Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (17): 3641-3649.doi: 10.12307/2025.629
Previous Articles Next Articles
Copper influences the occurrence and development of diabetic complications
Luo Yuncai1, Meng Maohua1, 2, Li Ying1, 2, Wang Huan1, Lu Jing1, Shu Jiayu1, Li Wenjie1, Sun Jinyi1, Dong Qiang1, 2
- 1School and Hospital of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Prosthodontic Implantation, Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2024-06-04Accepted:2024-08-05Online:2025-06-18Published:2024-11-06 -
Contact:Dong Qiang, MD, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; Department of Prosthodontic Implantation, Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Luo Yuncai, Master candidate, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Luo Yuncai, Meng Maohua, , Li Ying, , Wang Huan, Lu Jing, Shu Jiayu, Li Wenjie, Sun Jinyi, Dong Qiang, . Copper influences the occurrence and development of diabetic complications [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3641-3649.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
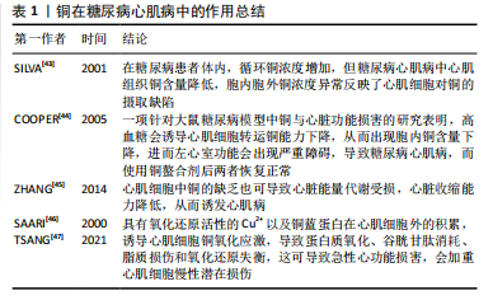
2.1 糖尿病及铜元素研究现状 2.1.1 糖尿病定义、临床表现及分类 糖尿病是一组由多种致病因子作用于机体引起的以慢性高血糖为特征的代谢性疾病,是由于胰岛素分泌和(或)利用缺陷所引起[1,3,19]。胰岛素主要由胰岛β细胞产生,能促进肝脏、肌肉和脂肪等组织摄取和利用葡萄糖,抑制肝糖原分解为糖原及糖异生作用,从而调节血糖平衡[20]。糖尿病典型病例可出现多饮、多食、多尿、体质量减轻等表现,即“三多一少”。糖尿病患者血糖控制欠佳会引发机体并发症,即机体内长期碳水化合物、脂肪、蛋白质等代谢紊乱,可引起机体内多系统损害,导致眼、肾、神经、心脏、血管等组织器官出现慢性进行性病变、功能减退及衰竭。当病情严重或应激时,可发生急性严重代谢紊乱,如糖尿病酮症酸中毒、高渗高血糖综合征等[5-6]。 WHO(1999年)有关糖尿病病因学的分型体系中[17],根据病因学证据将糖尿病分为3种类型,即1型糖尿病、2型糖尿病、特殊类型糖尿病。其中,1型糖尿病是自身免疫性疾病,病因及发病机制尚未完全明了,其显著的病理改变是胰岛β细胞数量显著减少乃至消失所导致的胰岛素分泌显著下降[21]。2型糖尿病属于慢性代谢紊乱疾病,主要影响因素有遗传因素、体质量及肥胖、饮食及生活方式等,其显著的病理改变为胰岛素调节血糖能力下降(即胰岛素抵抗)和胰岛β细胞功能缺陷所导致的胰岛素分泌减少[22]。特殊类型糖尿病是致病原因相对明确的糖尿病,比如药物或化学品所致糖尿病、妊娠糖尿病(即无糖尿病史的孕妇发生的糖尿病)。 2.1.2 糖尿病并发症定义及发病机制 随着糖尿病病程的延长以及血糖控制情况欠佳,机体各器官的损伤程度逐渐加重,会导致眼睛、肾脏、神经、心脏等多组织慢性病变,这类病变统称为糖尿病并发症,是糖尿病致死致残的主要原因[23]。糖尿病并发症的发病机制主要有以下2种,即多元醇途径和晚期糖基化终末产物的形成。多元醇途径将葡萄糖转化为山梨糖醇白糖醛糖还原酶,导致组织直接受损以至于出现糖尿病并发症。而晚期糖基化终末产物是在非酶促条件下,由蛋白质、脂类或核酸等大分子物质的游离氨基与还原糖的醛基之间的一系列反应形成的稳定化合物[24]。伴随高血糖而来的过量晚期糖基化终末产物在体内蓄积,是诱发糖尿病并发症发生发展的关键因素[25-26]。高血糖刺激线粒体产生过量的活性氧可以激活以上机制。根据现有研究发现,一方面,高血糖可以增加活性氧的产生,另一方面,高血糖对机体内抗氧化系统也有一定损伤作用[27-28]。虽然,也有文献表明,高血糖可能会激活机体潜在的保护途径来抵抗氧化应激的损伤[29]。 但长期暴露于高血糖环境,活性氧大量产生,线粒体通透性增加,线粒体β-烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸(NAD+)储存减少,导致机体能量代谢缺陷;同时活性氧直接破坏细胞脂质、蛋白质和核酸,导致细胞死亡。