Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (29): 6343-6350.doi: 10.12307/2025.794
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bioinformatic analysis on expression of Foxp3 in tumor microenvironment of ovarian cancer and its relationship with survival prognosis
Lin Rongqin1, Pan Xiuxie2, Bian Lihong3
- 1Chinese PLA Medical School, Beijing 100039, China; 2Beijing Immune Ark Medical Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing 100141, China; 3Fifth Medical Center of Chinese People’s Liberation Army General Hospital, Beijing 100071, China
-
Received:2024-09-10Accepted:2024-11-12Online:2025-10-18Published:2025-03-10 -
Contact:Bian Lihong, MD, Professor, Fifth Medical Center of Chinese People’s Liberation Army General Hospital, Beijing 100071, China -
About author:Lin Rongqin, MS, Chinese PLA Medical School, Beijing 100039, China -
Supported by:Beijing Natural Science Foundation Project, No. 18JS010 (to BLH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lin Rongqin, Pan Xiuxie, Bian Lihong. Bioinformatic analysis on expression of Foxp3 in tumor microenvironment of ovarian cancer and its relationship with survival prognosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6343-6350.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
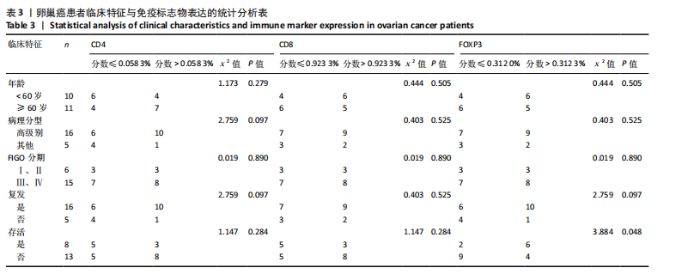
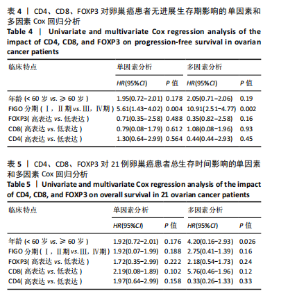
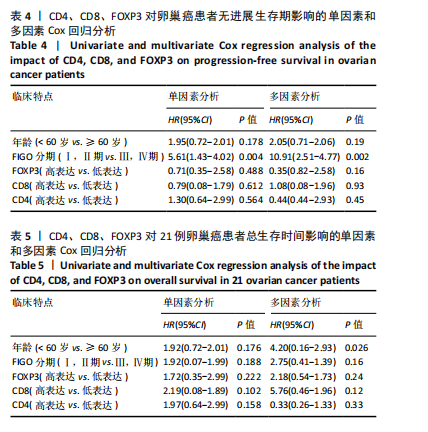
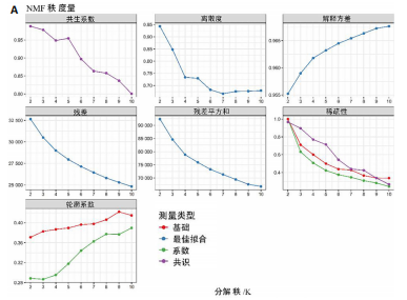
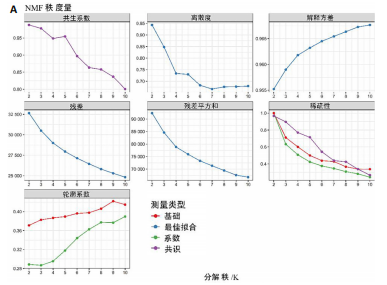
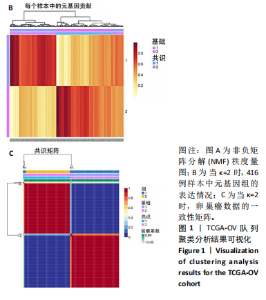
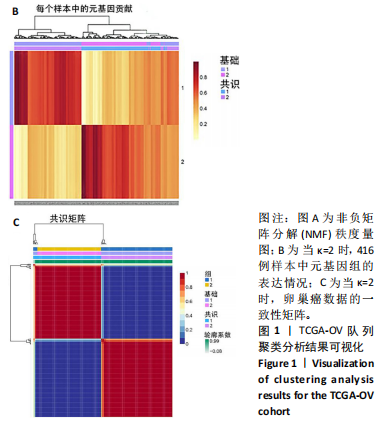
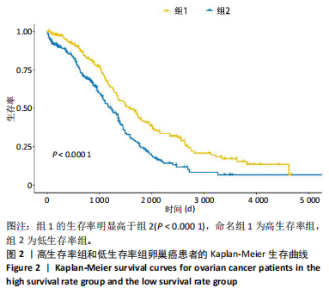
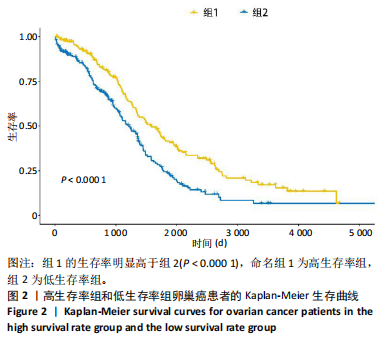
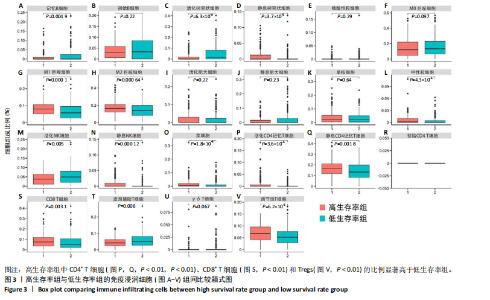
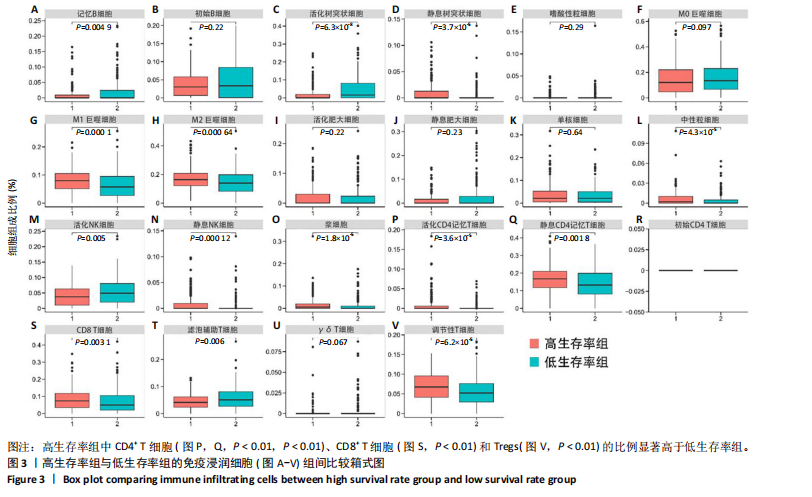
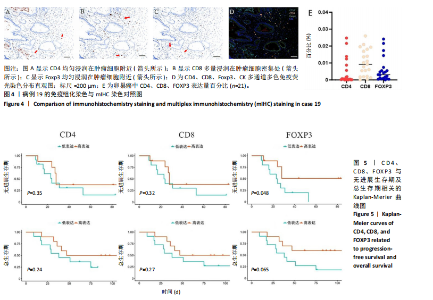
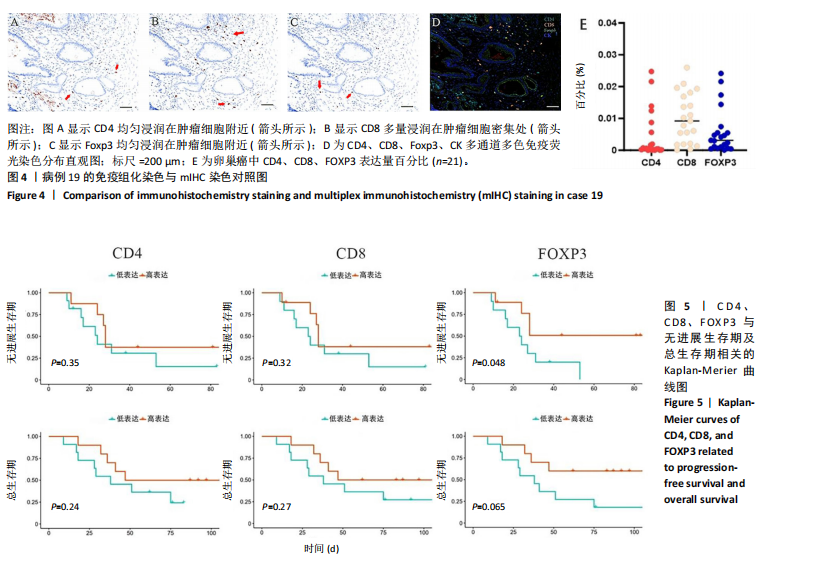
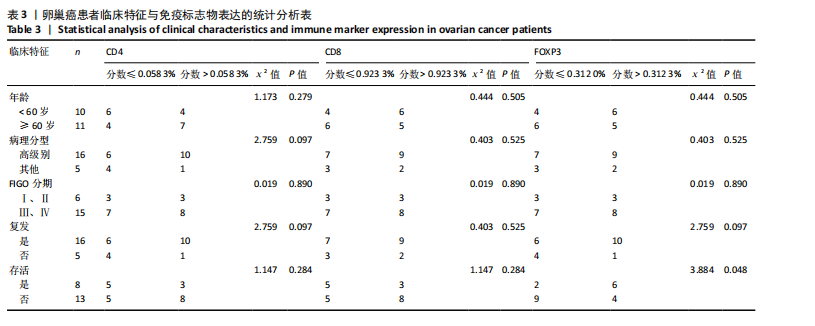
2.1 TCGA-OV患者聚类分析及生存分析 矩阵分解秩κ决定了NMF模型中基矩阵和系数矩阵的列数。见图1A,在κ=2时,多数评估指标(共生系数、离散度、解释方差、残差、残差平方和、稀疏性和轮廓系数)表现出理想的平衡状态,尽管某些指标在κ > 2时有所改善,但其增益减小且可能引入过拟合风险,因此κ=2确保模型稳健并提供良好解释方差和聚类质量。从图1B,C可以看出,当κ=2时,元基因组热图和一致性矩阵热图较为稳定,组间的差异明显。 根据NMF算法将卵巢癌患者分为2组:组1(高生存率组)包含225例患者,组2(低生存率组)包含191例患者。Kaplan-Meier生存分析结果显示,组1的生存率明显高于组2(P < 0.000 1),见图2。 2.2 对416例TCGA-OV患者免疫细胞浸润水平的比较分析 利用CIBERSORT算法统计了队列中亚组免疫细胞浸润水平,见图3。高生存率组中活化的记忆CD8+ T细胞(P < 0.001)、静息的记忆CD8+ T细胞(P < 0.01)、CD8+ T细胞(P < 0.01)和Tregs(P < 0.001)的浸润比例显著高于低生存组,提示这些细胞亚群在肿瘤免疫微环境中的作用可能与卵巢癌患者更好的预后相关。 2.3 患者上皮性卵巢癌肿瘤微环境中相关免疫细胞标志物的表达 见图4。CD8+ T细胞、CD8+ T细胞、Foxp3+ Tregs的标记物均以不同程度浸润在肿瘤组织中。以CD4、CD8和FOXP3的表达量中位数为分界点,将表达量高于中位数的样本归类为高表达组,而低于中位数的样本归类为低表达组。 2.4 患者上皮性卵巢癌患者肿瘤微环境中相关免疫细胞标志物表达与临床特征的关系 通过对卵巢癌患者的病理资料进行分析(见表3),Foxp3的高表达与患者的存活概率显著提高有统计学意义(χ2=3.884,P < 0.05),但与患者的年龄、病理类型、FIGO分期和复发情况等因素无显著"
