Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (11): 2310-2318.doi: 10.12307/2025.364
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparison of different intensity exercises to improve autophagy in diabetic rats by inhibiting renal phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway
Zhou Hongyan1, Zhang Yidan2, Ji Wei2, Liu Xia2
- 1College of Physical Education, Hunan University of Arts and Science, Changde 415000, Hunan Province, China; 2Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Physical Fitness and Exercise Rehabilitation, College of Physical Education, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410012, Hunan Province, China
-
Received:2024-03-18Accepted:2024-04-28Online:2025-04-18Published:2024-08-12 -
Contact:Liu Xia, MD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Physical Fitness and Exercise Rehabilitation, College of Physical Education, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410012, Hunan Province, China -
About author:Zhou Hongyan, Master, Associate professor, College of Physical Education, Hunan University of Arts and Science, Changde 415000, Hunan Province, China Zhang Yidan, Master candidate, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Physical Fitness and Exercise Rehabilitation, College of Physical Education, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410012, Hunan Province, China Zhou Hongyan and Zhang Yidan contributed equally to this work.
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Hongyan, Zhang Yidan, Ji Wei, Liu Xia. Comparison of different intensity exercises to improve autophagy in diabetic rats by inhibiting renal phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2310-2318.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
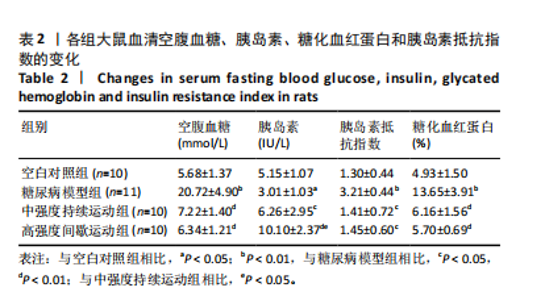
2.1 实验动物数量分析 60只大鼠参与实验,其中对照组10只,造模成功31只,进入结果分析41只。 2.2 各组大鼠空腹血糖、胰岛素、糖化血红蛋白水平及胰岛素抵抗指数比较 见表2。与空白对照组相比,糖尿病模型组大鼠血清空腹血糖、糖化血红蛋白的水平极显著增加(P < 0.01),胰岛素抵抗指数极显著增加(P < 0.01),而大鼠血清胰岛素显著减少(P < 0.05);与糖尿病模型组相比,中强度持续运动组以及高强度间歇运动组大鼠血清空腹血糖、糖化血红蛋白的水平极显著减少(P < 0.01),胰岛素抵抗指数显著减少(P < 0.05),而血清胰岛素显著增加(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);与中强度持续运动组相比,高强度间歇运动组大鼠空腹血糖、糖化血红蛋白水平和胰岛素抵抗指数无显著性差异,血清胰岛素水平显著增加(P < 0.05)。"
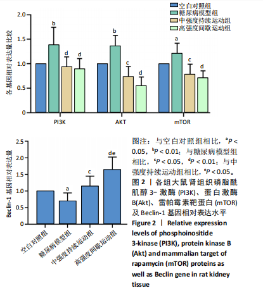
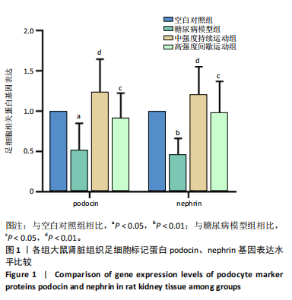
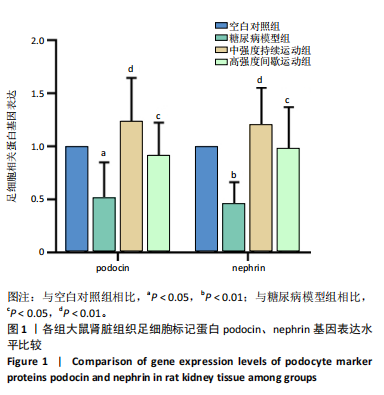
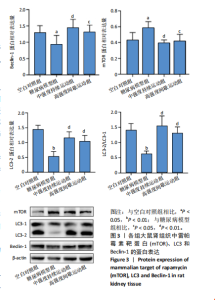
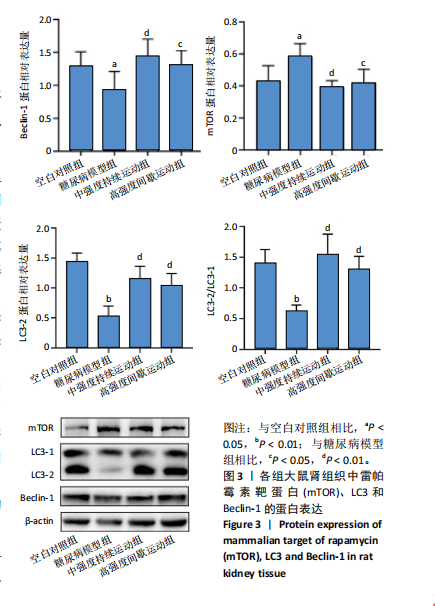
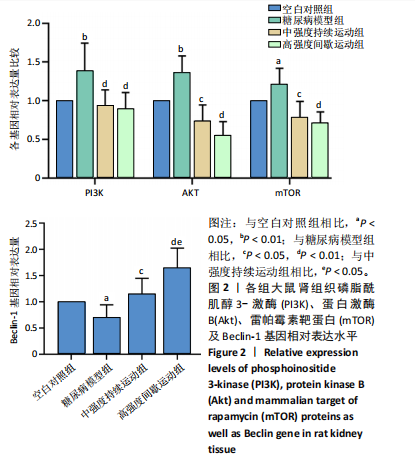
2.4 各组大鼠肾组织雷帕霉素靶蛋白自噬通路基因及Beclin-1基因相对表达水平比较 见图2。与空白对照组相比,糖尿病模型组大鼠肾组织的磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶和蛋白激酶B基因表达量呈极显著性增加(P < 0.01),雷帕霉素靶蛋白基因表达量呈显著性增加(P < 0.05),Beclin-1基因表达量呈显著性降低(P < 0.05)。与糖尿病模型组相比,中强度持续运动组大鼠磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶呈极显著性降低(P < 0.01),蛋白激酶B和雷帕霉素靶蛋白呈显著性降低(P < 0.05),Beclin-1基因表达量呈显著性增加(P < 0.05)。与糖尿病模型组相比,高强度间歇运动组大鼠肾组织中的磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶、蛋白激酶B以及雷帕霉素靶蛋白均极显著性降低(P < 0.01),Beclin-1基因表达量呈极显著性增加(P < 0.01)。与中强度持续运动组相比,高强度间歇运动组大鼠Beclin-1基因表达量呈显著性增加(P < 0.05),磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶、蛋白激酶B以及雷帕霉素靶蛋白均有一定程度降低,但无显著性差异。 2.5 各组大鼠肾组织雷帕霉素靶蛋白自噬通路相关蛋白表达水平比较 见图3。与空白对照组相比,糖尿病模型组"