除此之外,氧化应激对胰岛β细胞也会产生直接损伤作用,从而降低胰岛素敏感性。因为胰岛β细胞的抗氧化酶表达量很低,抗氧化应激能力较弱,所以极易引起糖耐量受损,加快糖尿病病程及其并发症的发生发展[30]。 2.1.3 铜元素的研究现状 铜是一种从海产品、器官肉类、谷物和水等多种食物来源中摄取的机体必需微量元素,作为相应酶的催化剂和结构辅助因子发挥着必不可少的作用,参与氧化还原、能量生成、细胞代谢、信号转导等许多过程[9-10]。Cu2+是具有较强氧化性的金属离子,过多的Cu2+可以促进活性氧的大量生成,诱导细胞氧化应激反应,导致细胞损伤甚至死亡[31-32]。 机体内铜稳态的调节是一个动态调节的过程,主要依赖于铜在机体和细胞内的吸收、转运、储存和排泄。铜进入机体后,由小肠吸收,转运至肝脏内代谢,然后通过血液运输至各组织器官,过量的铜元素通过胆汁排泄出体外[33]。铜参与机体抗氧化机制,是铜锌超氧化物歧化酶、细胞色素c氧化酶的组成成分;铜也参与神经递质的合成,从而对神经系统有重要作用[32]。现有研究表明,不论是铜缺乏或是铜过载都会导致机体血液系统、免疫系统、神经系统等多系统病变。环境外源因素铜暴露可导致细胞内铜代谢稳态失调,如病理性原因导致机体无法从外界摄取铜,或体内病理性铜元素蓄积,过度摄入含铜饮食等,此时铜转运蛋白表达异常,会导致铜积累过多或运输不当,细胞内铜浓度超过稳态机制维持的阈值时,就会导致细胞毒性和机体损伤效应[34]。由此可知,糖尿病患者体内铜稳态的失调对于机体组织与器官有一定的损伤作用。 当前有学者研究发现,铜在细胞死亡调控机制中有重要作用,例如:铜能通过氧化应激、细胞自噬等途径诱导细胞凋亡;铜经由活性氧依赖性DNA损伤诱导坏死性凋亡和毒性损伤;铜暴露诱导不同细胞焦亡介导炎症反应、细胞毒性作用;铜能诱导细胞铁死亡等[34]。2022年,TSVETKOV等[33]提出一个新的细胞死亡机制,与已知细胞死亡机制有明显不同,该死亡机制是一种铜依赖性的、受调节的细胞死亡机制,他将这种新的死亡方式命名为铜死亡。铜死亡是通过铜与三羧酸循环中的脂酰化酶结合而发生,随后引起铁硫簇蛋白质聚集、蛋白毒性应激,最终导致细胞死亡。铜死亡的提出,对于研究铜在糖尿病并发症中的作用机制提供了一个新的方向。 2014年,LIN等[35]的一项研究表明,在糖尿病患者体内,铜水平的升高、锌水平的降低与氧化应激标志物如超氧化物歧化酶、丙二醛水平的提高之间存在显著的关系。他们还表明,糖尿病患者的氧化应激水平与铜和锌水平有很大关系。在OZDEMIR等[36]的一项研究中评估了2型糖尿病患者体内作为氧化应激标志的丙二醛和同型半胱氨酸表达水平,该研究表明2型糖尿病患者血中丙二醛、同型半胱氨酸水平显著升高,谷胱甘肽和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶水平显著降低。有学者针对微量元素和氧化应激指标研究发现,2型糖尿病患者体内硒、铜等微量元素水平随丙二醛、超氧化物歧化酶水平升高而升高,与此同时,炎症因子白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α水平也相应升高[37]。 根据以上研究可以发现,随着糖尿病的发生,尤其是糖尿病并发症的发生,糖尿病患者体内微量元素的水平以及氧化应激水平发生了较显著的变化。氧化应激增加会增加炎症因子的产生,同样,炎症因子的增加也会刺激活性氧的生成。此文将针对不同类型并发症,结合铜元素作用与氧化应激之间的关系进行以下综述。 2.2 铜元素在糖尿病并发症中作用 2.2.1 糖尿病心肌病 糖尿病心肌病是指糖尿病患者在高血糖、胰岛素抵抗、氧化应激及炎症等因素共同作用后,出现的一种表现为心肌结构和功能异常的特殊心肌病变,其发生独立于冠心病及高血压等其他心血管危险因素[38]。而心血管疾病是糖尿病并发症中导致患者残疾和死亡的主要原因,伴有心脏能量改变、线粒体功能受损和氧化应激,临床表现为无冠状动脉疾病、高血压和瓣膜病的心室功能受损和心力衰竭[39]。糖尿病心肌病能够引起许多心脏病理改变,如心肌细胞肥大、间质纤维化等,同时也会伴随心肌细胞的细胞器受损,这些病理改变共同导致心肌收缩和舒张功能受损,进而发展为明显的心力衰竭[40-41]。 铜缺乏和铜过量状态均可导致体内氧化应激升高和抗氧化防御受损,从而加重炎性反应,以此诱导或加重糖尿病心肌病。除了心脏组织中铜分布异常引起的心脏损伤外,铜伴侣蛋白和铜转运蛋白的变化也在不同程度上促进了糖尿病心肌病的发生发展[42]。因此,铜被认为是糖尿病心血管损伤的重要催化剂,铜代谢缺陷与糖尿病心肌病的发病机制密切相关。 多项实验证实,糖尿病动物和糖尿病心肌病患者表现出全身铜水平增加的迹象,血浆铜和铜蓝蛋白水平正常或升高,肝和肾铜水平显著升高[12,34]。Cu+占总铜含量的95%,位于细胞内,而Cu2+占总铜含量的5%,位于细胞外[42]。在糖尿病患者体内,循环铜浓度增加,血浆中Cu2+水平增加至正常的两三倍,但细胞内Cu+水平降低。糖尿病心肌病中心肌组织铜含量降低,全身和血浆总铜含量升高反映了心肌细胞对铜的摄取缺陷[43]。这些观察结果表明,糖尿病患者体内发生的铜代谢紊乱,会在糖尿病心肌病中不同程度地损害心脏结构和功能。一项针对大鼠糖尿病模型中铜与心脏功能损害的研究表明,高血糖会诱导心肌细胞转运铜能力下降,从而导致心肌细胞内铜含量严重下降,进而左心室功能会出现严重障碍,进而导致糖尿病心肌病,而使用铜螯合剂后两者恢复正常[44],该实验同样证明了铜在高糖环境下对于心肌细胞的影响。