Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (25): 5434-5442.doi: 10.12307/2025.514
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role of different cell-derived exosomal miRNAs in progression, diagnosis, and prognosis of gastric cancer
Wang Lei1, Wang Baiyan1, Zhou Chunguang1, Ren Xiaoyun1, Dai Yueyou1, Feng Shuying1, 2
- 1Medical College, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 2Henan Engineering Research Center for Chinese Medicine Foods for Special Medical Purpose, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2024-04-25Accepted:2024-06-07Online:2025-09-08Published:2024-12-28 -
Contact:Feng Shuying, MD, Doctoral supervisor, Medical College, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; Henan Engineering Research Center for Chinese Medicine Foods for Special Medical Purpose, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
About author:Wang Lei, Master candidate, Medical College, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Henan Province Science and Technology Research Project, No. 222102310541 (to WBY); Key Research Project of Higher Education Institutions in Henan Province, No. 22A310016 (to WBY); China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, No. 2023M731023; Henan University of Chinese Medicine Zhongjing Backbone Scholars Research Initiation Fund, No. 0104311-2021 (to FSY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Lei, Wang Baiyan, Zhou Chunguang, Ren Xiaoyun, Dai Yueyou, Feng Shuying. Role of different cell-derived exosomal miRNAs in progression, diagnosis, and prognosis of gastric cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5434-5442.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
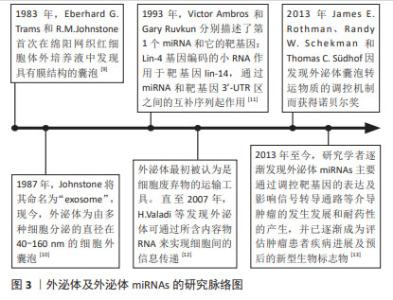
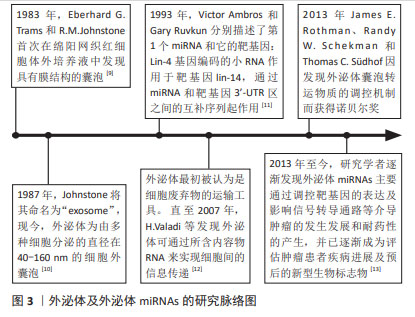
2.1 外泌体及外泌体miRNAs研究历程脉络 在1983年,Eberhard G.Trams和R.M.Johnstone首次在绵阳网织红细胞体外培养液中发现具有膜结构的囊泡。1987年Johnstone将其命名为“exosome”[9]。如今,外泌体为由多种细胞分泌的直径为40-160 nm,内含多种蛋白质、脂质及小分子RNA的细胞外囊泡,广泛存在于多种体液中,如唾液、脑脊液、尿液和乳汁[10]。在1993年,Victor Ambros和Gary Ruvkun分别描述了首个miRNA和它的靶基因:Lin-4基因编码的小RNA作用于靶基因lin-14,通过miRNA和靶基因3’-UTR区之间的互补序列起作用[11]。最初外泌体被认为是细胞代谢废物,直至2007年, VALADI等[12]发现鼠的肥大细胞分泌的外泌体可被人肥大细胞捕获,并且携带的mRNA及microRNA可进入胞浆被翻译为蛋白质或靶向调节细胞中mRNA水平,这一发现使得研究人员对外泌体的研究兴趣倍增。2013年,James E. Rothman、Randy W. Schekman和Thomas C.Südhof因发现外泌体囊泡转运物质的调控机制而获得了诺贝尔生理学或医学奖。他们的发现改变了人们对真核细胞间如何进行有效信息传递及细胞外囊泡如何分选、运输及释放货物的认识。进一步研究发现,外泌体miRNAs可参与多种疾病的发生发展,如心血管系统疾病、神经系统疾病和癌症[13]。其中外泌体miRNAs可通过调控靶基因的表达及影响信号转导通路进而调控肿瘤细胞增殖、凋亡、血管形成、侵袭与迁移、免疫应答和耐药性形成等多种作用。目前,外泌体miRNAs已成为肿瘤患者诊断、治疗及预后评估重要的生物标志物和潜在的治疗靶点,见图3。"
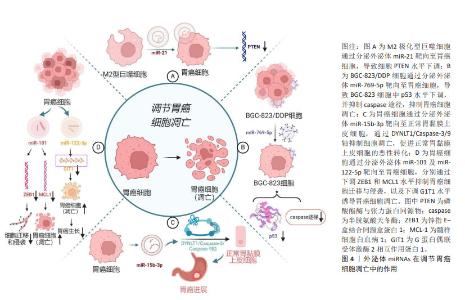
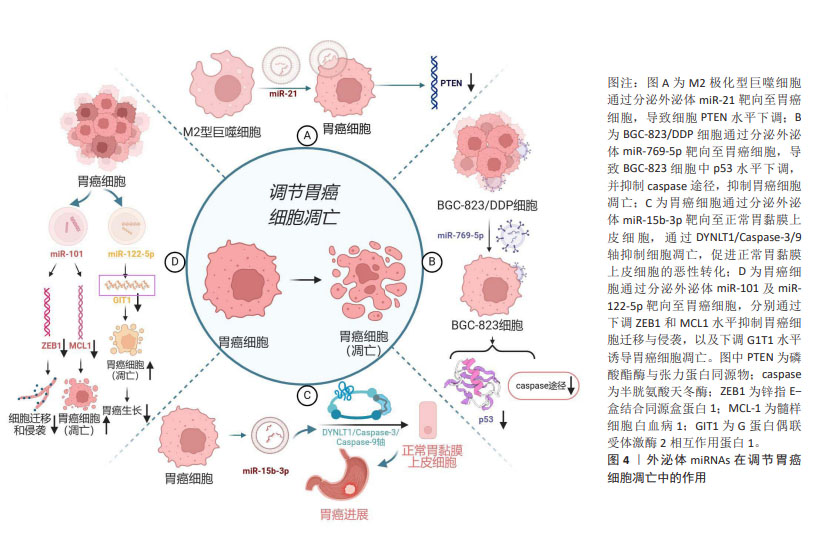
