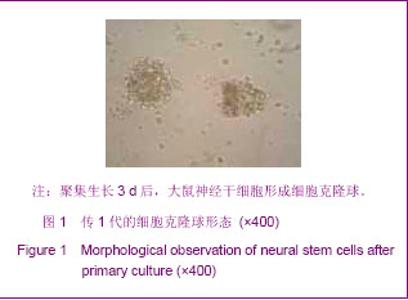
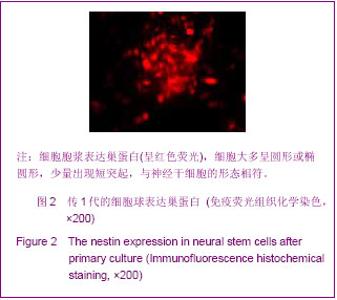
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Astragalus injection strengthens biological viability of rat neural stem cells
Zhang Li1, Luo Xiu-cheng1, Yang Shi-zhao1, Zhang Jun-feng1, Yang Ji-ping1, Zhao Zhao-hua1, Zhang Hui2
- 1Department of Human Anatomy, Xi’an Medical University, Xi’an 710021, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075000, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2013-03-11Revised:2013-05-04Online:2013-07-02Published:2013-07-02 -
Contact:Zhang Hui, Master, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075000, Hebei Province, China zhanghui6312@126.com -
About author:Zhang Li★, Master, Assistant teacher, Department of Human Anatomy, Xi’an Medical University, Xi’an 710021, Shaanxi Province, China xinhuoxc2013@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Li1, Luo Xiu-cheng, Yang Shi-zhao, Zhang Jun-feng, Yang Ji-ping, Zhao Zhao-hua, Zhang Hui . Astragalus injection strengthens biological viability of rat neural stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.27.017.
share this article
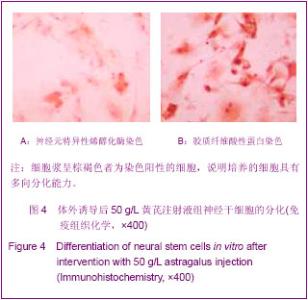
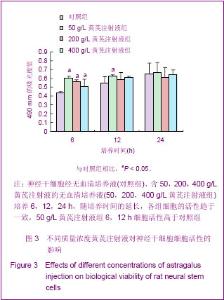
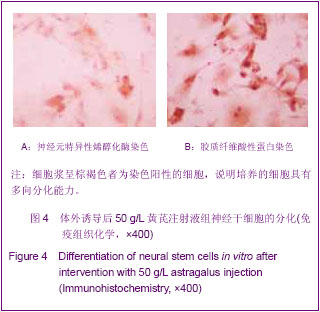
MTT检测结果显示,在24 h内不同质量浓度的黄芪注射液可使细胞活性增高。药物作用6 h,50,200, 400 g/L黄芪注射液组细胞的活性与对照组相比明显升高(P=0.000,0.001,0.035 < 0.05)。 药物作用12 h,200,400 g/L 黄芪注射液组细胞的活性与对照组间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),但 50 g/L黄芪注射液组细胞的活性仍高于对照组(P=0.047 < 0.05)。 药物作用24 h,不同质量浓度的黄芪注射液对细胞活性的作用逐渐趋于一致,各组差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.4 黄芪注射液增加神经干细胞的分化 免疫组织化学检测显示,与对照组相比,50 g/L的黄芪注射液组诱导的细胞分化快速,对培养的细胞有明显的影响,可见在50 g/L黄芪注射液组分化细胞中神经元特异性烯醇化酶阳性细胞数量增加。 细胞计数神经元特异性烯醇化酶阳性细胞率为(56.22±3.78)%,对照组为(35.76±4.71)%,差异有显著性意义(F=13.53,P=0.04 < 0.05),见图4。"
| [1] Lee HJ, Lim IJ, Lee MC, et al. Human neural stem cells genetically modified to overexpress brain-derived neurotrophic factor promote functional recovery and neuroprotection in a mouse stroke model. J Neurosci Res. 2010;88(15):3282-3294.[2] Gupta N, Henry RG, Strober J, et al. Neural stem cell engraftment and myelination in the human brain. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4(155):155ra137.[3] Clewes O, Narytnyk A, Gillinder KR, et al. Human epidermal neural crest stem cells (hEPI-NCSC)--characterization and directed differentiation into osteocytes and melanocytes. Stem Cell Rev. 2011;7(4):799-814. [4] Carpenter MK, Winkler C, Fricker R, et al. Generation and transplantation of EGF-responsive neural stem cells derived from GFAP-hNGF transgenic mice. Exp Neurol. 1997;148(1): 187-204.[5] 谭华.黄芪总苷和三七总皂苷配伍对脑缺血再灌注后早期损伤相关因素影响的研究[D].湖南中医药大学,2010.[6] 宋纯清,郑志仁,刘涤,等.膜荚黄芪中的异黄酮化合物[J].植物学报(英文版),1997,39(8):764-776.[7] Lu S, Chen KJ, Yang QY, et al. Progress in the research of Radix Astragali in treating chronic heart failure: effective ingredients, dose-effect relationship and adverse reaction. Chin J Integr Med. 2011;17(6):473-477.