Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (10): 1547-1553.doi: 10.12307/2024.318
Previous Articles Next Articles
Evaluation of antibacterial properties of uniaxial and coaxial minocycline hydrochloride-loaded bone scaffolds
Cao Yijing1, Wei Suiyan1, Zhao Shuai1, Li Dongyao1, Wei Qin2, Zhang Xujing3, Xu Yan3, Xu Guoqiang1
- 1Department of Prosthodontics and Implantology, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University (Affiliated Stomatological Hospital), Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Central Laboratory of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 3Mechanical Engineering College of Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830047, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-03-20Accepted:2023-05-08Online:2024-04-08Published:2023-08-19 -
Contact:Xu Guoqiang, Chief physician, Department of Prosthodontics and Implantology, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University (Affiliated Stomatological Hospital), Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Cao Yijing, Master candidate, Physician, Department of Prosthodontics and Implantology, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University (Affiliated Stomatological Hospital), Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 51965057 (to XGQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cao Yijing, Wei Suiyan, Zhao Shuai, Li Dongyao, Wei Qin, Zhang Xujing, Xu Yan, Xu Guoqiang. Evaluation of antibacterial properties of uniaxial and coaxial minocycline hydrochloride-loaded bone scaffolds[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(10): 1547-1553.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
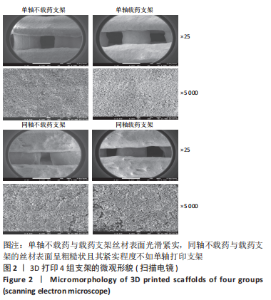
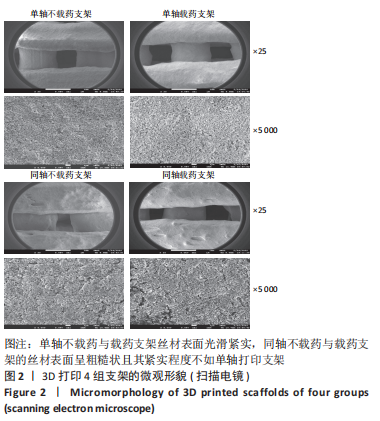
图2为各组支架的扫描电镜图,S1、S2支架丝材表面光滑紧实,而T1、T2支架的丝材表面呈粗糙状且其紧实程度不如单轴打印支架,这可能是因为同轴支架的外芯材料中未加入丝素蛋白。有研究表明指出,丝素蛋白的加入可以增强聚乙烯醇的黏性,使其更充分黏结羟基磷灰石,减少微观结构下微孔的出现[18]。同轴载药外芯材料更有利于药物的缓释,而内芯将丝素蛋白-聚乙烯醇与羟基磷灰石复合后也具备了致密而紧实的结构,有利于药物缓慢平稳通过外芯材料逐步释放出来。S1、S2支架孔径大小为700-800 μm,T1、T2支架孔径大小为400-500 μm,而目前国内外文献中普遍认为200-500 μm的孔径最利于新骨的生长[19],由此得出同轴复合骨支架更有利于新骨的生长。"
