Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (10): 1626-1633.doi: 10.12307/2024.267
Previous Articles Next Articles
Molecular mechanisms of anti-inflammatory effects of metal ions
Jiang Chunjing, Yang Chengxue, Yu Zhengwen, Zhang Jian
- School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563099, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2023-03-20Accepted:2023-04-25Online:2024-04-08Published:2023-08-21 -
Contact:Zhang Jian, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563099, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Jiang Chunjing, Master candidate, School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563099, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Talent Base of Medical Biomaterials Research of Guizhou Province, No. QRLF[2018]3 (to ZJ and YZW); Project of Basic Research of Guizhou Province, No. QKHJC-ZK[2023]-YB497 (to YZW); Project of Basic Research of Guizhou Province, No. QKHJC-ZK[2023]-YB536 (to YCX); Joint Project of Zunyi Science and Technology and Big Data Bureau and Hospital of Stomatology of Zunyi Medical University, No. ZSKHHZZ[2022]386 (to YZW); Joint Project of Zunyi Science and Technology and Big Data Bureau and Hospital of Stomatology of Zunyi Medical University, No. ZSKHHZZ[2022]427 (to ZJ); Project of Scientific and Technological Innovation Talent Team of Zunyi City, No. ZSKRC(2022)1 (to ZJ and YZW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiang Chunjing, Yang Chengxue, Yu Zhengwen, Zhang Jian. Molecular mechanisms of anti-inflammatory effects of metal ions[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(10): 1626-1633.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
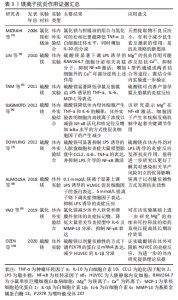
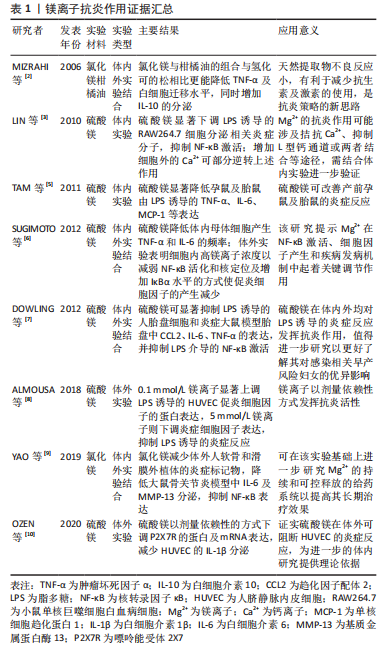
2.1 常见医用金属离子的抗炎作用。 2.1.1 镁离子的抗炎作用 镁离子是人体细胞内主要的阳离子之一,其含量在人体中仅次于钠、钾、钙,位居第4位[1]。在机体中镁离子参与所有主要的细胞过程,包括能量代谢、代谢周期和信号通路的调节,因此镁离子被誉为细胞新陈代谢的重要活化剂。 镁离子常以离子化合物的形式发挥优异的抗炎活性。氯化镁与柑橘油形成的混合物可改善小鼠皮下腔感染模型的炎症反应,二者产生的协同作用机制可能是由于萜类增加了细菌膜的流动性,这使得镁离子能够穿透细胞并影响对镁离子敏感的酶[2],该研究提供了一种有效的动物体内炎症模型,可供炎症造模参考应用。硫酸镁作为一种含镁化合物,已在临床得以广泛使用,以不同的给药途径呈现出不同的药理作用,主要用于治疗子痫、早产及妊娠性高血压等,同时将其50%浓度的溶液热敷至患处,可有消炎去肿的功效,在许多体内外体实验中对其抗炎作用有了明确验证,其不仅抑制脂多糖诱导的细胞炎症反应,还通过抑制核转录因子κB的激活来调节炎症反应。LIN等[3]用硫酸镁处理小鼠单核巨噬细胞白血病细胞测定炎性分子的产生证实了这一点。在缺镁动物模型中发现炎症是其第一个明显的变化,主要表现为促炎细胞因子水平升高,抗炎细胞因子水平下降[4]。而镁离子的补充则可抑制孕鼠对脂多糖诱导的炎症反应[5],减少Toll受体刺激导致的促炎细胞因子产生[6],这与DOWLING等[7]研究结果一致,提示镁离子具有优异的抗炎活性。在没有炎症刺激的情况下,低浓度的镁离子也会导致黏附分子和炎性细胞因子的表达增加,提供高浓度的镁离子可抑制炎症刺激反应[8]。高浓度的镁离子在体外可抑制人组织外植体中基质金属蛋白酶6和白细胞介素13的表达,而低浓度镁离子则可改善大鼠关节软骨退变和滑膜炎症[9]。由此看来,镁离子在不同实验类型及实验对象中发挥抗炎活性的浓度有所不同,需要进行更多研究以进一步探索其发挥作用的治疗浓度。嘌呤能受体2X7是分泌白细胞介素1β所必需的受体,可被镁离子等二价阳离子及自身拮抗剂亮蓝G所阻断,人脐静脉内皮细胞可表达该受体。硫酸镁可通过下调嘌呤能受体2X7的表达来抑制人脐静脉内皮细胞的炎症反应[10]。镁离子抗炎作用证据汇总见表1。"

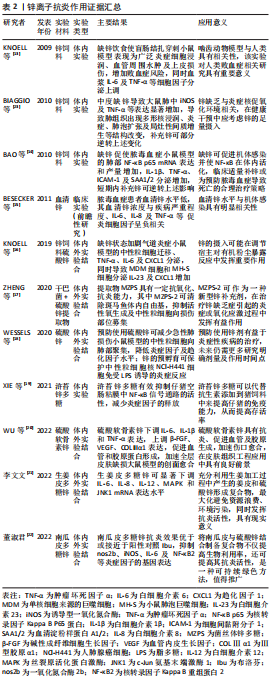
2.1.2 锌离子的抗炎作用 锌是公认的抗氧化剂与抗炎剂,在体内平衡、免疫功能、氧化应激、细胞凋亡和衰老中起着至关重要的作用。和镁相同,锌是人体必需的微量元素之一,其作为机体300多种酶的辅酶,参与机体DNA、RNA及蛋白质的合成,可影响生物膜的稳定性和多蛋白复合物的排列,调节激素及其受体的形成,当机体缺锌,不仅影响免疫状态,增加氧化应激,还会导致炎症的发生[11]。 锌可以影响许多炎症细胞因子的产生和信号传递,在体外可增强单核细胞对内皮细胞的黏附,并对促炎细胞因子的产生具有不利影响[12]。缺锌会引起对脂多糖的过度炎症反应,加重多微生物脓毒血症小鼠的全身炎症反应和脓毒血症诱导的器官损伤易感性[13],增加肺组织中炎性细胞因子表达[14],这种炎性细胞因子的表达水平或与血清锌浓度呈现负相关趋势[15]。锌缺乏除了导致炎性细胞因子分泌增多以外,还可加剧中性粒细胞迁移及上调趋化因子表达[16]。从这些相似的研究结果可以看出,缺锌使宿主各种促炎细胞因子增加,加重炎症反应,而补充锌可在一定程度上逆转该过程。锌多糖是一种理想的生物有机锌,具有有机锌和多糖的生物学功能。ZHENG等[17]在干巴菌中提取并纯化出的菌丝体锌多糖被证实对于斑马鱼体内的自由基具有高效清除能力及抗炎能力,可作为一种新型锌抗炎剂,但其具体治疗效应还需更多体内外研究来印证。类似的,锌的加入可显著改善小鼠急性炎症反应[18],仔猪肠道感染[19],一定程度上可代替抗生素的使用,是临床抗炎剂的潜在候选者。 硫酸软骨素是一种广泛存在于人和动物体内的碳水化合物,是细胞外基质的主要成分之一,具有促进细胞增殖、下调炎性细胞因子等特点,将锌与硫酸软骨素相结合形成稳定的多糖复合物,可下调促炎细胞因子表达,促进血管及胶原蛋白形成[20-23],这为组织创伤的修复与再生提供了新视角,前景广阔。还有学者从姜皮及南瓜皮中提取多糖与硫酸锌结合形成复合物,该复合物可通过多条信号通路及下调炎症细胞因子表达水平发挥抗炎活性[21-22]。这种从天然物质中提取有效抗炎成分的方式具有价格低廉、来源广泛及可持续等优点,可在未来进行更多研究以得到进一步推广。锌离子抗炎作用证据汇总见表2。"

