Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (1): 175-183.doi: 10.12307/2025.569
Previous Articles Next Articles
Stem cell exosomes and biomaterial-assisted exosomes in bone defect repair
Liu Nian1, Dong Xinyue2, Wang Songpeng1, Xu Yingjiang1, Zhang Xiaoming1
- 1Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China; 2Binzhou People’s Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2024-09-28Accepted:2024-12-14Online:2026-01-08Published:2025-07-02 -
Contact:Xu Yingjiang, MD, Associate chief physician, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China; Co-corresponding author: Zhang Xiaoming, MS, Chief physician, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Liu Nian, Master candidate, Physician, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China. Dong Xinyue, MS, Physician, Binzhou People’s Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China. Liu Nian and Dong Xinyue contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82200981 (to XYJ); Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, No. ZR2022QH358 (to XYJ); Shandong Taishan Scholars Program Special Fund, No. tsqn202312384 (to XYJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Nian, Dong Xinyue, Wang Songpeng, Xu Yingjiang, Zhang Xiaoming. Stem cell exosomes and biomaterial-assisted exosomes in bone defect repair[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 175-183.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
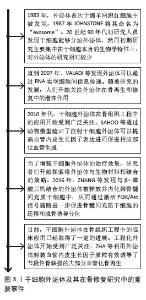
2.1 干细胞外泌体及其在骨修复研究中的重要事件 见图3。干细胞外泌体在骨组织工程中的发展历程是一个涉及科学研究和技术进步的动态过程,主要分为5个阶段。①干细胞外泌体的发现与初步研究:1983年,外泌体首次于绵羊网织红细胞中被发现[13],1987年JOHNSTONE将其命名为“exosome”[14]。20世纪90年代初研究人员发现干细胞能够分泌外泌体,然而初期研究主要集中在干细胞本身的生物学特性上,对外泌体的研究相对较少。②干细胞外泌体在骨组织工程中的潜在价值开始被发现:直到2007年,VALADI 等[15]发现外泌体可以通过RNA实现细胞间信息传递。随着研究的发展,人们开始关注外泌体在骨再生和修复中的潜在作用。③干细胞外泌体治疗骨缺损的临床前研究阶段:2010年,干细胞外泌体在骨组织工程中的应用开始受到广泛关注。研究者们通过动物模型验证了外泌体治疗骨缺损、骨折修复的有效性。SAHOO等[16]通过动物模型验证了注射干细胞外泌体可以提高血管内皮生长因子的表达进而促进相应部位血管生成。④干细胞外泌体与生物材料的结合阶段:为了增强干细胞外泌体的治疗效果,研究者们开始探索将外泌体与生物材料相结合的策略,这种策略可以提高外泌体在体内的稳定性和靶向性。例如,将外泌体加载到支架中以促进骨组织的再生。2016年,ZHANG等[17]发现与β-磷酸三钙结合的外泌体被释放并内化到骨髓间充质干细胞中,通过激活磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B(phosphoinositide 3 kinase/protein kinase B,PI3K/AKT)信号通路进一步促进骨髓间充质干细胞的迁移和成骨诱导分化。⑤临床应用与未来展望阶段:目前,干细胞外泌体在骨组织工程中的临床应用已经取得了一定的进展。一些临床试验正在评估外泌体治疗骨缺损的安全性和有效性。近年来工程化外泌体开始受到广泛关注,ZHA等[18]利用外泌体封装血管内皮生长因子质粒有效诱导了节段性骨缺损的大部分血管化骨再生。"
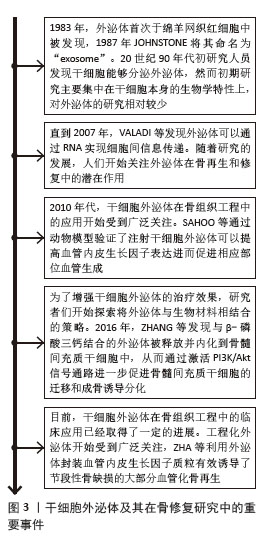

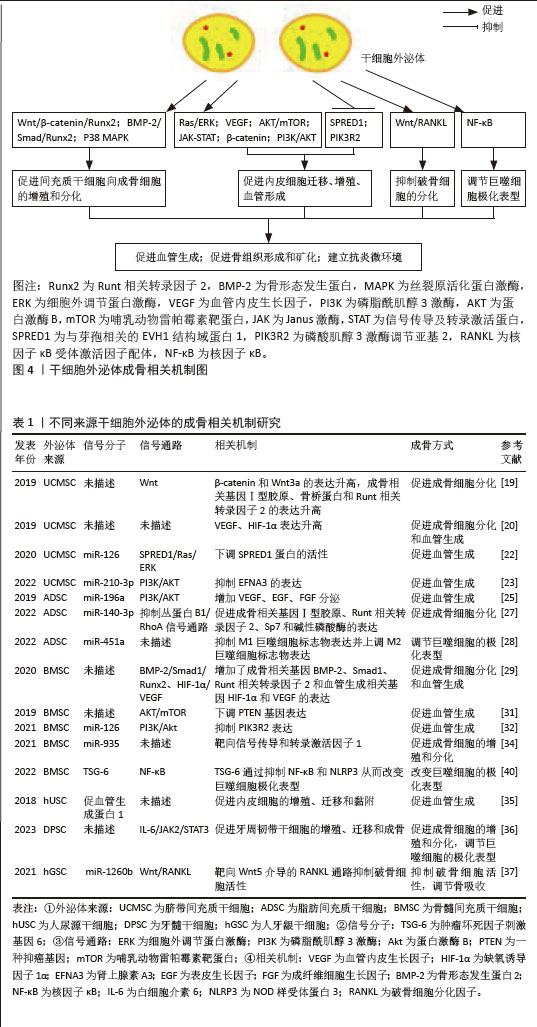
2.2 干细胞源性外泌体在骨修复中的机制 2.2.1 脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体 Wnt通路是重要的骨修复相关信号通路,有研究发现脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体能够促进骨折部位β‐catenin和Wnt3a的表达,并通过增加Ⅰ型胶原、骨桥蛋白和Runt相关转录因子2的表达来促进成骨细胞分化,这表明脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体可能通过Wnt信号通路参与骨折修复[19]。 ZHANG等[20]在股骨骨折大鼠模型中发现脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体明显促进血管生成和骨愈合,在体外实验中也发现其除了促进成骨分化外,还通过增加血管内皮生长因子和缺氧诱导因子1α的表达促进血管生成。 LIU等[21]在骨折模型中比较了低氧和常氧条件下脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体的作用,缺氧预处理通过激活缺氧诱导因子1α促进外泌体miR-126的产生,进而促进人脐静脉内皮细胞的血管生成、增殖和迁移[22]。此外,在体外实验中发现miR-126能够下调SPRED1蛋白的活性,从而激活Ras/ERK通路,促进骨折愈合。此后,ZHUANG等[23]通过体内研究发现缺氧条件下干细胞外泌体促进了人脐静脉内皮细胞的增殖、迁移和血管生成,进而增强了临界大小颅骨缺损模型的骨再生和新血管重建,进一步研究发现缺氧条件下,缺氧诱导因子1α可以诱导miR-210-3p的过表达,而miR-210-3p可以抑制肾上腺素A3的表达,从而激活PI3K/AKT通路来促进血管生成。 2.2.2 脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体 在骨组织工程中,新生组织的血管化程度影响着组织修复的质量。研究发现,脂肪间充质干细胞分泌的外泌体中含有大量血管内皮生长因子A等促血管生成因子,可增加新骨组织的血管化程度,促进骨组织修复[24]。在脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体中还有许多促进血管形成的miRNA,其中miR-196a可通过增加血管内皮生长因子、表皮生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子的分泌来促进血管生成,这一过程可能通过PI3K/AKT信号通路实现[25]。 