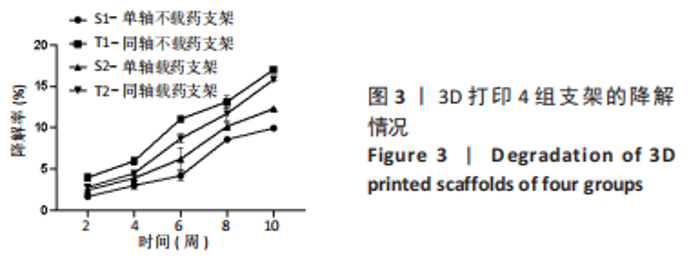
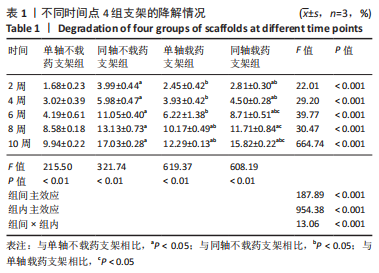
2.2 支架孔隙率检测结果 通过液体置换法得到骨支架孔隙率,S1、S2、T1、T2支架的孔隙率分别为(62.99±2.35)%,(62.88±2.16)%,(48.38±0.69)%,(51.16±0.46)%,数据满足正态分布及方差齐性检验,采用单因素方差分析结果,4 组支架间孔隙率比较差异有显著性意义(F=65.01,P < 0.001)。经LSD组间两两比较可知,S1与T2、S2与T2、S1和T1支架的孔隙率比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。有文献表明,松质骨的孔隙率在50%-90%之间,支架孔隙率在40%-70%时可满足支架生物相容性及力学性能的要求,而孔隙率为30%是允许新骨组织从支架外部长入内部的临界值[20-21]。4 组支架的孔隙率满足松质骨孔隙率,故4 组支架的孔隙率满足松质骨孔隙要求。 2.3 支架降解性能检测结果 如图3,表1是10 周内4 组支架的降解情况,数据满足正态分布及方差齐性检验,满足球型假设检验(P=0.11),经统计学分析得出4 组支架降解率比较差异有显著性意义(F=187.89,P < 0.001),不同时间点内支架降解率比较差异有显著性意义(F=954.38,P < 0.001),且时间与分组交互作用显著(F=13.06,P < 0.001);经简单效应分析及事后多重比较可得,4 组支架的降解率随着时间的推移在逐渐增加,与S1支架相比,T1、T2支架2-10 周的降解率升高(P < 0.05),S2支架8,10 周的降解率升高(P < 0.05);与T1支架相比,S2、T2支架2-10 周的降解率均降低(P < 0.05);与S2支架相比,T2支架6-10 周的降解率升高(P < 0.05)。"
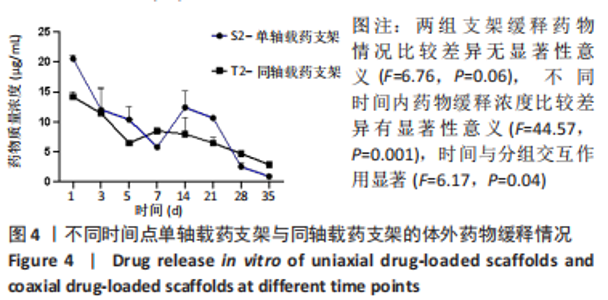
同轴打印骨支架的降解速率较对应单轴打印骨支架快,因为在降解初期时主要是PBS与支架孔隙之间发生的对流,造成支架孔径的改变,从而引发物理降解;对于同轴打印支架而言,由于外部壳层材料在打印时与内心芯材料接触可能改变了其实际配比,在与PBS接触后壳层材料溶解速率会比单轴打印支架材料溶解速度稍快一些。对于单轴载药支架的降解率较不载药支架快,而同轴载药支架的降解率却低于不载药支架,是因为:在打印同轴不载药支架时,为区分壳层材料与内芯材料保证出丝均匀,加入了少量红色墨水,内芯材料与壳层材料接触后改变了其整体配比,故不载药同轴支架的降解速率较载药后的同轴支架快。有研究发现,降解速率的快慢会影响新生骨的生长速率,降解过慢不利于新骨的生长及攀附,降解过快会导致支架坍塌,新骨无法填充进孔隙,修复过程中起不到支撑作用[18]。支架的降解速率应该与新骨生成速率匹配,植入颅骨和颌骨的支架降解周期应在3-6 个月。通过对比4 组支架10 周时的降解速率发现,S1支架的降解率为(9.94±0.22)%,S2支架的降解速率为(12.29±0.13)%,T1支架的降解速率为(17.03±0.28)%,T2支架的降解速率为(15.82±0.21)%,相比之下同轴打印骨支架的降解率更符合新骨生长速率。 2.4 支架药物缓释性能的检测结果 两组载药支架体外缓释情况如图4所示,数据为重复测量的定量资料,不满足球形假设,采用重复测量的方差分析结果,两组支架缓释药物情况比较差异无显著性意义(F=6.76,P=0.06),不同时间内药物缓释浓度比较差异有显著性意义(F=44.57,P=0.001),时间与分组交互作用显著(F=6.17,P=0.04)。"
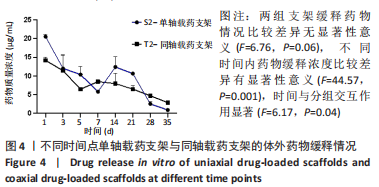
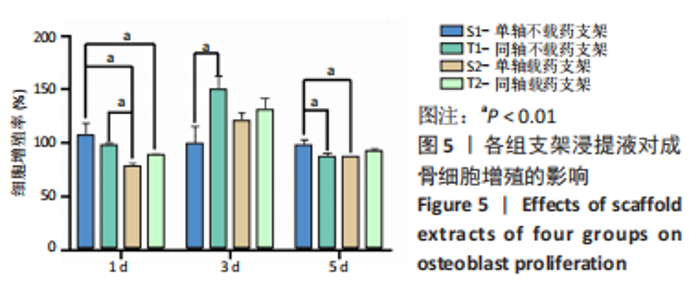
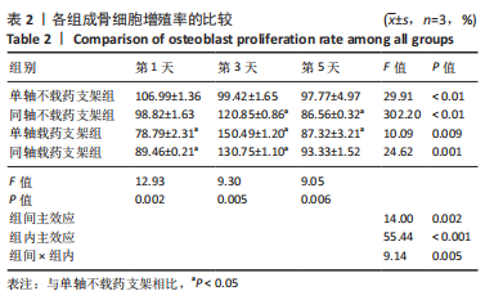