| [1] ZHANG S, CHENG C, LIN Z, et al. The global burden and associated factors of ovarian cancer in 1990–2019: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. BMC Public Health. 2022;22(1):1455. [2] 赵虹琳,李婷婷,丁国武.1990-2019年中国女性卵巢癌疾病负担趋势分析[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志,2023,30(9):507-512. [3] LV B, WANG Y, MA D, et al. Immunotherapy: Reshape the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Front Immunol. 2022;13:844142. [4] TANG Y, QIAO G, ZHENG H. CD8+ T cell-based cancer immunotherapy. J Transl Med. 2024;22(1):394. [5] RICHARDSON JR, SCHÖLLHORN A, GOUTTEFANGEAS C, et al. CD4+ T Cells: Multitasking Cells in the Duty of Cancer Immunotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(4):596. [6] DUTSCH-WICHEREK M, SZUBERT S, DZIOBEK K, et al. Analysis of the Treg cell population in the peripheral blood of ovarian cancer patients in relation to the long-term outcomes. Ginekol Pol. 2019;90(2):72-79. [7] SATO S, MATSUSHITA H, SHINTANI D, et al. Association between effector-type regulatory T cells and immune checkpoint expression on CD8+ T cells in malignant ascites from epithelial ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer. 2022;22(1):437. [8] PANIGORO SS, HERIYANTO DS, STEVEN R, et al. The association of immune cell infiltration with metastasis location in de novo metastatic triple negative breast cancer: A multicenter cross-sectional study in Indonesia. Acta Med Indones. 2023;55(4):376-384. [9] FANG D.Targeting a Treg-specific deubiquitinase module for antitumor immune therapy. Cancer Immunol Res. 2023;11(12_Supplement):B038. [10] YU M, ZHOU V, PISANO MD, et al. Transgenic Mouse Model for Translational Immunotherapy Studies on Multiple Myeloma. Blood. 2023;142(Supplement 1):6565. [11] Li C, JIANG P, WEI S, et al. Regulatory T cells in tumor microenvironment: new mechanisms, potential therapeutic strategies and future prospects. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):116. [12] SALMI S, LIN A, HIRSCHOVITS-GERZ B, et al. The role of FoxP3+ regulatory T cells and IDO+ immune and tumor cells in malignant melanoma - an immunohistochemical study. BMC Cancer. 2021; 21(1):641. [13] MA K, SUN Z, LI X, et al. Forkhead box M1 recruits FoxP3+ Treg cells to induce immune escape in hilar cholangiocarcinoma.Immun Inflamm Dis.2022;10(11):e727. [14] 田亚红,高向东,姚文兵,等.CD4+T细胞在肿瘤免疫治疗中的作用与应用研究进展[J].药学进展,2024,48(6):463-470. [15] Montauti E, Oh DY, Fong L.CD4 T cells in antitumor immunity. Trends Cancer. 2024;10(10):969-985. [16] Peres LC, Cushing-Haugen KL, Köbel M,et al.Invasive Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Survival by Histotype and Disease Stage. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2019;111(1):60-68. [17] LI L, CHEN D, LUO X, et al. Identification of CD8+ T Cell Related Biomarkers in Ovarian Cancer. Front Genet. 2022;13:860161. [18] SALEH R, ELKORD E.FoxP3+ T regulatory cells in cancer: Prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Cancer Lett. 2020;490:174-185. [19] SHOHAN, MUS, CHATTERJEE D, OISHY TA ,et al. Role of regulatory immune cells in tumour microenvironment (TME)//Interdisciplinary Cancer Research. Springer, Cham. 2024:1-14. [20] QIU Y, KE S, CHEN J,et al. FOXP3+ regulatory T cells and the immune escape in solid tumours. Front Immunol. 2022;13:982986. [21] XIAO J, CHEN X, XU J, et al. The Role of FOXP3 on Tumor Metastasis and Its Interaction with Traditional Chinese Medicine. Molecules. 2022;27(19):6706. [22] GOLZARI-SORKHEH M, ZÚÑIGA-PFLÜCKER JC. Development and function of FOXP3+ regulators of immune responses. Clin Exp Immunol. 2023;213(1):13-22. [23] DAKAL TC, GEORGE N, XU C, et al. Predictive and Prognostic Relevance of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells. Cancers (Basel). 2024;16(9):1626. [24] CHAUDHURI SM, WEINBERG SE, WANG D,et al.Mediator complex subunit 1 architects a tumorigenic Treg cell program independent of inflammation. Cell Rep Med. 2024;5(3):101441. [25] Hosseinalizadeh H, Rabiee F, Eghbalifard N, et al.Regulating the regulatory T cells as cell therapies in autoimmunity and cancer. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1244298. [26] LAUNONEN IM, LYYTIKÄINEN N, CASADO J, et al. Single-cell tumor-immune microenvironment of BRCA1/2 mutated high-grade serous ovarian cancer.Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):835. [27] SHANG B, LIU Y, JIANG SJ, et al. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2015;5:15179. [28] LEE S, CHO EY, PARK YH, et al. Prognostic impact of FOXP3 expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Acta Oncol. 2013;52(1):73-81. [29] UKITA M, HAMANISHI J, YOSHITOMI H, et al. CXCL13-producing CD4+ T cells accumulate in the early phase of t ertiary lymphoid structures in ovarian cancer. JCI Insight. 2022;7(12):e157215. [30] BOBISSE S, GENOLET R, ROBERTI A, et al. Sensitive and frequent identification of high avidity neo-epitope specific CD8+ T cells in immunotherapy-naive ovarian cancer. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1092. [31] DE MARTINO M, DAVIAUD C, DIAMOND JM,et al. Activin A Promotes Regulatory T-cell-Mediated Immunosuppression in Irradiated Breast Cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 2021;9(1):89-102. [32] KOS K, ASLAM MA, VAN DE VEN R, et al. Tumor-educated Tregs drive organ-specific metastasis in breast cancer by impairing NK cells in the lymph node niche.Cell Rep. 2022;38(9):110447. [33] WANG W, LOPEZ MCDONALD MC, KIM C, et al. The complementary roles of STAT3 and STAT1 in cancer biology: insights into tumor pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. Front Immunol. 2023;14: 1265818. [34] SHEIKHHOSSEIN HH, IOMMELLI F, DI PIETRO N, et al. Exosome-like Systems: From Therapies to Vaccination for Cancer Treatment and Prevention-Exploring the State of the Art.Vaccines (Basel). 2024; 12(5):519. [35] ZHOU Y, SHAO N, AIERKEN N, et al. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in patients with breast cancer: a meta-analysis. J Cancer. 2017;8(19):4098-4105. [36] ZHENG L, LIN L, SONG J, et al. Prognostic values of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and Treg-related genes in gastric cancer. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2023;48(1):14-25. [37] LI Y, ZHANG C, JIANG A, et al. Potential anti-tumor effects of regulatory T cells in the tumor microenvironment: a review.J Transl Med. 2024; 22(1):293. [38] YAMAMOTO T, KAWADA K, OBAMA K.Inflammation-Related Biomarkers for the Prediction of Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(15):8002. [39] SONG Z, ZHANG J, SUN Y, et al. Establishment and validation of an immune infiltration predictive model for ovarian cancer. BMC Med Genomics. 2023;16(1):227. |
| [1] | Wang Lei, Wang Baiyan, Zhou Chunguang, Ren Xiaoyun, Dai Yueyou, Feng Shuying. Role of different cell-derived exosomal miRNAs in progression, diagnosis, and prognosis of gastric cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5434-5442. |
| [2] | Guo Zhao, Zhuang Haoyan, Shi Xuewen. Crossroads of colorectal cancer progression and suppression: efficacy and challenges of mesenchymal stem cell therapy interventions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 5022-5030. |
| [3] | Liu Chunlei, , , Yao Xi, Wei Zhengbo, Xie Ying. Construction methods and application of assembloids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 113-120. |
| [4] | Li Mengfei, Zhang Hong, Zhao Shaojian, Yin Guanghao, Wang Qibao. Expression of forkhead box protein 3 in refractory periapical periodontitis in rats with Enterococcus faecalis infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1187-1192. |
| [5] | An Yishuai, Zhang Junxia, Li Hui, Zhang Yuxiao, Xu Guoliang, Gao Kun, Yu Shuhan, Liu Zelong. Synergistic characteristics of lower extremity muscles with unilateral knee flexion limitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4704-4711. |
