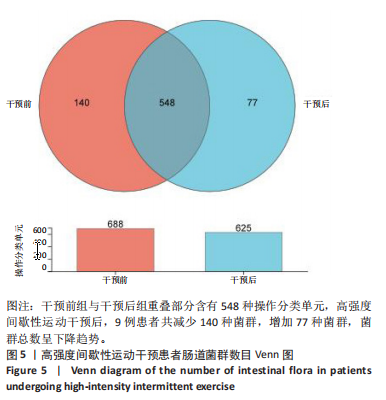
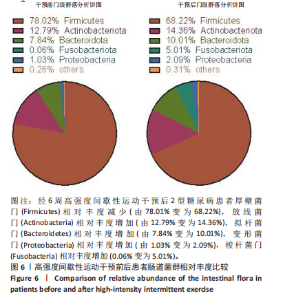
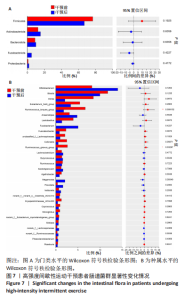
[1] 李想,孔令俊,薛旭,等.高糖调控MAPK信号通路在椎间盘退变中的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(9):1399-1404.
[2] XU X, YI H, WU J, et al. Therapeutic effect of berberine on metabolic diseases: Both pharmacological data and clinical evidence. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;133:110984.
[3] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J].中国实用内科杂志,2021,41(8):668-695.
[4] VALAIYAPATHI B,GOWER B, ASHRAF A. Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetesin children and adolescents. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2020;16(3): 220-229.
[5] 辨野義已. 益生菌研究最新进展[J].日本医学介绍,2004,25(11): 507-509.
[6] 吴立婷,黄偲偲,张辉,等.复合噬菌体与枯草芽孢杆菌对肠道产气荚膜梭菌的抑制效果及免疫代谢功能[J].微生物学通报,2024, 51(3):985-1001.
[7] 熊任芝,吴清明,龙辉.肠道菌群与肝硬化自发性细菌性腹膜炎关系的研究进展[J].临床消化病杂志,2019,31(3):190-194.
[8] LARSEN N, VOGENSEN FK, VAN DEN BERG FW, et al. Gut microbiota in human adults with type 2 diabetes differs from non-diabetic adults. PLoS One. 2010;5(2):e9085.
[9] 任威铭,战丽彬.从《黄帝内经》“移热”理论探讨消渴病病机演变规律[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2024,30(2):181-184.
[10] HINDY G, SONESTEDT E, ERICSON U, et al. Role of TCF7L2 risk variant and dietary fibre intake on incident type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2012;55(10):2646-2654.
[11] American Diabetes Association. Lifestyle Management: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(Suppl 1): S38-S50.
[12] TILG H, MOSCHEN AR. Microbiota and diabetes: an evolving relationship. Gut. 2014;63(9):1513-1521.
[13] ZHANG X, SHEN D, FANG Z, et al. Human Gut Micorbiota Changes Reveal the Progression of Glucose Intolerance. PLoS One. 2013;8(8): e71108.
[14] 赵海燕,郑玉珍,张国琴.住院老年糖尿病患者运动功能与衰弱的关系[J].中国老年学杂志,2023,43(24):6122-6125.
[15] 韦国继,陈然.糖尿病患者的运动干预研究——以2型糖尿病为例[J].体育科技,2023,44(4):23-25+28.
[16] 郭苏霞,袁薇娜,刘丹,等.冠心病患者心脏康复运动处方研究进展——以高强度间歇训练为例[J].健康研究,2023,43(6):678-682.
[17] KÁFUŇKOVÁ P, KVAPIL M. Interval training and compensation of type 2 diabetes. Open J Clin Diagnost. 2017;7(1):20-30.
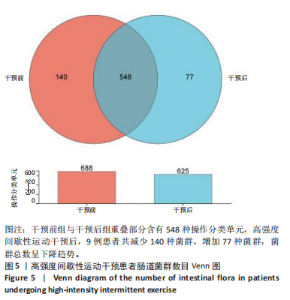
[18] 李亚梦,刘明宇,孙婧,等.运动与肠道菌群相关研究的热点主题和趋势——基于文献计量学分析[J].中国运动医学杂志,2023, 42(1):63-73.
[19] 张壬.循环抗阻训练与高强度间歇训练干预2型糖尿病患者糖脂代谢的效果对比研究[D].重庆:西南大学,2022.
[20] 张福蓉.太极拳运动对2型糖尿病患者肠道菌群及宿主代谢影响的研究[D].成都:成都中医药大学,2020.
[21] 刘诗琪.2型糖尿病患者运动响应与否与其肠道菌群特征的关系探究[D].重庆:西南大学,2022.
[22] 周雪雪.淫羊藿朝霍定C对2型糖尿病小鼠的作用及蛋白质组学研究[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2020.