经简单效应分析后,S2支架1,5,14,21 d的药物释放质量浓度高于T2支架(P < 0.05),7,35 d的药物释放质量浓度低于T2支架(P < 0.05)。第1 天时,S1支架药物释放质量浓度为(20.52±0.64) μg/mL,T2支架药物释放质量浓度为(14.18±0.85) μg/mL,T2支架3 d后的药物释放质量浓度基本处于10 μg/mL以内,在第7 天时药物释放质量浓度超过S2支架,在35 d时仍可检测到(2.89±0.06) μg/mL的药物。S2支架21 d内只有第7 天的药物释放质量浓度低于10 μg/mL,而在第35 天时检测出的药物释放质量浓度低于1 μg/mL。对比缓释曲线,单轴载药支架在缓释14 d时有一个药物突释现象,而同轴载药支架在第7 天时药物缓释曲线有较小幅度的改变,就整体而言同轴载药支架的缓释曲线更平缓,说明同轴外芯的作用可以较好地改善药物缓释曲线,与课题组前期研究结果相符[11]。有研究表明,盐酸米诺环素质量浓度在1-10 μg/mL之间对成骨细胞的增殖及成骨相关基因的表达有促进作用[22],并且1 μg/mL的盐酸米诺环素能抑制牙周袋内85%-95%的细菌[23],故此次实验药物缓释止点为1 μg/mL。由此看来,与单轴载药骨支架相比,同轴载药骨支架的缓释时间更长,且缓释药物质量浓度长期处于1-10 μg/mL之间,更有利于抑菌及成骨。 2.5 支架细胞毒性检测结果 图5,表2为CCK-8检测各组成骨细胞增殖情况,经统计学分析4组材料浸提液与细胞共培养后组间(F=14.00,P=0.002),因数据不满足球型假设(P < 0.05,W=0.038),经GG校正后组内比较差异有显著性意义(F=55.44,P < 0.001),且时间与分组之间交互作用显著(F=9.14,P=0.005);经事后多重比较及简单效应分析可得,与S1组相比,S2组、T2组第1 天的细胞增殖率降低(P < 0.01),T1组、S2组、T2组第3 天的细胞增殖率升高(P < 0.01),T1组、S2组第5 天的细胞增殖率降低(P < 0.01)。4 组细胞增殖率都大于75%,满足生物相容性要求。"

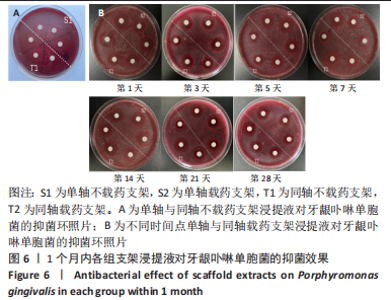
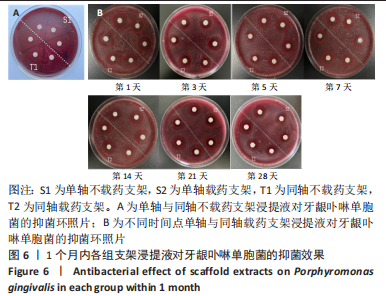
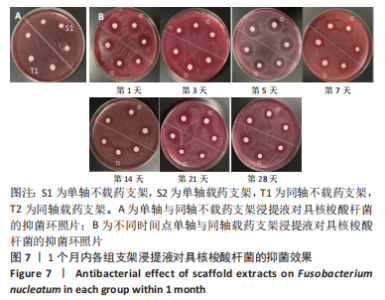
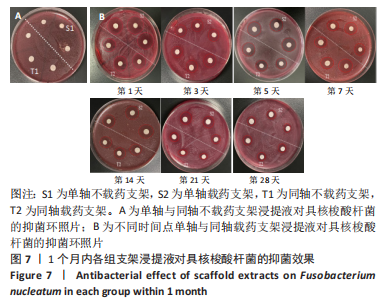
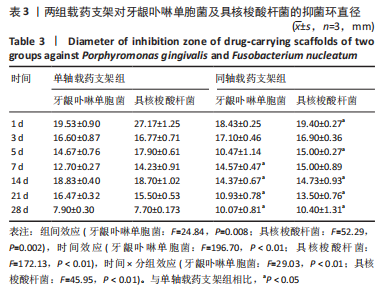
数据满足正态性及方差齐性,S2组与T2组抑菌环直径比较差异有显著性意义(牙龈卟啉单胞菌:F=24.84,P=0.008;具核梭酸杆菌:F=52.29,P=0.002);两组数据均不满足球型假设检验(P < 0.05,W < 0.75),使用GG进行校正后,不同时间内抑菌环直径比较差异有显著性意义(牙龈卟啉单胞菌:F=196.70,P < 0.01;具核梭酸杆菌:F=172.13,P < 0.01),时间与分组之间交互作用显著(牙龈卟啉单胞菌:F=29.03,P < 0.01;具核梭酸杆菌:F=45.95,P < 0.01);经事后比较及简单效应分析可得,对于牙龈卟啉单胞菌,S2组与T2组7,14,21,28 d的抑菌圈直径比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);对于具核梭酸杆菌,S2组与T2组1,5,14,21,28 d的菌圈直径比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表3。"
| [1] WANG R, NI S, MA L, et al. Porous construction and surface modification of titanium-based materials for osteogenesis: A review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:973297. [2] WU S, XU J, ZOU L, et al. Long-lastingrenewable antibacterial Porous Polymeric coatings enable titanium biomaterials to Prevent and treat Peri-imPlant infection. NatCommun. 2021;12(1):3303. [3] ZHANG T, QIN X, GAO Y, et al. Functional chitosan gel coating enhances antimicrobial ProPerties and osteogenesis of titanium alloy under Persistent chronic inflammation. FrontBioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1118487. [4] ROCCUZZO A, STÄHLI A, MONJE A, et al. Peri-ImPlantitis:A Clinical UPdate on Prevalence and Surgical Treatment Outcomes. J Clin Med. 2021;10(5):1107. [5] NIKOLOVA MP, APOSTOLOVA MD. Advances in Multifunctional Bioactive Coatings for Metallic Bone ImPlants. Materials (Basel). 