除了促进血管生成外,脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体也用于促进成骨分化。已有研究报道 miR-140-3p 具有抗炎作用[26],WANG等[27]在糖尿病大鼠骨缺损模型中发现脂肪间充质干细胞及骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体释放的miR-140-3p 可以促进成骨相关基因Ⅰ型胶原、Runt相关转录因子2、Sp7 和碱性磷酸酶的表达,通过抑制丛蛋白B1/RhoA信号通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化,plxnb1 可能是 miR-140-3p 调节成骨的下游靶点。 免疫细胞也参与骨代谢,并可受外泌体影响,外泌体通过改变巨噬细胞的极化表型进而促进骨形成和骨矿化,LI等[28]通过体内外实验均发现脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体抑制M1巨噬细胞标志物表达并上调M2巨噬细胞标志物表达,进一步研究发现这一现象与miR-451a在脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体中富集并靶向巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子有关,结果表明脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以通过miR-451a有效调节骨免疫代谢并进一步促进骨愈合,这可能为骨修复提供治疗方向。 2.2.3 骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体 近年来,骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体展现出了非凡的应用前景。ZHANG等[29]在小鼠股骨不愈合模型中发现骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体促进了骨形成,增加了成骨相关基因和血管生成相关基因的表达。此外,在骨形态发生蛋白2抑制剂存在的情况下,小鼠胚胎成骨前体细胞与骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体共培养时,Smad和Runt相关转录因子2的表达显著降低,结果表明骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体可能通过骨形态发生蛋白2/Smad1/Runt相关转录因子2信号通路激活成骨分化,促进骨折愈合,也可以通过缺氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子通路促进血管化[29]。 与上述研究一致,TAKEUCHI等[30]通过体外实验表明骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体通过增强细胞中成骨和血管生成基因的表达促进骨再生和血管生成。在体内实验中,骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体诱导了更快的骨形成和更多的新生血管形成。 LIANG等[31]也报道了骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体通过诱导血管生成来促进骨再生。骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体经过低剂量二甲氧基丙基甘氨酸预处理后,能够显著下调PTEN基因表达,激活蛋白激酶B/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin,AKT/mTOR)通路,从而在体外刺激人脐静脉内皮细胞血管生成。 ZHANG等[32]通过体外研究发现过表达miR-126的骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体通过转移miR-126来抑制PIK3R2激活,促进人脐静脉内皮细胞的增殖、迁移和血管生成。另外,骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体中miR-126通过加速血管生成和神经生成,抑制细胞凋亡,促进了脊髓损伤后的功能恢复,该结果也与上述研究一致[33]。 骨髓间充质干细胞分泌富含miR-935的外泌体通过靶向信号传导和转录激活因子1促进成骨细胞的增殖和分化[34]。 2.2.4 其他干细胞来源外泌体 CHEN等[35]发现人尿源干细胞外泌体富含促血管生成蛋白1,促进内皮细胞的增殖、迁移和黏附以及后肢缺血模型小鼠的血管生成。此外,QIAO等[36]研究发现牙髓干细胞来源外泌体在体外可以促进牙周韧带干细胞的增殖、迁移和成骨分化,调节巨噬细胞表型并改善牙周炎的微环境,可能与抑制白细胞介素6/Janus激酶2(Janus kinase 2,JAK2)/信号转导和转录活化因子3(signal transducer and activator of transcription 3,STAT3)信号通路有关。携带miR-1260b的牙龈来源干细胞外泌体通过靶向Wnt5介导的核因子κB配体受体激活因子通路抑制破骨细胞活性,有助于调节骨吸收[37]。此外,滑膜间充质干细胞外泌体来源的长链非编码RNASNHG14在骨关节炎中具有促进软骨合成和修复的潜在作用[38]。 综上所述,外泌体包含多种信号分子,包括蛋白质、脂质和miRNAs,它们可以影响细胞的活动进而影响骨形成。不同来源干细胞外泌体通过提高相关基因表达可以激活不同信号通路,如Wnt/β-catenin/Runx2、骨形态发生蛋白2(bone morphogenetic protein 2,BMP-2)/Smad/Runx2、P38 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)、Ras/细胞外调节蛋白激酶(extracellular regulated protein kinases,ERK)、血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF)、AKT/mTOR、JAK‐STAT、β‐catenin和Wnt/核因子κ B受体活化因子配体(receptor activator of nuclear factor-κ B ligand,RANKL),从而促进组织再生[22,39]。 外泌体还可通过激活核因子κB信号通路等途径改变巨噬细胞的极化表型[40-41]。这些机制有助于增强间充质干细胞、内皮细胞、破骨细胞和巨噬细胞的细胞特性,促进成骨细胞增殖和分化,增强血管生成,并调节破骨细胞活性和巨噬细胞表型进而促进骨形成和骨矿化,见图4。不同来源干细胞外泌体的成骨相关机制研究见表1。"
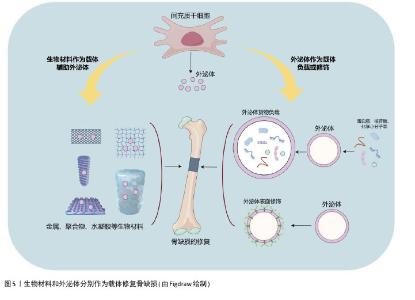
2.3 干细胞外泌体在骨缺损修复中的研究进展 传统的骨缺损修复研究主要集中于将间充质干细胞嵌入特定的骨骼生物材料中,以促进修复和再生[42]。然而,由于安全性、伦理、来源组织有限等问题,间充质干细胞的临床应用一直受到限制[5]。细胞治疗存在体内缺血微环境导致移植细胞生存困难、与内源性细胞竞争氧气和营养等问题,对于较大的骨缺损是一个挑战[43]。最近,随着无细胞疗法的出现,研究人员发现干细胞外泌体与其来源细胞有类似的再生效果[44]。此外,外泌体具有免疫豁免特性,因此可安全用于临床。它们的“货物”,包括miRNA和蛋白质,受到脂质双分子层的保护,可以通过内吞作用与靶细胞相互作用,因此在临界大小骨缺损中外泌体的输送具有潜在的优势。此外,对于骨质疏松和较大骨缺损,采用直接注射外泌体的方式可能存在效率低下等问题[45],因此将外泌体与生物材料支架结合,如生物陶瓷、聚合物、水凝胶和活性金属材料等,以增强多种疾病模型的骨再生能力(图5)。 "
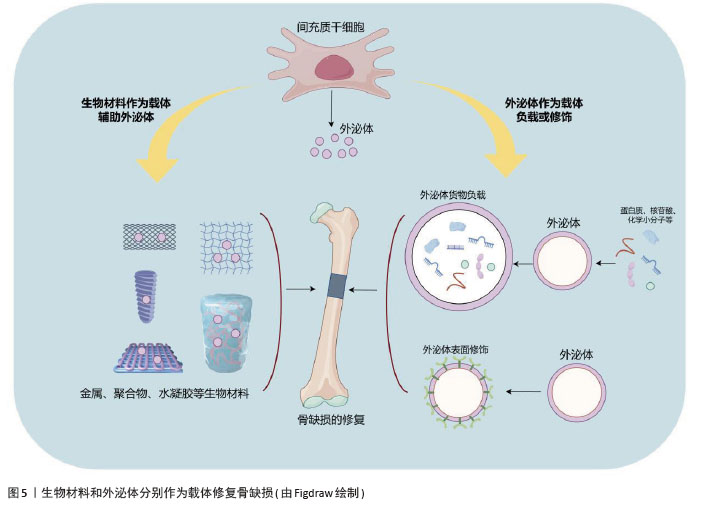
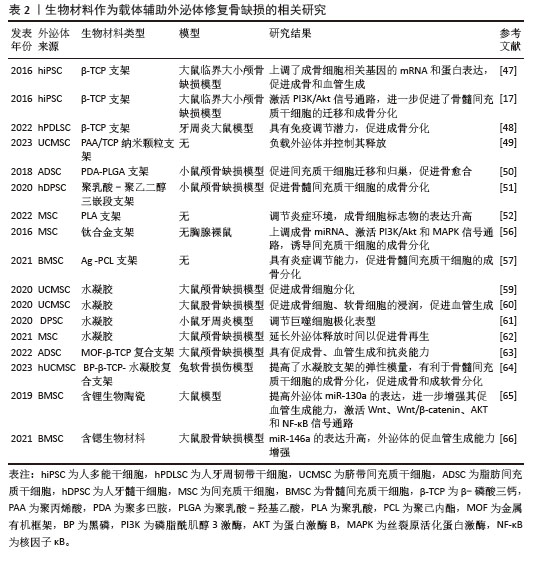
