Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (19): 2974-2980.doi: 10.12307/2024.150
Previous Articles Next Articles
Berberine promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a high-glucose environment
Gou Qiutong1, 2, 3, Luo Wenhao1, 2, 3, Wang Pin1, 2, 3, Lan Yuyan1, 2, 3, Liu Min1, 2, 3, Huang Haixia1, 2, 3
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, The Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2 Oral & Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration of Luzhou Key Laboratory, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 3Institute of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2023-03-09Accepted:2023-05-10Online:2024-07-08Published:2023-09-25 -
Contact:Huang Haixia, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Prosthodontics, The Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Oral & Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration of Luzhou Key Laboratory, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Institute of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Gou Qiutong, Master candidate, Department of Prosthodontics, The Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Oral & Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration of Luzhou Key Laboratory, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Institute of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Plan Project of Luzhou City, No. 2021-JYJ-68 (to HHX); General Program of Southwest Medical University, No. 2021ZKMS014 (to HHX); Sichuan Youth Innovation and Research Project Plan, No. Q22065 (to HHX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gou Qiutong, Luo Wenhao, Wang Pin, Lan Yuyan, Liu Min, Huang Haixia. Berberine promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a high-glucose environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(19): 2974-2980.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
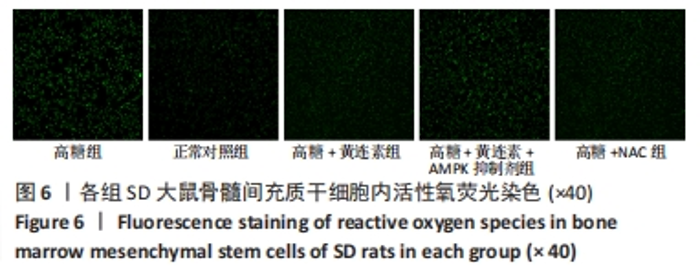
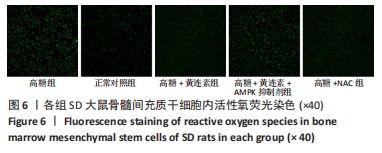
2.6 黄连素对高糖环境下BMSCs内活性氧水平的影响 图6,7显示了不同环境下BMSCs内的活性氧水平。如图6所示,高糖组的荧光强度较高,说明在高糖环境下BMSCs内的活性氧水平较高。正常对照组的荧光强度较低,说明在正常环境下BMSCs内仅有少量的活性氧。高糖+黄连素组的荧光强度较高糖组大幅度降低,与高糖+NAC组相似。高糖+黄连素+AMPK抑制剂组的荧光强度较高糖+黄连素组的荧光强度大幅度升高,与高糖组相似。如图7所示,半定量分析显示高糖组的平均荧光强度相比于正常对照组大幅度提升(P < 0.05)。高糖+黄连素组和高糖+NAC组的平均荧光强度比高糖组显著降低(P < 0.05)。高糖+黄连素+AMPK抑制剂组的荧光强度明显高于高糖+黄连素组和高糖+NAC组(P < 0.05)。高糖+黄连素组的荧光强度与高糖+NAC组相似(P > 0.05)。"
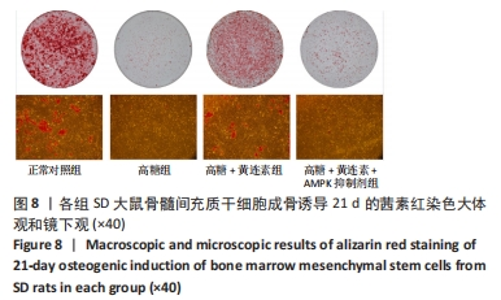
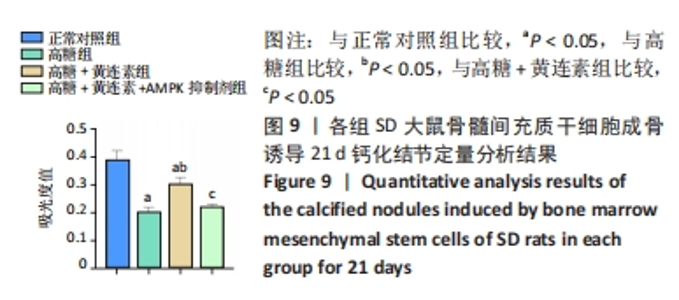
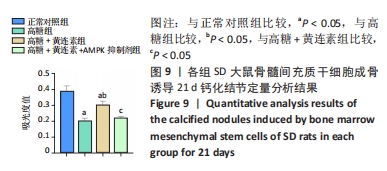
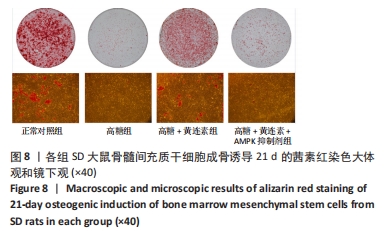
2.7 黄连素对高糖环境下BMSCs分泌矿化结节的影响 图8显示了BMSCs在不同条件下经21 d成骨诱导后分泌矿化结节的情况。茜素红染色结果显示正常对照组的红染结节数量较多、颜色较深,且被染色的面积较大,具有良好的矿化结节形成能力。高糖组的红染结节数量较少、颜色较浅,且被染色的面积较小,矿化能力不佳。高糖+黄连素组的红染结节多于高糖组,且染色更深。高糖+黄连素+AMPK抑制剂组的染色情况与高糖组相似。图9显示了各组矿化结节的定量分析,正常对照组的吸光度值最高,与其他3组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。高糖+黄连素组的吸光度值高于高糖组和高糖+黄连素+AMPK抑制剂组(P < 0.05)。"

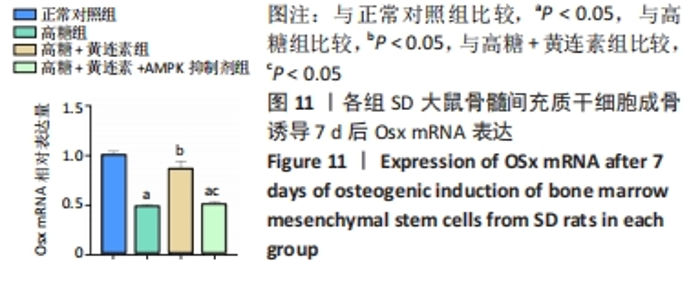
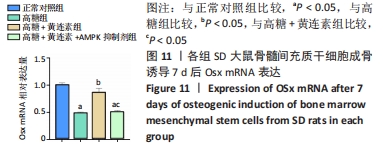
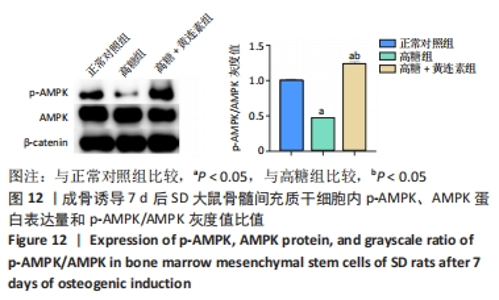
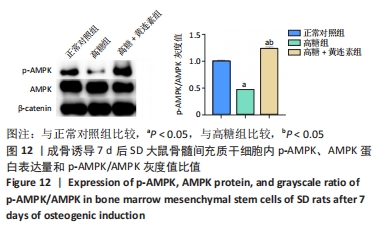
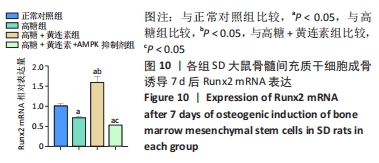
2.8 黄连素在高糖环境下对成骨分化特异基因Runx2、Osx表达水平的影响 图10,11显示了BMSCs在不同环境下成骨诱导7 d后,成骨基因Runx2和Osx的表达水平。如图10所示,高糖+黄连素组的Runx2 mRNA表达水平最高,与其他3组相比有显著差异(P < 0.05)。高糖组的Runx2 mRNA表达水平低于正常对照组(P < 0.05)。高糖+黄连素+AMPK抑制剂组的Runx2 mRNA表达水平也低于正常对照组(P < 0.05)。如图11所示,正常对照组Osx mRNA表达水平高于其余3组(P < 0.05)。高糖+黄连素组的Osx mRNA表达水平高于高糖组(P < 0.05)。高糖+黄连素+AMPK抑制剂组的Osx mRNA表达水平低于高糖+黄连素组(P < 0.05)。"
