Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (23): 5022-5030.doi: 10.12307/2025.078
Previous Articles Next Articles
Crossroads of colorectal cancer progression and suppression: efficacy and challenges of mesenchymal stem cell therapy interventions
Guo Zhao1, Zhuang Haoyan1, Shi Xuewen2
- 1First Clinical Medical College, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Anorectal Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province China
-
Received:2024-02-28Accepted:2024-05-09Online:2025-08-18Published:2024-09-30 -
Contact:Shi Xuewen, MD, Chief physician, Department of Anorectal Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province China -
About author:Guo Zhao, Master candidate, First Clinical Medical College, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Traditional Chinese Medicine Technology Development Plan Project of Shandong Province, No. 2019-0187 (to SXW); Qilu Traditional Chinese Medicine Advantage Specialist Cluster Construction Project, No. YWC2022ZKJQ0003 (to SXW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guo Zhao, Zhuang Haoyan, Shi Xuewen. Crossroads of colorectal cancer progression and suppression: efficacy and challenges of mesenchymal stem cell therapy interventions[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 5022-5030.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
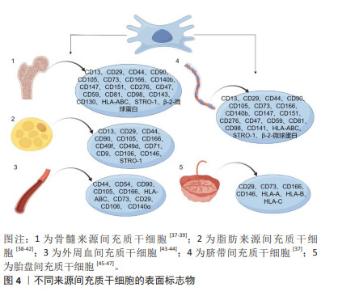
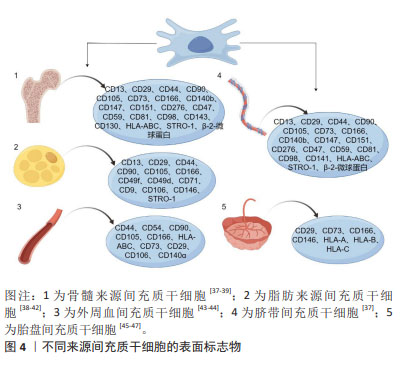
2.2 间充质干细胞 间充质干细胞可以从多种生物组织中提取出来,例如骨髓、脂肪组织、肝组织、脐血、外周血、经血等[30-32]。国际细胞治疗学会提出间充质干细胞的最低标准定义:首先它们需要表现出黏附在塑料表面的能力,其次具有表达特异性分化簇的能力,如CD73、CD90和CD105等[33],再次可以在体外分化为成骨、软骨或脂肪细胞,最后必须不表达CD14、CD34、CD45、CD11b、CD19和HLA-DR等分子标记[34]。此外,间充质干细胞还可以表达其他标志物,如神经细胞的巢蛋白,增强其治疗神经系统疾病的潜力[35],表达平滑肌α-肌动蛋白和平滑肌肌球蛋白重链,可作为平滑肌组织工程替代细胞[36]。然而,不同组织来源间充质干细胞的表面标志物谱也有不同。几种不同来源间充质干细胞的表面标志物见图4。"
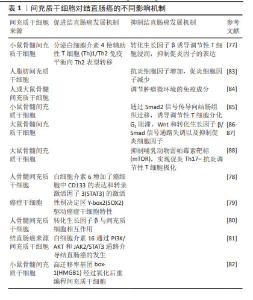
骨髓间充质干细胞一直是间充质干细胞中研究最多、最广泛的类型[48],目前已经成功应用于许多医学领域,尤其是再生医学领域[49]。然而由于骨髓穿刺带来的疼痛、伦理限制及获取的间充质干细胞数量有限等问题[50],科学家致力于研究骨髓间充质干细胞的替代源,因此脂肪间充质干细胞和脐带间充质干细胞在近几年来被深入研究。脂肪间充质干细胞具有很强的免疫抑制及抗炎、促血管生成的作用,对免疫性相关疾病如系统性硬化症[51]、克罗恩病等疾病具有优势[52]。脐带间充质干细胞同样也具备间充质干细胞的关键特性,现已被批准用于心血管[53]、关节炎[54]、神经系统疾病[55]。值得注意的是,无论是哪种类型的间充质干细胞,其免疫调节作用、控制炎症反应、促进细胞增殖、下调肿瘤坏死因子及特异性迁移到炎症和肿瘤位置的能力是毋庸置疑的。重要的是,研究表明间充质干细胞参与结直肠癌的发生、进展和转移[56]。此外,由于间充质干细胞具有肿瘤归巢特性,它们被认为是精确和选择性递送抗癌药物的有前途的载体[57]。近几年来,间充质干细胞在结直肠癌发展中发挥促进或抑制作用的机制被揭示出来,这导致了基于间充质干细胞治疗结直肠癌疗法的探索如雨后春笋般涌现[58]。 2.3 间充质干细胞、癌症干细胞、肿瘤微环境 尽管近几年来结直肠癌的研究已经有了很大的进展,但是结直肠癌的高死亡率仍然是临床面临的一大难题,特别是当结直肠癌发生远处转移时,治愈率将显著降低,因此,更好地了解肿瘤细胞向远处转移的生物学过程是非常有必要的。 癌症干细胞最早于 1800 年代被提出。癌症干细胞被认为是肿瘤发生的根源,并认为具有化疗耐药性的特点[59],这也充分解释了在使用化疗药物治疗后,虽然可以缩小肿瘤体积,但不能消除肿瘤,并且肿瘤仍可以复发。CD133是一种与器官特异性干细胞相关的表面糖蛋白,被认为是不同肿瘤类型中肿瘤起始细胞的标志物。从抗 CD133 磁珠的特异性[60],到CD133 仅是生物能量应激标志物的报道[61],以及其他报告表明CD133阴性胶质瘤细胞在裸鼠体内具有致瘤性,并且可以从这些肿瘤中获得 CD133阳性细胞[62],这也充分证明了CD133阳性、CD133阴性都与肿瘤的发生和进展有着密不可分的关系。研究表明,分化的结直肠癌细胞在化疗后被诱导死亡,而来自同一培养物的癌症干细胞在毒性损伤后存活[59],这充分表明了癌症干细胞可以抵抗化疗药物的有效作用。一项围绕肺癌展开的研究表明CD133的存在与肺癌的高度致瘤性及化疗耐药性有关[63]。另外也有实验证明,CD133与肝癌中的癌症干细胞会发生协同作用,二者通过优先激活Akt/PKB 细胞通路,从而导致化疗耐药性[64]。同样,在一项异种移植研究中观察到结直肠癌的生长与癌症干细胞有关,癌症干细胞可以产生白细胞介素4,而白细胞介素4对结直肠癌治疗具有抵抗作用[65]。此外,GINESTIER等[66]研究发现,乳腺癌干细胞对多种化疗药物表现耐药性。以上研究都可以证明癌症干细胞与肿瘤的发生及化疗耐药性有关。除了CD133被认为是癌症干细胞的标志物以外,醛脱羟氧酶(aldehyde dehydroxygenase,ALDH)也被认为是癌症干细胞的可靠标志物。最近的一份报告表明,ALDH1A3与乳腺肿瘤的发生和转移都显著相关,确定了ALDH1A3是一种新的乳腺癌干细胞标志物[67]。ALDH为癌症干细胞的标志物在其他实体肿瘤中也已被证明,例如ALDH1与头颈部鳞状细胞癌的进展有关[68];HUANG等[69]研究发现ALDH1是人结直肠癌症干细胞的特异性标志物,并且也证明了结直肠癌症干细胞过多的增殖可以驱动结直肠癌的进展,ALDH1水平对预测肺腺癌复发有独立的预后价值[70]。以上研究都证实了癌症干细胞与各种不同的实体肿瘤之间有着密不可分的联系。然而,到目前为止,研究报道的癌症干细胞标记物组合都不足以完全对其定义,有待进一步研究,从而为更好地利用癌症干细胞提供新思路,进而更好地进行靶向治疗。 肿瘤微环境由多种细胞类型组成,包括癌症相关成纤维细胞、免疫细胞、肿瘤脉管系统的内皮细胞和细胞外基质成分等[71]。越来越多的研究证明,肿瘤微环境中的细胞和非细胞成分可以重新编程肿瘤的发生、生长、侵袭、转移和对治疗药物的反应[72]。考虑到肿瘤微环境在肿瘤治疗中的重要性,肿瘤研究和治疗已经从以肿瘤为中心的模式转变为以肿瘤微环境为中心的模式。间充质干细胞作为肿瘤微环境的关键组成部分[73],已被证明可以促进肿瘤细胞的存活和增殖[74],并抑制天然抗肿瘤细胞的免疫反应[75]。因此,靶向肿瘤微环境中的间充质干细胞被认为是治疗肿瘤的潜在方法[76]。 2.4 间充质干细胞对结直肠癌进展的差异 间充质干细胞对结直肠癌的发生有积极和消极的影响,以促进或抑制结直肠癌细胞的生长。间充质干细胞对结直肠癌的不同影响与抗炎因子、抑炎因子水平及细胞通路有关,见表1。间充质干细胞促进结直肠癌的发展机制主要与结直肠癌细胞中的信号转导、趋化因子的表达状态及间充质干细胞向癌症相关成纤维细胞转化有关[77–82]。另外在最近的一项研究中发现性别决定区 Y-box2是胚胎和诱导多能干细胞的主要调节因子,具有驱动癌症干细胞的特性,促进肿瘤起始,并提高肿瘤侵袭性[79]。KISHI等[82]研究发现间充质干细胞的趋化因子高迁移率基团box-1经过氧化后可以重编程间充质干细胞和促进结直肠癌的发生。间充质干细胞对结直肠癌还有抑制作用。一方面,调控炎症因子状态及调节肿瘤环境免疫成分都是抑制结直肠癌进展的原因[77,83-85]。另外部分研究者认为Wnt和转化生长因子β信号通路对肿瘤发生都具有重要意义,间充质干细胞可以通过偶氮甲烷/葡聚糖硫酸钠结肠炎相关癌变模型中G1阻滞、Wnt和转化生长因子β/Smad信号通路失调以及抑制促炎细胞因子来抑制结直肠癌进展[86-87]。此外,LUO等[88]发现间充质干细胞可以通过抑制哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶标来促进促炎Th17向抗炎Treg的转化,实现Th17-Treg极化。这些不同的机制可以帮助了解间充质干细胞对结直肠癌的作用。"