2.2 外泌体及外泌体miRNAs的特征及生物学功能 大量研究表明,外泌体在细胞间通讯中发挥重要作用,包括参与免疫反应、抗原呈递、细胞迁移、细胞分化以及调节远处转移位点等[14]。近年来研究证实,外泌体主要通过激活靶细胞上的细胞表面受体、与受体细胞质膜融合、内吞作用3种途径实现细胞间信号传递,在调节肿瘤微环境方面发挥着重要作用[15]。miRNAs是一类控制多个靶基因表达的、长度为19-25个核苷酸的短链miRNA,是基因表达的重要介质,其通过与蛋白质编码信使RNA配对指导基因表达,进而调控多种重要的生物学功能,如细胞的增殖、凋亡和分化等[16]。肿瘤细胞释放的外泌体miRNAs可以介导肿瘤微环境中的细胞表型变化,进而调控肿瘤细胞的生长、转移以及获得性耐药。肿瘤源性外泌体miRNAs可诱导肿瘤微环境异质性,而肿瘤微环境的改变又可促进肿瘤的发展[4]。胃癌细胞外泌体中含有丰富的miR-27a,它可以将正常成纤维细胞激活为癌相关成纤维细胞。将过表达miR-27a的HSF-1细胞与胃癌SGC-7901细胞共培养24 h后发现,与正常miR-27a组相比,过表达miR-27a组SGC-7901细胞生长速度更快,同时展现出显著的迁移与侵袭能力。体内实验发现,在注射过表达miR-27a的成纤维细胞后胃癌细胞发生了肺转移。这些作用可能与外泌体miR-27a通过抑制半胱氨酸和甘氨酸富集蛋白2表达,促进胃癌细胞的转移与侵袭有关[8]。基于外泌体miRNAs可在循环血浆和血清中被稳定地检测到,且在健康人群与胃癌患者中差异表达[17],故外泌体miRNAs可作为胃癌不同临床分期、诊断及预后的潜在生物标志物,并为胃癌治疗提供新的潜在靶点。 2.3 外泌体miRNAs在胃癌发生发展中的作用机制 2.3.1 外泌体miRNAs与胃癌细胞凋亡 凋亡是由多基因调控的程序性细胞死亡方式,外泌体miRNAs参与调控这一过程。在大多实体瘤中,M2极化型巨噬细胞在肿瘤相关巨噬细胞中占主导地位。M2极化型巨噬细胞由白细胞介素4及白细胞介素13激活,激活的M2极化型巨噬细胞衍生的外泌体miR-21可直接从M2型巨噬细胞转移至胃癌细胞中,通过下调胃癌细胞内肿瘤抑制基因磷酸酯酶与张力蛋白同源物(PTEN)水平,发挥抑制胃癌细胞凋亡作用[18]。低分化腺癌细胞BGC-823来源的外泌体高表达miR-15b-3p,在共培养体系中可转移至正常胃黏膜上皮细胞GES-1和中分化腺癌细胞SGC-7901中,通过调节DYNLT1/Caspase-3/9轴抑制受体细胞凋亡,并诱导GES-1细胞的恶性转化[19]。 miRNA与靶mRNA相互作用及其调控网络广泛存在于肿瘤发生和人类癌症发展中,不同细胞分泌的外泌体miRNAs具有不同的生物学功能。除了抑制细胞凋亡外,外泌体miRNAs还可诱导胃癌细胞凋亡。如胃癌细胞外泌体miR-122-5p可通过降低胃癌细胞内G蛋白偶联受体激酶2相互作用蛋白1(GIT1)水平诱导细胞凋亡,抑制胃癌细胞增殖[20];胃癌细胞外泌体miR-101通过下调为髓样细胞白血病1(MCL1)诱导胃癌细胞凋亡,并通过下调锌指E-盒结合同源盒蛋白1(ZEB1)蛋白水平抑制胃癌细胞迁移和侵袭。在这里,miR-101及miR-122-5p在胃癌患者中表达水平下调,与胃癌发展呈负相关,见图4。miR-101抑制幽门螺杆菌相关胃癌细胞的生长,恢复miR-101a水平可能具有阻止由幽门螺杆菌引起的萎缩性胃炎癌前病变的潜力[21]。由此可见,外泌体miRNAs可通过靶向凋亡基因或影响信号转导来调节胃癌细胞凋亡,且不同外泌体miRNAs对胃癌细胞凋亡具有不同的作用。甄别不同来源外泌体中miRNAs的功能,合理运用其诱导剂或抑制剂可对胃癌细胞凋亡水平进行调控。"
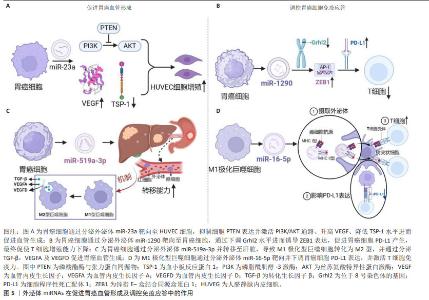
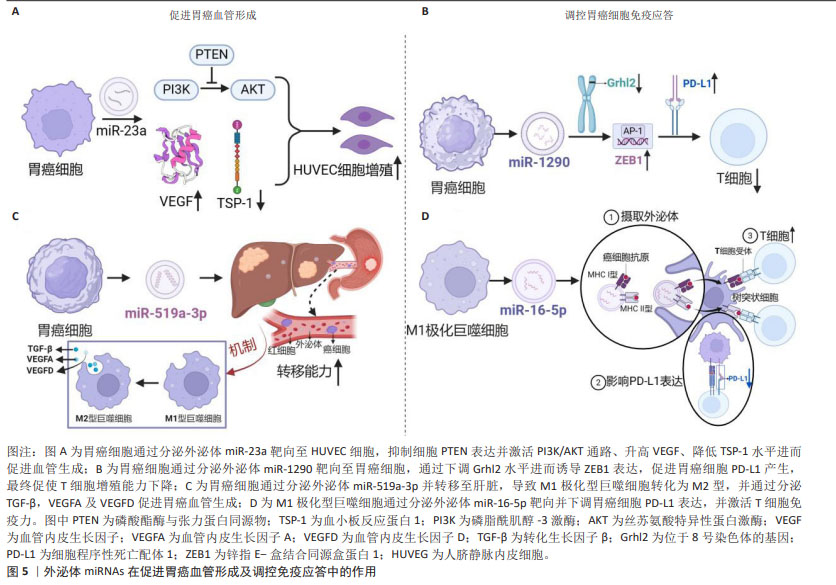
2.3.2 外泌体miRNAs与胃癌血管形成 目前几种胃癌细胞来源的miRNAs已被证明参与胃癌血管生成,包括miR-1,miR-29a/c和miR-616-3p等[22]。在胃癌HGC-27细胞外泌体miR-23a与人脐静脉内皮细胞共培养体系中,人脐静脉内皮细胞增殖能力显著增加,其机制可能与外泌体miR-23a抑制PTEN表达并激活PI3K/AKT通路、升高血管内皮生长因子、降低血小板反应蛋白1水平进而促进血管生成相关[23]。此项研究结果提示,miR-23a很可能成为胃癌迁移和血管生成的潜在生物标志物或抗血管生成治疗新靶标。如果通过外泌体向体内肿瘤部位精准递送miR-23a抑制剂,将有助于抑制肿瘤血管生成。另外,过表达外泌体miR-3184-5p的胃癌细胞HGC-27可进一步提高肿瘤血管生成能力及细胞活力[24]。外泌体miR-1273g-3p在胃癌患者血清中高表达,与胃癌的血管生成呈正相关[25]。另有研究表明,当转移前肿瘤微环境中M1极化型巨噬细胞被肿瘤细胞来源外泌体miR-519a-3p诱导为M2极化型,转移时间显著缩短,其机制主要为外泌体miR-519a-3p通过靶向DUSP2激活MAPK/ERK通路,进而引起巨噬细胞发生M2样极化,极化型M2巨噬细胞通过分泌促血管生成因子诱导血管形成的作用[26-27]。由此可见,外泌体miRNAs在肿瘤转移前肿瘤微环境的建立和血管的生成中扮演重要角色,见图5。"
| [1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. [2] AHADI A. Dysregulation of miRNAs as a signature for diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer and their involvement in the mechanism underlying gastric carcinogenesis and progression. Iubmb Life. 2020;72(5):884-898. [3] JELSKI W, MROCZKO B. Potential diagnostic utility of microRNAs in gastrointestinal cancers. Cancer Manag Res. 2023;15:863-871. [4] TANG XH, GUO T, GAO XY, et al. Exosome-derived noncoding RNAs in gastric cancer: functions and clinical applications. Mol Cancer. 