| [1] CHO N H, SHAW J E, KARURANGA S, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;138:271-281. [2] JONAS JB, WANG YX, WEI WB, et al. Chronic Kidney Disease and Eye Diseases: The Beijing Eye Study. Ophthalmology. 2017;124(10): 1566-1569. [3] SELBY NM, TAAL MW. An updated overview of diabetic nephropathy: Diagnosis, prognosis, treatment goals and latest guidelines. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020;22 Suppl 1:3-15. [4] GROSS JL, DE AZEVEDO MJ, SILVEIRO SP, et al. Diabetic nephropathy: diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(1):164-176. [5] PATEL DM, BOSE M, COOPER ME. Glucose and Blood Pressure-Dependent Pathways-The Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(6):2218. [6] KHAZIM K, GORIN Y, CAVAGLIERI RC, et al. The antioxidant silybin prevents high glucose-induced oxidative stress and podocyte injury in vitro and in vivo. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013;305(5):F691-700. [7] DUNI A, LIAKOPOULOS V, ROUMELIOTIS S, et al. Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis and Evolution of Chronic Kidney Disease: Untangling Ariadne’s Thread. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(15):3711. [8] LIN TA, WU V CC, WANG CY. Autophagy in Chronic Kidney Diseases. Cells. 2019;8(1):61. [9] MATBOLI M, IBRAHIM D, HASANIN AH, et al. Epigenetic modulation of autophagy genes linked to diabetic nephropathy by administration of isorhamnetin in Type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. Epigenomics. 2021; 13(3):187-202. [10] ZHOU XJ, KLIONSKY DJ, ZHANG H. Podocytes and autophagy: a potential therapeutic target in lupus nephritis.Autophagy. 2019;15(5):908-912. [11] NATARAJ M, MAIYA AG, NAGARAJU SP, et al. Effect of exercise on renal function in diabetic nephropathy-a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2022;18(3):526-537. [12] 孙波, 曾桂芳, 林森, 等. 不同运动方式对T2DM大鼠形成过程中肾脏氧化应激及细胞凋亡表达的影响[J]. 华南国防医学杂志,2022, 36(1):1-6. [13] 张敏, 彭朋, 秦永生, 等. 不同负荷剂量高强度间歇训练对高血压肾病大鼠肾脏损伤的影响[J]. 山东体育学院学报,2020,36(6):54-64. [14] 吴长艳, 吴霜, 余今红, 等. 不同运动形式在DN肾间质纤维化中的应用与实践[C]//第十三届全国体育科学大会论文摘要集——墙报交流(体质与健康分会)(三). 中国体育科学学会,2023. [15] 吴学敏, 谢欲晓, 孙启良, 等. 长期中等强度运动训练及依那普利对Thy-1肾炎慢性肾功能衰竭大鼠模型肾功能的影响[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2009,15(6):534-537. [16] 刘晓晨, 王改凤, 张社峰. 有氧运动可改善糖尿病肾病模型小鼠肾脏的氧化应激损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(17):2712-2717. [17] HE C, BASSIK MC, MORESI V, et al. Exercise-induced BCL2-regulated autophagy is required for muscle glucose homeostasis. Nature.2012;481(7382):511-515. [18] CAMPOS JC, QUELICONI BB, BOZI LHM, et al. Exercise reestablishes autophagic flux and mitochondrial quality control in heart failure. Autophagy.2017;13(8):1304-1317. [19] BRANDT N, GUNNARSSON TP, BANGSBO J, et al. Exercise and exercise training-induced increase in autophagy markers in human skeletal muscle. Physiol Rep. 2018;6(7):e13651. [20] 苏蓓蓓, 杨丽霞, 梁永林, 等. 