2022;16(1):183. [6] DHALIWAL JS, ABD RAHMAN NA, MING LC, et al. Microbial Biofilm Decontamination on Dental ImPlant Surfaces: A Mini Review. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11:736186. [7] ZHOU W, PENG X, MA Y, et al. Two-staged time-dePendent materials for the Prevention of imPlant-related infections. Acta Biomater. 2020;101:128-140. [8] ROMANDINI M, LIMA C, PEDRINACI I, et al. Prevalence and risk/Protective indicatorsof Peri-imPlant diseases:A university-rePresentative cross-sectional study. Clin Oral ImPlants Res. 2021;32(1):112-122. [9] ZHANG S, WANG M, JIANG T, et al. Roles of a new drug-delivery healing abutment in the Prevention and treatment of Peri-imPlant infections: a Preliminary study. RSC Adv. 2018;8(68):38836-38843. [10] GHAVIMI MA, SHAHI S, MALEKI DIZAJ S, et al. Antimicrobial effects of nanocurcumin gel on reducing the microbial count of gingival fluids of implant‒abutment interface: A clinical study. J Adv Periodontol Implant Dent. 2022;14(2):114-118. [11] 高欣欣.载药组织工程骨支架制备及释药特性研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆大学,2018. [12] ZHAO R, YANG R, COOPER PR, et al. Bone Grafts and Substitutes in Dentistry:A Review of Current Trends and DeveloPments. Molecules. 2021;26(10):3007. [13] XIE Y, LI S, ZHANG T, et al. Titanium mesh for bone augmentation in oral implantology: current aPPlication and Progress. Int J Oral Sci. 2020;12(1):37. [14] 范泽文,赵新宇,邱帅,等.聚乳酸/聚乙二醇/羟基磷灰石多孔骨支架的3D打印制备及其生物相容性[J].材料工程,2021,49(4):135-141. [15] HU X, ZHAO W, ZHANG Z, et al. Novel 3D printed shape-memory plla-tmc/ga-tmc scaffolds for bone tissue engineering with the improved mechanical properties and degradability. Chin Chem Lett. 2023;34(1):251-254. [16] DAI C, LI Y, PAN W, et al. Three-Dimensional High-Porosity Chitosan/HoneycombPorous Carbon/HydroxyaPatite Scaffold with Enhanced Osteoinductivity for Bone Regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(1):575-586. [17] 由少华.