Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (4): 824-831.doi: 10.12307/2025.994
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of type 2 diabetes mellitus on orthodontic tooth movement and bone microstructure parameters on the tension side in rats
Yan Chengbo1, Luo Qiuchi1, Fan Jiabing2, Gu Yeting1, Deng Qian1, Zhang Junmei1
- 1School of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Orthodontics 2, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2024-10-14Accepted:2024-12-25Online:2026-02-08Published:2025-05-15 -
Contact:Zhang Junmei, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, School of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Yan Chengbo, Master candidate, Physician, School of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Guizhou Provincial Health and Wellness Commission Project, No. gzwkj2023-61 (to ZJM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yan Chengbo, Luo Qiuchi, Fan Jiabing, Gu Yeting, Deng Qian, Zhang Junmei. Effect of type 2 diabetes mellitus on orthodontic tooth movement and bone microstructure parameters on the tension side in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 824-831.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

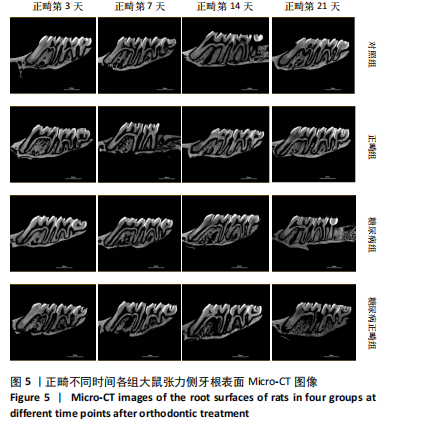
2.3 各组大鼠一般状态 对照组和正畸组大鼠活动正常,毛发柔软有光泽,垫料干燥;糖尿病组和糖尿病正畸组大鼠精神萎靡,垫料潮湿,毛色发黄,有刺激性气味,饮食及饮水量增加。 2.4 各组大鼠第一磨牙近中移动距离比较 4组大鼠正畸第3,7,14,21天的牙移动距离比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表3,图4。正畸第3天,正畸组、糖尿病正畸组牙移动距离均大于糖尿病组(P < 0.05);正畸第7天,正畸组、糖尿病正畸组牙移动距离均大于对照组(P < 0.01);正畸第14天,正畸组、糖尿病正畸组牙移动距离均大于对照组(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),糖尿病正畸组牙移动距离大于糖尿病组(P < 0.05);正畸第21天,糖尿病正畸组牙移动距离大于对照组、糖尿病组(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),正畸组牙移动距离均大于糖尿病组(P < 0.05)。 2.5 各组大鼠张力侧骨微结构参数比较 正畸不同时间各组大鼠张力侧牙根表面Micro-CT图像,见图5。 2.5.1 张力侧牙槽骨骨密度 正畸第3天,4组间张力侧牙槽骨骨密度比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);正畸第"


2.5.2 张力侧牙槽骨骨体积分数 正畸第3天,4组间张力侧牙槽骨骨体积分数比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);正畸第7,14,21天,4组间张力侧牙槽骨骨体积分数比较差异显著(P < 0.05),见表5,图7。正畸第7天,糖尿病正畸组张力侧牙槽骨骨体积分数低于对照组、正畸组(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);正畸第14天,糖尿病组、糖尿病正畸组张力侧牙槽骨骨体积分数低于对照组(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);正畸第21天,糖尿病组骨体积分数高于对照组、糖尿病正畸组(P < 0.05)。 2.5.3 张力侧牙槽骨骨小梁厚度 正畸第7,21天,4组间张力侧牙槽骨骨小梁厚度比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);正畸第3,14天,4组间张力侧牙槽骨骨小梁厚度比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表6,图8。 正畸第3天,糖尿病正畸组张力侧牙槽骨骨小梁厚度低于对照组、正畸组(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);正畸第14天,"

| [1] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)(上)[J].中国实用内科杂志,2021,41(8):668-695. [2] 周瑞雯,郭华,任忠英.青少年2型糖尿病国外研究进展的相关解读[J].糖尿病新世界,2023,26(7):194-198. [3] PABISCH S, AKABANE C, WAGERMAIER W, et al. The nanostructure of murine alveolar bone and its changes due to type 2 diabetes. J Struct Biol. 2016;196(2): 223-231. [4] ZHU L, ZHOU C, CHEN S, et al. Osteoporosis and Alveolar Bone Health in Periodontitis Niche: A Predisposing Factors-Centered Review. Cells. 2022;11(21): 3380. [5] ZHAO P, XU A, LEUNG WK. Obesity, Bone Loss, and Periodontitis: The Interlink. Biomolecules. 2022;12(7):865. [6] MAYTA-MAYORGA M, GUERRA-RODRÍGUEZ V, BERNABE-ORTIZ A. Association between type 2 diabetes and periodontitis: a population-based study in the North Peru. Wellcome Open Res. 2024;9:562. [7] 关禹哲,蒋玉坤,吴祖平,等.机械敏感离子通道Piezo1在糖尿病大鼠牙移动过程中的表达和功能研究[J]. 口腔医学,2022,42(6):487-493. [8] 孙慧颖,王东旭,张莹.糖尿病患者牙周病的正畸治疗对牙周状况及血糖水平的影响[J].糖尿病新世界,2019,22(9):183-184. [9] SUN J, DU J, FENG W, et al. Histological evidence that metformin reverses the adverse effects of diabetes on orthodontic tooth movement in rats. J Mol Histol. 2016;48(2):73-81. [10] SANTAMARIA-JR M, BAGNE L, ZANIBONI E, et al. Diabetes mellitus and periodontitis: Inflammatory response in orthodontic tooth movement. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2019;23(1):27-34. [11] ARITA K, HOTOKEZAKA H, HASHIMOTO M, et al. Effects of diabetes on tooth movement and root resorption after orthodontic force application in rats. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2016;19(2):83-92. [12] PLUT A, SPROGAR Š, DREVENŠEK G, et al. Bone remodeling during orthodontic tooth movement in rats with type 2 diabetes. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2015;148(6):1017-1025. [13] JEON HH, TEIXEIRA H, TSAI A. Mechanistic Insight into Orthodontic Tooth Movement Based on Animal Studies: A Critical Review. J Clin Med. 2021; 10(8):1733. [14] DING X, LAI L, JIA Y, et al. Effects of chronic fluorosis on the expression of VEGF/PI3K/AKT/eNOS in the gingival tissue of rats with orthodontic tooth movement. Exp Ther Med. 2024;27(3):121. [15] LI Y, ZHAN Q, BAO M, et al. Biomechanical and biological responses of periodontium in orthodontic tooth movement: up-date in a new decade. Int J Oral Sci. 2021;13(1):20. [16] GUO X, SHEN Y, DU T, et al. Elevations of N-Terminal Mid-Fragment of Osteocalcin and Cystatin C Levels are Associated with Disorders of Glycolipid Metabolism and Abnormal Bone Metabolism in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Complicated with Osteoporosis. J Physiol Investig. 2024;67(6):335-343. [17] 冯智敏,吴永生,闫桂艳.糖尿病大鼠正畸牙齿移动及组织学变化[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2007,21(2):188-191. [18] LI M, SUN H, CHEN H, et al. Type 2 diabetes and bone mineral density: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024;103(45):e40468. [19] ZHAO Q, LI Y, ZHANG Q, et al. Association between serum insulin-like growth factor-1 and bone mineral density in patients with type 2 diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024;15:1457050. [20] MURRAY CE, COLEMAN CM. Impact of Diabetes Mellitus on Bone Health. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(19):4873. [21] PSACHNA S, CHONDROGIANNI ME, STATHOPOULOS K, et al. The effect of antidiabetic drugs on bone metabolism: a concise review. Endocrine. 2024. doi: 10.1007/s12020-024-04070-1.. [22] 郭莉莉,张莹,潘多.胰岛素控制对糖尿病大鼠正畸牙齿移动的影响[J].糖尿病新世界,2019,22(9):23-24. [23] ABBASSY MA, WATARI I, BAKRY AS, et al. Calcitonin and vitamin D3 have high therapeutic potential for improving diabetic mandibular growth. Int J Oral Sci. 2016;8:39-44. [24] MADDALONI E, NGUYEN M, SHAH SH, et al. Osteoprotegerin, Osteopontin, and Osteocalcin Are Associated With Cardiovascular Events in Type 2 Diabetes: Insights From EXSCEL. Diabetes Care.2024:dc241455. doi:10.2337/dc24-1455. [25] ELAMIR Y, GIANAKOS AL, LANE JM, et al. The Effects of Diabetes and Diabetic Medications on Bone Health. J Orthop Trauma. 2020;34(3):e102-e108. [26] HUANG D, HE Q, PAN J, et al. Systemic immune-inflammatory index predicts fragility fracture risk in postmenopausal anemic females with type 2 diabetes mellitus: evidence from a longitudinal cohort study. BMC Endocr Disord. 2024; 24(1):256. [27] SHEU A, GREENFIELD JR, WHITE CP, et al. Assessment and treatment of osteoporosis and fractures in type 2 diabetes. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2022; 33(5):333-344. [28] ZHANG YS, ZHENG YD, YUAN Y, et al. Effects of Anti-Diabetic Drugs on Fracture Risk: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:735824. [29] MARIN C, TUTS J, LUYTEN FP, et al. Impaired soft and hard callus formation during fracture healing in diet-induced obese mice as revealed by 3D contrast-enhanced computed tomography imaging. Bone. 2021;150:116008. [30] SÁBADO-BUNDÓ H, SÁNCHEZ-GARCÉS MÁ, GAY-ESCODA C. Bone regeneration in diabetic patients. A systematic review. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2019; 24(4):e425-e432. [31] LUONG A, TAWFIK AN, ISLAMOGLU H, et al. Periodontitis and diabetes mellitus co-morbidity: A molecular dialogue. J Oral Biosci. 2021;63(4):360-369. [32] LI Y, HUANG Z, PAN S, et al. Resveratrol Alleviates Diabetic Periodontitis-Induced Alveolar Osteocyte Ferroptosis Possibly via Regulation of SLC7A11/GPX4. Nutrients. 2023;15(9):2115. [33] ZHAO P, YUE Z, NIE L, et al. Hyperglycaemia-associated macrophage pyroptosis accelerates periodontal inflamm-aging. J Clin Periodontol. 2021;48(10):1379-1392. [34] CAI F, LIU Y, LIU K, et al. Diabetes mellitus impairs bone regeneration and biomechanics. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):169. [35] BRAGA SM, TADDEI SR, ANDRADE JR I, et al. Effect of diabetes on orthodontic tooth movement in a mouse model. Eur J Oral Sci. 2011;119:7-14. [36] LI X, ZHANG L, WANG N, et al. Periodontal ligament remodeling and alveolar bone resorption during orthodontic tooth movement in rats with diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2010;12:65-73. [37] VILLARINO ME, LEWICKI M, UBIOS AM. Bone response to orthodontic forces in diabetic Wistar rats. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2011;139(4 Suppl):S76-82. [38] FERREIRA CL, DA ROCHA VC, DA SILVA URSI WJ, et al. Periodontal response to orthodontic tooth movement in diabetes-induced rats with or without periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 2018;89(3):341-350. [39] CHAPPLE IL, GENCO R; Working group 2 of the joint EFP/AAP workshop. Diabetes and periodontal diseases: consensus report of the joint EFP/AAP workshop on periodontitis and systemic diseases. J Periodontol. 2013;84(4 Suppl):S106-S112. [40] ZHANG L, LI X, BI LJ. Alterations of collagen-I, MMP-1 and TIMP-1 in the periodontal ligament of diabetic rats under mechanical stress. J Periodontal Res. 2011;46(4):448-455. |
| [1] | Pan Hongfei, Zhuang Zhenbing, Xu Baiyun, Yang Zhangyang, Lin Kairui, Zhan Bingqing, Lan Jinghan, Gao Heng, Zhang Nanbo, Lin Jiayu. Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of auranofin on M1 macrophage function and its therapeutic potential in diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1390-1397. |
| [2] | Peng Zhiwei, Chen Lei, Tong Lei. Luteolin promotes wound healing in diabetic mice: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [3] | Sun Yajie, Zhao Xinchen, Bo Shuangling. Spatiotemporal expression of bone morphologic protein 7 in mouse kidney development [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1156-1161. |
| [4] | Li Haojing, Wang Xin, Song Chenglin, Zhang Shengnan, Chen Yunxin. Therapeutic efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the upper trapezius muscle area combined with exercise control training in patients with chronic non-specific neck pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1162-1170. |
| [5] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [6] | Yu Huifen, Mo Licun, Cheng Leping. The position and role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the repair of tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1196-1206. |
| [7] | Wang Zhengye, Liu Wanlin, Zhao Zhenqun. Advance in the mechanisms underlying miRNAs in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1207-1214. |
| [8] | Bu Yangyang, Ning Xinli, Zhao Chen. Intra-articular injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the temporomandibular joint: different drugs with multiple combined treatment options [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1215-1224. |
| [9] | Wen Fan, Xiang Yang, Zhu Huan, Tuo Yanfang, Li Feng. Exercise improves microvascular function in patients with type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1225-1235. |
| [10] | Liu Xinyue, Li Chunnian, Li Yizhuo, Xu Shifang. Regeneration and repair of oral alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1247-1259. |
| [11] | Leng Xiaoxuan, Zhao Yuxin, Liu Xihua. Effects of different neuromodulatory stimulation modalities on non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s patients: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1282-1293. |
| [12] | Wen Xiaolong, Weng Xiquan, Feng Yao, Cao Wenyan, Liu Yuqian, Wang Haitao. Effects of inflammation on serum hepcidin and iron metabolism related parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1294-1301. |
| [13] | Yang Zeyu, Zhi Liang, Wang Jia, Zhang Jingyi, Zhang Qingfang, Wang Yulong, Long Jianjun. A visualized analysis of research hotspots in high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation from the macroscopic perspective [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1320-1330. |
| [14] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [15] | Yin Yongcheng, Zhao Xiangrui, Yang Zhijie, Li Zheng, Li Fang, Ning Bin. Effect and mechanism of peroxiredoxin 1 in microglial inflammation after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1106-1113. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||