Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (6): 1183-1191.doi: 10.12307/2025.269
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes
He Guanghui1, Yuan Jie1, Ke Yanqin1, Qiu Xiaoting1, Zhang Xiaoling1, 2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, The Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Xinhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200092, China
-
Received:2024-01-25Accepted:2024-03-07Online:2025-02-28Published:2024-06-21 -
Contact:Zhang Xiaoling, MD, Professor, Department of Orthopedics, The Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Xinhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200092, China -
About author:He Guanghui, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, The Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Key Research and Development Project of Shanxi Province, No. 201903D321097 (to ZXL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
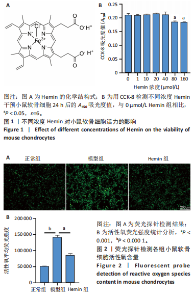
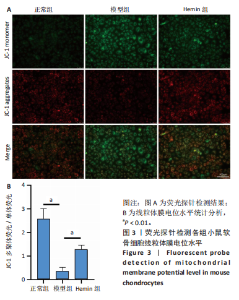
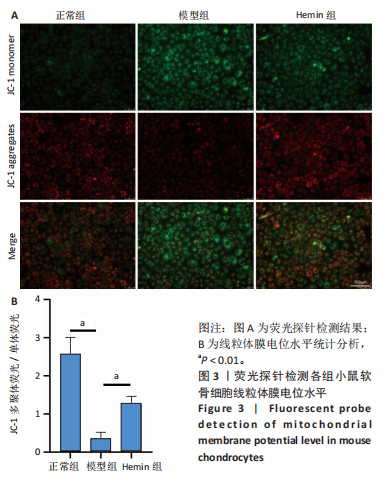
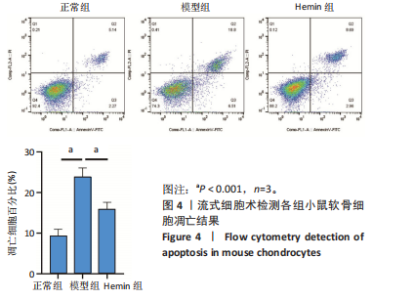
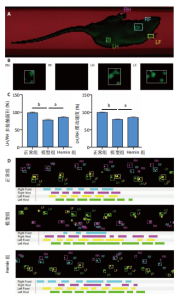
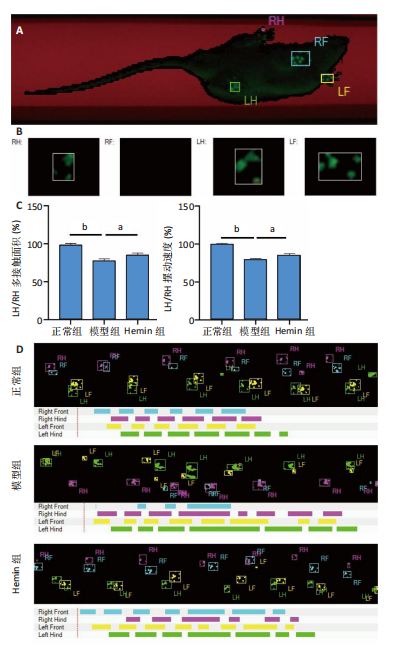
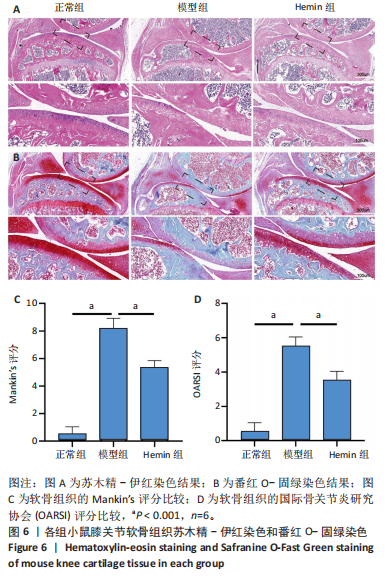
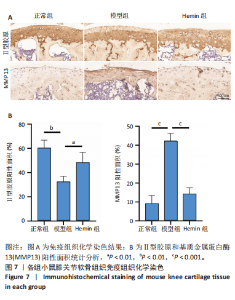
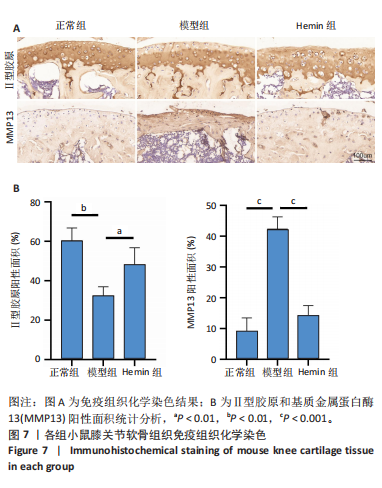
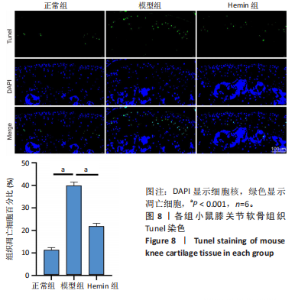
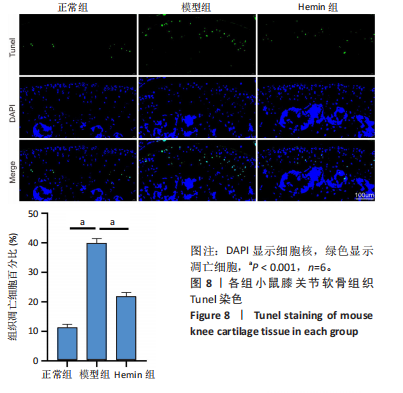
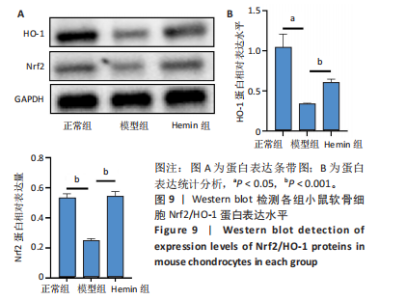
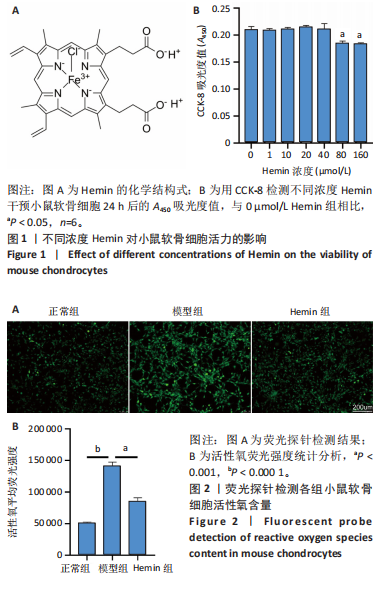
2.1 Hemin对软骨细胞的活性影响 0,1,10,20,40 μmol/L 的Hemin(分子式见图1A)处理24 h后对小鼠软骨细胞活力没有差异,但是80,160 μmol/L 的Hemin对小鼠软骨细胞活力有显著差异,见图1B。因而后续细胞实验选择Hemin的浓度为40 μmol/L。 2.2 各组软骨细胞活性氧水平 与正常组相比,模型组软骨细胞活性氧水平相对绿色荧光升高;相较于模型组,Hemin组软骨细胞活性氧水平相对绿色荧光降低,见图 2。结果表明Hemin能够降低炎症因子白细胞介素1β对小鼠软骨细胞的活性氧水平。 2.3 各组软骨细胞线粒体膜电位水平 与正常相比,模型组软骨细胞线粒体膜电位水平降低;与模型组相比,Hemin组软骨细胞线粒体膜电位水平升高,见图 3。结果说明Hemin可以增加炎症因子白细胞介素1β作用的软骨细胞线粒体膜电位水平。 2.4 各组软骨细胞凋亡情况 采用流式细胞术进行小鼠软骨细胞凋亡检测,结果发现,经白细胞介素1β处理后软骨细胞凋亡数量明显增加(P < 0.001),而给予Hemin治疗后软骨细胞凋亡水平降低(P < 0.001),表明经Hemin处理可以缓解白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨炎症,见图4。结果说明Hemin可以降低炎症因子白细胞介素1β对软骨细胞凋亡的影响。 2.5 实验动物情况分析 实验选用C57BL/6J雄性小鼠24只,随机分为3组,实验过程中动物无脱失,全部纳入结果分析。 2.6 各组小鼠行为学分析 治疗4周后使用CatWalk进行小鼠步态分析,小鼠自由通过固定跑道时能清晰记录四肢印记,见图5A,B。正常组小鼠节律整齐的通过固定跑道;模型组小鼠在通过跑道时节律紊乱,右后肢触地面积变少;与模型组相比,Hemin组小鼠下肢步态节律更齐,有显著的恢复效果,见图5C。进一步分析发现模型组形成后局部痛阈减小,小鼠触地面积以及摆动的时间减少,见图5D,Hemin组治疗后小鼠功能显著恢复。 2.7 各组小鼠膝关节软骨组织病理学变化 见图6。 2.7.1 苏木精-伊红染色 结果显示,模型组的膝关节表面非常粗糙,软骨下骨暴露于关节面,而Hemin组减少了关节表面的磨损,恢复了一定的软骨层,软骨表面相对平整光滑,软骨组织病理学表现有所改善,见图6A。根据Mankin’s评分从软骨结构、软骨细胞、软骨基质细胞染色和潮线完整性4个方面定量损伤结果,与正常组相比模型组的Mankin’s评分显著升高,而Hemin组的Mankin’s评分均显著降低,见图6C。 2.7.2 番红O-固绿染色 结果显示,模型组小鼠骨关节炎有明显的软骨损伤,与正常组小鼠相比,模型组小鼠膝关节软骨退变和侵蚀、以及番红O染色强度降低;相反,Hemin治疗可以恢复番红O染色强度,改善其他病理学变化,预防软骨损伤,见图6B。使用OARSI评分从软骨基质丢失、软骨损伤面积占比、垂直裂隙延伸长度不同程度等方面的软骨退变来定量损伤后,结果发现Hemin治疗显著降低了OARSI评分,见图6D。 2.8 各组小鼠软骨组织细胞外基质相关蛋白表达 相对于正常组,模型组的软骨组织中Ⅱ型胶原表达显著降低,而基质金属蛋白酶13表达则显著升高;与模型组相比,Hemin组的Ⅱ型胶原表达均显著升高,基质金属蛋白酶13表达显著降低,见图7。结果表明Hemin能够提高骨关节炎软骨的合成代谢,同时降低其分解代谢,改善骨关节炎软骨退变。 2.9 各组小鼠软骨组织细胞凋亡变化 与正常组相比,模型组软骨组织中凋亡软骨细胞显著增加;与模型组相比,Hemin组的凋亡软骨细胞显著均显著下降,见图 8。结果表明Hemin可以减少骨关节炎软骨细胞的凋亡数量。 2.10 各组小鼠软骨细胞Nrf2/HO-1蛋白的表达 与正常组相比,模型组软骨细胞中HO-1、Nrf2蛋白表达水平均显著下降,与模型组相比,Hemin组HO-1、Nrf2蛋白表达水平均显著上升,见图 9。结果表明Hemin可以激活炎症环境中软骨细胞的Nrf2/HO-1信号通路。"