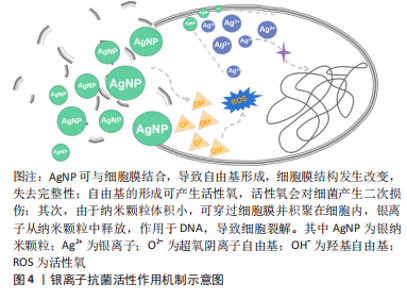
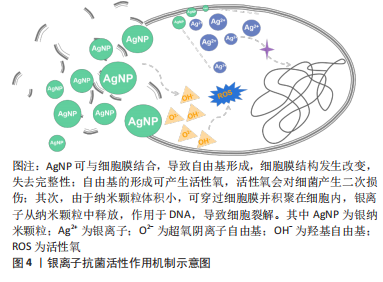
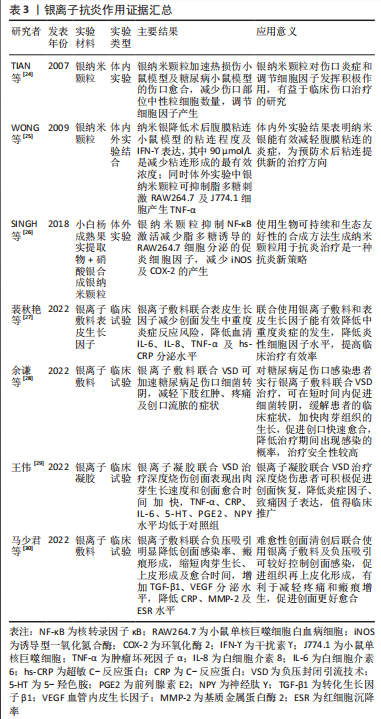
银纳米颗粒不仅具有优异的抗菌活性,同时可下调热损伤小鼠体内促炎细胞因子水平,上调抗炎细胞因子水平,减少术区中性粒细胞聚集,减轻损伤部位的炎症反应[24]。干扰素?是腹腔粘连形成的关键促炎细胞因子,银纳米颗粒可降低腹膜粘连小鼠的干扰素?表达,同时也降低脂多糖诱导巨噬细胞分泌肿瘤坏死因子α[25]。从小白杨成熟果实中提取合成天然的银纳米颗粒具有前文所述的镁离子同样的抗炎效应,抑制核转录因子κB激活从而减少脂多糖诱导的巨噬细胞分泌促炎细胞因子[26]。含银敷料能明显减少创面的局部感染,改善创面局部微环境,目前已应用于压疮、糖尿病足、烧伤及慢性难愈性伤口等,可明显降低炎性细胞因子及致痛因子分泌水平,减轻局部感染,促进创面愈合。基于目前的研究可以看出,银离子在抗炎作用方面的相关证据较少,主要研究领域仍局限于抗菌作用的相关研究,未来可将重心转移至其抗炎作用的研究,为应对生物植入材料所引发的局部炎症反应提供新的可能[24-30],银离子抗炎证据汇总见表3。"

值得一提的是,银离子还能与病毒相互作用,使病毒失活。银纳米颗粒已被证明对人类免疫缺陷病毒、腺病毒、乙型肝炎病毒、单纯疱疹病毒、呼吸道合胞病毒、诺如病毒和脊髓灰质炎病毒等均有抗病毒活性,是一种潜在的有效抗病毒制剂[31]。 2.1.4 铜离子的抗炎作用 铜是人体内的关键微量元素,在维持人体生理动态平衡和抗菌方面起着至关重要的作用,与细胞免疫和体液免疫之间存在一定联系。和银离子一样,铜离子常被报道具有良好的抗菌活性,其作为铜蓝蛋白的活性部位,通过刺激炎症细胞因子和低氧诱导因子的合成来促进铜蓝蛋白的合成和分泌[32]。此外,在炎症、感染和其他疾病的急性期反应中,铜的代谢明显增强,以不同的氧化还原状态,使金属在细胞生理学中作为催化辅因子在酶的氧化还原化学、线粒体呼吸、铁吸收、自由基清除和弹性蛋白交联中发挥关键作用[33]。 铜掺入生物活性玻璃陶瓷构造含铜生物活性玻璃陶瓷支架可诱导巨噬细胞向抗炎表型极化,减少促炎细胞因子的分泌,显著促进软骨和骨软骨界面的再生,对于缺损组织的修复与再生具有有益影响,是潜在植入材料候选[32]。释放的铜离子增加人细支气管上皮细胞分泌白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8和白细胞介素10等炎症细胞因子,使肿瘤坏死因子α的分泌显著减少[34],调节宿主炎症反应。然而有研究结果表明,随着铜离子浓度升高以及作用时间延长,其刺激人脐静脉内皮细胞、人肺微血管内皮细胞和人髂动脉内皮细胞合成和分泌白细胞介素8的释放量均同步增加,反而促进了机体的炎症反应,同时该实验结果可说明铜离子促进内皮细胞合成和分泌白细胞介素8这个过程具有时间-剂量依赖性的特点[35]。该研究与上述铜离子具有抗炎作用的结论相悖,分析原因认为问题的关键可能是铜离子的浓度不同,当其浓度超出治疗范围的最大阈值,铜离子通过分泌相关促炎递质以促进炎症反应,而在治疗浓度范围内,铜离子则同样具有一定抗炎能力,也提示研究者们可以通过控制铜离子的释放速率,调节为适宜浓度,达到对应治疗需求,但如何把握这个治疗浓度范围则仍然需要未来更多体内外研究作进一步探讨来确定。但总的来说,对于铜离子消除炎症的相关证据目前仍有很大空缺与不确定性,今后需要更多实验来进一步对铜离子抗炎作深入研究。 除了上述列举的金属离子所具有的抗炎作用以外,也有其他离子相继报道出有一定抑制炎症的能力。如关节内低剂量的镉通过诱导滑膜细胞凋亡来减少关节炎体内模型的细胞增殖、炎症和破坏[36];金纳米颗粒可改善大鼠关节炎的临床病程,减少巨噬细胞浸润,减轻大鼠的关节炎症等[37]。当然,还有很多金属离子的潜在抗炎活性未被发掘,未来仍需更多相关研究为解决植入材料所引发的局部炎症反应寻找更优的抗炎生物材料。同时,从上述金属离子抗炎证据的阐述中不难看出,相较于银、铜离子而言,镁、锌离子的抗炎活性更胜一筹,可下调多种促炎细胞因子表达,以多样化的形式调节宿主炎症反应,其中镁离子常以硫酸镁的形式在临床中得以广泛使用,锌离子则是在动物实验中以锌饲料的途径建立缺锌/富锌模型来验证其抗炎作用,而银及铜离子主要是在抗菌作用方面具有良好性能,在抗炎方面的确存在许多局限性,仅有少量研究报道了其具有一定的抗炎作用。综上所述,金属离子与炎症之间并非是简单的调节与被调节的关系,金属离子抗炎活性的效率高低是与离子的浓度、作用时间、作用部位等共同决定的,故而探究金属离子与炎症之间的时间-剂量依赖方式,调控离子的释放速率,是最大化利用金属离子抗炎活性的途径。"


2.2 常见医用金属离子的免疫调节 众所周知,巨噬细胞是机体免疫系统的核心组成成员之一,是十分重要的抗原提呈细胞及吞噬细胞,其作为一类具有高度可塑性及多能性的细胞群体,在不同环境和条件的刺激下可以极化为促炎型巨噬细胞和抗炎型巨噬细胞。当巨噬细胞由促炎型极化为抗炎型时,就会释放抗炎细胞因子,发出组织重塑和修复的信号。其中,金属离子可通过调节巨噬细胞表型来参与机体的免疫调节。 在炎症环境中将镁离子与巨噬细胞共培养可调节巨噬细胞表型,显著上调抗炎型巨噬细胞标志物水平,下调促炎型巨噬细胞标志物水平[38],并通过Toll样受体途径下调核转录因子κB信号通路,促进活化的抗炎型巨噬细胞分泌白细胞介素10等抗炎细胞因子以调节宿主炎症反应[39]。HU等[40]发现镁离子调节巨噬细胞表型的能力与其剂量有关,低浓度镁离子可抑制脂多糖和干扰素?诱导的炎症反应,显著降低促炎型巨噬细胞标志物百分比。一些镁基生物材料也表现出类似作用,由纤维蛋白原和镁组成的生物材料不仅可减少脂多糖诱导的巨噬细胞分泌肿瘤坏死因子α,同时降低促炎型巨噬细胞表面标志物表达,下调核转录因子κB磷酸化[41],以调节机体炎症反应。尽管多数研究都表明镁离子的参与使得巨噬细胞向抗炎型极化,但魏文发[42]的研究显示,随着镁离子浓度的升高,巨噬细胞促炎型基因上调,抗炎型基因下调,进一步佐证了HU等[40]的研究结果,说明镁离子使巨噬细胞极化的能力与其浓度有强相关性,具有剂量依赖性的特点,但不同实验方法、检测方式、检测时间等有所差异,还需更多体内外实验对该结果作进一步探索。 锌在调节炎症反应中起着关键作用,具有良好的抗炎活性。锌补充剂通过抑制与巨噬细胞向促炎型极化相关的跨膜受体蛋白1信号通路选择性下调促炎型巨噬细胞,从而抑制胆管结扎小鼠的肝脏炎症及纤维化[43]。在体外实验中,锌包被的磺化聚醚醚酮可显著促进巨噬细胞向抗炎表型极化,降低炎性细胞因子分泌水平,增加成骨细胞因子分泌,促进骨整合[44]。这表明锌离子具有抗炎、免疫调节和成骨的作用,是一种有良好前景的有效添加剂,可用于开发骨再生和免疫调节生物活性材料。GATA结合蛋白3是一种锌指转录因子,对许多细胞增殖、发育、分化起着重要促进作用,需要锌离子来维持其功能和稳定性。当锌缺乏时,使大鼠GATA结合蛋白3的锌指结构域丢失,影响辅助性T淋巴细胞2的分化,进而降低抗炎型巨噬细胞诱导剂——白细胞介素4和白细胞介素13分泌,抑制未成熟的巨噬细胞向抗炎型巨噬细胞极化,间接加重宿主的炎症反应,然而补充锌可逆转上述病理过程[45],说明锌对于机体的炎症反应以及巨噬细胞表型极化具有明显相关性。 银纳米颗粒及其负载二氧化钛纳米管作为植入材料可调节缺损术区的巨噬细胞表型,促进巨噬细胞向抗炎型极化,创造一个良好的骨免疫微环境,是一种很有前景的生物植入材料[46]。铜离子也被报道具有同样的效应。不同浓度氯化铜与巨噬细胞共培养,在一定浓度范围内可诱导巨噬细胞向抗炎表型转变[32]。同样地,DIEZ-TERCERO等[47]研究表明,铜离子浓度低于10 μmol/L时可诱导巨噬细胞向抗炎表型极化,而更高浓度的铜离子则会刺激巨噬细胞向促炎型极化,结果提示,尽管不同金属离子调节免疫的能力大小不同,但总体上都跟其浓度密切相关,故而在未来的研究中,应该重点考虑不同浓度条件下金属离子对免疫调节所产生的效果如何,为探索金属离子与免疫调节之间的潜在联系提供新方向。"


