Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (29): 6351-6359.doi: 10.12307/2025.788
Previous Articles Next Articles
Growth factors promote knee cartilage regeneration: a bibliometric analysis of research hotspots
Liu Jian, Liu Qing, Huang Ye, Cao Guanglei, Liu Yuan, Song Qingpeng
- Department of knee preservation surgery, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing 102208, China
-
Received:2024-10-16Accepted:2024-11-13Online:2025-10-18Published:2025-03-10 -
Contact:Huang Ye, MS, Chief physician, Department of Knee preservation Surgery, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing 102208, China -
About author:Liu Jian, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Knee preservation Surgery, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing 102208, China Liu Qing, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Knee preservation Surgery, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing 102208, China Liu Jian and Liu Qing contributed equally to this article.
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Jian, Liu Qing, Huang Ye, Cao Guanglei, Liu Yuan, Song Qingpeng. Growth factors promote knee cartilage regeneration: a bibliometric analysis of research hotspots[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6351-6359.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
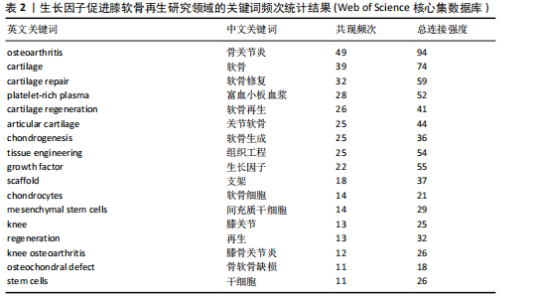
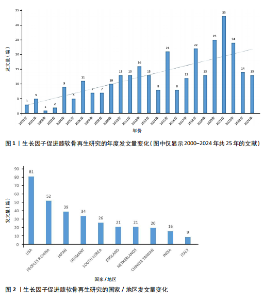
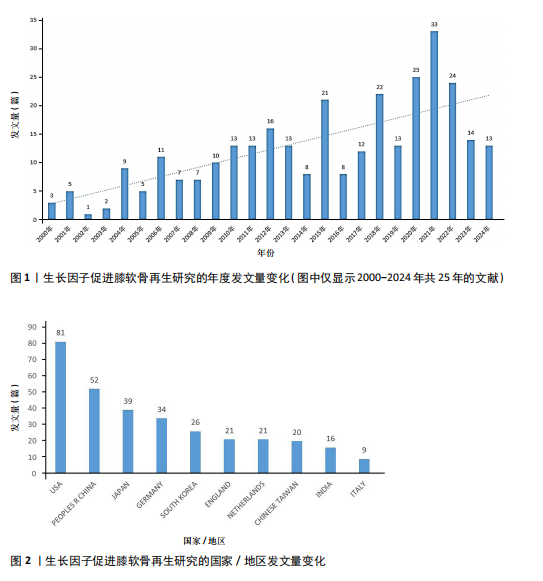
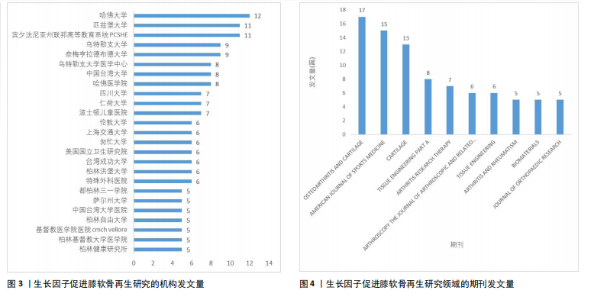
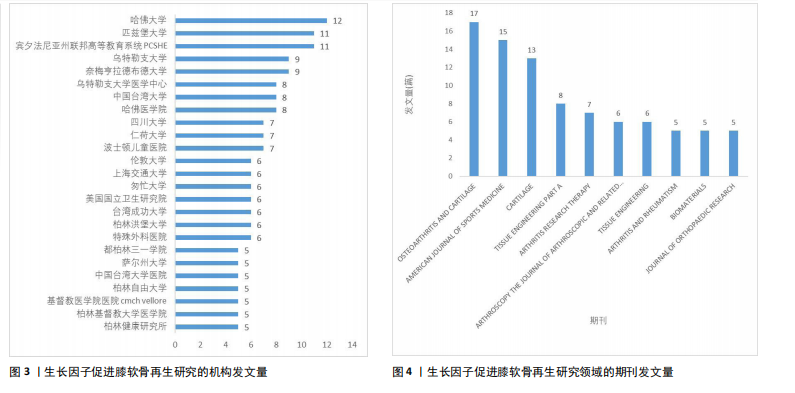
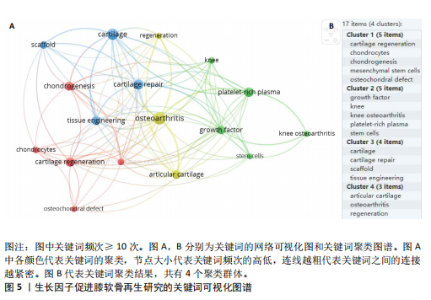
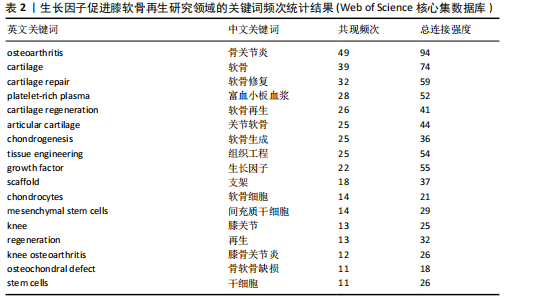
2.1 年度发文量分析 从2000-2024年,该领域的年度发文量总体趋势不断增加,其中2021年发文量最高(33篇),见图1。 2.2 国家/地区分析 该领域发文量最高的3个国家为美国81篇,中国52篇,日本39篇,见图2。 2.3 机构分析 该领域发文量最高的3个机构为哈佛大学12篇,匹兹堡大学11篇,宾夕法尼亚州联邦高等教育系统PCSHE 11篇,均为美国机构,中国台湾大学8篇和四川大学7篇分别位于第7,10位,见图3。 2.4 期刊分析 该领域发文量最高的前3个期刊为《AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SPORTS MEDICINE》17篇,《CARTILAGE》15篇,《TISSUE ENGINEERING PART A》13篇,见图4。 2.5 关键词分析 采用VOSveiwer 1.6.19软件绘制关键词可视化图谱。关键词频次最高的前5个关键词为骨关节炎、软骨、软骨修复、富血小板血浆、软骨再生,见表2。用关键词频次≥10次的关键词构建可视化图谱,见图5,图中可见关键词聚类分4类:聚类1:软骨再生,软骨细胞,软骨生成,间充质干细胞,骨软骨缺损(关注细胞疗法促进软骨再生);聚类2:生长因子,膝关节,膝骨关节炎,富血小板血浆,干细胞(关注生长因子疗法治疗膝骨关节炎);聚类3:软骨,软骨修复,支架,组织工程(关注软骨组织工程);聚类4:关节软骨,"

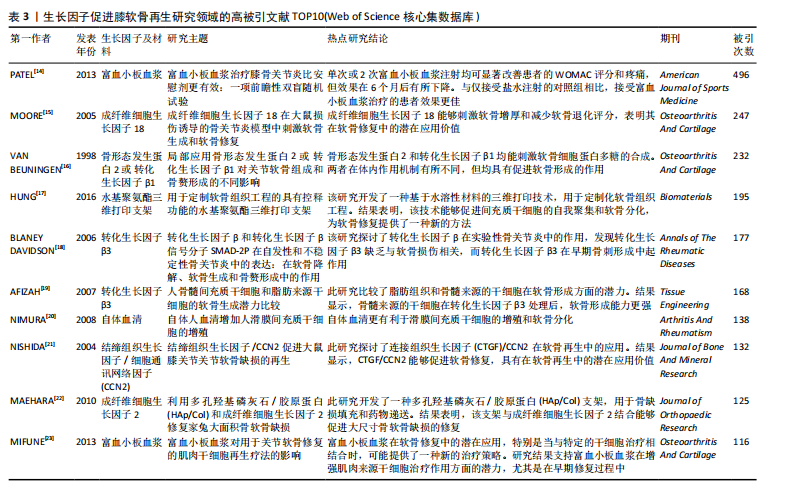
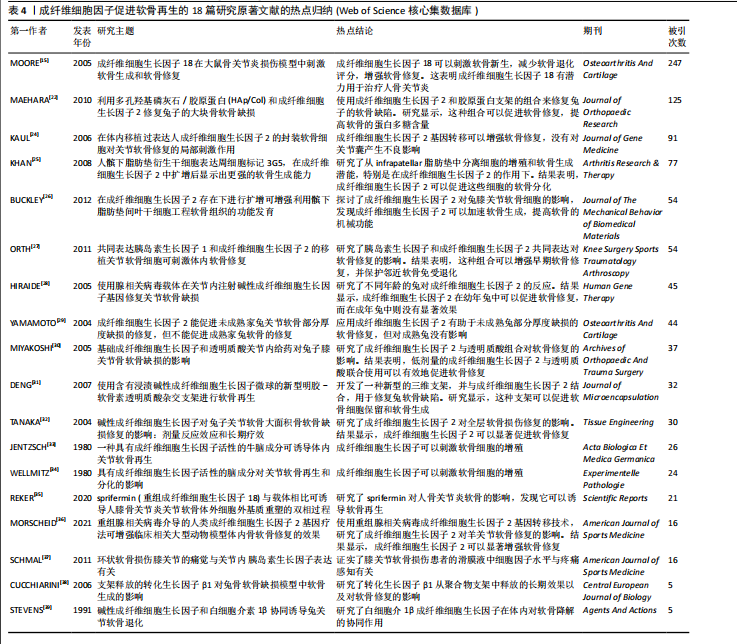
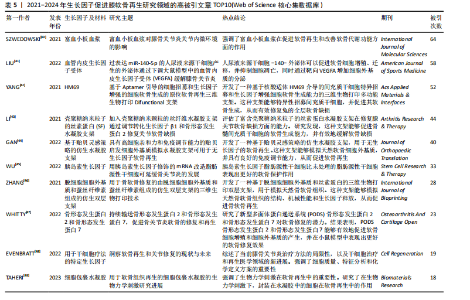
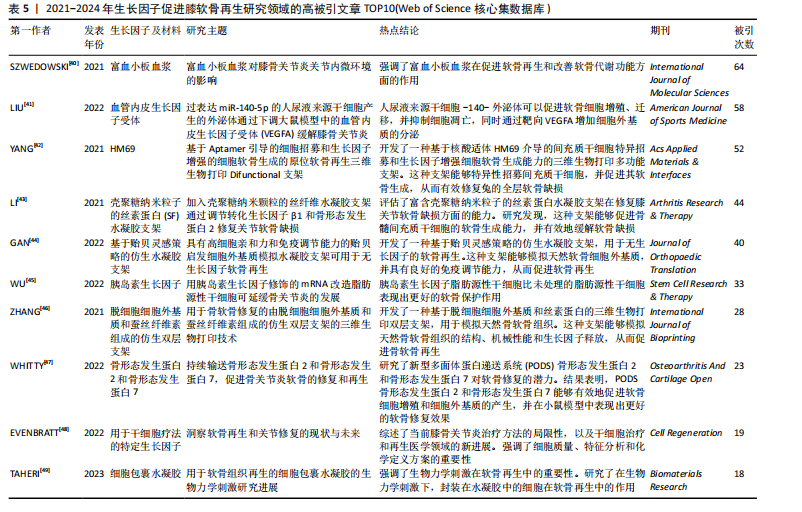
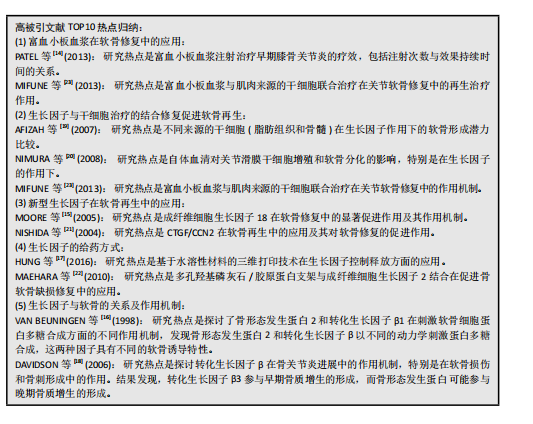