| [1] WAGNER J, SPILLE JH, WILTFANG J, et al. Systematic review on diabetes mellitus and dental implants: an update. Int J Implant Dent. 2022;8(1):1. [2] RENDRA E, RIABOV V, MOSSEL DM, et al. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) in macrophage activation and function in diabetes. Immunobiology. 2019;224(2):242-253. [3] IGHODARO OM. Molecular pathways associated with oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;108:656-662. [4] LI X, ZHAN J, HOU Y, et al. Coenzyme Q10 Regulation of Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress in H2O2 Induced BMSC Death by Modulating the Nrf-2/NQO-1 Signaling Pathway and Its Application in a Model of Spinal Cord Injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:6493081. [5] TREFTS E, SHAW RJ. AMPK: restoring metabolic homeostasis over space and time. Mol Cell. 2021;81(18):3677-3690. [6] WANG N, WANG L, YANG J, et al. Quercetin promotes osteogenic differentiation and antioxidant responses of mouse bone mesenchymal stem cells through activation of the AMPK/SIRT1 signaling pathway. Phytother Res. 2021 Jan 9. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7010. [7] CHENG Y, HUANG L, WANG Y, et al. Strontium promotes osteogenic differentiation by activating autophagy via the the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway in MC3T3‑E1 cells. Int J Mol Med. 2019;44(2):652-660. [8] XIE H, WANG Q, ZHANG X, et al. Possible therapeutic potential of berberine in the treatment of STZ plus HFD-induced diabetic osteoporosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;108:280-287. [9] ZHANG Y, MA J, ZHANG W. Berberine for bone regeneration: Therapeutic potential and molecular mechanisms. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;277:114249. [10] ZHANG JF, HUANG K, CAI HL, et al. Experimental study on the regulation of subchondral bone plate osteoprotegerin/receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand system by berberine to retard the development of osteoarthritis in rabbits. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2022; 35(5):464-469. [11] 郑晓明,王康振,郑炜宏,等.小檗碱可以通过改善氧化应激和成骨活性减少2型糖尿病大鼠骨量的流失[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2020,26(10):1426-1430,1450. [12] WANG X, WANG H, ZHANG T, et al. Current Knowledge Regarding the Interaction Between Oral Bone Metabolic Disorders and Diabetes Mellitus. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:536. [13] CHEN Y, ZHOU Y, LIN J, et al. Challenges to Improve Bone Healing Under Diabetic Conditions. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:861878. [14] HUO SC, YUE B. Approaches to promoting bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis on orthopedic implant surface. World J Stem Cells. 2020;12(7):545-561. [15] PANDEY C, ROKAYA D, BHATTARAI BP. Contemporary Concepts in Osseointegration of Dental Implants: A Review. Biomed Res Int. 2022; 2022:6170452. [16] FIJANY A, SAYADI LR, KHOSHAB N, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell dysfunction in diabetes. Mol Biol Rep. 2019;46(1):1459-1475. [17] LIU B, GAN X, ZHAO Y, et al. Inhibition of HMGB1 reduced high glucose-induced BMSCs apoptosis via activation of AMPK and regulation of mitochondrial functions. J Physiol Biochem. 