2.3.1 生物材料作为载体辅助外泌体进行骨缺损修复 (1)外泌体与生物陶瓷材料结合:生物陶瓷因优越的机械强度、生物相容性和生物降解性而成为修复大尺寸骨缺损的重要支架材料[46]。生物陶瓷包括可吸收的β-磷酸三钙、具有良好生物活性的玻璃和羟基磷灰石以及不可吸收的氧化锆和氧化铝等。QI等[47]研究表明,与纯支架相比,干细胞来源外泌体可以通过促进β-磷酸三钙支架上成骨细胞分化和血管生成来修复临界大小的骨缺损。研究表明,与β-磷酸三钙结合的外泌体释放并内化到骨髓间充质干细胞中,从而通过激活PI3K/Akt信号通路促进了骨髓间充质干细胞的迁移和成骨诱导分化[17]。此外,将人牙周韧带干细胞来源外泌体加载到β-磷酸三钙支架,促进了牙周炎大鼠牙槽骨的形成[48]。MORADI等[49]制备了一种聚丙烯酸/磷酸三钙纳米颗粒支架,可以负载脐带间充质干细胞外泌体并控制其释放,促进成骨分化。总之,生物陶瓷具有良好的临床潜力,可进一步改进制备策略,以结合外泌体并在体内条件下进行动态释放研究。 (2)外泌体与聚合物结合:合成聚合物具有可调机械性能,如聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物是广泛用于骨再生的生物相容性支架。研究人员将脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体固定在带有聚多巴胺涂层的聚乳酸-羟基乙酸支架上,结果显示外泌体能在体外持续释放,通过其骨诱导作用增强骨再生,在体内可有效促进颅骨缺损模型小鼠的骨愈合,这与外泌体促进间充质干细胞向骨损伤部位迁移和归巢的能力有关[50]。人们还探索了共聚物系统如聚乳酸-聚乙二醇三嵌段作为外泌体控制释放的递送平台,不断释放人牙髓干细胞衍生外泌体,促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,促进矿化和加速骨愈合[51]。聚乳酸是另一种多功能且可生物降解的支架,广泛用于修复组织缺损。有研究将间充质干细胞来源外泌体与多孔3D聚乳酸支架结合,显著增强了促成骨分化能力[52]。聚合物复合材料的弹性模量与骨相当,但生物活性需要提高,因此关于聚合物支架与外泌体结合的研究仍有巨大的空间。 (3)外泌体与金属结合:金属因优越的机械性能而成为最古老的骨移植物选 择[53]。在金属中,钛及其合金因具有良好的生物相容性、无毒性、细胞迁移和增殖所需的最佳孔隙度、较高的机械强度和耐腐蚀等特性而成为骨组织工程的首选。此外,它们还具有促进骨结合和骨生成的作用[54-55]。人间充质干细胞来源外泌体通过电荷的相互作用加载到3D打印的钛合金支架中,外泌体通过上调成骨miRNA、下调抗成骨miRNA以及激活PI3K/Akt和MAPK信号通路来诱导细胞的成骨分化进而实现骨再生[56]。此外,银也适合用作外泌体负载支架来促进骨再生,已有研究人员将间充质干细胞来源外泌体植入银纳米粒子混合支架诱导骨生成,从而成为能够实现骨再生的一种有前途的无细胞疗法[57]。 (4)外泌体与水凝胶结合:水凝胶具有生物相容性,是负载外泌体并将其输送到骨缺损部位的首选载体材料。水凝胶具有控制释放能力,可以向目标组织输送生长因子、蛋白质、药物和干细胞等[58]。最近,几种新型水凝胶复合材料作为外泌体载体用于促进骨再生。YANG等[59]制备了一种可注射的水凝胶,由嵌入交联透明质酸和海藻酸盐的羟基磷灰石组成,作为间充质干细胞来源外泌体的载体,显著促进了成骨细胞分化。在另一项研究中,一种由珊瑚状羟基磷灰石、丝素蛋白/乙二醇壳聚糖和双官能化聚乙二醇组成的新型水凝胶复合材料被证明是一种极佳的载体材料[60],具有良好的自修复性能和力学性能,进一步研究表明含外泌体的水凝胶可以促进大鼠骨缺损愈合。还有研究将牙髓干细胞源性外泌体整合到壳聚糖水凝胶中,用于改善大量炎性巨噬细胞引起的牙周炎,在miR-1246的作用下促炎巨噬细胞被转化为抗炎巨噬细胞,有效地加速了牙槽骨的再生[61]。另一个研究方向是提高封装效率,以延长外泌体的输送时间。HUANG等[62]通过将外泌体负载至光敏水凝胶上,可包裹长达7 d而不改变其功能完整性,同时还能在颅骨缺损模型中显著刺激骨再生。在大鼠颅骨缺损模型中,从复合水凝胶支架释放的外泌体可以诱导新骨形成和骨整合[63]。在一项含有黑磷、β-磷酸三钙和外泌体的3D打印水凝胶的研究中,β-磷酸三钙的加入显著提高了水凝胶支架的弹性模量,体外实验也证实双层支架可以分别促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化和成软骨分化[64]。 (5)生物材料对外泌体货物的调节作用:研究表明,在生物材料中掺杂某些微量元素可影响间充质干细胞来源外泌体内容物,增强其血管生成潜能。含锂生物活性玻璃陶瓷可促进骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体中miR-130a的表达从而增强血管生成能力,并激活Wnt、Wnt/β-catenin、AKT和核因子κB信号通路[65]。还有研究表明,含锶的生物材料刺激骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体中miR-146a的表达进而提高外泌体的促血管生成能力,促进新生血管的形成[66]。关于不同类型的生物材料对外泌体的具体调节作用,目前的研究结论非常有限。 生物材料作为载体辅助外泌体修复骨缺损的相关研究见表2。 "

2.3.2 工程化外泌体进行骨缺损修复 工程化外泌体可分为两类:外泌体的货物装载和外泌体的表面改性[67]。将货物载入外泌体可提高外泌体的治疗效果,可分为内源性货物装载法和外源性货物装载法[67]。内源性货物装载法通常用于装载具有治疗作用的内源性蛋白质和核苷酸[67]。过表达miR-181b的骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体通过分泌血管内皮生长因子和骨形态发生蛋白2来促进M2极化并通过激活PRKCD/AKT信号通路抑制炎症,从而促进体外成骨和体内成骨[68]。骨形态发生蛋白2过表达骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体促进了小鼠股骨缺损模型的骨再生和成骨诱导能力[69]。而外源性货物装载法通常用于装载小分子药物[70],包括皂素渗透、冻融循环和室温培养等[71]。将骨形态发生蛋白2直接载入骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体中可诱导体外和体内成骨再生[72]。此外,在大鼠桡骨缺损模型中,包裹有血管内皮生长因子基因的外泌体显示出极佳的骨再生能力,能够诱导形成大量新骨[18]。 表面修饰可用于增强干细胞外泌体的靶向能力。近年来,越来越多的研究人员考虑到干细胞来源外泌体直接用于骨损伤的治疗会导致大部分外泌体在肝和肺中积累,LUO等[73]将骨髓间充质干细胞特异性适体与外泌体结合(BMSCs-Exos-apt),结果显示BMSC‐Exos‐apt能够促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,也能促进BMSC‐Exos‐apt在损伤部位的积累,促进更多的骨形成。C-X-C基序趋化因子受体4被修饰到基因工程NIH-3T3细胞来源外泌体表面[74],然后将该复合物与携带拮抗素miR-188的脂质体结合以生成杂化纳米颗粒,杂化纳米颗粒通过特异性聚集在骨髓中并控制释放拮抗素miR-188来抑制脂肪生成并促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨。工程化外泌体修复骨缺损的相关研究见表3。 "