2021;20(1):99. [5] OUYANG J, XIE Z, LEI X, et al. Clinical crosstalk between microRNAs and gastric cancer. Int J Oncol. 2021;58(4):7. [6] TAN S, XIA L, YI P, et al. Exosomal miRNAs in tumor microenvironment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39(1):67. [7] SANTOS P, ALMEDIA F. Role of exosomal miRNAs and the tumor microenvironment in drug resistance. Cells. 2020;9(6):1450. [8] WANG J, GUAN X, ZHANG Y, et al. Exosomal miR-27a derived from gastric cancer cells regulates the transformation of fibroblasts into cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(3):869-883. [9] JEPPESEN DK, ZHANG Q, FRANKLIN JL, et al. Extracellular vesicles and nanoparticles: emerging complexities. Trends Cell Biol. 2023;33(8):667-681. [10] AGARWAL P, ANEES A, HARSIDDHARAY RK, et al. A comprehensive review on exosome: Recent progress and outlook. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2023. doi: 10.2174/2211738511666230523114311. [11] LEE RC, FEINBAUM RL, AMBROS V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993; 75(5):843-854. [12] VALADI H, EKSTROM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659. [13] NAIL HM, CHIU CC, LEUNG CH, et al. Exosomal miRNA-mediated intercellular communications and immunomodulatory effects in tumor microenvironments. J Biomed Sci. 2023;30(1):69. [14] WORTZEL I, DROR S, KENIFIC CM, et al. Exosome-mediated metastasis: communication from a distance. Dev Cell. 2019;49(3):347-360. [15] ALOI N, DRAGO G, RUGGIERI S, et al. Extracellular vesicles and immunity: at the crossroads of cell communication. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(2):1205. [16] MISHRA LC, PANDEY U, GUPTA A, et al. Alternating exosomes and their mimetics as an emergent strategy for targeted cancer therapy. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:939050. [17] PREETHI KA, SELVAKUMAR SC, ROSS K, et al. Liquid biopsy: Exosomal microRNAs as novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):54. [18] ZHENG P, CHEN L, YUAN X, et al. Exosomal transfer of tumor-associated macrophage-derived miR-21 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017;36(1):53. [19] WEI S, PENG L, YANG J, et al. Exosomal transfer of miR-15b-3p enhances tumorigenesis and malignant transformation through the DYNLT1/Caspase-3/Caspase-9 signaling pathway in gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39(1):32. [20] JIAO Y, ZHANG L, LI J, et al. Exosomal miR-122-5p inhibits tumorigenicity of gastric cancer by downregulating GIT1. Int J Biol Marker. 