Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (35): 7669-7678.doi: 10.12307/2025.953
Previous Articles Next Articles
Action mechanism of Gegenmaqi prescription in treatment of periarthritis of shoulder combined with type 2 diabetes based on TCMSP database
Wang Tong1, Zheng Yu2, Jia Chengming2, Yang Hu1, Zhang Guangfei1, Ji Yaoyao1
- 1Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712000, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Shaanxi Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Xi’an 710000, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2024-10-16Accepted:2024-12-14Online:2025-12-18Published:2025-05-07 -
Contact:Zheng Yu, MD, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Shaanxi Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Xi’an 710000, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Wang Tong, Master candidate, Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712000, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi Province, No. 2024JC-YBQN-0948 (to JCM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Tong, Zheng Yu, Jia Chengming, Yang Hu, Zhang Guangfei, Ji Yaoyao. Action mechanism of Gegenmaqi prescription in treatment of periarthritis of shoulder combined with type 2 diabetes based on TCMSP database[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7669-7678.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

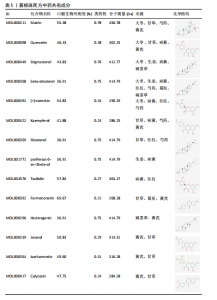
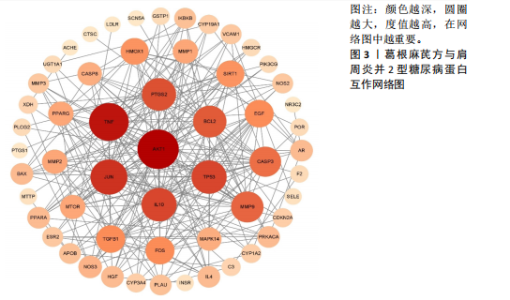
蛋白靶点63个;穿山龙有效成分1种,对应蛋白靶点15个;白芍有效成分8种,对应蛋白靶点92个;生姜有效成分4种,对应蛋白靶点54个;大枣有效成分17种,对应蛋白靶点117个;炙甘草有效成分 88种,对应蛋白靶点144个。将所有蛋白质靶点导入Uniprot数据库进行标准化处理,去除重复项,最终获得葛根麻芪方相关的蛋白靶点基因共217个,将数据以图片的形式可视化(图1)以表明各单味药之间的相互作用关系。 2.2 肩周炎和2型糖尿病蛋白靶点的收集 通过GenCards、OMIM、drugbank数据库分别获得肩周炎蛋白靶点1 236个、634个、64个,分别获得2型糖尿病蛋白靶点1 093个、522个、126个。利用 Uniprot 数据库进行确认并转换,剔除重复的蛋白靶点,整理得到肩周炎蛋白靶点1 843个,2型糖尿病蛋白靶点1 662个,共计肩周炎并2型糖尿病蛋白靶点2 830个。 2.3 葛根麻芪方蛋白靶点- 肩周炎并2型糖尿病蛋白靶点网络构建 通过数据库获得葛根麻芪方蛋白靶点217个,肩周炎并2型糖尿病疾病蛋白靶点2 830个。将两者靶点取交集,得到交集靶点基因65个,并制作韦恩图(图2)。 2.4 蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络的构建和核心靶点的筛选 通过导入数据,设置筛选条件后,将得到的剩余节点及其相互作用关系输入 Cytoscape 3.9.1 软件,以生成蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络图(图3)。此图共计56节点,251条边,颜色越深,圆圈越大,度值越高,在网络图中越重要。根据度值筛选核心靶点(表3),确定了AKT1、肿瘤坏死因子、JUN、TP53、白细胞介素10等5个核心靶点。因此作者猜想这些核心靶点在葛根麻芪方治疗肩周炎并2型糖尿病过程中发挥着关键作用。 2.5 靶点基因GO生物信息富集分析 David数据库是一个生物信息学资源系统,包括一个Web服务器和一个用于基因列表功能注释和富集分析的Web服务[15]。借助David数据库对65个交集靶点开展GO和KEGG富集分析。GO富集分析得到生物过程、"

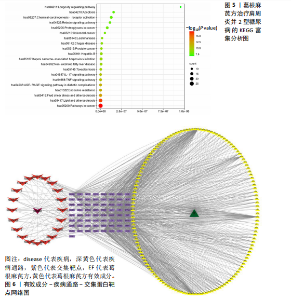
分子功能和细胞组分共计508条GO条目。其中生物过程相关条目390条,主要包括基因表达的调控、miRNA转录的正调控、DNA模板转录的正调控、细胞缺氧、细胞凋亡过程的正向调节、磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B信号转导的正调控、异种生物刺激的反应、对脂多糖的调控作用等。分子功能相关条目77条,主要涵盖蛋白质、酶、血红素的结合部位,以及类固醇结合蛋白、丝氨酸型内肽酶、蛋白同型二聚化、辅酶Ⅱ、核受体等细胞因子的活性。细胞组分相关条目41条,包括细胞核、细胞质基质、细胞外间隙、胞外区、内质网膜、线粒体等细胞结构。选择生物过程、分子功能、细胞组分前20条通路,利用微生信在线工具制作GO富集分析图(图4)。 2.6 靶点基因KEGG生物信息富集分析 KEGG富集分析得到146条KEGG功能条目(P < 0.05),取前20条通路进行富集分析,以网格图形式可视化。结果显示基因主要富集在高级糖基化终末产物-受体信号通路、脂质和动脉粥样硬化信号通路、肿瘤坏死因子信号通路、白细胞介素17信号通路(图5)。此外通过分析数据发现以上筛选的核心靶点AKT1、JUN、肿瘤坏死因子、TP53、白细胞介素10在此20条通路上显著出现。 2.7 中药有效成分-疾病通路-交集蛋白靶点网络图构建 将葛根麻芪方有效成分、KEGG前20条通路,通路对应靶点基因和交集靶点基因导入Cytoscape 3.9.1 软件构建网络图(图6)。 2.8 分子对接与分子动力学结果 分子对接结果显示,核心成分与核心靶点均有较好的结合活性(表4),一般认为,当结合能< -17.808 kJ/mol时,表示配体和受体之间存在一定的结合活性;结合能< -20.92 kJ/mol时,表示有较好的结合活性;而结合能< -29.288 kJ/mol时,则表示有强烈的结合活性[16]。研究所得结果均 < -20.92 kJ/mol,说明核心成分与核心靶点具有较好的结合活性。在葛根麻芪方治疗肩周炎并2型糖尿病的过程中,β-谷甾醇与核心靶点之间显示出较强的结合活性,这表明β-谷甾醇可能在其中扮演着关键角色。为了直观展示这一发现,使用Pymol软"