大黄糖络丸通过AMPK/mTOR/ULK1通路调控糖尿病肾病小鼠足细胞自噬的作用机制研究[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学,2024,29(3):260-269. [21] KIM YC, GUAN KL. mTOR: a pharmacologic target for autophagy regulation.J Clin Invest. 2015;125(1):25-32. [22] LAI W, LUO D, LI Y, et al. Irisin ameliorates diabetic kidney disease by restoring autophagy in podocytes. FASEB J. 2023;37(10):e23175. [23] 吴东,张庆红,何立群,等.黄芪多糖调控PI3K/AKT通路改善糖尿病大鼠肾损伤[J/OL].生物技术,1-7[2024-03-17].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/23.1319.Q.20240306.1042.004.html. [24] GUO XX, WANG Y, WANG K, et al. Beijing Key Laboratory of Functional Food from Plant Resources, College of Food Science and Nutritional Engineering,China Agricultural University Academy of State Administration of Grain Institute of Apicultural Research, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. Journal of Zhejiang University-Science B(Biomedicine & Biotechnology). 2018;19(7):559-569. [25] 徐国琴, 陈晓彬, 孟艳, 等. 不同强度有氧运动对糖尿病大鼠肝脏SREBP及肝脂肪变的影响[J]. 山东体育学院学报,2012,28(6):59-63+67. [26] 李颖, 林文弢, 翁锡全. 不同运动强度干预2型糖尿病模型大鼠的内脂素及糖代谢变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(26): 4196-4200. [27] 闫海龙, 陈乐琴, 张一民, 等. 高强度间歇性训练与中等强度持续运动对大鼠肝细胞自噬与凋亡相关因子表达的影响[J]. 山东体育学院学报,2019,35(3):71-77. [28] SEVER S, SCHIFFER M. Actin dynamics at focal adhesions: a common endpoint and putative therapeutic target for proteinuric kidney diseases. Kidney Int. 2018;93(6):1298-1307. [29] FISSELL WH, MINER JH. What Is the Glomerular Ultrafiltration Barrier?. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;29(9):2262-2264. [30] KOPP JB, ANDERS HJ, SUSZTAK K, et al. Podocytopathies. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020;6(1):68. [31] BARUTTA F, BELLINI S, GRUDEN G. Mechanisms of podocyte injury and implications for diabetic nephropathy. Clin Sci (Lond). 2022;136(7):493-520. [32] VERMA R, VENKATAREDDY M, KALINOWSKI A, et al. Nephrin is necessary for podocyte recovery following injury in an adult mature glomerulus. PLoS One. 2018;13(6):e0198013. [33] HU Y, YE S, XING Y, et al. Saxagliptin attenuates glomerular podocyte injury by increasing the expression of renal nephrin and podocin in type 2 diabetic rats. Acta Diabetol. 2020;57(3):279-286. [34] TANG C, LIVINGSTON M J, LIU Z, et al. Autophagy in kidney homeostasis and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020;16(9):489-508. [35] DING Y, CHOI ME. Autophagy in diabetic nephropathy. J Endocrinol. 2015;224(1):R15-30. [36] 宋晓妹, 杨红, 龙秋双, 等. 1,8-桉叶油素调节自噬改善高糖诱导的内皮细胞损伤[J]. 中国药理学通报,2021,37(4):472-477. [37] LENOIR O, JASIEK M, HÉNIQUE C, et al. Endothelial cell and podocyte autophagy synergistically protect from diabetes-induced glomerulosclerosis. Autophagy. 