心肌细胞中铜的缺乏也可导致心脏能量代谢受损,心脏收缩能力降低,从而诱发心肌病[45]。而高水平的铜与活性氧生成呈正相关[46-47],具有氧化还原活性的Cu2+以及铜蓝蛋白在心肌细胞外的积累,诱导心肌细胞铜氧化应激,导致蛋白质氧化、谷胱甘肽消耗、脂质损伤和氧化还原失衡,这可导致急性心功能损害,会加重心肌细胞慢性潜在损伤。见表1。 2.2.2 糖尿病肾病 肾脏对于糖尿病患者体内铜水平的变化有高度敏感性,高血糖、代谢紊乱、肾脏血流动力学的改变等都可以加重肾脏损伤,刺激炎症递质和炎症因子的产生,从而加快糖尿病肾病的进展[48]。 糖尿病肾病是指由糖尿病导致的慢性肾脏病,是糖尿病患者常见的微血管并发症之一[49]。全球约有30%的糖尿病患者发生糖尿病肾病,根据最新统计,国内慢性肾脏病患者中糖尿病肾病患者占26.7%,糖尿病肾病可以 "
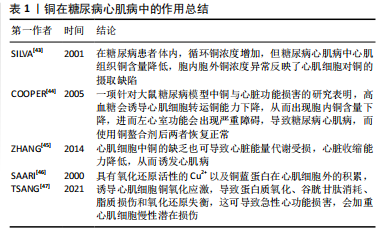

导致终末期肾病,是糖尿病患者死亡的主要原因之一[50]。 糖尿病肾病的临床特点是持续存在的进行性肾脏受损,如蛋白尿持续增加即24 h内尿蛋白> 300 mg或白蛋白-肌酐比值(> 300 mg/g),肾小球滤过率降低,血压升高,心血管事件发生率及相关死亡率提高,同时排除其他原因导致的肾脏慢性疾病。糖尿病肾病在患者肾脏中的病理变化有结节性肾小球硬化、肾小球系膜扩张、基底膜增厚等[51]。 肾脏被认为是受铜毒性影响的主要靶器官之一[52],过量铜元素的毒性作用可导致肾小管上皮细胞的颗粒状变性和空泡变性,最终导致慢性或急性肾功能衰竭[53]。AHMAD等[54]在一项孟德尔随机化遗传预测研究中发现体内过高的铜水平与较高的慢性肾脏疾病患病率相关。大量研究表明,铜暴露可引起氧化应激,进而导致多种类型的细胞的程序性死亡,糖尿病患者体内较高的铜水平会导致铜元素积累在肾脏内,过量铜元素导致近端小管坏死,从而介导氧化应激及细胞损伤,最终结果是肾功能下降[55]。 同时也有研究发现,糖尿病患者体内增加的活性氧介导高糖诱导的核因子κB 活化以及核因子κB依赖性单核细胞趋化蛋白1表达,从而导致肾小球系膜细胞的细胞毒性和增殖以及内皮功能障碍[49]。然而,铜和肾脏疾病之间的作用是双向的,因为慢性肾脏病患者的肾脏排泄受损和蛋白质代谢的变化也可能导致循环铜水平稳态的失衡[56]。见表2。"
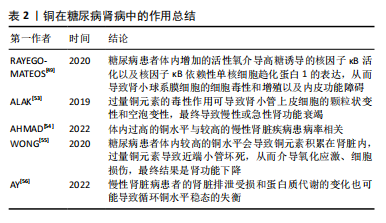
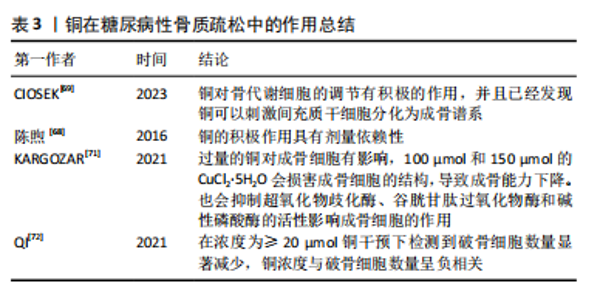
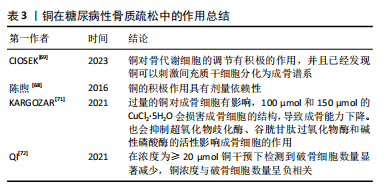
事实上,调节慢性肾脏病患者的体内铜元素水平对预防其并发症很重要。在既往的观察性研究中,铜循环水平的升高与慢性肾脏病相关[17,26]。但是目前二者因果关系尚不明确,血液中铜元素水平升高与肾脏损害、肾功能下降和慢性肾脏病风险增加之间的具体关系仍有待进一步实验确定。 2.2.3 糖尿病性视网膜病变 众所周知,视网膜是受糖尿病影响的主要靶器官,糖尿病性视网膜病变是糖尿病最常见的微血管并发症,也是导致视力丧失和失明的主要原因之一[57]。它是一种由高血糖引起的慢性进行性眼部疾病,损害视网膜微血管系统,导致血管通透性、视网膜缺血、新生血管形成、视网膜脱离和失明[58]。氧自由基引起的细胞损伤通常被认为是许多疾病发病的重要机制,糖尿病患者体内氧化应激的升高和抗氧化机制的失衡对于视网膜有不可逆的损伤,铜以其氧化还原特性,与氧自由基的生成密切相关[59]。高血糖直接导致视网膜内线粒体活性氧的形成,视网膜屏障的内皮细胞受到损伤,导致视力下降,最终失明。 氧化应激是糖尿病性视网膜病变主要发病机制之一。已有研究证实,高血糖诱导的视网膜损伤的发生和发展过程有多元醇途径、蛋白激酶C途径、氨基己糖途径和糖基化终末产物及其受体4个代谢途径[60]。有学者发现发生在线粒体中的自由基损伤是上述4个途径引发糖尿病性视网膜病变的统一机制[61],高糖状态下,上述4个途径的激活均能影响线粒体的呼吸链和亚甲基四氢叶酸还原酶的活性,导致机体内氧自由基产生增加和抗氧化剂的消耗过多,最终机体的氧化负荷增加,使得血管内皮细胞处于氧化应激状态[62]。体内铜水平直接影响具有抗氧化功能的铜蛋白的功能,如铜/锌超氧化物歧化酶、铜蓝蛋白和金属硫蛋白,并间接影响谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶活性。在细胞外环境中,H2O2与铁、铜等金属元素发生反应,产生高活性的羟基自由基(OH-),可与附近的大分子发生反应,造成细胞损伤[63]。超氧化物歧化酶是抵御超氧自由基细胞毒性作用的主要蛋白,并能有效保护视网膜组织免受膜磷脂的自由基氧化作用。已有研究证实,超氧化物歧化酶可以抑制炎症和细菌的吞噬作用[12],超氧化物歧化酶被认为是细胞内抗氧化防御的第一步,但在视网膜中,谷胱甘肽也被认为是主要的防御系统之一。有研究发现,在人体中,谷胱甘肽可以保护视网膜免受活性氧的毒性作用,并有助于维持正常的细胞氧化还原电位,从而在氧化应激作用中对视网膜起到一定保护作用[64]。 由于视网膜对氧需求量大,而且含有不饱和脂质,因此视网膜可能是产生氧自由基和脂质过氧化的常见场所。脂质过氧化产物对微血管壁有毒性,可能在糖尿病微血管损伤和血眼屏障的改变中起因果作用。一项观察特定糖尿病相关并发症的研究发现,与无并发症和对照受试者相比,伴有视网膜病变、高血压或微血管疾病的糖尿病受试者的血浆铜浓度更高[65-66]。 