解读GB/T16886《医疗器械生物学评价》系列标准[J].中国医疗器械信息,2005,11(1):20-24. [18] 安田田.多孔同轴载药组织工程骨支架的构建及性能研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆大学,2021. [19] 熊美萍,贾高智,袁广银.全降解镁合金组织工程支架孔隙特征与性能关系研究[J].口腔医学,2020,40(11):971-975. [20] WANG Z, WANG Y, YAN J, et al. Pharmaceutical electrospinning and 3D Printing scaffold design for bone regeneration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;174:504-534. [21] PUPILLI F, RUFFINI A, DAPPORTO M, et al. Design strategies and biomimetic approaches for calcium phosphate scaffolds in bone tissue regeneration. Biomimetics (Basel). 2022; 7(3):112. [22] 邵华英,张一弓,杨雪,等.抑菌浓度米诺环素对成骨细胞增殖、分化和矿化的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2018,36(2):140-145. [23] FU Y, BOTH SK, PLASS JRM, et al. Injectable Cell-Laden Polysaccharide Hydrogels:In Vivo Evaluation of Cartilage Regeneration. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(20):4292. [24] 陈菲,庄德舒,张洪波,等.生物活性透明质酸联合盐酸米诺环素对牙龈卟啉单胞菌抑菌作用研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2017,10(5):283-286. [25] BELIBASAKIS GN, MANOIL D. Microbial Community-Driven EtioPathogenesis of Peri-ImPlantitis. J Dent Res. 2021;100(1):21-28. [36] WANG C, CHEN P, QIAO Y, et al. Bacteria-activated chlorin e6 ionic liquid based on cation and anion dual-mode antibacterial action for enhanced photodynamic efficacy. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(4):1399-1410. [27] BARRAK I, BARÁTH Z, TIÁN T, et al. Effectsof different decontaminating solutions usedfor the treatment of peri-implantitis on the growth of porphyromonas gingivalis-an in vitro study. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2020. doi:10.1556/030.2020.01176 [28] 刘宁,林媛,韩林艺,等.淫羊藿苷与盐酸米诺环素联合应用的抗菌及促成骨性能研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2022,38(5):595-600. [29] ZHANG T, KALIMUTHU S, RAJASEKAR V, et al. Biofilm inhibition in oral pathogensby nanodiamonds. Biomater Sci. 2021;9:5127-5135. [30] SAQUIB SA, ALQAHTANI NA, AHMAD I, et al. Evaluation and comparisonof antibacterial efficacy of herbal extracts in combination with antibiotics on periodontal pathobionts:an in vitro microbiological study. Antibiotics (Basel). 