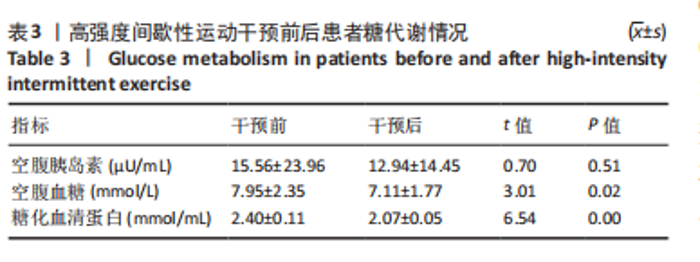
[23] 岳俊珂.血清糖化白蛋白、糖化血红蛋白、空腹血糖对妊娠期糖尿病孕妇的筛选价值分析[J].糖尿病新世界,2023,26(5):51-53+58.
[24] 贾新华.空腹血糖、血脂和糖耐量联合检测对糖尿病生化检验的影响[J].婚育与健康,2023,29(24):43-45.
[25] 冯臣,药家明,周国瑾,等.高强度间歇训练对2型糖尿病患者运动干预的效果:基于《WHO关于身体活动和久坐行为的指南》和WHO-FICs[J].中国康复理论与实践,2022,28(6):646-652.
[26] 王全,常陆,王梦莹.有氧运动联合抗阻训练对老年2型糖尿病伴骨质疏松症患者氧化应激、血糖水平及骨密度的影响[J].中国卫生工程学,2022,21(2):316-318.
[27] 匡峻洁.有氧与抗阻康复运动方式代谢组学特征研究[D].上海:上海体育学院,2022.
[28] RAVI AV, MUSTHAFA KS, JEGATHAMMBAL G, et al. Screening and evaluation of probiotics as a biocontrol agent against pathogenic Vibrios in marine aquaculture. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2007;45(2):219-223.
[29] CONTRERAS R, PANIAGUA-MICHEL J, OCHOA L, et al. Functional Feed Assessment on Litopenaeus vannamei Using 100% Fish Meal Replacement by Soybean Meal, High Levels of Complex Carbohydrates and Bacillus Probiotic Strains. Marine Drugs. 2011;9(6):1119-1132.
[30] FABBIANO S, SUÁREZ-ZAMORANO N, CHEVALIER C, et al. Functional gut microbiota remodeling contributes to the caloric restriction-induced metabolic improvements. Cell Metabolism. 2018;28(6):907-921.e7
[31] 褚欢,李雷.老年2型糖尿病早期肾病患者肠道菌群多样性[J].中国微生态学杂志,2021,33(8):916-919.
[32] 宋韡,汤丽群,张根生,等.高强度运动对摔跤运动员体成分及肠道菌群的影响[J].哈尔滨体育学院学报,2021,39(5):89-96.
[33] ZHONG F, WEN X, YANG M, et al. Effect of an 8-week exercise training on gut microbiota in physically inactive older women. Int J Sports Med. 2021;42(7):610-623.
[34] 韦薇,张秋,黄燕凤,等.不同运动方式对2型糖尿病小鼠肠道菌群及短链脂肪酸的影响[J].广西医科大学学报,2022,39(4):643-648.
[35] 地里努尔•帕尔汗德,郑小英,吴忠道,等.蚊虫肠道微生物在辐照不育技术中的应用前景[J].中国媒介生物学及控制杂志,2023, 34(4):579-584.
[36] 欧阳耀斌.厌氧消化链球菌通过TLR4/TRIF/NF-κB信号通路促进胃黏膜病变[D].南昌:南昌大学,2022.
[37] 王秋月.功能性消化不良患者胃黏膜TRPV1、TRPV2受体表达及菌群特征分析[D].青岛:青岛大学,2021.
[38] 鱼馨文.从双歧杆菌到活泼瘤胃球菌对2型糖尿病预测和干预的初步研究[D].西安:中国人民解放军空军军医大学,2022.
[39] 徐山茸,龚莉,储文文,等.12周高强度间歇性训练对人体肠道菌群的影响[J].微生物学通报,2021,48(4):1215-1226.
[40] 李丽丽.肠道菌群介导牙周炎对前驱糖尿病的影响及其机制研究[D].南京:南京大学,2021.
[41] ARNO H, RAINE T, SAKARI P, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila induces gut microbiota remodelling and controls islet autoimmunity in NOD mice. Gut. 2017;67(8):1445-1453.
[42] PRASANNA K, POORNIMA D, INDRANIL C. Could dysbiosis of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory gut bacteria have an implications in the development of type 2 diabetes? A pilot investigation. BMC Res Notes. 2021;14(1):52.
[43] ALLIN KH, TREMAROLI V, CAESAR R, et al. Aberrant intestinal microbiota in individuals with prediabetes. Diabetologia. 2018;61(4):810-820.
[44] LI G, YIN P, CHU S, et al. Correlation Analysis between GDM and Gut Microbial Composition in Late Pregnancy. J Diabetes Res. 2021: 2021:8892849.
[45] DONG S, JIAO J, JIA S, et al. 16S rDNA Full-Length Assembly Sequencing Technology Analysis of Intestinal Microbiome in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11:634981. |