2.2.4 糖尿病性骨质疏松 人体中的铜几乎有2/3存在于肌肉和骨骼中[67]。机体中的铜参与细胞代谢、抗炎反应、基因表达调控、蛋白质合成、矿化和骨形成过程。铜元素参与骨形成和矿化,其主要功能是作为辅酶调节铁代谢和转运和胶原代谢[68]。对于糖尿病并发症的研究以往常常聚焦于大脑、眼睛、神经和肾脏的微血管及大血管损伤,对于骨骼肌肉系统受到的损伤关注较少,然而,骨脆性的增加正在成为糖尿病严重的并发症。糖尿病性骨质疏松症是在糖尿病基础上形成的以骨量减少、骨的微细结构破坏、脆性增加为特点,进而容易发生骨折的一种代谢性骨病,其致病机制是破骨细胞介导的骨吸收和成骨细胞介导的骨形成之间的代谢平衡被破坏[67]。 各种体外研究已经证实了铜对调节骨代谢细胞的积极作用,一些体外研究发现,铜对骨代谢细胞的调节有积极作用,并且已经发现铜可以刺激间充质干细胞分化为成骨谱系,而其他学者证明铜的积极作用是具有剂量依赖性的[69]。低浓度的铜提高了成骨细胞的活力和增殖能力,而较高浓度的铜被证明具有细胞毒性[70]。糖尿病患者体内过量的铜可以产生活性氧,诱导脂质过氧化,干扰骨代谢。有实验显示,过量的铜对成骨细胞有影响,100 μmol和150 μmol的CuCl2?5H2O会损害成骨细胞的结构,导致成骨能力下降。此外,铜还通过抑制超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶和碱性磷酸酶活性影响成骨细胞的作用[71]。过量的铜对破骨细胞也有影响,在一项研究中,在浓度≥20 μmol铜干预下检测到破骨细胞数量显著减少,铜浓度与破骨细胞数量呈负相关[72]。见表3。"

2.2.5 糖尿病牙周炎 与糖尿病相关的口腔疾病包括龋病、口干、牙周炎和牙龈炎、口腔念珠菌病、灼口综合征等[73-74],其中牙周炎作为糖尿病最常见的口腔并发症,被认为是糖尿病的第6大并发症[75]。有学者发现牙周病与2型糖尿病的发展有明确的联系,糖尿病与牙周病之间是互相促进的关系[76-77]。 牙周炎(Periodontitis)是累及4种牙周支持组织(牙龈、牙周膜、牙槽骨和牙骨质)的感染性、炎症性、破坏性疾病,临床上除了表现出牙龈色形质的改变、牙龈出血,还会有牙周袋的形成、牙槽骨的吸收、牙齿松动移位等症状。流行病学研究表明,糖尿病患者患牙周炎的风险比普通患者高3倍[78]。与血糖控制良好的糖尿病患者或健康的患者相比,血糖控制情况欠佳的糖尿病患者的牙周附着丧失也更大[79-80]。有关于糖尿病和牙周健康之间相互关系的研究表明,糖尿病可导致牙周组织炎症,而牙周病反过来也会影响糖尿病患者血糖的控制情况[76,81]。牙周炎的恢复可能有利于血糖控制,但仍需要进一步证据来证明二者之间的具体关系[82-84]。 糖尿病患者体内铜水平显著增加,牙周指数对血清铜水平的回归分析表明,血清铜水平与牙周指数呈线性相关[85],其原因是Cu2+导致活性氧以及炎性因子的积累在牙周组织受损中起着重要作用。牙周炎时局部感染、炎症产物增多,而铜蓝蛋白具有抗氧化剂作用,它能清除体内过氧化物自由基,以增加局部抵抗力[86]。因此,在各型牙周炎中龈沟液铜蓝蛋白值也有显著升高,但各型牙周炎之间未见显著性差异[87]。"

| [1] HARREITER J, RODEN M. Diabetes mellitus – Definition, Klassifikation, Diagnose, Screening und Prävention (Update 2019) [Diabetes mellitus-Definition, classification, diagnosis, screening and prevention (Update 2019)]. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2019;131(Suppl 1):6-15. [2] ALBERTI KG, ZIMMET PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med. 1998;15(7):539-553. [3] 刘烨,王海宁. 2021年ADA/EASD《糖尿病缓解专家共识》与《2022年ADA糖尿病指南:2型糖尿病的预防和治疗中肥胖与体重管理》解读——糖尿病缓解的定义与治疗策略[J].临床内科杂志,2022,39(5):299-302. [4] International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th edn. (International Diabetes Federation, 2021). https://diabetesatlas.org/data/en/country/42/cn.html. Accessed 15 March 2021. [5] ZHENG Y, LEY SH, HU FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14(2):88-98. [6] KOCHER T, KÖNIG J, BORGNAKKE WS, et al. Periodontal complications of hyperglycemia/diabetes mellitus: Epidemiologic complexity and clinical challenge. Periodontol 2000. 