2.3 常见医用金属离子氧化应激调节能力 氧化应激是许多炎症性疾病发展的分子基础之一。在所有的生命系统中,细胞都需要足够水平的抗氧化防御,以避免产生过量活性氧而促发炎症反应。炎症过程中,吞噬细胞的激活或细菌产物与特定受体的作用都能够促进烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸氧化酶的组装,从而催化大量超氧化物产生,此时中性粒细胞和巨噬细胞会产生超氧化物和过氧化氢,这对防御吞噬入侵微生物至关重要[48]。 镁离子代谢紊乱与氧化应激具有一定相关性。在胃癌患者、酒精性肝损伤大鼠模型、非酒精性脂肪性肝病大鼠模型中,镁缺乏时可进一步加重损伤,补充镁则可抑制中性粒细胞浸润,降低丙二醛含量,提高超氧化物歧化酶活性以催化超氧阴离子自由基歧化生成氧和过氧化氢,调控氧化与抗氧化失衡以改善氧化应激水平,其作用机制或许与激活Kelch样环氧丙烷相关蛋白1/核转录因子E2相关因子2信号通路有 关[49–51]。胃溃疡患者体内氧自由基清除能力下降,铝碳酸镁联合奥美拉唑不仅可保护溃疡面,促进愈合,还可提高超氧化物歧化酶和一氧化氮水平,发挥显著抗氧化效果[52]。类似的,银纳米颗粒也可减少中性粒细胞的吞噬,抑制其产生活性氧和超氧化物的能力,减轻氧化应激反应[53]。同时,银纳米颗粒还可持续释放银离子以增强细胞黏附,清除活性氧[54]。 锌、铜等是常见的抗氧化剂,可调节其释放自由基的反应,以改善不同免疫功能,对于细菌、病毒或寄生虫等引起的感染具有重要保护意义。当机体长期处于缺锌状态,更易受到氧化应激所引起的损伤。其中,锌是细胞内外锌/铜超氧化物歧化酶的辅助因子,通过催化超氧化物自由基变性为危害较小的氧气和过氧化氢,起到活性氧清除剂的作用[55]。有证据显示,锌缺乏会增强人单核细胞白血病细胞砷诱导的氧化应激反应,增加活性氧生成和细胞氧化应激的敏感指标——血红素加氧酶1转录物的丰度,从而增加炎症反应[56]。核转录因子E2相关因子2是细胞抗氧化的关键因子,在稳态下核转录因子E2相关因子2常与其抑制蛋白形成复合体存在于细胞质中。在锌缺乏小鼠的氧化损伤显著增加,核转录因子E2相关因子2表达降低[57],人结肠癌细胞的血红素加氧酶1 mRNA和核转录因子E2相关因子2蛋白水平在高浓度锌的作用下显著升高[58]。此外,锌还可以通过核转录因子E2相关因子2依赖的谷胱甘肽生物合成刺激来保护内皮细胞免受过氧化氢的伤害,同时锌也通过这一途径上调核转录因子E2相关因子2,这有助于调节氧化应激诱导的细胞损伤[59]。 与上述金属离子不同的是,铜被证实可触发氧化应激。氧化铜纳米颗粒是一种常见的金属氧化物纳米材料,具有良好的导电、催化和抗菌性能。有研究证实氧化铜纳米颗粒使人脐静脉内皮细胞内超氧化物水平升高,血红素加氧酶1和谷氨酸半胱氨酸连接酶蛋白水平上调,还原型谷胱甘肽/氧化型谷胱甘肽比值降低,氧化铜纳米颗粒释放的铜离子介导了该病理过程,不仅促进人脐静脉内皮细胞发生氧化应激,同时激活p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路,从而引发人脐静脉内皮细胞的DNA损伤和细胞死亡,相反,铜离子螯合剂四硫钼酸盐可以剂量依赖性的方式显著降低氧化应激反应,抑制p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路的激活[60]。"

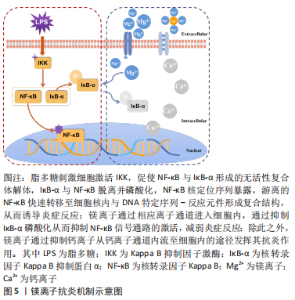
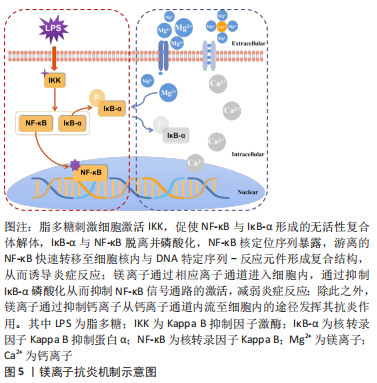
2.4 金属离子抗炎作用相关信号通路 2.4.1 核转录因子κB信号通路 核转录因子κB是具有多向调节作用的蛋白质分子,参与调控多种因子的基因表达,在免疫调控、炎症、应激反应及细胞凋亡中起重要作用。核转录因子κB信号通路是经典的炎症信号通路之一,有证据表明金属离子可通过抑制该信号通路调节宿主的炎症反应。 镁离子的抗炎作用与核转录因子κB经典炎症信号通路密切相关。异甘草酸镁降低大鼠核转录因子κB p65、核转录因子κB激酶抑制剂α/β、核转录因子κB α抑制剂等磷酸化蛋白水平来抑制肝脏炎症信号的激活,下调白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6的分泌,减轻果糖喂养的代谢综合征大鼠的肝脏炎症和脂质堆积[61]。L-苏糖酸镁是一种镁离子复合物,可通过抑制磷脂酰肌醇3激酶蛋白激酶B/核转录因子κB信号通路导致肿瘤坏死因子α的mRNA和蛋白表达水平下调,以抑制阿尔茨海默症小鼠脑内免疫炎症反应[62]。银离子也有类似效应。彭敏[63]利用银纳米颗粒的抗菌及抗炎能力构建载银高透氧化锆种植基台材料,发现该涂层中的银纳米颗粒能够抑制TLR4/核转录因子κB信号通路以抑制炎症反应,促进抗炎细胞因子释放,发挥抗炎功效。 锌离子与核转录因子κB之间具有一定联系。超氧化物歧化酶可通过清除细胞外的超氧化物分子发挥抗炎作用,而锌是提高超氧化物歧化酶活性的催化辅因子。据报道,锌可以剂量依赖性的方式抑制细胞核转录因子κB p65磷酸化,从而抑制核转录因子κB的激活,间接促进重组人超氧化物歧化酶3的抗炎作用[64]。事实上,已有证据证实锌离子是核转录因子κB信号通路的负调控因子,并提出了几种潜在的抑制机制。首先锌离子抑制环核苷酸磷酸二酯酶,随后升高环磷酸鸟苷,交叉激活蛋白激酶A,从而可抑制脂多糖诱导的Kappa B抑制因子激酶复合物及核转录因子κB的激活[65]。其次,锌转运蛋白8是核转录因子κB的转录靶点,其对细胞因子、细菌和败血症反应均表现出显著上调,可促进细胞外摄取或从亚细胞细胞器释放来增加细胞质锌的含量,通过锌介导的Kappa B抑制因子激酶复合物来直接抑制核转录因子κB[66]。除此之外,锌还可通过影响肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白3的表达而下调核转录因子κB信号通路。肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白3是一种锌指蛋白,作为一种抗炎蛋白,可负向调控由肿瘤坏死因子受体和Toll受体启动的核转录因子κB通路[67],而补充锌则能够上调肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白3的mRNA和DNA特异性结合,降低白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的基因表达,从而下调炎性细胞因子,进而抑制核转录因子κB激活[68]。 2.4.2 Toll样受体(Toll-like receptors,TLRs)信号通路 TLRs是一种与先天性免疫密切相关的病原体模式识别受体,用于免疫细胞识别病原体相关的分子模式,启动对入侵病原体的初级反应和适应性免疫反应的招募。现有的TLR家族有多个的不同配体成员,其中TLR4是介导内毒素反应的主要TLR[69]。TLR4通过与配体结合激活下游核转录因子κB,从而诱导一系列炎性细胞因子的表达。因此,TLR4/核转录因子κB信号通路也在炎症过程中发挥重要作用。激活TLR4/核转录因子κB信号通路可导致白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α等炎性细胞因子高度表达,促发机体炎症反应。 ZHENG等[70]研究发现,砷中毒可导致白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、TLR4、核转录因子κB蛋白水平明显升高,但异甘草酸镁处理后逆转上述变化,这表明异甘草酸镁抑制了TLR4/核转录因子κB炎症级联反应,降低了上述炎性细胞因子的释放。除此之外,镁离子可直接抑制TLR4的表达,从而抑制脂多糖诱导核转录因子κB的激活,降低促炎细胞因子白细胞介素6和白细胞介素8的表达[71]。再者,钙离子是TLR4激活炎症的主要启动子,而镁离子是天然钙离子拮抗剂,可通过降低细胞内钙离子浓度,从而降低TLR4活性,间接抑制核转录因子κB激活,降低炎性细胞因子的表达[72]。 与镁离子作用不同的是,锌离子可能是TLRs识别下游信号传导事件所必需的元素之一。经氧化锌纳米颗粒处理后的巨噬细胞炎症状态上调,TLR6可显著增强该过程,当沉默TLR6时可显著抑制促炎细胞因子水平、活性氧生成以及诱导型一氧化氮合酶表达[73],说明TLR6是氧化锌纳米颗粒诱导炎症反应的强激活剂,这也提示可将TLR6作为开发氧化锌纳米颗粒相关健康问题的新型抗炎药物治疗靶点。 