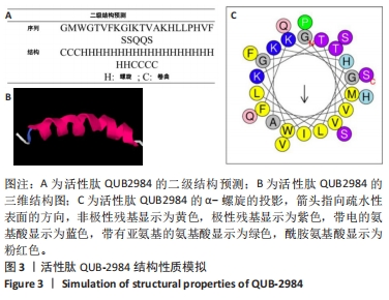
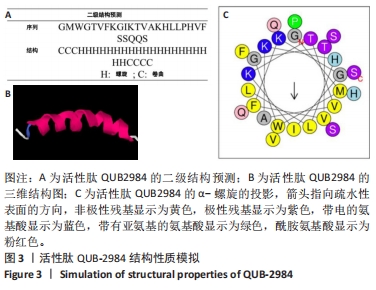
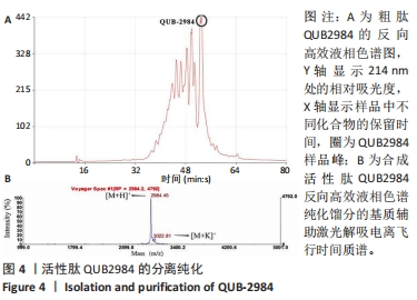
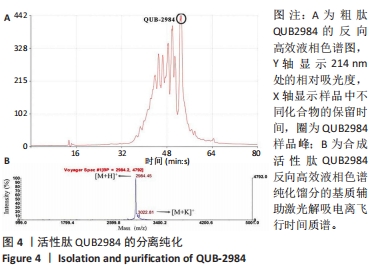
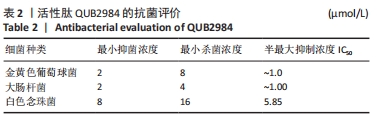
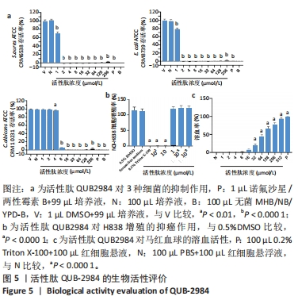
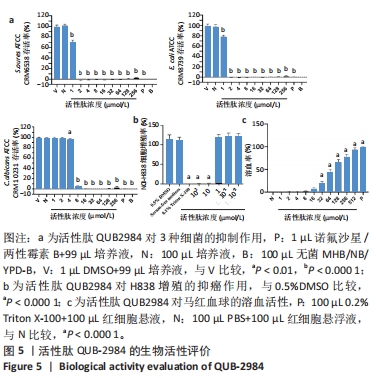
[1] ZHAO G, ZHANG Y, SUN D, et al. Recent Advances in Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Antibiotic Analysis. Molecules. 2023;28(1):335.
[2] XUAN J, FENG W, WANG J, et al. Antimicrobial peptides for combating drug-resistant bacterial infections. Drug Resist Updat. 2023;68:100954.
[3] ROLLINS-SMITH LA. The importance of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) in amphibian skin defense. Dev Comp Immunol. 2023;142:104657.
[4] LAZZARO BP, ZASLOFF M, ROLFF J. Antimicrobial peptides: application informed by evolution. Science. 2020;368:eaau5480.
[5] ZHU Y, HAO W, WANG X, et al. Antimicrobial peptides, conventional antibiotics, and their synergistic utility for the treatment of drug-resistant infections. Med Res Rev. 2022;42(4):1377-1422.
[6] 刘华.虎纹蛙皮肤分泌物活性肽的分离纯化及表征 [D]. 福州:福州大学,2013.
[7] FLATT PR, CONLON JM. Newer peptide-based agents for treatment of patients with Type 2 diabetes. Peptides. 2018;100:1-2.
[8] HASHEMI D, MA X, ANSARI R, et al. Design principles for the energy level tuning in donor/acceptor conjugated polymers. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2019;21(2):789-799.
[9] SUN E, BELANGER CR, HANEY EF, et al. Host defense (antimicrobial) peptides. Peptide applications in biomedicine, biotechnology and bioengineering. Elsevier, 2018: 253-285.