骨关节炎,再生(关注关节软骨的再生)。 2.6 高被引文献分析 该领域被引频次最高的文献为PATEL等[14]在2013年发表的临床研究“富血小板血浆治疗膝骨关节炎比安慰剂更有效:一项前瞻性双盲随机试验”,被引496次;其次是MOORE等[15]在2005年发表的基础研究“成纤维细胞生长因子18 在大鼠损伤诱导的骨关节炎模型中刺激软骨生成和软骨修复”,被引247次;被引次数排名第3位的是VAN BEUNINGEN等[16]与1998年发表的基础研究“局部应用骨形态发生蛋白2或转化生长因子β1对关节软骨组成和骨赘形成的不同影响”,被引232篇;以上3篇文章是该领域影响力最高的3篇文章。 表3中的高被引文献TOP10的热点体现了生长因子在软骨再生领域的多个关键问题,包括生长因子的选择、作用机制、与干细胞治疗的结合、给药方式、临床应用以及特定生长因子的应用[14-23]。 2.7 成纤维细胞因子的热点归纳 在321篇文献中,关于成纤维细胞因子与软骨再生的研究原著文献有18篇[15,22,24-39],被引次数最高的是上述表3提到的Moore[15](2005)的文章,被引247次;所涉及的因子主要包括成纤维细胞生长因子2,18,见表4。 表4表明,成纤维细胞生长因子2及其相关生长因子在软骨修复中具有重要作用,可以通过刺激软骨新生和减少软骨降解来促进软骨修复,这些研究为开发新的软骨修复策略提供了重要的基础。这些研究热点的共同目标是通过深入理解和优化生长因子的作用机制和应用方式,开发出更有效、更安全的软骨修复治疗方法,以应对骨关节炎等疾病引起的软骨损伤问题。目前的成纤维细胞生长因子与软骨再生文章热点集中在以下10个方面: 2.8 最新文献研究热点分析 作者检索了2021年1月至2024年9月的该领域文献,分析被引情况,列举了2021-2024年该领域高被引文章TOP10[40-49],见表5。表5中各文献总结的研究热点的主要是研究者们通过深入理解和优化生长因子的作用机制和应用方式,开发出更有效、更安全的软骨修复治疗方法,以应对骨关节炎等疾病引起的软骨损伤问题。 2021-2024年该领域高被引文章TOP10关于生长因子促进膝软骨再生的研究热点,主要为LIU等[41] (2022)的miR-140-5p工程化细胞外囊泡疗法;LI等[43] (2021)使用了丝素蛋白水凝胶支架递送转化生长因子β1和骨形态发生蛋白2;WHITTY等[47] (2022)研究了多面体蛋白(生长因子)递送系统(polyhedrin delivery system,PODS)与骨形态发生蛋白2和骨形态发生蛋白7的应用效果。"
| [1] XIE Y, ZINKLE A, CHEN L, et al. Fibroblast growth factor signalling in osteoarthritis and cartilage repair. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(10):547-564. [2] WEN C, XU L, XU X, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 in articular cartilage repair for osteoarthritis treatment. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):277. [3] SHAH SS, MITHOEFER K. Current applications of growth factors for knee cartilage repair and osteoarthritis treatment. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2020;13(6):641-650. [4] PUJOL JP, CHADJICHRISTOS C, LEGENDRE F, et al. Interleukin-1 and transforming growth factor-beta 1 as crucial factors in osteoarthritic cartilage metabolism. Connect Tissue Res. 2008;49(3):293-297. [5] VAN DEN BERG WB. The role of cytokines and growth factors in cartilage destruction in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Z Rheumatol. 1999;58(3):136-141. [6] BOEHME KA, ROLAUFFS B. Onset and progression of human osteoarthritis-can growth factors, inflammatory cytokines, or differential mirna expression concomitantly induce proliferation, ECM degradation, and inflammation in articular cartilage? Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(8):2282. [7] MURATA M, YUDOH K, MASUKO K. The potential role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in cartilage: how the angiogenic factor could be involved in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis? Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16(3):279-286. [8] 杨冠,杨晓. TGF-β超家族在软骨发生、发育和维持中的作用[J].遗传,2008, 30(8):953-959. [9] 谢杨丽,黄俊兰,陈涵纲,等.成纤维细胞生长因子信号在骨损伤修复中的作用[J].生命科学,2020,32(3):239-244. [10] 黄刚,任富川,冯程程,等.富血小板血浆在骨关节炎方面的全球研究特征及趋势:文献计量分析[J].四川生理科学杂志, 2023,45(9):1750-1756. [11] VAN ECK NJ, WALTMAN L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 2010; 84:523-538. [12] DONTHU N, KUMAR S, MUKHERJEE D, et al. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: an overview and guidelines. J Bus Res. 2021; 133:285-296. [13] RANJBARI M, SHAMS ESFANDABADI Z, GAUTAM S, et al. Waste management beyond the COVID-19 pandemic: bibliometric and text mining analyses. Gondwana Res. 2023;114:124-137. [14] PATEL S, DHILLON MS, AGGARWAL S, et al. Treatment with platelet-rich plasma is more effective than placebo for knee osteoarthritis: a prospective, double-blind, randomized trial. Am J Sports Med. 2013; 41(2):356-364. [15] MOORE EE, BENDELE AM, THOMPSON DL, et al. Fibroblast growth factor-18 stimulates chondrogenesis and cartilage repair in a rat model of injury-induced osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005;13(7):623-631. [16] VAN BEUNINGEN HM, GLANSBEEK HL, VAN DER KRAAN PM, et al. Differential effects of local application of BMP-2 or TGF-beta 1 on both articular cartilage composition and osteophyte formation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1998;6(5):306-317. [17] HUNG KC, TSENG CS, DAI LG, et al. Water-based polyurethane 3D printed scaffolds with controlled release function for customized cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2016;83:156-168. [18] BLANEY DAVIDSON EN, VITTERS EL, VAN DER KRAAN PM, et al. Expression of transforming growth factor-beta (TGFbeta) and the TGFbeta signalling molecule SMAD-2P in spontaneous and instability-induced osteoarthritis: role in cartilage degradation, chondrogenesis and osteophyte formation. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(11):1414-1421. [19] AFIZAH H, YANG Z, HUI JH, et al. A comparison between the chondrogenic potential of human bone marrow stem cells (BMSCs) and adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) taken from the same donors. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(4):659-666. [20] NIMURA A, MUNETA T, KOGA H, et al. Increased proliferation of human synovial mesenchymal stem cells with autologous human serum: comparisons with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and with fetal bovine serum. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(2):501-510. [21] NISHIDA T, KUBOTA S, KOJIMA S, et al. Regeneration of defects in articular cartilage in rat knee joints by CCN2 (connective tissue growth factor). J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19(8):1308-1319. [22] MAEHARA H, SOTOME S, YOSHII T, et al. Repair of large osteochondral defects in rabbits using porous hydroxyapatite/collagen (HAp/Col) and fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2). J Orthop Res. 2010;28(5): 677-686. [23] MIFUNE Y, MATSUMOTO T, TAKAYAMA K, et al. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on the regenerative therapy of muscle derived stem cells for articular cartilage repair. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(1):175-185. [24] KAUL G, CUCCHIARINI M, ARNTZEN D, et al. Local stimulation of articular cartilage repair by transplantation of encapsulated chondrocytes overexpressing human fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF-2) in vivo. J Gene Med. 2006;8(1):100-111. [25] KHAN WS, TEW SR, ADESIDA AB, et al. Human infrapatellar fat pad-derived stem cells express the pericyte marker 3G5 and show enhanced chondrogenesis after expansion in fibroblast growth factor-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(4):R74. [26] BUCKLEY CT, KELLY DJ. Expansion in the presence of FGF-2 enhances the functional development of cartilaginous tissues engineered using infrapatellar fat pad derived MSCs. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012;11:102-111. [27] ORTH P, KAUL G, CUCCHIARINI M, et al. Transplanted articular chondrocytes co-overexpressing IGF-I and FGF-2 stimulate cartilage repair in vivo. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(12):2119-2130. [28] HIRAIDE A, YOKOO N, XIN KQ, et al. Repair of articular cartilage defect by intraarticular administration of basic fibroblast growth factor gene, using adeno-associated virus vector. Hum Gene Ther. 2005;16(12):1413-1421. [29] YAMAMOTO T, WAKITANI S, IMOTO K, et al. Fibroblast growth factor-2 promotes the repair of partial thickness defects of articular cartilage in immature rabbits but not in mature rabbits. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2004;12(8):636-641. [30] MIYAKOSHI N, KOBAYASHI M, Nozaka K, et al. Effects of intraarticular administration of basic fibroblast growth factor with hyaluronic acid on osteochondral defects of the knee in rabbits. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005;125(10):683-692. [31] DENG T, HUANG S, ZHOU S, et al. Cartilage regeneration using a novel gelatin-chondroitin-hyaluronan hybrid scaffold containing bFGF-impregnated microspheres. J Microencapsul. 2007;24(2):163-174. [32] TANAKA H, MIZOKAMI H, SHIIGI E, et al. ffects of basic fibroblast growth factor on the repair of large osteochondral defects of articular cartilage in rabbits: dose-response effects and long-term outcomes. Tissue Eng. 2004;10(3-4):633-641. [33] JENTZSCH KD, WELLMITZ G, HEDER G, et al. A bovine brain fraction with fibroblast growth factor activity inducing articular cartilage regeneration in vivo. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1980;39(8-9):967-971. [34] WELLMITZ G, PETZOLD E, JENTZSCH KD, et al.The effect of brain fraction with fibroblast growth-factor activity on regeneration and differentiation of articular-cartilage. Exp Pathol-Jena. 1980;18(5):282-287. [35] REKER D, SIEBUHR AS, THUDIUM CS, et al. Sprifermin (rhFGF18) versus vehicle induces a biphasic process of extracellular matrix remodeling in human knee OA articular cartilage ex vivo. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):6011. [36] MORSCHEID YP, VENKATESAN JK, SCHMITT G, et al. rAAV-mediated human FGF-2 gene therapy enhances osteochondral repair in a clinically relevant large animal model over time in vivo. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49(4):958-969. [37] SCHMAL H, NIEMEYER P, SÜDKAMP NP, et al. Pain perception in knees with circumscribed cartilage lesions is associated with intra-articular IGF-1 expression. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(9):1989-1996. [38] CUCCHIARINI M, SOHIER J, MITOSCH K, et al. Effect of transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) released from a scaffold on chondrogenesis in an osteochondral defect model in the rabbit. Cent Eur J Biol. 2006;1(1):43-60. [39] STEVENS P, SHATZEN EM. Synergism of basic fibroblast growth factor and interleukin-1 beta to induce articular cartilage-degradation in the rabbit. Agents Actions. 1991;34(1-2):217-219. [40] SZWEDOWSKI D, SZCZEPANEK J, PACZESNY Ł, et al. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on the intra-articular microenvironment in knee osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(11):5492. [41] LIU Y, ZENG Y, SI HB, et al. Exosomes derived from human urine-derived stem cells overexpressing miR-140-5p alleviate knee osteoarthritis through downregulation of VEGFA in a rat model. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(4):1088-1105. [42] YANG Z, ZHAO T, GAO C, et al. 3D-Bioprinted difunctional scaffold for in situ cartilage regeneration based on aptamer-directed cell recruitment and growth factor-enhanced cell chondrogenesis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(20):23369-23383. [43] LI Y, LIU Y, GUO Q. Silk fibroin hydrogel scaffolds incorporated with chitosan nanoparticles repair articular cartilage defects by regulating TGF-β1 and BMP-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):50. [44] GAN D, JIANG Y, HU Y, et al. Mussel-inspired extracellular matrix-mimicking hydrogel scaffold with high cell affinity and immunomodulation ability for growth factor-free cartilage regeneration. J Orthop Translat. 2022;33:120-131. [45] WU H, PENG Z, XU Y, et al. Engineered adipose-derived stem cells with IGF-1-modified mRNA ameliorates osteoarthritis development. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022; 13(1):19. [46] ZHANG X, LIU Y, ZUO Q, et al. 3D Bioprinting of biomimetic bilayered scaffold consisting of decellularized extracellular matrix and silk fibroin for osteochondral repair. Int J Bioprint. 2021;7(4):401. [47] WHITTY C, PERNSTICH C, MARRIS C, et al. Sustained delivery of the bone morphogenetic proteins BMP-2 and BMP-7 for cartilage repair and regeneration in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil Open. 2022; 4(1):100240. [48] EVENBRATT H, ANDREASSON L, BICKNELL V, et al. Insights into the present and future of cartilage regeneration and joint repair. Cell Regen. 2022;11(1):3. [49] TAHERI S, GHAZALI HS, GHAZALI ZS, et al. Progress in biomechanical stimuli on the cell-encapsulated hydrogels for cartilage tissue regeneration. Biomater Res. 2023; 27(1):22. |
| [1] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Ma Chi, Wang Ning, Chen Yong, Wei Zhihan, Liu Fengji, Piao Chengzhe. Application of 3D-printing patient-specific instruments combined with customized locking plate in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1863-1869. |
| [3] | Han Haihui, Ran Lei, Meng Xiaohui, Xin Pengfei, Xiang Zheng, Bian Yanqin, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling to improve bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1905-1912. |