2015;11(7):1130-1145. [38] HILL SM, WROBEL L, RUBINSZTEIN DC. Post-translational modifications of Beclin 1 provide multiple strategies for autophagy regulation. Cell Death Differ. 2019;26(4):617-629. [39] RUNWAL G, STAMATAKOU E, SIDDIQI FH, et al. LC3-positive structures are prominent in autophagy-deficient cells. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):10147. [40] 王世强, 胥祉涵, 王少堃, 等. 运动改善糖尿病大鼠心肌功能:自噬的可能调节作用[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2021,40(2):121-128. [41] SHEN K, LIU X, CHEN D, et al. Voluntary wheel-running exercise attenuates brain aging of rats through activating miR-130a-mediated autophagy. Brain Res Bull. 2021;172:203-211. [42] LI Y, SUN D, ZHENG Y, et al. Swimming exercise activates aortic autophagy and limits atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2020;14(3):264-270. [43] TAGAWA A, YASUDA M, KUME S, et al. Impaired Podocyte Autophagy Exacerbates Proteinuria in Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes. 2016; 65(3):755-767. [44] YANG L, LI D X, CAO B Q, et al. Exercise training ameliorates early diabetic kidney injury by regulating the H2S/SIRT1/p53 pathway. FASEB J. 2021;35(9):e21823. [45] ISHIKAWA Y, GOHDA T, TANIMOTO M, et al. Effect of exercise on kidney function, oxidative stress, and inflammation in type 2 diabetic KK-A(y) mice. Exp Diabetes Res. 2012:2012:702948. [46] LAPLANTE M, SABATINI DM. Regulation of mTORC1 and its impact on gene expression at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2013;126(Pt 8):1713-1719. [47] MENON S, DIBBLE CC, TALBOTT G, et al. Spatial Control of the TSC Complex Integrates Insulin and Nutrient Regulation of mTORC1 at the Lysosome. Cell. 2014;156(4):771-785. [48] ZHU M, QIN YC, GAO CQ, et al. Extracellular Glutamate-Induced mTORC1 Activation via the IR/IRS/PI3K/Akt Pathway Enhances the Expansion of Porcine Intestinal Stem Cells. J Agric Food Chem. 2019; 67(34):9510-9521. [49] RAMAIAN SANTHASEELA A, JAYAVELU T. Does mTORC1 inhibit autophagy at dual stages?: A possible role of mTORC1 in late-stage autophagy inhibition in addition to its known early-stage autophagy inhibition. Bioessays. 2021;43(2):e2000187. [50] HOSOKAWA N, HARA T, KAIZUKA T, et al. Nutrient-dependent mTORC1 association with the ULK1-Atg13-FIP200 complex required for autophagy. Mol Biol Cell. 2009;20(7):1981-1991. [51] 白彩虹, 邹坤, 贺海波, 等. 自噬:肿瘤细胞凋亡缺陷下的另一个细胞死亡开关[J]. 中药药理与临床,2013,29(5):146-150. [52] YANG L, LIANG B, LI J, et al. Dapagliflozin alleviates advanced glycation end product induced podocyte injury through AMPK/mTOR mediated autophagy pathway. Cell Signal. 2022;90:110206. [53] JIN D, LIU F, YU M, et al. Jiedu Tongluo Baoshen formula enhances podocyte autophagy and reduces proteinuria in diabetic kidney disease by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022;293:115246. [54] WANG X, JIANG L, LIU X qi, et al. Paeoniflorin binds to VEGFR2 to restore autophagy and inhibit apoptosis for podocyte protection in diabetic kidney disease through PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. Phytomedicine. 