2.4.3 其他相关信号通路 丝裂原激活蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)在多种细胞类型的各种炎症相关基因表达的调节中连接上游信号事件,以响应广泛的刺激[73]。细胞内锌螯合可阻断脂多糖诱导的MAPK和核转录因子κB DNA结合活性的激活,降低促炎细胞因子如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6的表达和分泌,而添加生理浓度的锌可增强脂多糖处理后MAPK激活和细胞因子的产生[74]。 白细胞介素6是经典炎性细胞因子之一,可诱导急性期蛋白表达,后者随后与TLRs相互作用并诱导炎症反应的发生。有研究表明,信号转导因子和转录激活因子3(signal transducer and activator of transcription 3,STAT3)的磷酸化受锌稳态的广泛影响,缺锌可增加白细胞介素6诱导的JAK-STAT3信号通路激活;而补锌则可抑制白细胞介素6和白细胞介素1诱导的STAT3磷酸化,从而降低炎症发生风险[75]。 NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3 (Nod-like receptor protein 3,NLRP3)炎症小体是由NLRP3、半胱氨酸蛋白酶1和含有caspase募集结构域的凋亡相关斑点样蛋白组成的多蛋白复合体,对调节机体免疫至关重要[76]。NLRP3炎性小体的激活导致白细胞介素1β上调和细胞凋亡,这是一种促炎细胞死亡,其特征是细胞大小增加和膜完整性丧失[77]。MURAKAMI等[78]学者的研究结果显示,硫酸镁可抑制NLRP3上调,减弱半胱氨酸蛋白酶1激活,减缓凋亡相关斑点样蛋白聚集,最终降低人单核细胞白血病细胞的白细胞介素1β上调和焦亡。前文提到,镁离子是一种有效的钙离子拮抗剂,而钙离子在NLRP3炎性小体激活过程起着关键作用[79],因此推测硫酸镁可能通过抑制细胞内钙离子来发挥其抑制NLRP3炎性小体的作用。在其他镁基化合物中也观察到类似的情况,例如,异甘草酸镁和石精镁B均可抑制NLRP3炎性小体,从而降低炎性细胞因子分泌,减轻炎症反应[61]。镁离子还可通过抑制钙离子从L型电压依赖性钙通道内流的途径从而减轻炎症反应[80],镁离子抗炎机制示意图见图5。"

事实上,炎症反应所涉及的分子机制是一个复杂网络,并非是某个单一信号通路在发挥作用,更应该是多个信号通路交替进行,或是产生级联效应,上下游分子激活共同作用而产生,故而单一谈论某个信号通路是不恰当的,应该从整体出发。如镁、锌等金属离子通过TLR与核转录因子κB信号通路产生级联效应来共同发挥抗炎活性;镁、锌、银、铜等金属离子通过调节巨噬细胞表型,减少活性氧生成等途径减轻炎症反应,但实际上,也因为这些下调的炎症细胞因子及减少的活性氧等刺激因素避免了诱发各炎症信号通路,从而间接减轻炎症反应。因此,应该综合思考各个信号通路之间的联系,构建炎症信号通路网络。综上所述,金属离子可通过降低机体氧化应激,调节免疫细胞表型,抑制核转录因子κB、TLR、TLR/核转录因子κB、STAT3及NOD等信号通路的激活等途径来发挥其抗炎活性。但仍有许多潜在的抗炎分子机制还未详述,未来需要更加系统的阐明各个信号通路之间的相互联系,为抗炎相关研究打下坚实理论基础。"

| [1] TANG CF, DING H, JIAO RQ, et al. Possibility of magnesium supplementation for supportive treatment in patients with COVID-19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;886:173546. [2] MIZRAHI B, SHAPIRA L, DOMB AJ, et al. Citrus oil and MgCl2 as antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents. J Periodontol. 2006;77(6):963-968. [3] LIN CY, TSAI PS, HUNG YC, et al. L-type calcium channels are involved in mediating the anti-inflammatory effects of magnesium sulphate. Br J Anaesth. 2010;104(1):44-51. [4] MATHEW AA, PANONNUMMAL R. ‘Magnesium’-the master cation-as a drug-possibilities and evidences. Biometals. 2021;34(5):955-986. [5] TAM TAM HB, DOWLING O, XUE X, et al. Magnesium sulfate ameliorates maternal and fetal inflammation in a rat model of maternal infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2011;204(4):364.e1-364.e8. [6] SUGIMOTO J, ROMANI AM, VALENTIN-TORRES AM, et al. Magnesium decreases inflammatory cytokine production: a novel innate immunomodulatory mechanism. J Immunol. 2012;188(12):6338-6346. [7] DOWLING O, CHATTERJEE PK, GUPTA M, et al. Magnesium sulfate reduces bacterial LPS-induced inflammation at the maternal-fetal interface. Placenta. 2012;33(5):392-398. [8] ALMOUSA LA, SALTER AM, LANGLEY-EVANS SC. Magnesium deficiency heightens lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and enhances monocyte adhesion in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Magnes Res. 2018;31(2):39-48. [9] YAO H, XU JK, ZHENG NY, et al. Intra-articular injection of magnesium chloride attenuates osteoarthritis progression in rats. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(12):1811-1821. [10] OZEN M, XIE H, SHIN N, et al. Magnesium sulfate inhibits inflammation through P2X7 receptors in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Pediatr Res. 2020;87(3):463-471. [11] ROOHANI N, HURRELL R, KELISHADI R, et al. Zinc and its importance for human health: an integrative review. J Res Med Sci. 2013;18(2):144-157. [12] JAROSZ M, OLBERT M, WYSZOGRODZKA G, et al. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of zinc. Zinc-dependent NF-κB signaling. Inflammopharmacology. 