2018;78(1):59-97. [7] CHEN Y, HUA Y, LI X, et al. Distinct Types of Cell Death and the Implication in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:42. [8] NIBALI L, GKRANIAS N, MAINAS G, et al. Periodontitis and implant complications in diabetes. Periodontol 2000. 2022;90(1):88-105. [9] ALI MK, PEARSON-STUTTARD J, SELVIN E, et al. Interpreting global trends in type 2 diabetes complications and mortality. Diabetologia. 2022;65(1):3-13. [10] FANG Y, XING C, WANG X, et al. Activation of the ROS/HO-1/NQO1 signaling pathway contributes to the copper-induced oxidative stress and autophagy in duck renal tubular epithelial cells. Sci Total Environ. 2021;757:143753. [11] YIN J, WANG X, LI S, et al. Interactions between plasma copper concentrations and SOD1 gene polymorphism for impaired glucose regulation and type 2 diabetes. Redox Biol. 2019;24:101172. [12] LI P, YIN J, ZHU Y, et al. Association between plasma concentration of copper and gestational diabetes mellitus. Clin Nutr. 2019;38(6): 2922-2927. [13] 周琪. 1型糖尿病小鼠模型与1型糖尿病病人铜、锌、镁、钙变化的研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2018. [14] Dey A, Manna S, Adhikary J, et al. Biodistribution and toxickinetic variances of chemical and green Copper oxide nanoparticles in vitro and in vivo. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2019;55:154-169. [15] Sebio RM, Ferrarotti N, Lairion F, et al. Brain oxidative stress in rat with chronic iron or copper overload. J Inorg Biochem. 2019;199: 110799. [16] Fahmy HM, Ebrahim NM, Gaber MH. In-vitro evaluation of copper/copper oxide nanoparticles cytotoxicity and genotoxicity in normal and cancer lung cell lines. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020;60:126481. [17] 殷佳伟. 微量元素铜与2型糖尿病的关联性研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2020 [18] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)(上)[J].中国实用内科杂志,2021,41(8):668-695. [19] MARQUES CMS, NUNES EA, LAGO L, et al. Generation of Advanced Glycation End-Products (AGEs) by glycoxidation mediated by copper and ROS in a human serum albumin (HSA) model peptide: reaction mechanism and damage in motor neuron cells. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2017;824:42-51. [20] ALBERTI KG, ZIMMET PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med. 1998;15(7):539-553.
