantarum TWK10 Supplementation Improves Exercise Performance and Increases Muscle Mass in Mice. Nutrients. 2016;8(4):205. [14] PLOUG T, STALLKNECHT BM, PEDERSEN O, et al. Effect of endurance training on glucose transport capacity and glucose transporter expression in rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1990;259(6 Pt 1):E778-786. [15] MUNDEL P, REISER J. Proteinuria: an enzymatic disease of the podocyte? Kidney Int. 2010;77(7):571-580. [16] JUNG I, NAM S, LEE DY, et al. Association of Succinate and Adenosine Nucleotide Metabolic Pathways with Diabetic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(6):1126-1134. [17] SUN X, ZHOU X, LI S, et al. Association between frequency of self-monitoring of blood glucose and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2024;209:111027. [18] YARLAGADDA C, ABUTINEH M, REDDY AJ, et al. An Investigation on the Efficacy of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists Drugs in Reducing Urine Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Potential Treatment for Diabetic Nephropathy. Cureus. 2023;15(3):e36438. [19] HUANG XM, MA X, LU JY, et al. Relationship between serum IL-6, VAP-1, Cys C, Scr, BUN, and type 2 diabetic kidney disease. Minerva Endocrinol (Torino). 2023;48(1):121-122. [20] YUAN HQ, MIAO JX, XU JP, et al. Increased serum cystatin C levels and responses of pancreatic α- and β-cells in type 2 diabetes. Endocr Connect. 2022;11(3):e210597. [21] 庄云,高现芬,吴畏.尿清蛋白/肌酐、胱抑素C对早期糖尿病肾病患者的诊断效果分析[J].糖尿病新世界,2024,27(15):52-55. [22] 范丽妃,郭玉琴,林敏,等.基于自噬途径探讨补阳还五汤合抵挡汤改善尿酸性肾病大鼠肾脏损伤的作用机制[J].中华中医药杂志,2024,39(8):3989-3995. [23] BONORA BM, MORIERI ML, MARASSI M, et al. Improved prediction of long-term kidney outcomes in people with type 2 diabetes by levels of circulating haematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Diabetologia. 2023;66(12):2346-2355. [24] TUTTLE KR, AGARWAL R, ALPERS CE, et al. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets for diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2022; 102(2):248-260. [25] BAI Y, LI H, DONG J. Up-regulation of miR-20a weakens inflammation and apoptosis in high-glucose-induced renal tubular cell mediating diabetic kidney disease by repressing CXCL8 expression. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2022;128(6):1603-1610. [26] ZAMANI B, TABATABIZADEH SM, GILASI H, et al. Effects of pioglitazone and linagliptin on glycemic control, lipid profile and hs-CRP in metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes: a comparative study. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2023;44(4):385-391. [27] DAVARI M, HASHEMI R, MIRMIRAN P, et al. Effects of cinnamon supplementation on expression of systemic inflammation factors, NF-kB and Sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) in type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double blind, and controlled clinical trial. Nutr J. 2020;19(1):1. [28] LIU J, ZHUANG Y, WU J, et al. IKKβ mediates homeostatic function in inflammation via competitively phosphorylating AMPK and IκBα. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022;12(2):651-664. [29] 王晓娟,刘素筠.罗格列酮对糖尿病大鼠肾脏中磷酸化IKK和IκBα表达及肾组织超微结构改变的影响[J].实用糖尿病杂志,2011, 7(1):26-27. [30] 余杭林,向秋,田浩冬,等.高强度间歇性训练干预2型糖尿病患者糖脂代谢及炎症因子的变化[J/OL].中国免疫学杂志,1-10[2025-04-08].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/22.1126.r.20241202.1418.002.html. [31] OTHMAN MA, FADEL R, TAYEM Y, et al. Caffeine protects against hippocampal alterations in type 2 diabetic rats via modulation of gliosis, inflammation and apoptosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2023;392(2):443-466. [32] BAGHERI F, AMRI J, SALEHI M, et al. Effect of Artemisia absinthium ethanolic extract on oxidative stress markers and the TLR4, S100A4, Bax and Bcl-2 genes expression in the kidney of STZ-induced diabetic rats. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2020;41(4):1-10. [33] JOSEPH L, SRINIVASAN KK. Triacontanoic ester of 5’’-hydroxyjustisolin: Tumour suppressive role in cervical cancer via Bcl-2, BAX and caspase-3 mediated signalling. Toxicol Rep. 2019;6:1198-1205. [34] WANG Y, SUN H, ZHANG J, et al. Streptozotocin-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats: ameliorative effect of PIPERINE via Bcl2, Bax/Bcl2, and caspase-3 pathways. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2020; 84(12):2533-2544. [35] YUQIANG C, LISHA Z, JIEJUN W, et al. Pifithrin-α ameliorates glycerol induced rhabdomyolysis and acute kidney injury by reducing p53 activation. Ren Fail. 2022;44(1):473-481. [36] AHMED OM, EBAID H, EL-NAHASS ES, et al. Nephroprotective Effect of Pleurotus ostreatus and Agaricus bisporus Extracts and Carvedilol on Ethylene Glycol-Induced Urolithiasis: Roles of NF-κB, p53, Bcl-2, Bax and Bak. Biomolecules. 2020;10(9):1317. [37] AHMED OM, ALI TM, ABDEL GAID MA, et al. Effects of enalapril and paricalcitol treatment on diabetic nephropathy and renal expressions of TNF-α, p53, caspase-3 and Bcl-2 in STZ-induced diabetic rats. PLoS One. 2019;14(9):e0214349. [38] 刘俊峰,孙晓娟,吴迪,等.苁归益肾胶囊对DKD大鼠血管内皮损伤的保护作用及VCAM-1、Bcl-2、Bax、Caspase-3表达的影响[J].新疆医科大学学报,2022,45(8):896-900. [39] 程丽彩,何玉秀.补充葛根素对力竭游泳训练大鼠海马细胞凋亡及Bcl-2、P53蛋白表达的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2010,29(3): 332-334. [40] ALIPOUR MR, NADERI R, ALIHEMMATI A, et al. Swimming training attenuates pancreatic apoptosis through miR-34a/Sirtu in1/P53 Axis in high-fat diet and Streptozotocin-induced Type-2 diabetic rats. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2020;19(2):1439-1446. [41] MORGAN D, GARG M, TERGAONKAR V, et al. Pharmacological significance of the non-canonical NF-κB pathway in tumorigenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2020;1874(2):188449. [42] ZHANG C, WANG X, WANG C, et al. Qingwenzhike Prescription Alleviates Acute Lung Injury Induced by LPS via Inhibiting TLR4/NF-kB Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:790072. [43] PAQUISSI FC, ABENSUR H. The Th17/IL-17 Axis and Kidney Diseases, With Focus on Lupus Nephritis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:654912. [44] WU Y, XIAO W, PEI C, et al. Astragaloside IV alleviates PM2.5-induced lung injury in rats by modulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signalling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;91:107290. [45] LUO Q, HUANG S, ZHAO L, et al. Chang qing formula ameliorates colitis-associated colorectal cancer via suppressing IL-17/NF-κB/STAT3 pathway in mice as revealed by network pharmacology study. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:893231. [46] MOHAMED YT, SALAMA A, RABIE MA, et al. Neuroprotective effect of secukinumab against rotenone induced Parkinson’s disease in rat model: Involvement of IL-17, HMGB-1/TLR4 axis and BDNF/TrKB cascade. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;114:109571. [47] QIU D, SONG S, CHEN N, et al. NQO1 alleviates renal fibrosis by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways in diabetic nephropathy. Cell Signal. 2023;108:110712. [48] SUN T, DONG W, JIANG G, et al. Cordyceps militaris Improves Chronic Kidney Disease by Affecting TLR4/NF-κB Redox Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:7850863. [49] 池杨峰,刘爽,黄洁波,等.黄芪汤通过TLR4/NF-κB信号通路改善糖尿病肾病大鼠炎症反应的研究[J].临床肾脏病杂志,2022, 22(1):39-45. |
| [1] | Pan Hongfei, Zhuang Zhenbing, Xu Baiyun, Yang Zhangyang, Lin Kairui, Zhan Bingqing, Lan Jinghan, Gao Heng, Zhang Nanbo, Lin Jiayu. Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of auranofin on M1 macrophage function and its therapeutic potential in diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1390-1397. |
| [2] | Wen Xiaolong, Weng Xiquan, Feng Yao, Cao Wenyan, Liu Yuqian, Wang Haitao. Effects of inflammation on serum hepcidin and iron metabolism related parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1294-1301. |
| [3] | Yan Chengbo, Luo Qiuchi, Fan Jiabing, Gu Yeting, Deng Qian, Zhang Junmei. Effect of type 2 diabetes mellitus on orthodontic tooth movement and bone microstructure parameters on the tension side in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 824-831. |
| [4] | Wang Jie, Huang Rui, Zhang Ye, Shou Zhaoxi, Yao Jie, Liu Chenxi, Liao Jian. Role and mechanism of probiotics in peri-implantitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 901-907. |
| [5] | Xu Jiamu, Yang Cheng, Li Weimin, Wang Chunqing. Role and pathogenesis of pyroptosis and inflammatory factors in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 691-700. |
| [6] | Jiang Kai, Rong Yifa, Jia Haifeng, Li Hanzheng, Lu Bowen, Liang Xuezhen, Li Gang. Relationship between inflammatory factors and rheumatoid arthritis: a large-sample analysis based on the FinnGen R10 database and genome-wide association studies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2629-2640. |
| [7] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [8] | Wang Tong, Zheng Yu, Jia Chengming, Yang Hu, Zhang Guangfei, Ji Yaoyao. Action mechanism of Gegenmaqi prescription in treatment of periarthritis of shoulder combined with type 2 diabetes based on TCMSP database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7669-7678. |
| [9] | Xu Biao, Dong Yuzhen, Lu Tan. Effect of dihydroquercetin on the expression of inflammatory response markers in rats with spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6843-6850. |
| [10] | Geng Longyu, Sheng Li, Bai Shuo, Gao Beiyao, Ge Ruidong, Jiang Shan . Role and molecular mechanism of pyroptosis in motor system diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5695-5703. |
| [11] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: data analysis of serum metabolite and inflammatory factor in the European population [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5263-5271. |
| [12] | Chen Chunlan, Ye Meiyi, Pan Yuwei, Yuan Jia, Zhou Pengjun. Immunomodulatory effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 5031-5040. |
| [13] | Yu Hanglin, Tian Haodong, Wen Shiyuan, Huang Li, Liu Haowei, Li Hansen, Wang Peisong, Peng Li. Changes in glucose metabolism and intestinal flora in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus after high-intensity intermittent exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 286-293. |
| [14] | Wang Liping, Lian Tianxing, Hu Yongrong, Yang Hongsheng, Zeng Zhimou, Liu Hao, Qu Bo. HU value of chest CT vertebral body in the opportunistic screening of type 2 diabetes mellitus osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 950-954. |
| [15] | Huang Wenzhuo, Xiang Haizhu, Ma Weiwei, Huang Xin, Fu Hongjun, Xiong Yong. Effect of type 2 diabetes mellitus on bone mineral density in different age groups: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5662-5668. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||