2017;25(1):11-24. [13] KNOELL DL, JULIAN MW, BAO S, et al. Zinc deficiency increases organ damage and mortality in a murine model of polymicrobial sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2009;37(4): 1380-1388. [14] BAO S, LIU MJ, LEE B, et al. Zinc modulates the innate immune response in vivo to polymicrobial sepsis through regulation of NF-kappaB. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010;298(6):L744-L754. [15] BESECKER BY, EXLINE MC, HOLLYFIELD J, et al. A comparison of zinc metabolism, inflammation, and disease severity in critically ill infected and noninfected adults early after intensive care unit admission. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;93(6):1356-1364. [16] KNOELL DL, SMITH DA, SAPKOTA M, et al. Insufficient zinc intake enhances lung inflammation in response to agricultural organic dust exposure. J Nutr Biochem. 2019; 70:56-64. [17] ZHENG L, MA Y, ZHANG YJ, et al. Distribution of Zinc in mycelial cells and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of mycelia Zinc polysaccharides from thelephora ganbajun TG-01. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:2308017. [18] WESSELS I, PUPKE JT, VON TROTHA KT, et al. Zinc supplementation ameliorates lung injury by reducing neutrophil recruitment and activity. Thorax. 2020;75(3):253-261. [19] XIE C, ZHANG Y, NIU K, at al. Enteromorpha polysaccharide-zinc replacing prophylactic antibiotics contributes to improving gut health of weaned piglets. Anim Nutr. 2021; 7(3):641-649. [20] WU GF, MA FB, XUE YZB, et al. Chondroitin sulfate zinc with antibacterial properties and anti-inflammatory effects for skin wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;278:118996. [21] 李文文.生姜皮多糖锌的制备与抗炎活性评价[D].泰安:山东农业大学,2022. [22] 董淑君.南瓜皮多糖锌的制备与抗炎活性评价[D].泰安:山东农业大学,2022. [23] BIAGGIO VS, PÉREZ CHACA MV, VALDÉZ SR, et al. Alteration in the expression of inflammatory parameters as a result of oxidative stress produced by moderate zinc deficiency in rat lung. Exp Lung Res. 2010;36(1):31-44. [24] TIAN J, WONG KK, HO CM, et al. Topical delivery of silver nanoparticles promotes wound healing. Chem Med Chem. 2007;2(1):129-136. [25] WONG KK, CHEUNG SO, HUANG L, et al. Further evidence of the anti-inflammatory effects of silver nanoparticles. Chem Med Chem. 2009;4(7):1129-1135. [26] SINGH P, AHN S, KANG JP, et al. In vitro anti-inflammatory activity of spherical silver nanoparticles and monodisperse hexagonal gold nanoparticles by fruit extract of Prunus serrulata: a green synthetic approach. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018; 46(8):2022-2032. [27] 裴秋艳,王平,李志刚,等.表皮生长因子联合银离子敷料对Ⅲ期、Ⅳ期压力性损伤患者血清炎性细胞因子和临床疗效的影响[J].四川医学,2022,43(1):63-66. [28] 余谦,盛小辉,郑若.银离子敷料联合负压封闭引流技术治疗糖尿病足伤口感染的效果[J].糖尿病新世界,2022,25(24):189-192. [29] 王伟.银离子凝胶联合切削痂植皮术及负压封闭引流术治疗深度烧伤创面的效果及对炎症因子、致痛因子的影响[J].临床与病理杂志,2022,42(11):2713-2718. [30] 马少君,栾文康,刘圣洁,等.银离子敷料覆盖联合负压吸引在慢性难愈性创面修复中的应用效果[J].中国美容医学,2022,31(1):23-26. [31] RATAN ZA, MASHRUR FR, CHHOAN AP, et al. Silver nanoparticles as potential antiviral agents. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(12):2034. [32] LIN R, DENG C, LI X, et al. Copper-incorporated bioactive glass-ceramics inducing anti-inflammatory phenotype and regeneration of cartilage/bone interface. Theranostics. 2019;9(21):6300-6313. [33] TAPIERO H, TOWNSEND DM, TEW KD. Trace elements in human physiology and pathology. Copper. Biomed Pharmacother. 2003;57(9):386-398. [34] KOUADRI A, CORMENIER J, GEMY K, et al. Copper-associated oxidative stress contributes to cellular inflammatory responses in cystic fibrosis. Biomedicines. 