| [1] LIU Q, WANG S, LIN J, et al. The burden for knee osteoarthritis among Chinese elderly: estimates from a nationally representative study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(12):1636-1642. [2] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA. 2021;325(6):568-578. [3] Hunter DJ, Bierma-Zeinstra S. Osteoarthritis. The Lancet. 2019; 393(10182):1745-1759. [4] 赵彦萍, 林志国, 林书典, 等. 骨关节炎诊疗规范[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2022,61(10):1136-1143. [5] ROBINSON WH, LEPUS CM, WANG Q, et al. Low-grade inflammation as a key mediator of the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(10):580-592. [6] PEAT G, THOMAS MJ. Osteoarthritis year in review 2020: epidemiology & therapy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(2):180-189. [7] RIEGGER J, SCHOPPA A, RUTHS L, et al. Oxidative stress as a key modulator of cell fate decision in osteoarthritis and osteoporosis: a narrative review. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023;28(1):76. [8] LIU X, LI Y, ZHAO J, et al. Pyroptosis of chondrocytes activated by synovial inflammation accelerates TMJ osteoarthritis cartilage degeneration via ROS/NLRP3 signaling. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023; 124(Pt A):110781. [9] LEPETSOS P, PAPAVASSILIOU AG. ROS/oxidative stress signaling in osteoarthritis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1862(4):576-591. [10] BISSELL DM, LONGO DL, ANDERSON KE, et al. Porphyria. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(9):862-872. [11] KUMAR D, JENA GR, RAM M, et al. Hemin attenuated oxidative stress and inflammation to improve wound healing in diabetic rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2019;392(11):1435-1445. [12] WANG YJ, PENG QY, DENG SY, et al. Hemin protects against oxygen–glucose deprivation-induced apoptosis activation via neuroglobin in SH-SY5Y cells. Neurochem Res. 2017;42(8):2208-2217. [13] WU B, WU Y, FAN C, et al. Heme supplementation ameliorates lupus nephritis through rectifying the disorder of splenocytes and alleviating renal inflammation and oxidative damage. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;94:107482. [14] MANKIN HJ, LIPPIELLO L. Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteo-arthritic human hips. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970;52(3):424-34. [15] GLASSON SS, CHAMBERS MG, VAN DEN BERG WB, et al. The OARSI histopathology initiative – recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the mouse. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010:18 Suppl 3:S17-S23. [16] KLOPPENBURG M, BERENBAUM F. Osteoarthritis year in review 2019: epidemiology and therapy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(3):242-248. [17] Abdel-Rahman R, Alsharif I, Abd-Elsalam R, et al. Crataegus sinaica defatted methanolic extract ameliorated monosodium iodoacetate-induced oxidative stress andinhibited inflammation in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Res Pharm Sci. 2022;17(5):493-507. [18] WAN C, LIU W, JIANG L, et al. Knockdown of MKL1 ameliorates oxidative stress-induced chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage matrix degeneration by activating TWIST1-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in rats. Autoimmunity 2022;55(8):559-566. [19] WANG S, DENG Z, MA Y, et al. The Role of Autophagy and Mitophagy in Bone Metabolic Disorders. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(14):2675-2691. [20] OH J, SON YS, KIM WH, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells genetically engineered to express platelet-derived growth factor and heme oxygenase-1 ameliorate osteoarthritis in a canine model. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):43. [21] PAN Z, HE Q, ZENG J, et al. Naringenin protects against iron overload-induced osteoarthritis by suppressing oxidative stress. Phytomedicine. 2022;105:154330. [22] COLLINO M, PINI A, MUGELLI N, et al. Beneficial effect of prolonged heme oxygenase 1 activation in a rat model of chronic heart failure. Dis Model Mech. 2013;6(4):1012-1020. [23] VAAMONDE-GARCIA C, COURTIES A, PIGENET A, et al. The nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor/heme oxygenase-1 axis is critical for the inflammatory features of type 2 diabetes–associated osteoarthritis. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(35):14505-14515. [24] SHENG W, YANG H, NIU Z, et al. Anti-apoptosis effect of heme oxygenase-1 on lung injury after cardiopulmonary bypass. J Thorac Dis. 2020;12(4):1393-1403. [25] TAKADA T, MIYAKI S, ISHITOBI H, et al. Bach1 deficiency reduces severity of osteoarthritis through upregulation of heme oxygenase-1. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:285. [26] SANADA Y, TAN SJO, ADACHI N, et al. Pharmacological Targeting of Heme Oxygenase-1 in Osteoarthritis. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021; 10(3):419. [27] BAI F, FAN C, LIN X, et al. Hemin protects UVB-induced skin damage through inhibiting keratinocytes apoptosis and reducing neutrophil infiltration. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2023;238:112604. [28] HASHIMOTO M, NAKASA T, HIKATA T, et al. Molecular network of cartilage homeostasis and osteoarthritis. Med Res Rev. 2008;28(3): 464-481. [29] 宋永周, 关健, 李明, 等.Nrf2介导姜黄素对软骨细胞氧化应激损伤的保护作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(51):8218-8222. [30] TAN Z, ZHANG B. Echinacoside alleviates osteoarthritis in rats by activating the Nrf2-HO-1 signaling pathway. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022;44(6):850-859. [31] SHIN HJ, PARK H, SHIN N, et al. p47phox siRNA-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles Suppress ROS/Oxidative Stress-Induced Chondrocyte Damage in Osteoarthritis. Polymers (Basel). 2020;12(2):443. [32] PARK C, JEONG JW, LEE DS, et al. Sargassum serratifolium Extract Attenuates Interleukin-1β-Induc ed Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response in Chondrocytes by Suppr essing the Activation of NF-κB, p38 MAPK, and PI3K/Akt. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(8):2308. [33] LIU L, ZHANG W, LIU T, et al. The physiological metabolite α-ketoglutarate ameliorates osteoarthritis by regulating mitophagy and oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2023;62:102663. [34] MAWATARI T, NAKAMICHI I, SUENAGA E, et al. Effects of heme oxygenase‐1 on bacterial antigen‐induced articular chondrocyte catabolism in vitro. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(12):1943-1949. [35] ZHOU Y, WANG T, HAMILTON JL, et al. Wnt/β-catenin Signaling in Osteoarthritis and in Other Forms of Arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017;19(9):53. [36] DING Y, WANG L, ZHAO Q, et al. MicroRNA‑93 inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation in osteoar thritis by targeting the TLR4/NF‑κB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med.2019;43(2):779-790. [37] HE Z, LI H, HAN X, et al. Irisin inhibits osteocyte apoptosis by activating the Erk signaling pa thway in vitro and attenuates ALCT-induced osteoarthritis in mice. Bone. 2020;141:115573. [38] CAI D, FENG W, LIU J, et al. 7,8‑Dihydroxyflavone activates Nrf2/HO‑1 signaling pathways and protects against osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18(3):1677-1684. [39] KENSLER TW, WAKABAYASHI N, BISWAL S. Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-A. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;47:89-116. [40] LOBODA A, DAMULEWICZ M, PYZA E, et al. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: an evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(17):3221-3247. [41] PAN X, CHEN T, ZHANG Z, et al. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signal with Myricetin for attenuating ECM degr adation in human chondrocytes and ameliorating the murine osteoarthrit is. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;75:105742. |
| [1] | Yang Xuetao, Zhu Menghan, Zhang Chenxi, Sun Yimin, Ye Ling. Applications and limitations of antioxidant nanomaterials in oral cavity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2044-2053. |