[10] SERVENT D, CARDOSO FC, DE LIMA ME. Venom peptides: A rich combinatorial library for drug development, volume II. Front Mol Biosci. 2023;10:1186828.
[11] LI Y, WANG M, LI Y, et al. Two novel antimicrobial peptides against vegetative cells, spores and biofilm of Bacillus cereus. Food Control. 2023;149:109688.
[12] GAO F, WANG X, LI Z, et al. Identification of anti-tumor components from toad venom. Oncol Lett. 2017;14(1):15-22.
[13] AGUILAR S, BRUNETTI AE, GARAY AV, et al. Structure and function of cationic hylin bioactive peptides from the tree frog Boana pulchella in interaction with lipid membranes. Peptides. 2023;159:170900.
[14] URMI UL, VIJAY AK, KUPPUSAMY R, et al. A review of the antiviral activity of cationic antimicrobial peptides. Peptides. 2023;166:171024.
[15] ZENG J, WANG J, WU J, et al. A novel antimicrobial peptide M1‐8 targets the lysosomal pathway to inhibit autolysosome formation and promote apoptosis in liver cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2023;27(3):340-352.
[16] NIKYAR A, BOLHASSANI A, AGI E. LL-37 antimicrobial peptide and heterologous prime-boost vaccination regimen significantly induce HIV-1 Nef-Vpr antigen-and virion-specific immune responses in mice. Biotechnol Lett. 2023;45(1):33-45.
[17] AmphibiaWeb [Online]. Available: www.amphibiaweb.org [Accessed May 12 2020].
[18] MILLS JW, PRUM BE. Morphology of the exocrine glands of the frog skin. Am J Anat. 1984;171(1):91-106.
[19] DELFINO G, BRIZZI R, CALLONI C. A morpho-functional characterization of the serous cutaneous glands in Bombina orientalis (Anura: Discoglossidae). Zool Anz. 1990;225(5-6):295-310.
[20] ROLLINS-SMITH LA. The importance of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) in amphibian skin defense. Dev Comp Immunol. 2023;142:104657.
[21] GE L, LYU P, ZHOU M, et al. AcT-2: a novel myotropic and antimicrobial type 2 tryptophyllin from the skin secretion of the Central American red-eyed leaf frog, Agalychnis callidryas. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:158546.
[22] WONG H, BOWIE JH, CARVER JA. The solution structure and activity of caerin 1.1, an antimicrobial peptide from the Australian green tree frog, Litoria splendida. Eur J Biochem. 1997;247(2):545-557.
[23] LADRAM A, NICOLAS P. Antimicrobial peptides from frog skin: biodiversity and therapeutic promises. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2016;21(7):1341-1371.
[24] MARQUETTE A, BECHINGER B. Biophysical investigations elucidating the mechanisms of action of antimicrobial peptides and their synergism. Biomolecules. 2018;8(2):18.
[25] BUDA DE CESARE G, CRISTY SA, GARSIN DA, et al. Antimicrobial peptides: A new frontier in antifungal therapy. mBio. 2020;11(6):e02123-20.
[26] NARAYANA JL, CHEN JY. Antimicrobial peptides: possible anti-infective agents. Peptides. 2015;72:88-94.
[27] RAMÍREZ-CARRETO S, JIMÉNEZ-VARGAS JM, RIVAS-SANTIAGO B, et al. Peptides from the scorpion Vaejovis punctatus with broad antimicrobial activity. Peptides. 2015;73:51-59.
[28] YANG M, ZHANG C, ZHANG MZ, et al. Beta-defensin derived cationic antimicrobial peptides with potent killing activity against gram negative and gram positive bacteria. BMC Microbiol. 2018;18(1):54.
[29] BAXTER AA, LAY FT, POON IK, et al. Tumor cell membrane-targeting cationic antimicrobial peptides: novel insights into mechanisms of action and therapeutic prospects. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017;74(20):3809-3825. |