2021;9(4):329. [35] BAR-OR D, THOMAS GW, YUKL RL, et al. Copper stimulates the synthesis and release of interleukin-8 in human endothelial cells: a possible early role in systemic inflammatory responses. Shock. 2003;20(2):154-158. [36] BONAVENTURA P, COURBON G, LAMBOUX A, et al. Protective effect of low dose intra-articular cadmium on inflammation and joint destruction in arthritis. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):2415. [37] TSAI CY, SHIAU AL, CHEN SY, et al. Amelioration of collagen-induced arthritis in rats by nanogold. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(2):544-554. [38] ZHU Y, ZHAO S, CHENG L, et al. Mg2+-mediated autophagy-dependent polarization of macrophages mediates the osteogenesis of bone marrow stromal stem cells by interfering with macrophage-derived exosomes containing miR-381. J Orthop Res. 2022;40(7):1563-1576. [39] 陈玮,张旭芳,陈庆飘,等.镁金属抗炎和促进成骨的作用及分子机制[C]//中华口腔医学会口腔生物医学专业委员会.2018全国口腔生物医学学术年会论文汇编. 2018:28-29. [40] HU T, XU H, WANG C, et al. Magnesium enhances the chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by inhibiting activated macrophage-induced inflammation. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):3406. [41] BESSA-GONÇALVES M, SILVA AM, BRÁS JP, et al. Fibrinogen and magnesium combination biomaterials modulate macrophage phenotype, NF-kB signaling and crosstalk with mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. Acta Biomater. 2020;114:471-484. [42] 魏文发.巨噬细胞响应镁离子浓度分泌的外泌体对内皮细胞功能的影响[D].太原:太原理工大学,2020. [43] XIE C, WAN L, LI C, et al. Selective suppression of M1 macrophages is involved in zinc inhibition of liver fibrosis in mice. J Nutr Biochem. 2021;97:108802. [44] LIU W, LI JH, CHENG MQ, et al. Zinc-modified sulfonated polyetheretherketone surface with immunomodulatory function for guiding cell fate and bone regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018;5(10):1800749. [45] KIDO T, ISHIWATA K, SUKA M, et al. Inflammatory response under zinc deficiency is exacerbated by dysfunction of the T helper type 2 lymphocyte-M2 macrophage pathway. Immunology. 2019;156(4):356-372. [46] CHEN YMF, GUAN M, REN RY, et al. Improved immunoregulation of ultra-low-dose silver nanoparticle-loaded TiO2 nanotubes via M2 macrophage polarization by regulating GLUT1 and autophagy. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:2011-2026. [47] DIEZ-TERCERO L, DELGADO LM, BOSCH-RUE E, et al. Evaluation of the immunomodulatory effects of cobalt, copper and magnesium ions in a pro inflammatory environment. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):11707. [48] PUERTOLLANO MA, PUERTOLLANO E, DE CIENFUEGOS GÁ, et al. Dietary antioxidants: immunity and host defense. Curr Top Med Chem. 2011;11(14):1752-1766. [49] 陆芸,袁晓龙,侯慧科.异甘草酸镁预防胃癌患者化疗后肝损伤的效果及其对血清炎性因子及氧化应激水平的影响[J].四川生理科学杂志,2022,44(12):2093-2096. [50] 王丹丹,乔进,赵彦.异甘草酸镁对酒精性肝损伤模型大鼠的影响[J].中国药业, 2022,31(16):41-44. [51] 赵文明,赵飞,宋志玉,等.基于Keap-1/Nrf2信号通路探究异甘草酸镁改善非酒精性脂肪性肝病大鼠糖脂代谢紊乱的作用机制[J].广东药科大学学报,2022,38(5): 33-38. [52] 焦小红.铝碳酸镁片联合奥美拉唑治疗胃溃疡的临床效果及对氧化应激指标的影响[J].现代医学与健康研究电子杂志,2022,6(11):141-144. [53] HUANG MR, YE K, HU T, et al. Silver nanoparticles attenuate the antimicrobial activity of the innate immune system by inhibiting neutrophil-mediated phagocytosis and reactive oxygen species production. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:1345-1360. [54] GAO CH, CHENG H, XU N, et al. Poly (dopamine) and Ag nanoparticle-loaded TiO2 nanotubes with optimized antibacterial and ROS-scavenging bioactivities. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2019;14(7):803-818. [55] MARIANI E, MANGIALASCHE F, FELIZIANI FT, et al. Effects of zinc supplementation on antioxidant enzyme activities in healthy old subjects. Exp Gerontol. 