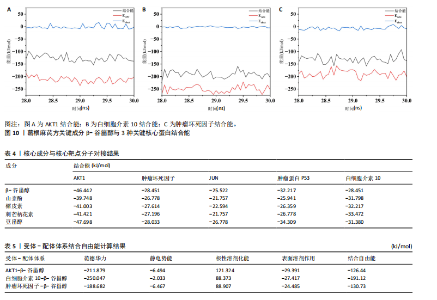
件对β-谷甾醇效果最佳的对接结果进行了可视化展示(图7)。 均方根偏差是评价蛋白质结构变化的指标,此次对配体-受体复合物进行常规30 ns的分子动力学模拟,图8展示了主链Cα的均方根偏差波动情况。在5 ns之后AKT1-β-谷甾醇体系的均方根偏差趋于稳定;白细胞介素10-β-谷甾醇体系在15 ns 后波动趋势稳定;肿瘤坏死因子-β-谷甾醇体系在10 ns后波动趋势稳定。3个体系在模拟过程中均达到了平衡,说明β-谷甾醇与3种关键核心蛋白的结合比较稳定。 均方根波动值能够体现每个氨基酸残基在模拟过程中的稳定性,如图9所示,AKT1-β-谷甾醇体系中残基4-45,245-273,286-293,315-343位点波动极小,很有可能通过氢键、疏水作用等作用力将配体包裹在活性口袋中,形成稳定复合物体系。白细胞介素10-β-谷甾醇体系在31-45氨基酸位点波动极大,不易形成氢键和疏水作用区域。肿瘤坏死因子-β-谷甾醇体系在30-58,71-95,98-115,118-133,137-146,160-175,180-195位点波动< 0.3,相对稳定,有理由猜测这些位点易形成活性空腔,配体可在其中稳定存在。 AKT1-β-谷甾醇、白细胞介素10-β-谷甾醇、肿瘤坏死因子-β-谷甾醇体系平均结合自由能分别是-126.44,-191.12,-130.73 kJ/mol(表5)。结合自由能越小,配体与受体之间的亲和力越高,配体越能稳定嵌入蛋白的活性口袋,利用ORIGIN 2022软件绘制在28-30 ns的能量变化曲线图(图10),其中EVDW代表范德华力,Elect代表静电势能。综合以上分析,白细胞介素10-β-谷甾醇的亲和力最高,与分子对接结果一致,白细胞介素10的Pro141,Phe139和Arg138与β-谷甾醇之间形成3个氢键(图7)。"

| [1] WALKER-BONE K, PALMER KT, READING I, et al. Prevalence and impact of musculoskeletal disorders of the upper limb in the general population. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;51(4):642-651. [2] ABUDULA X, MAIMAITI P, YASHENG A, et al. Factors associated with frozen shoulder in adults: a retrospective study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024;25(1):493. [3] GREEN HD, BURDEN E, CHEN J, et al. Hyperglycaemia is a causal risk factor for upper limb pathologies. Int J Epidemiol. 2024;53(1):dyad187. [4] 蔡玲.葛根汤辅助治疗糖尿病合并高血压患者的临床治疗体会[J].糖尿病新世界,2018,21(16):71-72. [5] LIU S, WANG L, ZHANG Z, et al. The potential of astragalus polysaccharide for treating diabetes and its action mechanism. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1339406. [6] GUO M, GAO J, JIANG L, et al. Astragalus Polysaccharide Ameliorates Renal Inflammatory Responses in a Diabetic Nephropathy by Suppressing the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023; 17:2107-2118. [7] LI YS, ZHANG J, TIAN GH, et al. Kirenol, darutoside and hesperidin contribute to the anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of Siegesbeckia pubescens makino by inhibiting COX-2 expression and inflammatory cell infiltration. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;268:113547. [8] SANG W, ZHONG Z, LINGHU K, et al. Siegesbeckia pubescens Makino inhibits Pam3CSK4-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophages through suppressing TLR1/TLR2-mediated NF-κB activation. Chin Med. 2018;13:37. [9] YU H, ZHENG L, XU L, et al. Potent effects of the total saponins from Dioscorea nipponica Makino against streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus in rats. Phytother Res. 2015;29(2):228-240. [10] RU J, LI P, WANG J, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform. 2014;6:13. [11] UNIPROT CONSORTIUM. UniProt: the Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51(D1):D523-D531. [12] BARSHIR R, FISHILEVICH S, INY-STEIN T, et al. GeneCaRNA: A Comprehensive Gene-centric Database of Human Non-coding RNAs in the GeneCards Suite. J Mol Biol. 2021;433(11):166913. [13] KNOX C, WILSON M, KLINGER CM, et al. DrugBank 6.0: the DrugBank Knowledgebase for 2024. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024;52(D1):D1265-D1275. [14] HAMOSH A, AMBERGER JS, BOCCHINI C, et al. Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM®): Victor McKusick’s magnum opus. Am J Med Genet A. 2021;185(11):3259-3265. [15] SHERMAN BT, HAO M, QIU J, et al. DAVID: a web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022; 50(W1):W216-W221. [16] 左文明,李锦萍,李彩明,等.UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS结合网络药理学和分子对接探讨椭圆叶花锚抗肝炎的药效物质及作用机制[J].天然产物研究与开发,2021, 33(11):1946-1956. [17] NEVIASER AS, NEVIASER RJ. Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011;19(9):536-542. [18] RAMÍREZ-ALARCÓN K, VICTORIANO M, MARDONES L, et al. Phytochemicals as Potential Epidrugs in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:656978. [19] CAGLIERO E, APRUZZESE W, PERLMUTTER GS, et al. Musculoskeletal disorders of the hand and shoulder in patients with diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 2002;112(6):487-490. [20] LU Y, WANG W, LIU J, et al. Vascular complications of diabetes: A narrative review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(40): e35285. [21] WU B, NIU Z, HU F. Study on Risk Factors of Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Establishment of Prediction Model. Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):526-538. [22] GREEN HD, JONES A, EVANS JP, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies 5 loci associated with frozen shoulder and implicates diabetes as a causal risk factor. PLoS Genet. 2021;17(6):e1009577. [23] ERRAHALI Y, MAJJAD A, ISSOUANI J, et al. Shoulder capsulitis: What relation with diabetes mellitus in a moroccan population? Ann Afr Med. 2023;22(1):45-48. [24] CHEN K, TIAN T, GAO P, et al. Unveiling potential therapeutic targets for diabetes-induced frozen shoulder through Mendelian randomization analysis of the human plasma proteome. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2024;12(3):e003966. [25] CSONKA V, VARJÚ C, LENDVAY M. Diabetes mellitus-related musculoskeletal disorders: Unveiling the cluster of diseases. Prim Care Diabetes. 2023;17(6):548-553. [26] DEEPIKA, MAURYA PK. Health Benefits of Quercetin in Age-Related Diseases. Molecules. 2022;27(8):2498. [27] BABU S, JAYARAMAN S. An update on β-sitosterol: A potential herbal nutraceutical for diabetic management. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110702. [28] 周强,张坤,李富强,等.β-谷甾醇缓解LPS诱导的急性肺损伤大鼠炎症反应和纤维化[J].西部医学,2022,34(6):813-818. [29] KHAN Z, NATH N, RAUF A, et al. Multifunctional roles and pharmacological potential of β-sitosterol: Emerging evidence toward clinical applications. Chem Biol Interact. 2022;365:110117. [30] VALITOVA J, RENKOVA A, BECKETT R, et al. Stigmasterol: An Enigmatic Plant Stress Sterol with Versatile Functions. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(15):8122. [31] Bakrim S, Benkhaira N, Bourais I, et al. Health Benefits and Pharmacological Properties of Stigmasterol. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(10):1912. [32] ALAM W, KHAN H, SHAH MA, et al. Kaempferol as a Dietary Anti-Inflammatory Agent: Current Therapeutic Standing. Molecules. 2020;25(18):4073. [33] PERIFERAKIS A, PERIFERAKIS K, BADARAU IA, et al. Kaempferol: Antimicrobial Properties, Sources, Clinical, and Traditional Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(23):15054. [34] BANGAR SP, CHAUDHARY V, SHARMA N, et al. Kaempferol: A flavonoid with wider biological activities and its applications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(28):9580-9604. [35] IMRAN M, SALEHI B, SHARIFI-RAD J, et al. Kaempferol: A Key Emphasis to Its Anticancer Potential. Molecules. 2019; 24(12):2277. [36] ZU G, SUN K, LI L, et al. Mechanism of quercetin therapeutic targets for Alzheimer disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):22959. [37] NGUYEN TLA, BHATTACHARYA D. Antimicrobial Activity of Quercetin: An Approach to Its Mechanistic Principle. Molecules. 20222;27(8):2494. [38] TIAN J, WANG XQ, TIAN Z. Focusing on Formononetin: Recent Perspectives for its Neuroprotective Potentials. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:905898. [39] XU HT, ZHENG Q, TAI ZG, et al. Formononetin attenuates psoriasiform inflammation by regulating interferon signaling pathway. Phytomedicine. 2024; 128:155412. [40] SIDDIKA T, BALASURIYA N, FREDERICK MI, et al. Delivery of Active AKT1 to Human Cells. Cells. 2022;11(23):3834. [41] CHEN J, SOMANATH PR, RAZORENOVA O, et al. Akt1 regulates pathological angiogenesis, vascular maturation and permeability in vivo. Nat Med. 2005;11(11):1188-1196. [42] FU J, YU MG, LI Q, et al. Insulin’s actions on vascular tissues: Physiological effects and pathophysiological contributions to vascular complications of diabetes. Mol Metab. 2021;52:101236. [43] BRADLEY JR. TNF-mediated inflammatory disease. J Pathol. 2008;214(2):149-160. [44] PARK JE, KANG E, HAN JS. HM-chromanone attenuates TNF-α-mediated inflammation and insulin resistance by controlling JNK activation and NF-κB pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022;921: 174884. [45] ZHU P, LIU G, WANG X, et al. Transcription factor c-Jun modulates GLUT1 in glycolysis and breast cancer metastasis. BMC Cancer. 2022;22(1):1283. |
| [1] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Chen Yueping, Chen Feng, Peng Qinglin, Chen Huiyi, Dong Panfeng . Based on UHPLC-QE-MS, network pharmacology, and molecular dynamics simulation to explore the mechanism of Panax notoginseng in treating osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1751-1760. |
| [3] | Fang Yuan, Qian Zhiyong, He Yuanhada, Wang Haiyan, Sha Lirong, Li Xiaohe, Liu Jing, He Yachao, Zhang Kai, Temribagen. Mechanism of Mongolian medicine Echinops sphaerocephalus L. in proliferation and angiogenesis of vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7519-7528. |