[21] HEISE T. The future of insulin therapy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2021; 175:108820. [22] KAKLEAS K, SOLDATOU A, KARACHALIOU F, et al. Associated autoimmune diseases in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). Autoimmun Rev. 2015;14(9):781-797. [23] XU L, LI Y, DAI Y, et al. Natural products for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: Pharmacology and mechanisms. Pharmacol Res. 2018;130:451-465. [24] ZHENG Y, LEY SH, HU FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018; 14(2):88-98. [25] SINGH R, BARDEN A, MORI T, et al. Advanced glycation end-products: a review. Diabetologia. 2001;44(2):129-146. [26] MAURI-OBRADORS E, ESTRUGO-DEVESA A, JANÉ-SALAS E, et al. Oral manifestations of Diabetes Mellitus. A systematic review. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2017;22(5):e586-e594. [27] SWEENEY SC. Alterations in tissue and serum ceruloplasmin concentration associated with inflammation. J Dent Res. 1967;46(6): 1171-1176. [28] ZHANG C, LI Q, LAI S, et al. Attenuation of diabetic nephropathy by Sanziguben Granule inhibiting EMT through Nrf2-mediated anti-oxidative effects in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017;205:207-216. [29] HUANG H, JIANG Y, MAO G, et al. Protective effects of allicin on streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats. J Sci Food Agric. 2017;97(4):1359-1366. [30] RAMALINGAM L, MENIKDIWELA K, LEMIEUX M, et al. The renin angiotensin system, oxidative stress and mitochondrial function in obesity and insulin resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017;1863(5):1106-1114. [31] YARIBEYGI H, ATKIN SL, SAHEBKAR A. Mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetes and the regulatory roles of antidiabetic agents on the mitochondrial function. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(6):8402-8410. [32] ACKERMAN CM, CHANG CJ. Copper signaling in the brain and beyond. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(13):4628-4635. [33] TSVETKOV P, COY S, PETROVA B, et al. Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science. 2022;375(6586): 1254-1261. [34] 林锦贤,王攀,吴欣谋,等.铜稳态失调诱导调节性细胞死亡及其调控的研究进展[J].江苏大学学报(医学版),2022,32(4):306-317. [35] LIN CC, HUANG HH, HU CW, et al. Trace elements, oxidative stress and glycemic control in young people with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2014;28(1):18-22. [36] OZDEMIR G, OZDEN M, MARAL H, et al. Malondialdehyde, glutathione, glutathione peroxidase and homocysteine levels in type 2 diabetic patients with and without microalbuminuria. Ann Clin Biochem. 2005; 42(Pt 2):99-104. [37] SEBIO RM, FERRAROTTI N, LAIRION F, et al. Brain oxidative stress in rat with chronic iron or copper overload. J Inorg Biochem. 2019; 199:110799. [38] LIEW G, LEI Z, TAN G, et al. Metabolomics of Diabetic Retinopathy.Curr Diab Rep. 2017;17(11):102. [39] LIU Y, MIAO J. An Emerging Role of Defective Copper Metabolism in Heart Disease. Nutrients. 2022;14(3):700. [40] CUI X, WANG Y, LIU H, et al. The Molecular Mechanisms of Defective Copper Metabolism in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:5418376. [41] BOUDINA S, ABEL ED. Diabetic cardiomyopathy revisited. Circulation. 2007;115(25):3213-3223. [42] ZHANG L, WARD ML, PHILLIPS AR, et al. Protection of the heart by treatment with a divalent-copper-selective chelator reveals a novel mechanism underlying cardiomyopathy in diabetic rats. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013;12:123. [43] SILVA J, WILLIAMS R. The Biological Chemistry of the Elements: The Inorganic Chemistry of Life, 2nd ed; Clarendon: Oxford, UK, 2001:418-435. [44] COOPER GJ, CHAN YK. Demonstration of a Hyperglycemia-Driven Pathogenic Abnormality of Copper Homeostasis in Diabetes and Its Reversibility by Selective Chelation: Quantitative Comparisons Between the Biology of Copper and Eight Other Nutritionally Essential Elements in Normal and Diabetic Individuals. Diabetes. 2005;54: 1468-1476. [45] ZHANG S, LIU H, AMARSINGH GV, et al. Diabetic cardiomyopathy is associated with defective myocellular copper regulation and both defects are rectified by divalent copper chelation. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014;13:100. [46] SAARI JT. Copper deficiency and cardiovascular disease: role of peroxidation, glycation, and nitration. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2000; 78(10):848-855. [47] TSANG T, DAVIS CI, BRADY DC. Copper biology. Curr Biol. 2021;31(9): R421-R427. [48] FERNÁNDEZ-RODARTE BA, SOTO-DOMÍNGUEZ A, GONZÁLEZNAVARRO A, et al. Copper induces damage, oxidative stress and cell death in endothelium of chronic intoxicated Wistar rats. Int J Morphol. 2022; 40(1): 10-17. [49] RAYEGO-MATEOS S, MORGADO-PASCUAL JL, OPAZO-RÍOS L, et al. Pathogenic Pathways and Therapeutic Approaches Targeting Inflammation in Diabetic Nephropathy. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(11):3798. [50] 党佳蓉,党琳慧,郭煦妍,等.糖尿病肾病的发病机制研究[J].医学信息,2022,35(17):161-165. [51] YANG C, GAO B, ZHAO X, et al. Executive summary for China Kidney Disease Network (CK-NET) 2016 Annual Data Report. Kidney Int. 2020;98(6):1419-1423. [52] PERSSON F, ROSSING P. Diagnosis of diabetic kidney disease: state of the art and future perspective. Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 2018;8(1):2-7. [53] ALAK G, YELTEKIN AÇ, UÇAR A, et al. Borax Alleviates Copper-Induced Renal Injury via Inhibiting the DNA Damage and Apoptosis in Rainbow Trout. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019;191(2):495-501. [54] AHMAD S, ÄRNLÖV J, LARSSON SC. Genetically Predicted Circulating Copper and Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients. 2022;14(3):509. [55] WONG A, WILSON-FRANK CR, HOOSER SB, et al. Chronic copper toxicosis in a crossbred heifer calf. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2020;32(3):458-462. [56] AY A, ALKANLI N, USTUNDAG S. Investigation of the Relationship Between IL-18 (- 607 C/A), IL-18 (- 137 G/C), and MMP-2 (- 1306 C/T) Gene Variations and Serum Copper and Zinc Levels in Patients Diagnosed with Chronic Renal Failure. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022; 200(5):2040-2052. [57] NIU YY, ZHANG YY, ZHU Z, et al. Elevated intracellular copper contributes a unique role to kidney fibrosis by lysyl oxidase mediated matrix crosslinking. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(3):211. [58] ANTONETTI DA, KLEIN R, GARDNER TW. Diabetic retinopathy. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(13):1227-1239.