| [1] SCHMIDT AH. Autologous bone graft: Is it still the gold standard? Injury. 2021;52 Suppl 2: S18-S22. [2] JURCZAK P, LACH S. Hydrogels as Scaffolds in Bone-Related Tissue Engineering and Regeneration. Macromol Biosci. 2023;23(11): e2300152. [3] DUTTA S, ROY M. Recent Developments in Engineered Magnesium Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(6):3010-3031. [4] AUGUSTINE R, GEZEK M, NIKOLOPOULOS VK, et al. Stem Cells in Bone Tissue Engineering: Progress, Promises and Challenges. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024;20(7):1692-1731. [5] ITE K, TOYODA M, AKIYAMA S, et al. Stem cell challenges and opportunities. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2023;199:379-395. [6] MONDAL J, PILLARISETTI S, JUNNUTHULA V, et al. Hybrid exosomes, exosome-like nanovesicles and engineered exosomes for therapeutic applications. J Control Release. 2023;353:1127-1149. [7] WATANABE Y, TSUCHIYA A, TERAI S. The development of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in the present, and the perspective of cell-free therapy in the future. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2021;27(1):70-80. [8] YANG D, CHEN Z, XU Z, et al. Roles of Stem Cell Exosomes and their MicroRNA Carrier in Bone and Cartilage Regeneration. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;18(7):917-925. [9] HUANG Y, ZHANG X, ZHAN J, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-206 promotes osteoblast proliferation and differentiation in osteoarthritis by reducing Elf3. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(16):7734-7745. [10] HE L, HE T, XING J, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protect cartilage damage and relieve knee osteoarthritis pain in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1): 276. [11] HAO Z, REN L, ZHANG Z, et al. A multifunctional neuromodulation platform utilizing Schwann cell-derived exosomes orchestrates bone microenvironment via immunomodulation, angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Bioact Mater. 2022;23:206-222. [12] LU Y, MAI Z, CUI L, et al. Engineering exosomes and biomaterial-assisted exosomes as therapeutic carriers for bone regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):55. [13] JEPPESEN DK, ZHANG Q, FRANKLIN JL, et al. Extracellular vesicles and nanoparticles: emerging complexities. Trends Cell Biol. 2023; 33(8):667-681. [14] AGARWAL P, ANEES A, HARSIDDHARAY RK, et al. A Comprehensive Review on Exosome: Recent Progress and Outlook. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2023. doi: 10.2174/2211738511666230523114311. [15] VALADI H, EKSTRÖM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007; 9(6):654-659. [16] SAHOO S, KLYCHKO E, THORNE T, et al. Exosomes from human CD34(+) stem cells mediate their proangiogenic paracrine activity. Circ Res. 2011;109(7):724-728. [17] ZHANG J, LIU X, LI H, et al. Exosomes/tricalcium phosphate combination scaffolds can enhance bone regeneration by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016; 7(1):136. [18] ZHA Y, LI Y, LIN T, et al. Progenitor cell-derived exosomes endowed with VEGF plasmids enhance osteogenic induction and vascular remodeling in large segmental bone defects. Theranostics. 2021;11(1):397-409. [19] ZHOU J, LIU HX, LI SH, et al. Effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on fracture healing in rats through the Wnt signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(11):4954-4960. [20] ZHANG Y, HAO Z, WANG P, et al. Exosomes from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance fracture healing through HIF-1α-mediated promotion of angiogenesis in a rat model of stabilized fracture. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(2):e12570. [21] LIU H, LIU S, QIU X, et al. Donor MSCs release apoptotic bodies to improve myocardial infarction via autophagy regulation in recipient cells. Autophagy. 