2021;36(1):36-46. [21] IMAMURA T, KOMATSU S, ICHIKAWA D, et al. Low plasma levels of miR-101 are associated with tumor progression in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(63):106538-106550. [22] GIUPPI M, LA SALVIA A, EVANGELISTA J, et al. The role and expression of angiogenesis-related miRNAs in gastric cancer. Biology(Basel). 2021;10(2):146. [23] DU J, LIANG Y, LI J, et al. Gastric cancer cell-derived exosomal microRNA-23a promotes angiogenesis by targeting PTEN. Front Oncol. 2020;10:326. [24] LIN S, QUE Y, QUE C, et al. Exosome miR-3184-5p inhibits gastric cancer growth by targeting XBP1 to regulate the AKT, STAT3 and IRE1 signalling pathways. Asia-Pac J Clin Onco. 2022;19(2):e27-e38. [25] 任志俭.外泌体miR-1273g-3p在胃癌中的作用及机制研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2022. [26] QIU S, XIE L, LU C, et al. Gastric cancer-derived exosomal miR-519a-3p promotes liver metastasis by inducing intrahepatic M2-like macrophage-mediated angiogenesis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022;41(1):296. [27] XU L, XIE X, LUO Y. The role of macrophage in regulating tumour microenvironment and the strategies for reprogramming tumour-associated macrophages in antitumour therapy. Eur J Cell Biol. 2021;100(2):151153. [28] ZHU L, ZHANG S, CHEN S, et al. Exosomal miR-552-5p promotes tumorigenesis and disease progression via the PTEN/TOB1 axis in gastric cancer. J Cancer. 2022;13(3):890-905. [29] XIA X, WANG S, NI B, et al. Hypoxic gastric cancer-derived exosomes promote progression and metastasis via MiR-301a-3p/PHD3/HIF-1α positive feedback loop. Oncogene. 2020;39(39):6231-6244. [30] FENG C, SHE J, CHEN X, et al. Exosomal miR-196a-1 promotes gastric cancer cell invasion and metastasis by targeting SFRP1. Nanomedicine. 2019; 14(19):2579-2593. [31] 朱萌,张宁,卢新兰,等. 肿瘤源性外泌体miR-106a调控间皮细胞Smad7表达影响胃癌腹膜转移[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2020, 41(3):340-346. [32] WEI R, LIU S, ZHANG S, et al. Cellular and extracellular components in tumor microenvironment and their application in early diagnosis of cancers. Anal Cell Pathol. 2020;2020:6283796. [33] LIANG Y, LIU Y, ZHANG Q, et al. Corrigendum to tumor-derived extracellular vesicles containing microRNA-1290 promote immune escape of cancer cells through the Grhl2/ZEB1/PD-L1 axis in gastric cancer. Transl Res. 2021;231:102-112. [34] 李军涛.胃癌外泌体miR-135b-5p调控γδT细胞免疫功能的作用和机制研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2021. [35] LIU F, BU Z, ZHAO F, et al. Increased T-helper 17 cell differentiation mediated by exosome-mediated microRNA-451 redistribution in gastric cancer infiltrated T cells. Cancer Sci. 2018;109:65-73. [36] ZHOU, J, TANG, Z, GAO, S, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages: recent insights and therapies. Front Oncol. 