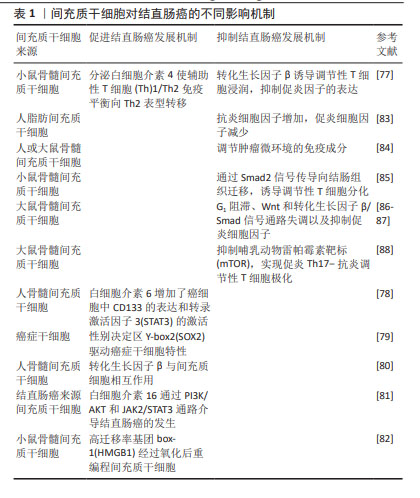

2.5 间充质干细胞治疗结直肠癌的突破口 间充质干细胞与结直肠癌之间错综复杂的相互作用机制使得研究人员在结直肠癌中使用间充质干细胞时保持谨慎的态度。首先间充质干细胞的肿瘤归巢特性使它们能够准确迁移到肿瘤位置并释放药物,基于这一特性,增加了治疗的安全性和有效性。其次,越来越多的研究表明,间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体作为良好的药物载体,在肿瘤靶向治疗中显示出良好的应用前景。此外,基因工程技术的快速发展使得使用病毒载体、非病毒载体或其他转染工具将具有成熟抗肿瘤作用的药物加载到间充质干细胞中成为可能[89]。最后,间充质干细胞与化疗药物联合使用以提高化疗药物疗效并降低化疗药物不良反应的潜力正在被挖掘[90]。 2.5.1 间充质干细胞作为抗肿瘤治疗的载体 作为抗肿瘤药物的载体,间充质干细胞可以被基因修饰以表达或分泌多种抑制癌症生长和进展的物质。这些物质可分为3大类:治疗性蛋白质、自杀基因、溶瘤病毒[91]。抑制肿瘤生长或作为促肿瘤因子抑制剂的治疗性蛋白质是一种新型的抗癌药物,例如细胞因子[92]、生长因子[93]、干扰素等[94],间充质干细胞可以作为运输此类治疗性蛋白质的优势载体。间充质干细胞除了表达抗癌细胞因子外,还可以被设计为秘密自杀基因,这些基因可以将无毒试剂转化为有毒的抗肿瘤药物。例如,在一项研究中发现,工程化表达自杀基因胞嘧啶脱氨酶: : 尿嘧啶磷酸核糖转移酶(CD: : UPRT)的脂肪间充质干细胞将相对无毒性的5-氟胞嘧啶转化为高毒性抗肿瘤5-氟尿嘧啶后可以抑制肿瘤生长[95]。分泌CD::UPRT的间充质干细胞在小鼠结肠癌模型中被证明有效[96]。KALIMUTHU等[97]研究发现工程化表达自杀基因的单纯疱疹病毒胸苷激酶(HSV1-sr39TK)可以增强多西环素对结直肠癌的疗效。此外,能够选择性杀死癌细胞的溶瘤病毒还可以被间充质干细胞应用于癌症的治疗中[98]。溶瘤病毒通过靶向癌细胞上的表面蛋白,识别癌细胞并结合癌细胞,导致溶瘤[99]。例如BABAEI等[100]研究表明,载有Dearing 呼肠孤病毒(ReoT3D)载体的间充质干细胞通过诱导细胞凋亡、阻滞细胞周期以增加ReoT3D的抗癌活性,抑制结直肠癌的进展。见表2。"

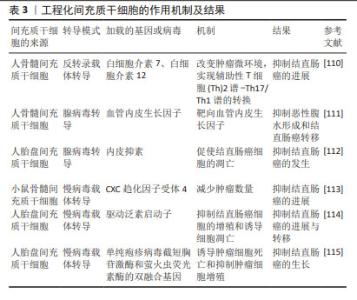
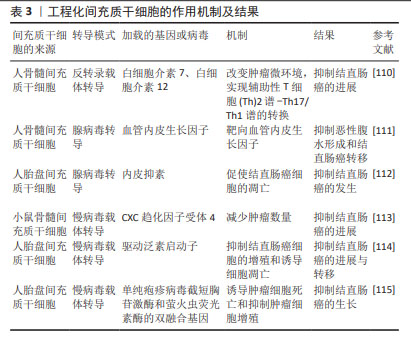
2.5.2 间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体作为抗肿瘤治疗的载体 间充质干细胞的治疗作用与旁分泌因子的分泌有关,包括细胞因子、生长因子、mRNA、miRNA和信号脂质。最近很多研究都集中在间充质干细胞的外泌体上。外泌体是由双层脂质和没有细胞器的细胞质组成的细胞外囊泡,直径为50-200 nm[102]。间充质干细胞是生产外泌体最有效的细胞类型之一[103]。间充质干细胞可以通过外泌体与其他细胞相互作用来转运物质,并可以利用其归巢特性作为载体来提高抗癌药物的靶向疗效,增加药物在肿瘤部位的积累。间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体搭载化疗药物或者靶向治疗剂到达特定的肿瘤位置,可以降低全身肿瘤毒性,同时可以克服耐药性的问题。在PESSINA等[104]的实验中发现,在没有任何基因操作的情况下,间充质干细胞可以迅速摄取紫杉醇并随后缓慢释放,载有紫杉醇的间充质干细胞可以获得有效的抗肿瘤活性[104]。间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体可以通过细胞间连接、P-糖蛋白的高表达[104]、隧道纳米管与癌细胞相互作用[105]。此外,LEE等[106]发现源自间充质干细胞的外泌体可以通过下调血管内皮生长因子的表达来抑制血管生成,从而抑制肿瘤细胞的发展。间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体具有基因转移能力、生物相容性、免疫原性更低、靶向更精确和更高稳定性的特点,使其成为优越的药物递送载体[107]。李香影等[108]研究表明脐带间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体可以通过参与免疫反应、抑制肿瘤细胞增殖等方式来发挥抗肿瘤作用。间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体显示出了无细胞疗法的特色优势,在将来可能比全细胞疗法更具前途。 2.5.3 工程化间充质干细胞 全球首个利用基因工程间充质干细胞治疗人类晚期胃肠道肿瘤的临床试验取得了成功,该试验在γ-反转录病毒转导下,使用骨髓间充质干细胞递送单纯疱疹病毒(HSV-TK),抑制了结直肠癌的进展与转移,这是一项成功的Ⅰ/Ⅱ期临床试验[109]。目前,基因工程技术的大力发展,使得很多研究将间充质干细胞与基因工程技术联系起来,如使用慢病毒载体转导、腺病毒转导和反转录病毒载体转导,以修饰间充质干细胞,使其发挥更积极的作用,见表3。通过反转录病毒载体转导,并经过工程改造以释放白细胞介素7 和白细胞介素12 的骨髓间充质干细胞可以将肿瘤微环境中的慢性炎症性Th2谱转变为具有抑制炎性反应的Th17/Th1谱,相比未修饰过的间充质干细胞,对于抑制结直肠癌的发展更具优势[110]。人骨髓间充质干细胞采用腺病毒转导,通过靶向血管内皮生长因子明显限制结直肠癌的发生和转移[111]。通过腺病毒转导人脂肪间充质干细胞,体内和体外研究都共同证明了表达内皮抑素的工程化人脂肪间充质干细胞可以抑制结直肠癌的发生[112]。小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞通过慢病毒载体转导,加载CXC趋化因子受体4后可以明显减少肿瘤细胞数量[113]。人胎盘间充质干细胞采用慢病毒载体转导,通过驱动启动子,可以明显抑制结直肠癌细胞的增殖并诱导肿瘤细胞的凋亡,从而抑制了结直肠癌的进展与转移[114]。人胎盘间充质干细胞采用慢病毒载体转导,通过加载单纯疱疹病毒截短胸苷激酶和萤火虫荧光素酶的双融合基因,诱导了肿瘤细胞的凋亡,从而抑制结直肠癌的进展[115]。基于以上研究,可以看出工程化间充质干细胞在结直肠癌治疗方面具有巨大的潜力。"
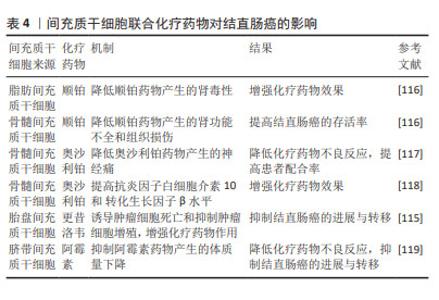
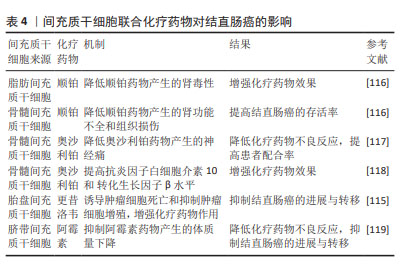
2.5.4 间充质干细胞联合化疗药物治疗结直肠癌 化疗是目前结直肠癌晚期患者的主流治疗方法,但是化疗的不良反应大且具有严重的耐药性,导致很多患者不愿积极主动地配合治疗,这就会增加结直肠癌远处转移的发生。间充质干细胞具有归巢伤口和组织修复的能力,基于这一特点,越来越多的研究证明间充质干细胞可以与化疗药物相结合,以增强化疗药物的疗效并恢复受损组织,见表4。例如KIM等[116]研究证实了人脂肪间充质干细胞在多个靶位点对顺铂肾毒性发挥旁分泌保护作用,人脂肪间充质干细胞与顺铂共培养时,可以抑制顺铂诱导的促炎症递质的释放,另外人骨髓间充质干细胞与顺铂共同输注也可以改善顺铂引起的肾功能不全和组织损伤,从而提高结直肠癌的存活率。在一些实验中发现,骨髓间充质干细胞可以减轻奥沙利铂引起的神经性疼痛[117-118],并且可以增加小鼠脊髓中抗炎细胞因子白细胞介素10和 转化生长因子β的水平[118]。此外,还有研究已经证明人脂肪间充质干细胞与更昔洛韦合用可以增强药物治疗的效果,并恢复结直肠癌患者对化疗耐药的敏感性[115]。DI等[119]研究发现,结直肠癌模型小鼠静脉注射人脂肪间充质干细胞和阿霉素,不会促进结直肠癌的进展,并且可以减轻阿霉素引起的不良反应。由此可见,间充质干细胞联合化疗药物治疗结直肠癌在很多研究中已经得到了充分的证明。"
| [1] IONESCU VA, GHEORGHE G, BACALBASA N, et al. Colorectal Cancer: From Risk Factors to Oncogenesis. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023;59(9):1646. [2] MORGAN E, ARNOLD M, GINI A, et al. Global burden of colorectal cancer in 2020 and 2040: incidence and mortality estimates from GLOBOCAN. Gut. 2023;72(2):338-344. [3] GLOBAL BURDEN OF DISEASE CANCER COLLABORATION, FITZMAURICE C, ABATE D, et al. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years for 29 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. 2019; 5(12):1749-1768. [4] WYLD L, AUDISIO RA, POSTON GJ. The evolution of cancer surgery and future perspectives. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015;12(2):115-124. [5] CREMOLINI C, ANTONIOTTI C, ROSSINI D, et al. Upfront FOLFOXIRI plus bevacizumab and reintroduction after progression versus mFOLFOX6 plus bevacizumab followed by FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab in the treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (TRIBE2): a multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21(4):497-507. [6] DAVERN M, LYSAGHT J. Cooperation between chemotherapy and immunotherapy in gastroesophageal cancers. Cancer Lett. 2020;495: 89-99. [7] PUSULURI A, WU D, MITRAGOTRI S. Immunological consequences of chemotherapy: Single drugs, combination therapies and nanoparticle-based treatments. J Control Release. 2019;305:130-154. [8] CARVELLO M, LIGHTNER A, YAMAMOTO T, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Perianal Crohn’s Disease. Cells. 2019;8(7):764. [9] GRÉGOIRE C, LECHANTEUR C, BRIQUET A, et al. Review article: mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for inflammatory bowel diseases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;45(2):205-221. [10] BOURIN P, BUNNELL BA, CASTEILLA L, et al. Stromal cells from the adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction and culture expanded adipose tissue-derived stromal/stem cells: a joint statement of the International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science (IFATS) and the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT). Cytotherapy. 2013;15(6):641-648. [11] LOMBARDI F, PALUMBO P, AUGELLO FR, et al. Secretome of Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells (ASCs) as a Novel Trend in Chronic Non-Healing Wounds: An Overview of Experimental In Vitro and In Vivo Studies and Methodological Variables. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(15):3721. [12] 吴齐翔,房辰雨,张蕾.炎症环境下白细胞介素1β增强间充质干细胞的迁移及黏附能力[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(31): 5048-5054. [13] TIAN LL, YUE W, ZHU F, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells play a dual role on tumor cell growth in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Physiol. 2011; 226(7):1860-1867. [14] HE N, KONG Y, LEI X, et al. MSCs inhibit tumor progression and enhance radiosensitivity of breast cancer cells by down-regulating Stat3 signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(10):1026. [15] LI W, ZHOU Y, YANG J, et al. Gastric cancer-derived mesenchymal stem cells prompt gastric cancer progression through secretion of interleukin-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015;34(1):52. [16] ZOU W, ZHAO J, LI Y, et al. Rat Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote the Migration and Invasion of Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:6617-6628. [17] KABASHIMA-NIIBE A, HIGUCHI H, TAKAISHI H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor progression of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2013;104(2):157-164. [18] LIN R, MA H, DING Z, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells favor the immunosuppressive T cells skewing in a Helicobacter pylori model of gastric cancer. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(21):2836-2848. [19] SHI H, JIANG C, YAO H, et al. CD44 fucosylation on bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhances homing and promotes enteric nervous system remodeling in diabetic mice. Cell Biosci. 2021; 11(1):118. [20] HONG YS, AHN YT, PARK JC, et al. 1H NMR-based metabonomic assessment of probiotic effects in a colitis mouse model. Arch Pharm Res. 2010;33(7):1091-101. [21] BOUMAZA I, SRINIVASAN S, WITT WT, et al. Autologous bone marrow-derived rat mesenchymal stem cells promote PDX-1 and insulin expression in the islets, alter T cell cytokine pattern and preserve regulatory T cells in the periphery and induce sustained normoglycemia. J Autoimmun. 2009;32(1):33-42. [22] KAVANAGH H, MAHON BP. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells prevent allergic airway inflammation by inducing murine regulatory T cells. Allergy. 2011;66(4):523-531. [23] BAI L, LENNON DP, EATON V, et al. Human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells induce Th2-polarized immune response and promote endogenous repair in animal models of multiple sclerosis. Glia. 2009;57(11):1192-1203. [24] BATTEN P, SARATHCHANDRA P, ANTONIW JW, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells induce T cell anergy and downregulate T cell allo-responses via the TH2 pathway: relevance to tissue engineering human heart valves. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(8):2263-2273. [25] CARRIÓN F, NOVA E, LUZ P, et al. Opposing effect of mesenchymal stem cells on Th1 and Th17 cell polarization according to the state of CD4+ T cell activation. Immunol Lett. 2011;135(1-2):10-16. [26] LIU H, DENG S, HAN L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells, exosomes and exosome-mimics as smart drug carriers for targeted cancer therapy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022;209(Pt 1):112163. [27] BAEK G, CHOI H, KIM Y, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Therapeutics and as a Drug Delivery Platform. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(9):880-886. [28] TAKAYAMA Y, KUSAMORI K, TSUKIMORI C, et al. Anticancer drug-loaded mesenchymal stem cells for targeted cancer therapy. J Control Release. 2021;329:1090-1101. [29] 杨小倩,宋爱梅,宋晖.间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞的共培养技术[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(31):5055-5062. [30] TEIXEIRA FG, PANCHALINGAM KM, ANJO SI, et al. Do hypoxia/normoxia culturing conditions change the neuroregulatory profile of Wharton Jelly mesenchymal stem cell secretome? Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6(1):133. [31] KISIEL AH, MCDUFFEE LA, MASAOUD E, et al. Isolation, characterization, and in vitro proliferation of canine mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue, muscle, and periosteum. Am J Vet Res. 2012;73(8):1305-1317. [32] MURPHY MB, MONCIVAIS K, CAPLAN AI. Mesenchymal stem cells: environmentally responsive therapeutics for regenerative medicine. Exp Mol Med. 2013;45(11):e54. [33] LV FJ, TUAN RS, CHEUNG KM, et al. Concise review: the surface markers and identity of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2014; 32(6):1408-1419. [34] DOMINICI M, LE BLANC K, MUELLER I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317. [35] TONDREAU T, LAGNEAUX L, DEJENEFFE M, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells already express specific neural proteins before any differentiation. Differentiation. 2004;72(7):319-326. [36] CHO SW, KIM IK, LIM SH, et al. Smooth muscle-like tissues engineered with bone marrow stromal cells. Biomaterials. 2004;25(15):2979-2986. [37] AMATI E, PERBELLINI O, ROTTA G, et al. High-throughput immunophenotypic characterization of bone marrow- and cord blood-derived mesenchymal stromal cells reveals common and differentially expressed markers: identification of angiotensin-converting enzyme (CD143) as a marker differentially expressed between adult and perinatal tissue sources. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):10. [38] DE UGARTE DA, ALFONSO Z, ZUK PA, et al. Differential expression of stem cell mobilization-associated molecules on multi-lineage cells from adipose tissue and bone marrow. Immunol Lett. 2003;89(2-3):267-270. [39] ZHANG J, LIU Y, YIN W, et al. Adipose-derived stromal cells in regulation of hematopoiesis. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2020;25:16. [40] XU T, YU X, YANG Q, et al. Autologous Micro-Fragmented Adipose Tissue as Stem Cell-Based Natural Scaffold for Cartilage Defect Repair. Cell Transplant. 2019;28(12):1709-1720. [41] ZHA K, LI X, TIAN G, et al. Evaluation of CD49f as a novel surface marker to identify functional adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell subset. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(5):e13017. [42] SCHÄFFLER A, BÜCHLER C. Concise review: adipose tissue-derived stromal cells--basic and clinical implications for novel cell-based therapies. Stem Cells. 2007;25(4):818-827. [43] LI S, HUANG KJ, WU JC, et al. Peripheral blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells: candidate cells responsible for healing critical-sized calvarial bone defects. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(4):359-368. [44] CAO C, DONG Y, DONG Y. Study on culture and in vitro osteogenesis of blood-derived human mesenchymal stem cells. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2005;19(8):642-647. [45] FUKUCHI Y, NAKAJIMA H, SUGIYAMA D, et al. Human placenta-derived cells have mesenchymal stem/progenitor cell potential. Stem Cells. 2004;22(5):649-658. [46] OLIVEIRA MS, BARRETO-FILHO JB. Placental-derived stem cells: Culture, differentiation and challenges. World J Stem Cells. 