2021;77(2):227-235. [18] LAO A, CHEN Y, SUN Y, et al. Transcriptomic analysis provides a new insight: Oleuropein reverses high glucose-induced osteogenic inhibition in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Wnt10b activation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:990507. [19] LIU B, GAN X, ZHAO Y, et al. Inhibition of HMGB1 Promotes Osseointegration under Hyperglycemic Condition through Improvement of BMSC Dysfunction. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:1703709. [20] DONG X, WANG X, XING M, et al. Inhibition of the negative effect of high glucose on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells by silicon ions from calcium silicate bioceramics. Regen Biomater. 2020;7(1):9-17. [21] ZHOU R, MA Y, QIU S, et al. Metformin promotes cell proliferation and osteogenesis under high glucose condition by regulating the ROS‑AKT‑mTOR axis. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(4):3387-3395. [22] DIEMAR SS, MØLLEHAVE LT, QUARDON N, et al. Effects of age and sex on osteocalcin and bone-specific alkaline phosphatase-reference intervals and confounders for two bone formation markers. Arch Osteoporos. 2020;15(1):26. [23] ASSIS RIF, SCHMIDT AG, RACCA F, et al. DNMT1 Inhibitor Restores RUNX2 Expression and Mineralization in Periodontal Ligament Cells. DNA Cell Biol. 2021;40(5):662-674. [24] WU X, ZHANG Y, XING Y, et al. High-fat and high-glucose microenvironment decreases Runx2 and TAZ expression and inhibits bone regeneration in the mouse. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):55. [25] TU Q, VALVERDE P, CHEN J. Osterix enhances proliferation and osteogenic potential of bone marrow stromal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;341(4):1257-1265. [26] CHEN M, JING D, YE R, et al. PPARβ/δ accelerates bone regeneration in diabetic mellitus by enhancing AMPK/mTOR pathway-mediated autophagy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):566. [27] GAO Q. Oxidative Stress and Autophagy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1206: 179-198. [28] SUN H, XU J, WANG Y, et al. Bone microenvironment regulative hydrogels with ROS scavenging and prolonged oxygen-generating for enhancing bone repair. Bioact Mater. 2023;24:477-496. [29] ALI F, AZIZ F, WAJID N. Effect of type 2 diabetic serum on the behavior of Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2017;3(2):105-111. [30] LEE S, LE NH, KANG D. Melatonin alleviates oxidative stress-inhibited osteogenesis of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells through AMPK activation. Int J Med Sci. 2018;15(10):1083-1091. [31] FAN D, LU J, YU N, et al. Curcumin Prevents Diabetic Osteoporosis through Promoting Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis Coupling via NF-κB Signaling. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:4974343. [32] LI X, LI B, SHI Y, et al. Targeting reactive oxygen species in stem cells for bone therapy. Drug Discov Today. 2021;26(5):1226-1244. [33] LI Y, WANG X. Chrysin Attenuates High Glucose-Induced BMSC Dysfunction via the Activation of the PI3K/AKT/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022;16:165-182. [34] SUN R, LIANG C, SUN Y, et al. Effects of metformin on the osteogenesis of alveolar BMSCs from diabetic patients and implant osseointegration in rats. Oral Dis. 2022;28(4):1170-1180. |
