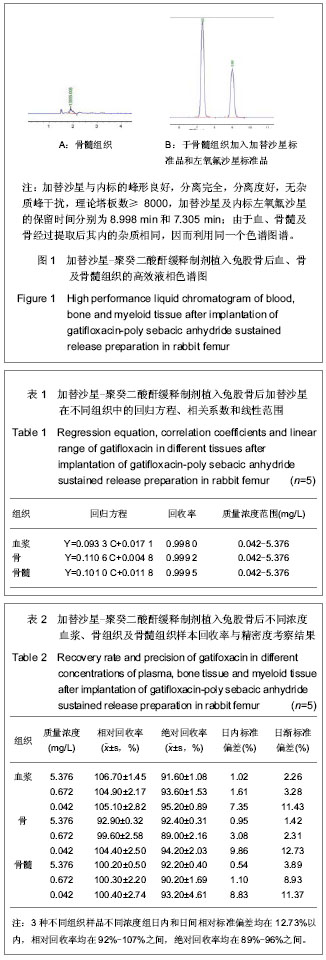
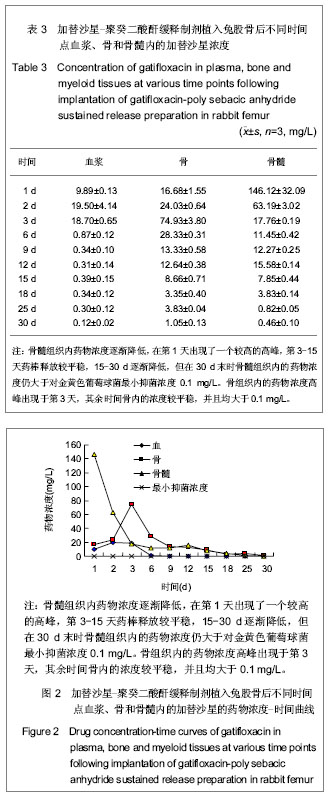
| [1] 冯惠东,郭毅,王永祥,等.国产盐酸加替沙星对临床常见致病菌的体外抗菌活性研究[J].河北医科大学学报,2003,24(4):211-213.[2] Stahlberg HJ,Cohler K,Cuillane M,et al. Effects of gatifloxacin mesylate(GTFX)On the pharmacokinetics of theophyline in heathly young volunteers. Antimierob Agents Chemther.1999; 44(sup A):136.[3] 邓立东,程强,徐勤. HPLC法测定加替沙星的血药浓度[J].华夏医学,2002,15(2):159-163.[4] 朱曼,王虞,方翼,等.人体血浆及尿液中甲磺酸加替沙星浓度的HPLC测定法[J].药物分析杂志,2003,23(1):53-56.[5] 李绪春,朱红.单剂量加替沙星口服在Beagle犬体内药代动力学研究[J].中国药业,2006,15(10):6-7.[6] Cai QX,Zhu KJ,Chen D,et al.Synthesis, characterization and in vitro release of 5-aminosalicylic acid and 5-acetyl aminosalicylic acid of polyanhydride P(CBFAS). Eur J Pharma Biopharms.2003;55(2):203-208.[7] Berkland C,Kipper MJ,Narasimhan B,et al.Micro- sphere size, precipitation kinetics and drug distribution control drug release from biodegradable polyanhydride microspheres.J Controlled Release.2004;94(1):129-141. |