2022;106:154400. [55] YANG F, QU Q, ZHAO C, et al. Paecilomyces cicadae-fermented Radix astragali activates podocyte autophagy by attenuating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways to protect against diabetic nephropathy in mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;129:110479. [56] 陈峰, 徐瑜琳, 陈红波, 等. 消瘀泄浊饮介导PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路改善糖尿病肾病小鼠肾纤维化[J]. 浙江中医杂志,2021,56(3): 157-160. [57] 李佳航. 不同形式运动介导PI3K/AKT/mTOR通路调节自噬缓解非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠肝脏纤维化[D]. 武汉:武汉体育学院,2024. [58] 刘佳宝. 运动诱导的Meteorin-like蛋白通过抑制PI3K/Akt/NF-κB和NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD通路缓解软骨细胞炎症和焦亡[D]. 沈阳:中国医科大学,2023. [59] 郭苏霞, 袁薇娜, 刘丹, 等. 冠心病患者心脏康复运动处方研究进展——以高强度间歇训练为例[J]. 健康研究,2023,43(6):678-682. [60] SCHENK S, HARBER MP, SHRIVASTAVA CR, et al. Improved insulin sensitivity after weight loss and exercise training is mediated by a reduction in plasma fatty acid mobilization, not enhanced oxidative capacity. J Physiol. 2009;587(Pt 20):4949-4961. [61] RYAN BJ, SCHLEH MW, AHN C, et al. Moderate-Intensity Exercise and High-Intensity Interval Training Affect Insulin Sensitivity Similarly in Obese Adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105(8):e2941-e2959. [62] HWANG CL, LIM J, YOO JK, et al. Effect of all-extremity high-intensity interval training vs. moderate-intensity continuous training on aerobic fitness in middle-aged and older adults with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Exp Gerontol. 2019;116:46-53. [63] 刘羽佳, 徐建方, 张斌, 等. 不同强度有氧运动改善肥胖大鼠慢性肾功能研究[C]. 第十三届全国体育科学大会, 天津:2023. [64] LI J, SUN Y B Y, CHEN W, et al. Smad4 promotes diabetic nephropathy by modulating glycolysis and OXPHOS. EMBO Rep. 2020;21(2):e48781. |
| [1] | Li Huayuan, Li Chun, Liu Junwei, Wang Ting, Li Long, Wu Yongli. Effect of warm acupuncture on PINK1/Parkin pathway in the skeletal muscle of rats with chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1618-1625. |
| [2] | Zhou Panpan, Cui Yinglin, Zhang Wentao, Wang Shurui, Chen Jiahui, Yang Tong . Role of cellular autophagy in cerebral ischemic injury and the regulatory mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1650-1658. |
| [3] | Zhu Hanmin, Wang Song, Xiao Wenlin, Zhang Wenjing, Zhou Xi, He Ye, Li Wei, . Mitophagy regulates bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1676-1683. |
| [4] | Zhao Ruihua, Chen Sixian, Guo Yang, Shi Lei, Wu Chengjie, Wu Mao, Yang Guanglu, Zhang Haoheng, Ma Yong. Wen-Shen-Tong-Du Decoction promoting spinal cord injury repair in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1118-1126. |