2020;16(12):2140-2155. [22] LIU W, LI L, RONG Y, et al. Hypoxic mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote bone fracture healing by the transfer of miR-126. Acta Biomater. 2020;103:196-212. [23] ZHUANG Y, CHENG M, LI M, et al. Small extracellular vesicles derived from hypoxic mesenchymal stem cells promote vascularized bone regeneration through the miR-210-3p/EFNA3/PI3K pathway. Acta Biomater. 2022; 150:413-426. [24] ZHAO Z, SUN W, GUO Z, et al. Mechanisms of lncRNA/microRNA interactions in angiogenesis. Life Sci. 2020;254:116900. [25] JEPPESEN DK, FENIX AM, FRANKLIN JL, et al. Reassessment of Exosome Composition. Cell. 2019;177(2):428-445.e18. [26] MIN Z, ZHANG R, YAO J, et al. MicroRNAs associated with osteoarthritis differently expressed in bone matrix gelatin (BMG) rat model. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(1):1009-1017. [27] WANG N, LIU X, TANG Z, et al. Increased BMSC exosomal miR-140-3p alleviates bone degradation and promotes bone restoration by targeting Plxnb1 in diabetic rats. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):97. [28] LI R, LI D, WANG H, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells regulate M1/M2 macrophage phenotypic polarization to promote bone healing via miR-451a/MIF. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):149. [29] ZHANG L, JIAO G, REN S, et al. Exosomes from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells enhance fracture healing through the promotion of osteogenesis and angiogenesis in a rat model of nonunion. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):38. [30] TAKEUCHI R, KATAGIRI W, ENDO S, et al. Exosomes from conditioned media of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote bone regeneration by enhancing angiogenesis. PLoS One. 2019;14(11):e0225472. [31] LIANG B, LIANG JM, DING JN, et al. Dimethyloxaloylglycine-stimulated human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes enhance bone regeneration through angiogenesis by targeting the AKT/mTOR pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):335. [32] ZHANG L, OUYANG P, HE G, et al. Exosomes from microRNA-126 overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells promote angiogenesis by targeting the PIK3R2-mediated PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2021; 25(4):2148-2162. [33] HUANG JH, XU Y, YIN XM, et al. Exosomes Derived from miR-126-modified MSCs Promote Angiogenesis and Neurogenesis and Attenuate Apoptosis after Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. Neuroscience. 2020;424:133-145. [34] ZHANG Y, CAO X, LI P, et al. microRNA-935-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes enhance osteoblast proliferation and differentiation in osteoporotic rats. Life Sci. 2021;272:119204. [35] CHEN CY, RAO SS, REN L, et al. Exosomal DMBT1 from human urine-derived stem cells facilitates diabetic wound repair by promoting angiogenesis. Theranostics. 2018;8(6):1607-1623. [36] QIAO X, TANG J, DOU L, et al. Dental Pulp Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Regulate Anti-Inflammatory and Osteogenesis in Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells and Promote the Repair of Experimental Periodontitis in Rats. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:4683-4703. [37] NAKAO Y, FUKUDA T, ZHANG Q, et al. Exosomes from TNF-α-treated human gingiva-derived MSCs enhance M2 macrophage polarization and inhibit periodontal bone loss. Acta Biomater. 2021;122:306-324. [38] ZHENG D, YANG K, CHEN T, et al. Inhibition of LncRNA SNHG14 protects chondrocyte from injury in osteoarthritis via sponging miR-137. Autoimmunity. 