| [2] |
Dong Chunyang, Zhou Tianen, Mo Mengxue, Lyu Wenquan, Gao Ming, Zhu Ruikai, Gao Zhiwei.
Action mechanism of metformin combined with Eomecon chionantha Hance dressing in treatment of deep second-degree burn wounds#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2001-2013.
|
| [3] | Lyu Xiaofan, Huang Yi, Ding Liucheng . Mitochondrial mechanism and intervention therapy in diabetic cystopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1508-1515. |
| [4] | Jia Jinwen, Airefate·Ainiwaer, Zhang Juan. Effects of EP300 on autophagy and apoptosis related to allergic rhinitis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1439-1449. |
| [5] | Hou Chaowen, Li Zhaojin, Kong Jianda, Zhang Shuli. Main physiological changes in skeletal muscle aging and the multimechanism regulatory role of exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1464-1475. |
| [6] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [7] | Wang Zhengye, Liu Wanlin, Zhao Zhenqun. Advance in the mechanisms underlying miRNAs in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1207-1214. |
| [8] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [9] | Bao Zhuoma, Hou Ziming, Jiang Lu, Li Weiyi, Zhang Zongxing, Liu Daozhong, Yuan Lin. Effect and mechanism by which Pterocarya hupehensis skan total flavonoids regulates the proliferation, migration and apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 816-823. |
| [10] | Wang Zhengye, Liu Wanlin, Zhao Zhenqun. Mechanism by which vascular endothelial growth factor A targets regulation of angiogenesis in the treatment of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 671-679. |
| [11] | Chen Ling, Mao Qiuhua, Xu Pu, Zhang Wenbo. Effect of water-soluble matrix of nano-pearl powder on proliferation, migration and apoptosis of mouse fibroblasts#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 338-344. |
| [12] | Dong Chao, Zhao Mohan, Liu Yunan, Yang Zeli, Chen Leqin, Wang Lanfang. Effects of magnetic nano-drug carriers on exercise-induced muscle injury and inflammatory response in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 345-353. |
| [13] | Chen Qiheng, Weng Tujun, Peng Jiang. Effect of dimethylglyoxal glycine on osteogenic, adipogenesis differentiation, and mitophagy of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 50-57. |
| [14] | Wu Zhijing, Li Jiali, Zhang Jiaxin, Wang Tangrong, Zheng Yuzhou, Sun Zixuan. Alpha-ketoglutarate engineered small extracellular vesicles delay skin aging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 120-129. |
| [15] | Zhao Yang, Li Jialin, Wu Xiao, Zou Yourui, Liu Yang, Ma Hui. Choline kinase alpha silencing affects proliferation and apoptosis in glioma cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 130-138. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||