| [1] | Wang Wen, Zheng Pengpeng, Meng Haohao, Liu Hao, Yuan Changyong. Overexpression of Sema3A promotes osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and MC3T3-E1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 993-999. |
| [2] | Mei Jingyi, Liu Jiang, Xiao Cong, Liu Peng, Zhou Haohao, Lin Zhanyi. Proliferation and metabolic patterns of smooth muscle cells during construction of tissue-engineered blood vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1043-1049. |
| [3] | Wang Shanshan, Shu Qing, Tian Jun. Physical factors promote osteogenic differentiation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [4] | Lin Feng, Cheng Ling, Gao Yong, Zhou Jianye, Shang Qingqing. Hyaluronic acid hydrogel-encapsulated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote cardiac function in myocardial infarction rats (III) [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 355-359. |
| [5] | Bi Yujie, Ma Dujun, Peng Liping, Zhou Ziqiong, Zhao Jing, Zhu Houjun, Zhong Qiuhui, Yang Yuxin. Strategy and significance of Chinese medicine combined with medical hydrogel for disease treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 419-425. |
| [6] | Xie Ting, Liu Tingting, Zeng Xuehui, Li Yamin, Zhou Panghu, Yi Nianhua. Fucoxanthin alleviates glucocorticoid-induced osteoblast apoptosis by activating nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3609-3614. |
| [7] | Han Yue, Wang Yufei, Liu Wanqing, Dong Ming, Niu Weidong. Effects of icariin on proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells in an inflammatory environment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3709-3714. |
| [8] | Wang Zengshun, Suonan Angxiu, Liu Limin, Zhou Jingyuan. Role and mechanism of miR-155/leptin receptor/adenosine phosphate-dependent protein kinase axis in tuberculin-induced osteoclast formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3190-3195. |
| [9] | Wang Qian, Lu Ziang, Li Lihe, Lyu Chaoliang, Wang Meng, Zhang Cunxin. Sinomenine effectively inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 224-230. |
| [10] | Wang Xu, Wu Yajie, Zhang Xinfu, Shi Zhi, Yang Tengyun, Xiong Bohan, Lu Xiaojun, Zhao Daohong. Expression and action mechanism of stromal cell-derived factor 1 in tendon-bone healing of rabbit rotator cuff [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(19): 3049-3054. |
| [11] | Guo Qin, Wu Minmin, Tao Ying. Oxidized high-density lipoprotein promotes rat ovarian granulosa cell apoptosis through reactive oxygen species-initiated p38 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(19): 3055-3060. |
| [12] | Song Yue, Shu Qing, Jia Shaohui, Tian Jun. Photobiomodulation-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(19): 3069-3075. |
| [13] | Xiao Ziteng, Wang Tingyu, Zhang Wenwen, Tan Fengyi, Su Haiwei, Li Siting, Wu Yahui, Zhou Yanfang, Peng Xinsheng. Exosomes and skin wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(19): 3104-3110. |
| [14] | Chen Na, Wang Yanlin, Sun Huifang, Fan Feiyan, Li Donghong, Zhang Yunke. Shexiang Huangqi compound dripping pills-containing serum promotes proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(19): 2960-2966. |
| [15] | Xie Ting, Liu Tingting, Zeng Xuehui, Li Yamin, Zhou Panghu, Yi Nianhua. Vitamin D3 attenuates high-glucose exposure-induced oxidative stress to promote osteogenic differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(19): 2981-2987. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||