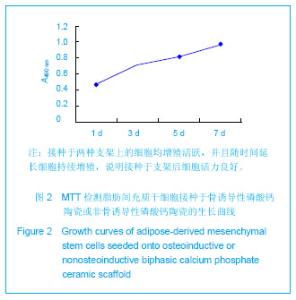
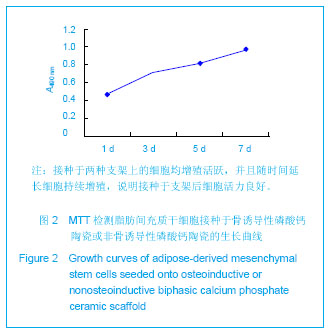
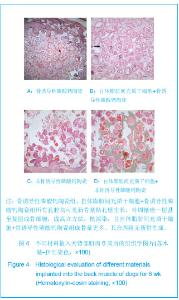
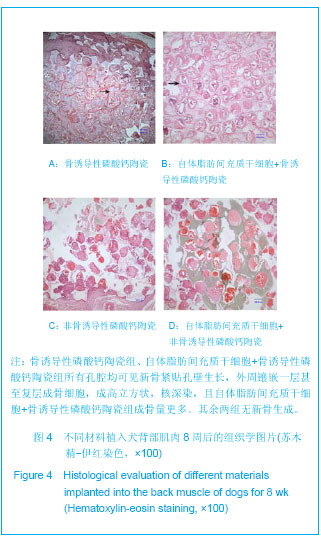
| [1] Mendes SC,Tibbe JM,Veenhof M,et al. Bone tissue- engineered implants using human bone marrow stromal cells: effect of culture conditions and donor age. Tissue Eng.2002;8:911-920. [2] Yuan H,van Blitterswijk CA,de Groot K,et al.Cross-species comparison of ectopic bone formation in biphasic calcium phosphate (BCP) and hydroxyapatite (HA) scaffolds.Tissue Eng.2006;12:1607-1615.[3] Yuan H,van den Doel M,Li S,et al.A comparison of the osteoinductive potential of two calcium phosphate ceramics implanted intramuscularly in goats.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2002;13:1271-1275. [4] Yuan J,Cui L,Zhang WJ,et al.Repair of canine mandibular bone defects with bone marrow stromal cells and porous beta-tricalcium phosphate.Biomaterials.2007;28:1005-1013. [5] Cai X,Lin Y,Ou G,et al.Ectopic osteogenesis and chondrogenesis of bone marrow stromal stem cells in alginate system.Cell Biol Int.2007; 31:776-783. [6] Cowan CM,Shi YY,Aalami OO,et al.Adipose-derived adult stromal cells heal critical-size mouse calvarial defects.Nat Biotechnol.2004;22: 560-567.[7] Zuk PA,Zhu M,Mizuno H,et al.Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies.Tissue Eng.2001;7: 211-228. [8] Zuk PA,Zhu M,Ashjian P,et al.Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells.Mol Biol Cell.2002;13: 4279-4295. [9] Mankani MH,Kuznetsov SA,Fowler B,et al.In vivo bone formation by human bone marrow stromal cells: effect of carrier particle size and shape. Biotechnol Bioeng.2001;72:96-107. [10] CIOMS International guiding principles for biomedical research involving animals.Altern Lab Anim.1985;12:2.[11] Yuan H,Yang Z,De Bruij JD,et al.Material-dependent bone induction by calcium phosphate ceramics: a 2.5-year study in dog. Biomaterials.2001; 22(19): 2617-2623.[12] Li X,Yao J,Wu L,et al.Osteogenic Induction of Adipose-derived Stromal Cells:Not an Indispensable Step for Bone Formation In Vivo.Artif Organs. 2010;34(1):46-54.[13] Jones AC,Arns CH,Sheppard AP,et al.Assessment of bone ingrowth into porous biomaterials using MICRO-CT. Biomaterials. 2007;28:2491-2504. [14] Habibovic P,Yuan H,van der Valk CM,et al.3D microenvironment as essential element for osteoinduction by biomaterials.Biomaterials.2005;26: 3565-3575.[15] Habibovic P,Yuan H,van den Doel M,et al.Relevance of osteoinductive biomaterials in critical-sized orthotopic defect.J Orthop Res.2006;24: 867-876.[16] Habibovic P,Sees TM,van den Doel MA,et al.Osteoinduction by biomaterials--physicochemical and structural influences.J Biomed Mater.Res A.2006;77:747-762. [17] Ripamonti U.Bone Engineering.Tornto, Canada, em sqared incorporated, 2000:215.[18] Ripamonti U,Crooks J,Kirkbride AN.Sintered porous hydroxyapatites with intrinsic osteoinductive activity: geometric induction of bone formation.South African J Sci. 1999;95(8):335-343. [19] Kroese-Deutman HC,Ruhe PQ,Spauwen PH,et al.Bone inductive properties of rhBMP-2 loaded porous calcium phosphate cement implants inserted at an ectopic site in rabbits.Biomaterials.2005;26:1131-1138. [20] Hsu HP,Zanella JM,Peckham SM,et al.Comparing ectopic bone growth induced by rhBMP-2 on an absorbable collagen sponge in rat and rabbit models. J Orthop Res.2006;24:1660-1669.[21] Kato M,Namikawa T,Terai H,et al.Ectopic bone formation in mice associated with a lactic acid/dioxanone/ethylene glycol copolymer-tricalcium phosphate composite with added recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2. Biomaterials. 2006;27:3927-3933. [22] Hofmann S,Hagenmuller H,Koch AM,et al.Control of in vitro tissue-engineered bone-like structures using human mesenchymal stem cells and porous silk scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2007;28:1152-1162. [23] Csaki C,Matis U,Mobasheri A,et al.Chondrogenesis, osteogenesis and adipogenesis of canine mesenchymal stem cells: a biochemical, morphological and ultrastructural study.Histochem Cell Biol.2007;128: 507-520. [24] Niemeyer P,Kornacker M,Mehlhorn A,et al.Comparison of immunological properties of bone marrow stromal cells and adipose tissue-derived stem cells before and after osteogenic differentiation in vitro.Tissue Eng.2007;13: 111-121.[25] Miyahara Y,Nagaya, N,Kataoka M,et al.Monolayered mesenchymal stem cells repair scarred myocardium after myocardial infarction.Nat Med.2006;12: 459-465.[26] Phinney DG.Biochemical heterogeneity of mesenchymal stem cell populations: clues to their therapeutic efficacy.Cell Cycle. 2007;6: 2884-2889.[27] Raffaghello L,Bianchi G,Bertolotto M,et al.Human mesenchymal stem cells inhibit neutrophil apoptosis: a model for neutrophil preservation in the bone marrow niche.Stem Cells. 2008;26:151-162. [28] Mastrogiacomo M,Papadimitropoulos A,Cedola A,et al. Engineering of bone using bone marrow stromal cells and a silicon-stabilized tricalcium phosphate bioceramic: evidence for a coupling between bone formation and scaffold resorption. Biomaterials.2007;28(15):1376-1384. [29] van Lenthe GH,Hagenmüller H,Bohner M,et al. Nondestructive micro-computed tomography for biological imaging and quantification of scaffold-bone interaction in vivo. Biomaterials.2007;28:2479-2490.[30] Tuan HS,Hutmacher DW.Application of micro CT and computation modeling in bone tissue engineering. Computeraided Design.2005;37:1151-1161. [31] Ho ST,Hutmacher DW.A comparison of micro CT with other techniques used in the characterization of scaffolds. Biomaterials.2006;27:1362-1376. |