[8] 王永红,罗雪,石永江,等.银杏内酯 B 对神经干细胞分化的影响及其机制研究[J].中国康复理论与实践,2007,13(8):701- 703.[9] 石永江,罗雪,王永红,等.人参皂甙Rgl和Rbl对培养大鼠室管膜前下区神经干细胞谷氨酸兴奋毒性的保护作用及其与STAT3表达的关系[J].国际脑血管病杂志, 2007,15(3):172-176.[10] Wang XS, Li HF, Zhao Y, et al. Radix Astragali-induced differentiation of rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Neural Regen Res. 2009;4(7):497-502.[11] 黄进,张进,徐志伟.黄芪多糖对体外培养骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和干细胞因子表达的刺激作用[J].复旦学报(医学版),2011,38(4): 343-348.[12] Tohda C, Tamura T, Matsuyama S, et al. Promotion of axonal maturation and prevention of memory loss in mice by extracts of Astragalus mongholicus. Br J Pharmacol. 2006;149(5): 532-541.[13] Tohda C, Matsumoto N, Zou K, et al. Abeta(25-35)-induced memory impairment, axonal atrophy, and synaptic loss are ameliorated by M1, A metabolite of protopanaxadiol-type saponins. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004;29(5):860-868.[14] 陈国辉,黄文凤.黄芪的化学成分及药理作用研究进展.中国新药杂志,2008,17(17):1482-1485.[15] 中华人民共和国科学技术部. 关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.[16] 孟涛,林玲,郑志竑,等.大鼠胚胎中脑腹侧细胞和大脑皮质神经干细胞移植治疗帕金森病大鼠的比较[J].神经解剖学杂志,2009(5): 493-496.[17] Rietze RL, Reynolds BA. Neural stem cell isolation and characterization. Methods Enzymol. 2006;419:3-23.[18] 韦云飞,赵伟佳,郝永楠,等.黄芪注射液对缺血后脑组织神经干细胞增殖和分化的影响[J].临床神经病学杂志,2012,25(3): 192-195.[19] Liu JJ, Yao ZX, Qin ML, et al. Effect of simple astragali, flos carthami, salvia miltiorrhiza injection on differentiation of neural stem cell. Acta Acad Med Milit Tertiae. 2006; 28(14): 1470-1472.[20] 张力,张辉,孙黎,等.神经干细胞在创伤性脑损伤灶周边的成活和迁移[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(36): 6715-6719.[21] Xiao WL, Motley TJ, Unachukwu UJ, et al. Chemical and genetic assessment of variability in commercial Radix Astragali (Astragalus spp.) by ion trap LC-MS and nuclear ribosomal DNA barcoding sequence analyses. J Agric Food Chem. 2011;59(5):1548-1556.[22] 姚美村,齐莹,毕开顺,等.黄芪药效物质基础研究[J].中国野生植物资源,2000,19(2):33-36.[23] Yuan W, Zhang Y, Ge Y, et al. Astragaloside IV inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis in rat vascular smooth muscle cells under high glucose concentration in vitro. Planta Med. 2008;74(10):1259-1264.[24] Wang D, Zhuang Y, Tian Y, et al. Study of the effects of total flavonoids of Astragalus on atherosclerosis formation and potential mechanisms. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012;2012: 282383.[25] Frøkiær H, Henningsen L, Metzdorff SB, et al. Astragalus root and elderberry fruit extracts enhance the IFN-β stimulatory effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus in murine-derived dendritic cells. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47878. [26] Yuan Y, Sun M, Li KS. Astragalus mongholicus polysaccharide inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced production of TNF-alpha and interleukin-8. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15(29):3676-3680.