2023;56(1):2270185. [39] LEE Y, KIM HJ, PARK CK, et al. MicroRNA-124 regulates osteoclast differentiation. Bone. 2013;56(2):383-389. [40] LI C, LI X, SHI Z, et al. Exosomes from LPS-preconditioned bone marrow MSCs accelerated peripheral nerve regeneration via M2 macrophage polarization: Involvement of TSG-6/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway. Exp Neurol. 2022;356:114139. [41] FAN L, GUAN P, XIAO C, et al. Exosome-functionalized polyetheretherketone-based implant with immunomodulatory property for enhancing osseointegration. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(9):2754-2766. [42] ALTUNDAG Ö, ÖTEYAKA MÖ, ÇELEBI-SALTIK B. Co- and Triaxial Electrospinning for Stem Cell-based Bone Regeneration. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024;19(6):865-878. [43] KADRI N, AMU S, IACOBAEUS E, et al. Current perspectives on mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for graft versus host disease. Cell Mol Immunol. 2023;20(6):613-625. [44] WANG X, THOMSEN P. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles and bone regeneration. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021;128(1):18-36. [45] RIAU AK, ONG HS, YAM GHF, et al. Sustained Delivery System for Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:1368. [46] LIN H, ZHANG L, ZHANG Q, et al. Mechanism and application of 3D-printed degradable bioceramic scaffolds for bone repair. Biomater Sci. 2023;11(21):7034-7050. [47] QI X, ZHANG J, YUAN H, et al. Exosomes Secreted by Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Repair Critical-Sized Bone Defects through Enhanced Angiogenesis and Osteogenesis in Osteoporotic Rats. Int J Biol Sci. 2016; 12(7):836-849. [48] LEI F, LI M, LIN T, et al. Treatment of inflammatory bone loss in periodontitis by stem cell-derived exosomes. Acta Biomater. 2022;141:333-343. [49] MORADI N, KAVIANI S, SOUFIZOMORROD M, et al. Preparation of poly(acrylic acid)/tricalcium phosphate nanoparticles scaffold: Characterization and releasing UC-MSCs derived exosomes for bone differentiation. Bioimpacts. 2023;13(5):425-438. [50] LI W, LIU Y, ZHANG P, et al. Tissue-Engineered Bone Immobilized with Human Adipose Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes Promotes Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(6):5240-5254. [51] SWANSON WB, ZHANG Z, XIU K, et al. Scaffolds with controlled release of pro-mineralization exosomes to promote craniofacial bone healing without cell transplantation. Acta Biomater. 2020;118:215-232. [52] ZHANG Y, HUO M, WANG Y, et al. A tailored bioactive 3D porous poly(lactic-acid)-exosome scaffold with osteo-immunomodulatory and osteogenic differentiation properties. J Biol Eng. 2022;16(1):22. [53] ZHAO R, YANG R, COOPER PR, et al. Bone Grafts and Substitutes in Dentistry: A Review of Current Trends and Developments. Molecules. 2021;26(10):3007. [54] MATEO-SIDRÓN ANTÓN MC, PÉREZ-GONZÁLEZ F, MENIZ-GARCÍA C. Titanium mesh for guided bone regeneration: a systematic review. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2024;62(5):433-440. [55] BOSSHARDT DD, CHAPPUIS V, BUSER D. Osseointegration of titanium, titanium alloy and zirconia dental implants: current knowledge and open questions. Periodontol 2000. 2017;73(1):22-40. [56] NARAYANAN R, HUANG CC, RAVINDRAN S. Hijacking the Cellular Mail: Exosome Mediated Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:3808674. [57] LU H, ZHANG Y, XIONG S, et al. Modulatory Role of Silver Nanoparticles and Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosome-Modified Barrier Membrane on Macrophages and Osteogenesis. Front Chem. 2021;9:699802. [58] SHAN BH, WU FG. Hydrogel-Based Growth Factor Delivery Platforms: Strategies and Recent Advances. Adv Mater. 