| [4] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [5] | Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Wan Haili, Chang Ying, Xiong Wenjuan, Xia Yuan. Effect of neuromuscular exercise for knee osteoarthritis pain and function: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [6] | Liang Haobo, Wang Zeyu, Ma Wenlong, Liu Hao, Liu Youwen. Hot issues in the field of joint revision: infection, rehabilitation nursing, bone defect, and prosthesis loosening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1963-1971. |
| [7] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [8] | Wang Peiguang, Zhang Xiaowen, Mai Meisi, Li Luqian, Huang Hao. Generalized equation estimation of the therapeutic effect of floating needle therapy combined with acupoint embedding on different stages of human knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1565-1571. |
| [9] | Wang Juan, Wang Guanglan, Zuo Huiwu. Efficacy of exercise therapy in the treatment of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients: #br# a network meta-analysis #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1714-1726. |
| [10] | Xie Liugang, Cui Shuke, Guo Nannan, Li Aoyu, Zhang Jingrui. Research hotspots and frontiers of stem cells for Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1475-1485. |
| [11] | Chang Jinxia, Liu Yufei, Niu Shaohui, Wang Chang, Cao Jianchun. Visualization analysis of macrophage polarization in tissue repair process [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1486-1496. |
| [12] | Peng Hongcheng, Peng Guoxuan, Lei Anyi, Lin Yuan, Sun Hong, Ning Xu, Shang Xianwen, Deng Jin, Huang Mingzhi . Role and mechanism of platelet-derived growth factor BB in repair of growth plate injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1497-1503. |
| [13] | Chen Yuning, Jiang Ying, Liao Xiangyu, Chen Qiongjun, Xiong Liang, Liu Yue, Liu Tong. Buqi Huoxue Compounds intervene with the expression of related factors and autophagy related proteins in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1152-1158. |
| [14] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [15] | Ma Haoyu, Qiao Hongchao, Hao Qianqian, Shi Dongbo. Causal effects of different exercise intensities on the risk of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1305-1311. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||