[59] STITT AW, CURTIS TM, CHEN M, et al. The progress in understanding and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016;51: 156-186.
[60] AUGUSTINE J, TROENDLE EP, BARABAS P, et al. The Role of Lipoxidation in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Retinopathy. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;11:621938. [61] 万文萃,龙洋.糖尿病视网膜病变的流行病学、病因学与发病机制研究现状[J].眼科新进展,2022,42(9):673-679. [62] BROWNLEE M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature. 2001;414(6865):813-820. [63] GUZIK TJ, MUSSA S, GASTALDI D, et al. Mechanisms of increased vascular superoxide production in human diabetes mellitus: role of NAD(P)H oxidase and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circulation. 2002;105(14):1656-1662. [64] YILDIRIM Z, UÇGUN NI, KILIÇ N, et al. Antioxidant enzymes and diabetic retinopathy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1100:199-206. [65] 陶玉滨,许勇臣.糖尿病视网膜病变中血清铜蓝蛋白水平变化的意义[J]. 实用预防医学,2009,16(5):1591-1592. [66] WALTER RM JR, URIU-HARE JY, OLIN KL, et al. Copper, zinc, manganese, and magnesium status and complications of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1991;14(11):1050-1056. [67] DOŞA MD, HANGAN LT, CRAUCIUC E, et al. Influence of therapy with metformin on the concentration of certain divalent cations in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2011;142(1):36-46. [68] 陈煦,王新力,邹远康,等.微小RNA在骨质疏松症治疗中的作用及机制的研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(6):786-790. [69] CIOSEK Ż, KOT K, ROTTER I. Iron, Zinc, Copper, Cadmium, Mercury, and Bone Tissue. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(3):2197. [70] DING H, GAO YS, WANG Y, et al. Dimethyloxaloylglycine increases the bone healing capacity of adipose-derived stem cells by promoting osteogenic differentiation and angiogenic potential. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23(9):990-1000. [71] KARGOZAR S, MOZAFARI M, GHODRAT S, et al. Copper-containing bioactive glasses and glass-ceramics: From tissue regeneration to cancer therapeutic strategies. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021; 121:111741. [72] QI Y, WANG H, CHEN X, et al. The role of TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway and oxidative stress in the inhibition of osteoblast mineralization by copper chloride. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2021; 84:103613. [73] BERNHARDT A, BACOVA J, GBURECK U, et al. Influence of Cu2+ on Osteoclast Formation and Activity In Vitro. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:2451. [74] ALBERT DA, WARD A, ALLWEISS P, et al. Diabetes and oral disease: implications for health professionals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012;1255:1-15. [75] American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2013;36 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S67-S74. [76] AHMAD R, HAQUE M. Oral Health Messiers: Diabetes Mellitus Relevance. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021;14:3001-3015. [77] NIBALI L, GKRANIAS N, MAINAS G, et al. Periodontitis and implant complications in diabetes. Periodontol 2000. 2022;90(1):88-105. [78] DEMMER RT, JACOBS DR JR, DESVARIEUX M. Periodontal disease and incident type 2 diabetes: results from the First National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey and its epidemiologic follow-up study. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(7):1373-1379. [79] KOCHER T, KÖNIG J, BORGNAKKE WS, et al. Periodontal complications of hyperglycemia/diabetes mellitus: Epidemiologic complexity and clinical challenge. Periodontol 2000. 2018;78(1):59-97. [80] MAURI-OBRADORS E, ESTRUGO-DEVESA A, JANÉ-SALAS E, et al. Oral manifestations of Diabetes Mellitus. A systematic review. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2017;22(5):e586-e594. [81] KUDIYIRICKAL MG, PAPPACHAN JM. Diabetes mellitus and oral health. Endocrine. 2015;49(1):27-34. [82] MOORE PA, WEYANT RJ, MONGELLUZZO MB, et al. Type 1 diabetes mellitus and oral health: assessment of periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 1999;70(4):409-417. [83] TEEUW WJ, GERDES VE, LOOS BG. Effect of periodontal treatment on glycemic control of diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(2):421-427. [84] JANKET SJ, WIGHTMAN A, BAIRD AE, et al. Does periodontal treatment improve glycemic control in diabetic patients? A meta-analysis of intervention studies. J Dent Res. 2005;84(12):1154-1159. [85] DARRÉ L, VERGNES JN, GOURDY P, et al. Efficacy of periodontal treatment on glycaemic control in diabetic patients: A meta-analysis of interventional studies. Diabetes Metab. 2008;34(5):497-506. [86] DOMMISCH H, KUZMANOVA D, JÖNSSON D, et al. Effect of micronutrient malnutrition on periodontal disease and periodontal therapy. Periodontol 2000. 2018;78(1):129-153. [87] VASILYEV VB. Looking for a partner: ceruloplasmin in protein-protein interactions. Biometals. 2019;32(2):195-210. [88] WU H, GUO H, LIU H, et al. Copper sulfate-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress promotes hepatic apoptosis by activating CHOP, JNK and caspase-12 signaling pathways. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020; 191:110236. [89] LIU H, GUO H, JIAN Z, et al. Copper Induces Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in the Mouse Liver. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020: 1359164. [90] LUO Q, SONG Y, KANG J, et al. mtROS-mediated Akt/AMPK/mTOR pathway was involved in Copper-induced autophagy and it attenuates Copper-induced apoptosis in RAW264.7 mouse monocytes. Redox Biol. 2021;41:101912. [91] KRUMSCHNABEL G, EBNER HL, HESS MW, et al. Apoptosis and necroptosis are induced in rainbow trout cell lines exposed to cadmium. Aquat Toxicol. 2010;99(1):73-85. [92] DEIGENDESCH N, ZYCHLINSKY A, MEISSNER F. Copper Regulates the Canonical NLRP3 Inflammasome. J Immunol. 2018;200(5):1607-1617. [93] LIAO J, YANG F, TANG Z, et al. Inhibition of Caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis attenuates copper-induced apoptosis in chicken hepatocytes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019;174:110-119. [94] RAKSHIT A, KHATUA K, SHANBHAG V, et al. Cu2+ selective chelators relieve copper-induced oxidative stress in vivo. Chem Sci. 2018;9(41): 7916-7930. [95] MAHER P. Potentiation of glutathione loss and nerve cell death by the transition metals iron and copper: Implications for age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018;115:92-104. |
| [1] | Cai Zhixing, Xia Qiufang, Chen Lili, Zhu Danyang, Zhu Huiwen, Sun Yanan, Liang Wenyu, Zhao Heqian. Effect of Roujishuncuiyin on the improvement of skeletal muscle insulin resistance in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7537-7543. |
| [2] | Zeng Yu, Xie Chengwei, Hong Yuanqi, Su Shenghui, Dong Xieping. In vitro angiogenesis and osteogenesis properties of copper-doped mesoporous bioactive glass [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 5941-5949. |
| [3] | Cheng Xinqi, Shao Longhui, Shen Huaqiao, Liu Hongwei. Osteogenic and antibacterial effects of titanium alloy modified with copper-strontium binary doped calcium silicate coating [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4639-4646. |
| [4] | Gao Hongli, Qin Yufeng, Zhang Yuehan, Shu Jiayu, Chen Helin. Copper metabolism and diagnosis and treatment of oral diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4316-4324. |
| [5] | Qian Zuping, Chen Yong, Ran Yan, Da Jingjing, Zha Yan. Diabetic nephropathy model: animal model, two-dimensional cell simulation and three-dimensional organoid model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3632-3640. |
| [6] | Zhou Hongyan, Zhang Yidan, Ji Wei, Liu Xia. Comparison of different intensity exercises to improve autophagy in diabetic rats by inhibiting renal phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2310-2318. |
| [7] | Guan Zhenju, Xie Yonglin, Xiang Shougang, Zhang Chengdong, Li Xiaolong, Li Xingping, Pu Chao, Zhang Bo, Luo Xuwei, Xiao Dongqin. Preparation of polyphenol-mediated copper ion coating on titanium surface and antibacterial and antioxidant properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 1997-2005. |
| [8] | Wang Jiani, Chen Junyu. Angiogenesis mechanism of metal ions and their application in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 804-812. |
| [9] | Liu Junpeng, Yao Xingchen, Zhao Hui, Xu Ziyu, Wu Yue, Pei Fuchun, Zhang Lin, Du Xinru. Antibiotic-loaded bone cement enhances ability of tibial cortex transverse transport for treating infected wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(29): 4599-4604. |
| [10] | Zeng Cheng, Yu Huanhuan, Gong Yukang, Wang Chenhao, Zhang Yinen, Gao Wenshan. Biological and physicochemical properties of bioactive ion modified brushite cements [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(22): 3561-3568. |
| [11] | Wu Yaru, Mi Yan, Wei Kaiyue, Gao Heping, Zhang Dingyu, Wang Caili. Regulatory effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on intestinal barrier function in diabetic nephropathy rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(19): 2967-2973. |
| [12] | Xie Ting, Liu Tingting, Zeng Xuehui, Li Yamin, Zhou Panghu, Yi Nianhua. Vitamin D3 attenuates high-glucose exposure-induced oxidative stress to promote osteogenic differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(19): 2981-2987. |
| [13] | Jiang Chunjing, Yang Chengxue, Yu Zhengwen, Zhang Jian. Molecular mechanisms of anti-inflammatory effects of metal ions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(10): 1626-1633. |
| [14] | Zhao Lu, Zhao Yifei, Gao Da, Liu Yanfang, Fu Tingting, Xu Jiangyan. Expression of suppressor of Zeste 12 in kidney tissues of rats with diabetic nephropathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1179-1186. |
| [15] | Shen Yong, Liu Shizhang. Research progress on antibacterial properties of medical copper-containing titanium alloys [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(21): 3430-3437. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||