2024;36(5): e2210707. [59] YANG S, ZHU B, YIN P, et al. Integration of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes with Hydroxyapatite-Embedded Hyaluronic Acid-Alginate Hydrogel for Bone Regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(3):1590-1602. [60] WANG L, WANG J, ZHOU X, et al. A New Self-Healing Hydrogel Containing hucMSC-Derived Exosomes Promotes Bone Regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:564731. [61] SHEN Z, KUANG S, ZHANG Y, et al. Chitosan hydrogel incorporated with dental pulp stem cell-derived exosomes alleviates periodontitis in mice via a macrophage-dependent mechanism. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(4): 1113-1126. [62] HUANG CC, KANG M, SHIRAZI S, et al. 3D Encapsulation and tethering of functionally engineered extracellular vesicles to hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2021;126:199-210. [63] KANG Y, XU C, MENG L, et al. Exosome-functionalized magnesium-organic framework-based scaffolds with osteogenic, angiogenic and anti-inflammatory properties for accelerated bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2022;18:26-41. [64] SUN T, FENG Z, HE W, et al. Novel 3D-printing bilayer GelMA-based hydrogel containing BP,β-TCP and exosomes for cartilage-bone integrated repair. Biofabrication. 2023;16(1): 015008. [65] LIU L, LIU Y, FENG C, et al. Lithium-containing biomaterials stimulate bone marrow stromal cell-derived exosomal miR-130a secretion to promote angiogenesis. Biomaterials. 2019; 192:523-536. [66] LIU L, YU F, LI L, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells stimulated by strontium-substituted calcium silicate ceramics: release of exosomal miR-146a regulates osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2021;119: 444-457. [67] CHEN S, SUN F, QIAN H, et al. Preconditioning and Engineering Strategies for Improving the Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Cell-Free Therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2022;2022:1779346. [68] LIU W, YU M, CHEN F, et al. A novel delivery nanobiotechnology: engineered miR-181b exosomes improved osteointegration by regulating macrophage polarization. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):269. [69] LI F, WU J, LI D, et al. Engineering stem cells to produce exosomes with enhanced bone regeneration effects: an alternative strategy for gene therapy. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022; 20(1):135. [70] CHENG J, SUN Y, MA Y, et al. Engineering of MSC-Derived Exosomes: A Promising Cell-Free Therapy for Osteoarthritis. Membranes (Basel). 2022;12(8):739. [71] HANEY MJ, KLYACHKO NL, ZHAO Y, et al. Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for Parkinson’s disease therapy. J Control Release. 2015;207:18-30. [72] YERNENI SS, ADAMIK J, WEISS LE, et al. Cell trafficking and regulation of osteoblastogenesis by extracellular vesicle associated bone morphogenetic protein 2. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10(12):e12155. [73] LUO ZW, LI FX, LIU YW, et al. Aptamer-functionalized exosomes from bone marrow stromal cells target bone to promote bone regeneration. Nanoscale. 2019;11(43): 20884-20892. [74] CHEN C, FU L, LUO Y, et al. Engineered Exosome-Functionalized Extracellular Matrix-Mimicking Hydrogel for Promoting Bone Repair in Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023;15(24):28891-28906. [75] LAI P, CHEN X, GUO L, et al. A potent immunomodulatory role of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stromal cells in preventing cGVHD. J Hematol Oncol. 2018;11(1):135. [76] BANKS WA, SHARMA P, BULLOCK KM, et al. Transport of Extracellular Vesicles across the Blood-Brain Barrier: Brain Pharmacokinetics and Effects of Inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(12):4407. [77] YANG Z, YANG Y, XU Y, et al. Biomimetic nerve guidance conduit containing engineered exosomes of adipose-derived stem cells promotes peripheral nerve regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):442. |