2020;10:188. [37] LI Z, SUO B, LONG G, et al. Exosomal miRNA-16-5p derived from M1 macrophages enhances T cell-dependent immune response by regulating PD-L1 in gastric cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:572689. [38] RAUE R, FRANK AC, SYED SN, et al. Therapeutic targeting of microRNAs in the tumor microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):2210. [39] MOWLA M, HASHEMI A. Functional roles of exosomal miRNAs in multi-drug resistance in cancer chemotherapeutics. Exp Mol Pathol. 2020;118:9104592. [40] GUO QR, WANG H, YAN YD, et al. The role of exosomal microRNA in cancer drug resistance. Front Oncol. 2020;10:472. [41] LIN H, ZHANG L, ZHANG C, et al. Exosomal miR-500a-3p promotes cisplatin resistance and stemness via negatively regulating FBXW7 in gastric cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(16):8930-8941. [42] JING X, XIE M, DING K, et al. Exosome-transmitted miR-769-5p confers cisplatin resistance and progression in gastric cancer by targeting CASP9 and promoting the ubiquitination degradation of p53. Clin Transl Med. 2022;12(5):e780. [43] ZHANG X, WANG S, WANG H, et al. Circular RNA circNRIP1 acts as a microRNA-149-5p sponge to promote gastric cancer progression via the AKT1/mTOR pathway. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):20. [44] SANG H, ZHANG W, PENG L, et al. Exosomal circRELL1 serves as a miR-637 sponge to modulate gastric cancer progression via regulating autophagy activation. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(1):56. [45] CHEN Y, LIU H, ZOU J, et al. Exosomal circ_0091741 promotes gastric cancer cell autophagy and chemoresistance via the miR-330-3p/TRIM14/Dvl2/Wnt/β-catenin axis. Hum Cell. 2022;36(1):258-275. [46] ZHANG H, DENG T, LIU R, et al. CAF secreted miR-522 suppresses ferroptosis and promotes acquired chemo-resistance in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):43. [47] GAO H, MA J, CHENG Y, et al. Exosomal transfer of macrophage-derived miR-223 confers doxorubicin resistance in gastric cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:12169-12179. [48] JI R, ZHANG X, GU H, et al. MiR-374a-5p: a new target for diagnosis and drug Resistance therapy in gastric cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;18: 320-331. [49] ZHOU M, DONG J, HUANG J, et al. Chitosan-gelatin-EGCG nanoparticle-meditated LncRNA TMEM44-AS1 silencing to activate the P53 signaling pathway for the synergistic reversal of 5-FU resistance in gastric cancer. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(22):e2105077. [50] JIN L, MA X, ZHANG N, et al. Targeting oncogenic miR-181a-2-3p inhibits growth and suppresses cisplatin resistance of gastric cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2021;13:8599-8609. [51] 唐德平,邢梦洁,宋文涛,等. MicroRNA治疗在癌症及其他疾病中的研究进展[J].