| [5] | Zheng Rongfa, Mo Weibin, Huang Peng, Chen Junji, Liang Ting, Zi Fangyu, Li Guofeng. Effects of electroacupuncture on the expression of metabolic enzymes and autophagy genes in gastrocnemius muscle tissues of exercising rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1127-1136. |
| [6] | Chen Yuning, Jiang Ying, Liao Xiangyu, Chen Qiongjun, Xiong Liang, Liu Yue, Liu Tong. Buqi Huoxue Compounds intervene with the expression of related factors and autophagy related proteins in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1152-1158. |
| [7] | Liu Lingyun, He Guixin, Qin Weibin, Song Hui, Zhang Liwen, Tang Weizhi, Yang Feifei, Zhu Ziyi, Ou Yangbin . Improvement of myocardial injury by traditional Chinese medicine: mitochondrial calcium homeostasis mediates macrophage autophagy and pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1276-1284. |
| [8] | Xu Tianjie, Fan Jiaxin, Guo Xiaoling, Jia Xiang, Zhao Xingwang, Liu kainan, Wang Qian. Metformin exerts a protective effect on articular cartilage in osteoarthritis rats by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1003-1012. |
| [9] | Li Tingyue, Guo Qian, He Wenxi, Wu Jiayuan. Long noncoding RNA TP53TG1 promotes odontogenic and osteogenic differentiation of stem cells from the apical papilla [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7776-7782. |
| [10] |
Li Yunzhe, Niu Zefan, Wang Zirou, Ai Chongyi, Chen Gang, Wang Xinxing.
Asperosaponin VI promotes osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells under hypoxia environment #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7481-7489.
|
| [11] | Liu Xuan, Ding Yuqing, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang, Hu Shujuan. Exercise prevention and treatment of insulin resistance: role and molecular mechanism of Keap1/nuclear factor erythroid2-related factor 2 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7578-7588. |
| [12] | Gong Yuehong, Wang Mengjun, Ren Hang, Zheng Hui, Sun Jiajia, Liu Junpeng, Zhang Fei, Yang Jianhua, Hu Junping. Machine learning combined with bioinformatics screening of key genes for pulmonary fibrosis associated with cellular autophagy and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7679-7689. |
| [13] | Zhang Fei, Zuo Jun. Inhibition of hypertrophic scar in rats by beta-sitosterol-laden mesoporous silica nanoparticles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7301-7309. |
| [14] | Zhou Ying, Tian Yong, Zhong Zhimei, Gu Yongxiang, Fang Hao. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6 regulates mTORC1/ULK1 signaling and promotes autophagy to improve myocardial injury in sepsis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6434-6440. |
| [15] | Wang Jiaqian, , Jiang Changjun, Peng Yi, Ma Mi, Li Junhan. Study on the role of aerobic exercise in regulating the CNPY2-mediated AKT/GSK3β pathway for improving non-alcoholic fatty liver [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6441-6448. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||