2015;7(4):769-775. [47] ULRICH C, ABRUZZESE T, MAERZ JK, et al. Human Placenta-Derived CD146-Positive Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Display a Distinct Osteogenic Differentiation Potential. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(13):1558-1569. [48] YIN JQ, ZHU J, ANKRUM JA. Manufacturing of primed mesenchymal stromal cells for therapy. Nat Biomed Eng. 2019;3(2):90-104. [49] CICCOCIOPPO R, BERNARDO ME, SGARELLA A, et al. Autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in the treatment of fistulising Crohn’s disease. Gut. 2011;60(6):788-798. [50] MARIA AT, MAUMUS M, LE QUELLEC A, et al. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Autoimmune Disorders: State of the Art and Perspectives for Systemic Sclerosis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017;52(2):234-259. [51] FARGE D, LOISEL S, LANSIAUX P, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells for systemic sclerosis treatment. Autoimmun Rev. 2021;20(3):102755. [52] CHO YB, PARK KJ, YOON SN, et al. Long-term results of adipose-derived stem cell therapy for the treatment of Crohn’s fistula. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(5):532-537. [53] CHEN Y, SHEN H, DING Y, et al. The application of umbilical cord-derived MSCs in cardiovascular diseases. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(17):8103-8114. [54] ARRIGONI C, D’ARRIGO D, ROSSELLA V, et al. Umbilical Cord MSCs and Their Secretome in the Therapy of Arthritic Diseases: A Research and Industrial Perspective. Cells. 2020;9(6):1343. [55] SUZUKI H, SAKAI T. Current Concepts of Stem Cell Therapy for Chronic Spinal Cord Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(14):7435. [56] YUAN J, WEI Z, XU X, et al. The Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell on Colorectal Cancer. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:9136583. [57] KHAKOO AY, PATI S, ANDERSON SA, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells exert potent antitumorigenic effects in a model of Kaposi’s sarcoma. J Exp Med. 2006;203(5):1235-1247. [58] LIN W, HUANG L, LI Y, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Cancer: Clinical Challenges and Opportunities. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019: 2820853. [59] COLAK S, ZIMBERLIN CD, FESSLER E, et al. Decreased mitochondrial priming determines chemoresistance of colon cancer stem cells. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21(7):1170-1177. [60] CLÉMENT V, DUTOIT V, MARINO D, et al. Limits of CD133 as a marker of glioma self-renewing cells. Int J Cancer. 2009;125(1):244-248. [61] GRIGUER CE, OLIVA CR, GOBIN E, et al. CD133 is a marker of bioenergetic stress in human glioma. PLoS One. 2008;3(11):e3655. [62] WANG J, SAKARIASSEN PØ, TSINKALOVSKY O, et al. CD133 negative glioma cells form tumors in nude rats and give rise to CD133 positive cells. Int J Cancer. 2008;122(4):761-768. [63] BERTOLINI G, ROZ L, PEREGO P, et al. Highly tumorigenic lung cancer CD133+ cells display stem-like features and are spared by cisplatin treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(38): 16281-16286. [64] MA S, LEE TK, ZHENG BJ, et al. CD133+ HCC cancer stem cells confer chemoresistance by preferential expression of the Akt/PKB survival pathway. Oncogene. 2008;27(12):1749-1758. [65] TODARO M, ALEA MP, DI STEFANO AB, et al. Colon cancer stem cells dictate tumor growth and resist cell death by production of interleukin-4. Cell Stem Cell. 2007;1(4):389-402. [66] GINESTIER C, LIU S, DIEBEL ME, et al. CXCR1 blockade selectively targets human breast cancer stem cells in vitro and in xenografts. J Clin Invest. 2010;120(2):485-497. [67] MARCATO P, DEAN CA, PAN D, et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase activity of breast cancer stem cells is primarily due to isoform ALDH1A3 and its expression is predictive of metastasis. Stem Cells. 2011;29(1):32-45. [68] BHAIJEE F, PEPPER DJ, PITMAN KT, et al. Cancer stem cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a review of current knowledge and future applications. Head Neck. 2012;34(6):894-899. [69] HUANG EH, HYNES MJ, ZHANG T, et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 is a marker for normal and malignant human colonic stem cells (SC) and tracks SC overpopulation during colon tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2009;69(8):3382-3389. [70] OKUDELA K, WOO T, MITSUI H, et al. Expression of the potential cancer stem cell markers, CD133, CD44, ALDH1, and β-catenin, in primary lung adenocarcinoma--their prognostic significance. Pathol Int. 2012;62(12):792-801. [71] BALKWILL FR, CAPASSO M, HAGEMANN T. The tumor microenvironment at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2012;125(Pt 23):5591-5596. [72] JIN MZ, JIN WL. The updated landscape of tumor microenvironment and drug repurposing. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):166. [73] HASS R. Role of MSC in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(8):2107. [74] MAFFEY A, STORINI C, DICEGLIE C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from tumor microenvironment favour breast cancer stem cell proliferation, cancerogenic and metastatic potential, via ionotropic purinergic signalling. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):13162. [75] NAUTA AJ, FIBBE WE. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stromal cells. Blood. 2007;110(10):3499-3506. [76] POGGI A, MUSSO A, DAPINO I, et al. Mechanisms of tumor escape from immune system: role of mesenchymal stromal cells. Immunol Lett. 2014;159(1-2):55-72. [77] HU W, WANG W, JIANG X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells can prevent or promote the progression of colon cancer based on their timing of administration. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):227. [78] TSAI KS, YANG SH, LEI YP, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote formation of colorectal tumors in mice. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(3): 1046-1056. [79] ZHU Y, HUANG S, CHEN S, et al. SOX2 promotes chemoresistance, cancer stem cells properties, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by β-catenin and Beclin1/autophagy signaling in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(5):449. [80] MELE V, MURARO MG, CALABRESE D, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells induce epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human colorectal cancer cells through the expression of surface-bound TGF-β. Int J Cancer. 2014;134(11):2583-2594. [81] ZHANG X, HU F, LI G, et al. Human colorectal cancer-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote colorectal cancer progression through IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(2):25. [82] KISHI S, FUJIWARA-TANI R, HONOKI K, et al. Oxidized high mobility group B-1 enhances metastability of colorectal cancer via modification of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. Cancer Sci. 2022;113(8):2904-2915. [83] GONZÁLEZ MA, GONZALEZ-REY E, RICO L, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate experimental colitis by inhibiting inflammatory and autoimmune responses. Gastroenterology. 2009; 136(3):978-989. [84] FRANÇOIS S, USUNIER B, FORGUE-LAFITTE ME, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Administration Attenuates Colon Cancer Progression by Modulating the Immune Component within the Colorectal Tumor Microenvironment. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(3):285-300. [85] TANG RJ, SHEN SN, ZHAO XY, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-regulated Treg cells suppress colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6(1):71. [86] NASUNO M, ARIMURA Y, NAGAISHI K, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells cancel azoxymethane-induced tumor initiation. Stem Cells. 2014;32(4):913-925. [87] CHEN Z, HE X, HE X, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate colitis-associated tumorigenesis in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;450(4):1402-1408. [88] LUO Y, GUO J, ZHANG P, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Protects Injured Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells by Regulating mTOR-Mediated Th17/Treg Axis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:684197. [89] WU HH, ZHOU Y, TABATA Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-based drug delivery strategy: from cells to biomimetic. J Control Release. 2019;294:102-113. [90] ZURMUKHTASHVILI M, MACHAVARIANI A, DUGASHVILI G, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation attenuates growth of chemotherapy treated oral squamous cell carcinoma in an animal model. J Oral Pathol Med. 2020;49(7):655-664. [91] STUDENY M, MARINI FC, CHAMPLIN RE, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells as vehicles for interferon-beta delivery into tumors. Cancer Res. 2002;62(13):3603-3608. [92] OKADA H, POLLACK IF. Cytokine gene therapy for malignant glioma. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2004;4(10):1609-1620. [93] WITSCH E, SELA M, YARDEN Y. Roles for growth factors in cancer progression. Physiology (Bethesda). 2010;25(2):85-101. [94] AUDSLEY KM, WAGNER T, TA C, et al. IFNβ Is a Potent Adjuvant for Cancer Vaccination Strategies. Front Immunol. 2021;12:735133. [95] CAVARRETTA IT, ALTANEROVA V, MATUSKOVA M, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells expressing prodrug-converting enzyme inhibit human prostate tumor growth. Mol Ther. 2010;18(1):223-231. [96] KUCEROVA L, ALTANEROVA V, MATUSKOVA M, et al. Adipose tissue-derived human mesenchymal stem cells mediated prodrug cancer gene therapy. Cancer Res. 2007;67(13):6304-6313. [97] KALIMUTHU S, ZHU L, OH JM, et al. Regulated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Mediated Colon Cancer Therapy Assessed by Reporter Gene Based Optical Imaging. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4):1002. [98] PARATO KA, SENGER D, FORSYTH PA, et al. Recent progress in the battle between oncolytic viruses and tumours. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5(12):965-976. [99] PIDELASERRA-MARTÍ G, ENGELAND CE. Mechanisms of measles virus oncolytic immunotherapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020;56:28-38. [100] BABAEI A, SOLEIMANJAHI H, SOLEIMANI M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells loaded with oncolytic reovirus enhances antitumor activity in mice models of colorectal cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;190:114644. [101] WONG VL, RIEMAN DJ, ARONSON L, et al. Growth-inhibitory activity of interferon-beta against human colorectal carcinoma cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1989;43(3):526-530. [102] MAROFI F, ALEXANDROVNA KI, MARGIANA R, et al. MSCs and their exosomes: a rapidly evolving approach in the context of cutaneous wounds therapy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):597. [103] YEO RW, LAI RC, ZHANG B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell: an efficient mass producer of exosomes for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(3):336-341. [104] PESSINA A, BONOMI A, COCCÈ V, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells primed with paclitaxel provide a new approach for cancer therapy. PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28321. [105] GOODARZI A, VALIKHANI M, AMIRI F, et al. The mechanisms of mutual relationship between malignant hematologic cells and mesenchymal stem cells: Does it contradict the nursing role of mesenchymal stem cells? Cell Commun Signal. 2022;20(1):21. [106] LEE JK, PARK SR, JUNG BK, et al. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells suppress angiogenesis by down-regulating VEGF expression in breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e84256. [107] NAM GH, CHOI Y, KIM GB, et al. Emerging Prospects of Exosomes for Cancer Treatment: From Conventional Therapy to Immunotherapy. Adv Mater. 2020;32(51):e2002440. [108] 李香影,刚乔健,牟力圆,等.脐带间充质干细胞外泌体在肿瘤治疗中的研究进展[J].实用临床医药杂志,2022,26(23):108-112,118. [109] NIESS H, VON EINEM JC, THOMAS MN, et al. Treatment of advanced gastrointestinal tumors with genetically modified autologous mesenchymal stromal cells (TREAT-ME1): study protocol of a phase I/II clinical trial. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:237. [110] HOMBACH AA, GEUMANN U, GÜNTHER C, et al. IL7-IL12 Engineered Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) Improve A CAR T Cell Attack Against Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cells. 2020;9(4):873. [111] YANG L, ZHANG Y, CHENG L, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Engineered to Secrete Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor Inhibit Tumor Metastasis and the Formation of Malignant Ascites in a Murine Colorectal Peritoneal Carcinomatosis Model. Hum Gene Ther. 2016;27(3):267-277. [112] ZHANG D, ZHENG L, SHI H, et al. Suppression of peritoneal tumorigenesis by placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells expressing endostatin on colorectal cancer. Int J Med Sci. 2014;11(9):870-879. [113] CHEN MJ, CHUNG-FAYE GA, SEARLE PF, et al. Gene therapy for colorectal cancer: therapeutic potential. BioDrugs. 