中国生物工程杂志,2021,41(11):64-73. [52] YANG J, LI X, WEI S, et al. Evaluation of the diagnostic potential of a plasma exosomal miRNAs panel for gastric cancer. Front Oncol. 2021;11:683465. [53] LIU X, CHU K. Abstract 2765: Exosomal miRNAs as circulating biomarkers for prediction of metastasis in stage II/III gastric cancer Cancer Res. 2019; 79(13):2765-2765. [54] ZHENG GD, XU ZY, HU C, et al. Exosomal miR-590-5p in serum as a biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:636566. [55] OHZAWA H, SAITO A, KUMAGAI Y, et al. Reduced expression of exosomal miR29s in peritoneal fluid is a useful predictor of peritoneal recurrence after curative resection of gastric cancer with serosal involvement. Oncol Rep. 2020;43(4):1081-1088. [56] LU X, LU J, WANG S, et al. Circulating serum exosomal miR-92a-3p as a novel biomarker for early diagnosis of gastric cancer. Future Oncol. 2021; 17(8):907-919. [57] ZHAO G, ZHOU A, LI X, et al. The significance of exosomal RNAs in the development, diagnosis, and treatment of gastric cancer. Genes (Basel). 2021;12(1):73. [58] ZHANG Z, WU H, CHONG W, et al. Liquid biopsy in gastric cancer: predictive and prognostic biomarkers. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(10):903. [59] KOH, HB, KIM, HJ, KANG, SW, et al. Exosome-based drug delivery: translation from bench to clinic. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(8):2042. [60] LIU X, ABRAHAM JM, CHENG Y, et al. Synthetic circular RNA functions as a miR-21 sponge to suppress gastric carcinoma cell proliferation. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018;13:312-321. [61] GU J, CHU X, HUO Y, et al. Gastric cancer-derived exosomes facilitate pulmonary metastasis by activating ERK-mediated immunosuppressive macrophage polarization. J Cell Biochem. 2023;124(4):557-572. [62] 石亮.胃癌细胞源性外泌体miR-431-5p通过诱导铁死亡对胃癌的抑制作用及其机制研究[D].石家庄:河北大学,2023. [63] REN W, ZHANG X, LI W, et al. Exosomal miRNA-107 induces myeloid-derived suppressor cell expansion in gastric cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:4023-4040. [64] HUANG J, SHEN M, YAN M, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of miR-1290 promotes cell proliferation and invasion in gastric cancer via NKD1. Acta Bioch Bioph Sin. 2019;51(9):900-907. [65] XU G, ZHANG B, YE J, et al. Exosomal miRNA-139 in cancer-associated fibroblasts inhibits gastric cancer progression by repressing MMP11 expression. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15(11):2320-2329. [66] LIN XM, WANG ZJ, LIN YX, et al. Decreased exosome-delivered miR-486-5p is responsible for the peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer cells by promoting EMT progress. World J Surg Oncol. 2021;19(1):312. [67] JI R, LIN J, GU H, et al. Gastric cancer derived mesenchymal stem cells promote the migration of gastric cancer cells through miR-374a-5p. Curr Stem Cell Rest. 2023;18(6):853-863. [68] YANG H, FU H, WANG B, et al. Exosomal miR-423-5p targets SUFU to promote cancer growth and metastasis and serves as a novel marker for gastric cancer. Mol Carcinogen. 2018;57(9):1223-1236. [69] HE J, WU J, DONG S, et al. Exosome-encapsulated miR-31, miR-192, and miR-375 serve as clinical biomarkers of gastric cancer. J Oncol. 2023; 2023:7335456. [70] ZHANG Y, HAN T, FENG D, et al. Screening of non-invasive miRNA biomarker candidates for metastasis of gastric cancer by small RNA sequencing of plasma exosomes. Carcinogenesis. 2020;41(5):582-590. [71] OHZAWA H, KUMAGAI Y, YAMAGUCHI H, et al. Exosomal microRNA in peritoneal fluid as a biomarker of peritoneal metastases from gastric cancer. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2019;4(1):84-93. [72] SHI Y, WANG Z, ZHU X, et al. Exosomal miR-1246 in serum as a potential biomarker for early diagnosis of gastric cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2019; 25(1):89-99. [73] YUN J, HAN SB, KIM HJ, et al. Exosomal miR-181b-5p downregulation in ascites serves as a potential diagnostic biomarker for gastric cancer-associated malignant ascites. J Gastric Cancer. 2019;19(3):301-314. [74] SOEDA N, IINUMA H, SUZUKI Y, et al. Plasma exosome-encapsulated microRNA-21 and microRNA-92a are promising biomarkers for the prediction of peritoneal recurrence in patients with gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. 2019;18(5):4467-4480. [75] 李金昌,王俊壹,张其德,等. MiR-494-3p在胃癌患者血清外泌体中的表达及价值[J].临床检验杂志,2023,41(7):508-511. [76] 孙婧悦,王啸.血清外泌体miRNAs联合CA72-4在胃癌诊断中的价值分析[J].中国肿瘤临床,2022,49(12):636-641. [77] KUMATA Y, IINUMA H, SUZUKI Y, et al. Exosomeencapsulated microRNA23b as a minimally invasive liquid biomarker for the prediction of recurrence and prognosis of gastric cancer patients in each tumor stage. Oncol Rep. 2018;40(1):319-330. |
| [1] | Li Zikai, Zhang Chengcheng, Xiong Jiaying, Yang Xirui, Yang Jing, Shi Haishan. Potential effects of ornidazole on intracanal vascularization in endodontic regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Deng Keqi, Li Guangdi, Goswami Ashutosh, Liu Xingyu, He Xiaoyong. Screening and validation of Hub genes for iron overload in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [3] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [4] | Li Huayuan, Li Chun, Liu Junwei, Wang Ting, Li Long, Wu Yongli. Effect of warm acupuncture on PINK1/Parkin pathway in the skeletal muscle of rats with chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1618-1625. |