| [4] | Cai Zhixing, Xia Qiufang, Chen Lili, Zhu Danyang, Zhu Huiwen, Sun Yanan, Liang Wenyu, Zhao Heqian. Effect of Roujishuncuiyin on the improvement of skeletal muscle insulin resistance in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7537-7543. |
| [5] | Jiang Qiyu, Zeng Huiyan. A novel analysis and prediction method for potential mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine based on artificial intelligence and omics data-driven approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7552-7561. |
| [6] | Liu Xuan, Ding Yuqing, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang, Hu Shujuan. Exercise prevention and treatment of insulin resistance: role and molecular mechanism of Keap1/nuclear factor erythroid2-related factor 2 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7578-7588. |
| [7] | Wang Xuepeng, , He Yong, . Effect of insulin-like growth factor family member levels on inflammatory arthritis: a FinnGen biobank-based analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7656-7662. |
| [8] | Xu Biao, Dong Yuzhen, Lu Tan. Effect of dihydroquercetin on the expression of inflammatory response markers in rats with spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6843-6850. |
| [9] | Cui Yuena, Chen Xiaoyu, Liang Meiting, Chen Wujin, He Yi, Dilinur·Ekpa, Du Manxi, Zhu Yuqiu, Abuduwupuer·Haibier, Sun Yuping. Differences of calorie restriction and time-restricted feeding on metabolic indices and gut microbiota of mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6449-6456. |
| [10] | Zhang Xin, Guo Baojuan, Xu Huixin, Shen Yuzhen, Yang Xiaofan, Yang Xufang, Chen Pei. Protective effects and mechanisms of 3-N-butylphthalide in Parkinson’s disease cell models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6466-6473. |
| [11] | Liu Jian, Liu Qing, Huang Ye, Cao Guanglei, Liu Yuan, Song Qingpeng. Growth factors promote knee cartilage regeneration: a bibliometric analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6351-6359. |
| [12] | Geng Longyu, Sheng Li, Bai Shuo, Gao Beiyao, Ge Ruidong, Jiang Shan . Role and molecular mechanism of pyroptosis in motor system diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5695-5703. |
| [13] | Liu Yuan, Qu Yuan, Wan Yakun, Guo Jingyu, Jiang Ping. Transcriptomic analysis and drug prediction of basement membrane-related genes in different traditional Chinese medicine patterns of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5486-5500. |
| [14] | Lin Yixin, Wang Wenyi, Lei Xiaoqing, Ma Dezun, Huang Yanfeng, Fu Changlong, Ye Jinxia. Tougu Xiaotong Capsules for treating arthritis according to the principle of “Same Treatment for Different diseases”: analysis based on integrated pharmacology, molecular docking techniques and molecular dynamics simulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5093-5101. |
| [15] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: data analysis of serum metabolite and inflammatory factor in the European population [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5263-5271. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||