| [1] | Sun Lei, Zhang Qi, Zhang Yu. Pro-osteoblastic effect of chlorogenic acid protein microsphere/polycaprolactone electrospinning membrane [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1877-1884. |
| [2] | Wu Yanting, Li Yu, Liao Jinfeng. Magnesium oxide nanoparticles regulate osteogenesis- and angiogenesis-related gene expressions to promote bone defect healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895. |
| [3] | Liu Dawei, Cui Yingying, Wang Fanghui, Wang Zixuan, Chen Yuhan, Li Yourui, Zhang Ronghe. Epigallocatechin gallate-mediated bidirectional regulation of reactive oxygen species and its application in nanomaterials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2101-2112. |
| [4] | Lai Yu, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun. Research hotspots and frontier trends of bioactive materials in treating bone infections [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2132-2144. |
| [5] | Liu Xinyue, Li Chunnian, Li Yizhuo, Xu Shifang. Regeneration and repair of oral alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1247-1259. |
| [6] | Xu Shencong, Fang Zifei, Ji Mingyi, Xu Chengrui, Li Binhong, Cao Jiayu, Xu Junfeng. Application of Onlay bone grafts from mandibular lateral oblique line in implant restoration of bone defects in upper anterior teeth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 841-848. |
| [7] | Cao Wenqi, Feng Xiuzhi, Zhao Yi, Wang Zhimin, Chen Yiran, Yang Xiao, Ren Yanling. Effect of macrophage polarization on osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 917-925. |
| [8] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [9] | Yu Shiyu, Yu Sutong, Xu Yang, Zhen Xiangyan, Han Fengxuan. Advances in research and application of tissue engineering therapeutic strategies in oral submucous fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 936-948. |
| [10] | Yang Hu, Zheng Yu, Jia Chengming, Wang Tong, Zhang Guangfei, Ji Yaoyao. Immune microenvironment regulates bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 701-710. |
| [11] | Yuan Qian, Zhang Hao, Pang Jie. Characterization and biological properties of naringin-loaded chitosan/beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 424-432. |
| [12] | Bai Xiangyu, Huo Feng, Hao Yan, Wang Zecheng, Guo Xiaoyu. Platelet-derived growth factor BB-loaded chitosan/reduced graphene oxide scaffold for repairing alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 329-337. |
| [13] | Dong Chao, Zhao Mohan, Liu Yunan, Yang Zeli, Chen Leqin, Wang Lanfang. Effects of magnetic nano-drug carriers on exercise-induced muscle injury and inflammatory response in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 345-353. |
| [14] | Zhou Shibo, Yu Xing, Chen Hailong, Xiong Yang. Nanocrystalline collagen-based bone combined with Bushen Zhuangjin Decoction repairs bone defects in osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 354-361. |
| [15] | Yang Fengli, Zhou Chao, Xiong Wei, Zhou Yuxiang, Li Dengshun, Wang Xin, Li Zhanzhen. 3D printed poly-L-lactic acid bone scaffolds in repair of bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 507-515. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||