| [5] | Zhou Panpan, Cui Yinglin, Zhang Wentao, Wang Shurui, Chen Jiahui, Yang Tong . Role of cellular autophagy in cerebral ischemic injury and the regulatory mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1650-1658. |
| [6] | Zhu Hanmin, Wang Song, Xiao Wenlin, Zhang Wenjing, Zhou Xi, He Ye, Li Wei, . Mitophagy regulates bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1676-1683. |
| [7] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [8] | Lou Guo, Zhang Min, Fu Changxi. Exercise preconditioning for eight weeks enhances therapeutic effect of adipose-derived stem cells in rats with myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1363-1370. |
| [9] | Cao Yue, Ye Xinjian, Li Biyao, Zhang Yining, Feng Jianying. Effect of extracellular vesicles for diagnosis and therapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1523-1530. |
| [10] | Zheng Rongfa, Mo Weibin, Huang Peng, Chen Junji, Liang Ting, Zi Fangyu, Li Guofeng. Effects of electroacupuncture on the expression of metabolic enzymes and autophagy genes in gastrocnemius muscle tissues of exercising rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1127-1136. |
| [11] | Chen Yuning, Jiang Ying, Liao Xiangyu, Chen Qiongjun, Xiong Liang, Liu Yue, Liu Tong. Buqi Huoxue Compounds intervene with the expression of related factors and autophagy related proteins in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1152-1158. |
| [12] | Liu Lingyun, He Guixin, Qin Weibin, Song Hui, Zhang Liwen, Tang Weizhi, Yang Feifei, Zhu Ziyi, Ou Yangbin . Improvement of myocardial injury by traditional Chinese medicine: mitochondrial calcium homeostasis mediates macrophage autophagy and pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1276-1284. |
| [13] | Han Haihui, Meng Xiaohu, Xu Bo, Ran Le, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Effect of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 inhibitor on bone destruction in rats with collagen-induced arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 968-977. |
| [14] | Xu Tianjie, Fan Jiaxin, Guo Xiaoling, Jia Xiang, Zhao Xingwang, Liu kainan, Wang Qian. Metformin exerts a protective effect on articular cartilage in osteoarthritis rats by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1003-1012. |
| [15] | Yang Dingyan, Yu Zhenqiu, Yang Zhongyu. Machine learning-based analysis of neutrophil-associated potential biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7909-7920. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||