2008;43(5):445-451. [56] WONG CP, DASHNER-TITUS EJ, ALVAREZ SC, et al. Zinc deficiency and arsenic exposure can act both independently or cooperatively to affect zinc status, oxidative stress, and inflammatory response. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019;191(2):370-381. [57] ZHAO Y, TAN Y, DAI J, et al. Exacerbation of diabetes-induced testicular apoptosis by zinc deficiency is most likely associated with oxidative stress, p38 MAPK activation, and p53 activation in mice. Toxicol Lett. 2011;200(1-2):100-106. [58] SMITH AF, LOO G. Upregulation of haeme oxygenase-1 by zinc in HCT-116 cells. Free Radic Res. 2012;46(9):1099-1107. [59] CORTESE MM, SUSCHEK CV, WETZEL W, et al. Zinc protects endothelial cells from hydrogen peroxide via Nrf2-dependent stimulation of glutathione biosynthesis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2008;44(12):2002-2012. [60] HE H, ZOU Z, WANG B, et al. Copper oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative DNA damage and cell death via copper ion-mediated P38 MAPK activation in vascular endothelial cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:3291-3302. [61] ZHAO XJ, YANG YZ, ZHENG YJ, et al. Magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate blocks fructose-induced hepatic NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome activation and lipid metabolism disorder. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017;809:141-150. [62] 于欣.镁离子通过抑制TNF-α介导的炎症反应延缓APP/PS1转基因小鼠病理进程的机制研究[D].沈阳:东北大学,2018. [63] 彭敏.载银高透氧化锆种植基台材料的制备及其性能和机理研究[D].成都:电子科技大学,2021. [64] KIM Y, JEON YJ, RYU K, et al. Zinc (II) ion promotes anti-inflammatory effects of rhSOD3 by increasing cellular association. BMB Rep. 2017;50(2):85-90. [65] VON BULOW V, DUBBEN S, ENGELHARDT G, et al. Zinc-dependent suppression of TNF-alpha production is mediated by protein kinase A-induced inhibition of Raf-1, I kappa B kinase beta, and NF-kappa B. J Immunol. 2007;179(6):4180-4186. [66] LIU MJ, BAO S, GALVEZ-PERALTA M, et al. ZIP8 regulates host defense through zinc-mediated inhibition of NF-κB. Cell Rep. 2013;3(2):386-400. [67] GAMMOH NZ, RINK L. Zinc in Infection and Inflammation. Nutrients. 2017;9(6):624. [68] PRASAD AS, BAO B, BECK FW, et al. Antioxidant effect of zinc in humans. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004;37(8):1182-1190. [69] AVLAS O, FALLACH R, SHAINBERG A, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 stimulation initiates an inflammatory response that decreases cardiomyocyte contractility. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;15(7):1895-1909. [70] ZHENG B, YANG Y, LI J, et al. Magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate alleviates arsenic trioxide-induced cardiotoxicity: contribution of Nrf2 and TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021;15:543-556. [71] ALMOUSA LA, SALTER AM, LANGLEY-EVANS SC. Varying magnesium concentration elicits changes in inflammatory response in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Magnes Res. 2018;31(3):99-109. [72] LIBAKO P, NOWACKI W, CASTIGLIONI S, et al. Extracellular magnesium and calcium blockers modulate macrophage activity. Magnes Res. 2016;29(1):11-21. [73] ROY R, SINGH SK, DAS M, et al. Toll-like receptor 6 mediated inflammatory and functional responses of zinc oxide nanoparticles primed macrophages. Immunology. 2014;142(3):453-464. [74] HAASE H, OBER-BLOBAUM JL, ENGELHARDT G, et al. Zinc signals are essential for lipopolysaccharide-induced signal transduction in monocytes. J Immunol. 