| [6] | Liu Chao, Zeng Zhaomu, Wen Xichao, Wu Wensong, Sun Chengyuan, Zheng Kebin. Role and clinical application prospects of exosomal non-coding RNAs in the occurrence and development of glioma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3928-3936. |
| [7] | Gan Zhoujie, Pei Xibo. Enzyme-responsive nanoparticles in tumor therapy: superiority of nanoparticles in accumulation and drug release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2562-2568. |
| [8] | Liu Chang, Song Keguan. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway: multiple roles in osteosarcoma, bone remodeling and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5213-5220. |
| [9] | Han Hui, Dai Xingliang, Cheng Hongwei, Lan Qing. Human glioma-initiating cells stably transfected with red fluorescent protein gene can spontaneously fuse with host-derived bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and induce malignant transformation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(25): 3944-3950. |
| [10] | Ji Zhongjiao, Guo Yibing, Lu Yuhua. Acellular scaffolds for tumor tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(34): 5571-5576. |
| [11] | Yang Juan, Zheng Sheng, Chen Wen-qin, Liu Jing, Zhang Fan, Wang Yu-bo. Transdifferentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into cancer-associated mesenchymal stem cells induced by hepatocellular carcinoma HepG-2 supernatant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(1): 25-31. |
| [12] | Wu Yu-jiao, Fei Xiao-ming, Ye Wei, Tang Yu, Lei Fang, Zhu Yan . Interleukin-1beta regulates stem cell gene and chemokine receptor gene expression of myeloma cell lines via pretreatment on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(1): 54-59. |
| [13] | Han Xiao-dong1, Wang Lei2, Zheng Jun2, He Xiao-long2, Ji Jin-shan1, Fu Zhao-ying1. Three-dimensional scaffold materials for cell culture and their application in tumor tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(42): 6371-6377. |
| [14] | Gao Zhuo-yue, Liu Yong-qi, He Jian-xin, Wu Zhi-wei, Luo Ya-li, Su Yun, Zhang Li-ying, Zhang Qi, Wu You-ming, Zhou Ni-na. Regulatory effects of warming yang and invigorating qi treatment on the inflammatory balance and genetic stability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under tumor microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2267-2272. |
| [15] | Zhang Shu-qing, Zhang Bo, Hong Liang, Zhou Yong-an, Zhao Liang. Identification and differentiation of breast cancer stem cells under tumor microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2155-2160. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||