2001;15(6):357-367. [114] TAHIR M, AHMAD N, LEI D, et al. Emerging role of oncolytic viruses and stem cells in gene therapy: Should they be integrated? Drug Discov Today. 2022;27(8):2244-2251. [115] YANG J, LV K, SUN J, et al. Anti-tumor effects of engineered mesenchymal stem cells in colon cancer model. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:8443-8450. [116] KIM JH, PARK DJ, YUN JC, et al. Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect kidneys from cisplatin nephrotoxicity in rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012;302(9):F1141-1150. [117] BOUKELMOUNE N, LAUMET G, TANG Y, et al. Nasal administration of mesenchymal stem cells reverses chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in mice. Brain Behav Immun. 2021;93:43-54. [118] DI CESARE MANNELLI L, TENCI B, MICHELI L, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells decrease pain in a rat model of oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy: Role of VEGF-A modulation. Neuropharmacology. 2018;131:166-175. [119] DI GH, JIANG S, LI FQ, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells mitigate chemotherapy-associated tissue injury in a pre-clinical mouse model. Cytotherapy. 2012;14(4):412-422. |
| [1] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [3] | Su Xiaoyang, Chen Wenting, Fu Yidan, Zhao Yan, Lan Danfeng, Yang Qiuping. Correlation between Mer receptor tyrosine kinase and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in Sprague-Dawley rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1593-1599. |
| [4] | Li Kaiying, Wei Xiaoge, Song Fei, Yang Nan, Zhao Zhenning, Wang Yan, Mu Jing, Ma Huisheng. Mechanism of Lijin manipulation regulating scar formation in skeletal muscle injury repair in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1600-1608. |
| [5] | Li Jun, Gong Jingjing, Sun Guobin, Guo Rui, Ding Yang, Qiang Lijuan, Zhang Xiaoli, Fang Zhanhai . miR-27a-3p promotes the proliferation of human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts by regulating mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1609-1617. |
| [6] | Li Huayuan, Li Chun, Liu Junwei, Wang Ting, Li Long, Wu Yongli. Effect of warm acupuncture on PINK1/Parkin pathway in the skeletal muscle of rats with chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1618-1625. |
| [7] | Jing Ruyi, Chen Yingxin, Cao Lei . Prognosis of deep lamellar keratoplasty versus penetrating keratoplasty in the treatment of stromal corneal dystrophy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1626-1633. |
| [8] | Wang Xuanqiang, Zhang Wenyang, Li Yang, Kong Weiqian, Li Wei, Wang Le, Li Zhongshan, Bai Shi. Effects of chronic exposure to low-frequency pulsed magnetic fields on contractility and morphology of the quadriceps muscle in healthy adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1634-1642. |
| [9] | Zhang Yuxin, Yu Cong, Zhang Cui, Ding Jianjun, Chen Yan. Differences in postural control ability between older adults with mild cognitive impairment and those with normal cognition under different single-task and dual-task conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1643-1649. |
| [10] | Zhou Panpan, Cui Yinglin, Zhang Wentao, Wang Shurui, Chen Jiahui, Yang Tong . Role of cellular autophagy in cerebral ischemic injury and the regulatory mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1650-1658. |
| [11] | Yu Jingbang, Wu Yayun. Regulatory effect of non-coding RNA in pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [12] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [13] | Zhu Hanmin, Wang Song, Xiao Wenlin, Zhang Wenjing, Zhou Xi, He Ye, Li Wei, . Mitophagy regulates bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1676-1683. |
| [14] | Yuan Weibo, Liu Chan, Yu Limei. Potential application of liver organoids in liver disease models and transplantation therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [15] | Wang Yida, Liu Jun, Wang Xiaoling, Wang Liyan, Yang Chengru, Zhang Xuexiao. Effects of wearable electronic device-based interventions on physical activity and sedentary behavior in healthy adolescents: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1693-1704. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||