2008;181(9): 6491-6502. [75] LIU MJ, BAO SY, NAPOLITANO JR, et al. Zinc regulates the acute phase response and serum amyloid A production in response to sepsis through JAK-STAT3 signaling. PLoS One. 2014;9(4):e94934. [76] MAN SM, KANNEGANTI TD. Regulation of inflammasome activation. Immunol Rev. 2015;265(1):6-21. [77] MAN SM, KARKI R, KANNEGANTI TD. Molecular mechanisms and functions of pyroptosis, inflammatory caspases and inflammasomes in infectious diseases. Immunol Rev. 2017;277(1):61-75. [78] MURAKAMI T, OCKINGER J, YU J, et al. Critical role for calcium mobilization in activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(28):11282-11287. [79] CHANG YY, KAO MC, LIN JA, et al. Effects of MgSO4 on inhibiting Nod-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome involve decreasing intracellular calcium. J Surg Res. 2018;221: 257-265. [80] LOPEZ-BALTANAS R, ENCARNACION RODRIGUEZ-ORTIZ M, CANALEJO A, et al. Magnesium supplementation reduces inflammation in rats with induced chronic kidney disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 2021;51(8):e13561. |
| [1] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [2] | Wei Juan, Li Ting, Huan Mengting, Xie Ying, Xie Zhouyu, Wei Qingbo, Wu Yunchuan. Mechanism by which static exercise improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [3] | Lou Guo, Zhang Yan, Fu Changxi. Role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in exercise preconditioning-induced improvement of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1283-1288. |
| [4] | Wang Weiqing, Zhou Yue. Chronic inflammation regulates adipose tissue fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1307-1312. |
| [5] | Yue Yun, Wang Peipei, Yuan Zhaohe, He Shengcun, Jia Xusheng, Liu Qian, Li Zhantao, Fu Huiling, Song Fei, Jia Menghui. Effects of croton cream on JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [6] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Li Wenbo, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. Effect of aerobic exercise on glycolipid metabolism, skeletal muscle inflammation and autophagy in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1200-1205. |
| [7] | Liu Xin, Hu Man, Zhao Wenjie, Zhang Yu, Meng Bo, Yang Sheng, Peng Qing, Zhang Liang, Wang Jingcheng. Cadmium promotes senescence of annulus fibrosus cells via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [8] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [9] | Mu Bingtao, Yu Jingwen, Liu Chunyun, Guo Minfang, Meng Tao, Yang Pengwei, Wei Wenyue, Song Lijuan, Yu Jiezhong, Ma Cungen. Immunomodulatory effect of astragaloside IV on T cells of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1057-1062. |
| [10] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [11] | Zhang Ya, Mu Qiuju, Wang Zilin, Liu Hongjie, Zhu Lili. Hydrogel loaded with platelet-rich plasma promotes wound healing in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 690-696. |
| [12] | Wang Jiani, Chen Junyu. Angiogenesis mechanism of metal ions and their application in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 804-812. |
| [13] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [14] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Effect of gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel loaded with salvianolic acid B on intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 380-386. |
| [15] | Gao Xueyu, Zhang Wentao, Sun Tianze, Zhang Jing, Li Zhonghai. Application of metal ions in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 439-444. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||