[27] Li XT, Zhang YK, Kuang HX, et al. Mitochondrial Protection and Anti-aging Activity of Astragalus Polysaccharides and Their Potential Mechanism. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(2): 1747-1761. [28] 国家药典委员会.中华人民共和国药典2010年版.2010: 212-213.[29] Zhang RP, Zhang XP, Ruan YF, et al. Protective effect of Radix Astragali injection on immune organs of rats with obstructive jaundice and its mechanism. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15(23):2862-2869.[30] Zuo C, Xie XS, Qiu HY, et al. Astragalus mongholicus ameliorates renal fibrosis by modulating HGF and TGF-beta in rats with unilateral ureteral obstruction. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2009;10(5):380-390. [31] Xiping Z, Ke W, Yaping Y, et al. Protective effect and mechanisms of radix astragali injection on the intestinal mucosa of rats with obstructive jaundice. Mediators Inflamm. 2010;2010:757191.[32] Yao C, Li A, Gao W, et al. Improving the angiogenic potential of collagen matrices by covalent incorporation of Astragalus polysaccharides. Int J Burns Trauma. 2011;1(1):17-26. [33] 颜玲,黄德斌.黄芪多糖对缺血脑损伤大鼠海马神经递质及c-fos mRNA表达的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2012,28(2):263-268.[34] 贾瑞喆,蒋犁,乔立兴,等.黄芪对新生鼠乏氧缺血脑损伤海马区神经保护作用的研究[J].中国中药杂志,2003,28(12):1174-1177.[35] 曲友直,李敏,高国栋.黄芪注射液对脑缺血再灌注后血脑屏障的保护作用及ZO-1蛋白表达的影响[J].中国中医急症,2012,21(1): 47-48. [36] De Filippis L, Delia D. Hypoxia in the regulation of neural stem cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011;68(17):2831-2844.[37] 吴宏伟,高健,李韶菁,等.基于液相色谱-串联质谱的氨基酸代谢组学方法研究黄芪注射液治疗脑缺血[J].分析化学,2013,41(3): 344-348.[38] Porlan E, Perez-Villalba A, Delgado AC, et al. Paracrine regulation of neural stem cells in the subependymal zone. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2013;534(1-2):11-19.[39] Leung KW, Yung KK, Mak NK, et al. Neuroprotective effects of ginsenoside-Rg1 in primary nigral neurons against rotenone toxicity. Neuropharmacology. 2007;52(3):827-835.[40] 谢睿,张艳,刘建军,等.神经干细胞的特征及中药黄芪对其影响[J].局解手术学杂志,2004,13(14):275-277.[41] 蒋犁,贾瑞喆,乔立兴,等.黄芪对新生鼠乏氧缺血脑损伤后海马区神经的保护及学习记忆能力的干预[J].中国临床康复,2006, 10(7): 154-157.[42] 庄朋伟,张艳军.中药调控神经干细胞促进中枢神经系统神经再生与修复的研究进展[J].中国医药生物技术,2008,3(2):134-136. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [3] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [4] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [5] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [6] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [7] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [8] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [9] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [10] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [11] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [12] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [13] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [14] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [15] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||