2019;8(3):89. [31] DODO CG, MEIRELLES L, AVILES-REYES A, et al. Pro-inflammatory Analysis of MacroPhages in Contact with Titanium Particles and PorPhyromonas gingivalis. Braz Dent J. 2017;28(4):428-434. [32] 庞诗梦,夏荣, 李趁趁,等.钛表面新型抗菌涂层的生物相容性研究 安徽医科大学学报[J].2022,57(9):1355-1359. [33] CROSS LM, THAKUR A, JALILI NA, et al. Nanoengineered biomaterials for rePair and regeneration of orthoPedic tissue interfaces. Acta Biomater. 2016;42:2-17. [34] CHEN L, WEI L, SU X, et al. PreParation and Characterization of Biomimetic Functional Scaffold with Gradient Structure for Osteochondral Defect RePair.Bioengineering(Basel). 2023;10(2):213. [35] 张世明,陶树清.评价医疗器械体外细胞毒性的常用方法概述[J].现代医学,2020, 48(1):146-150. [36] TOLEDANO-OSORIO M, VALLECILLO C, TOLEDANO R, et al. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Systemic Antibiotic TheraPy in the Treatment of Peri-ImPlantitis.Int J Environ ResPublic Health. 2022;19(11):6502. [37] 陈菲,庄德舒,张洪波,等.生物活性透明质酸联合盐酸米诺环素对牙龈卟啉单胞菌抑菌作用研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2017,10(5):283-286. [38] WNEK GE. 3.ElectrosPun Polymer fibers as a versatile delivery Platform for smallmolecules and macromolecules: Original research article: Release of tetracycline hydrochloridefrom electrosPun Poly (ethylene-co-vinylacetate), Poly (lactic acid), a blend,2002. J Control Release. 2014;190:34-36. [39] SHAO HY, ZHANG YG, YANG X, et al. Effects of inhibitory concentration minocyclineon the Proliferation, differentiation, andmineralization of osteoblasts. Hua Xi Kou QiangYi Xue Za Zhi. 2018;36(2):140-145. |
| [1] | Wang Menghan, Qi Han, Zhang Yuan, Chen Yanzhi. Three kinds of 3D printed models assisted in treatment of Robinson type II B2 clavicle fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1403-1408. |
| [2] | Yang Yufang, Yang Zhishan, Duan Mianmian, Liu Yiheng, Tang Zhenglong, Wang Yu. Application and prospects of erythropoietin in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [3] | Chen Kaijia, Liu Jingyun, Cao Ning, Sun Jianbo, Zhou Yan, Mei Jianguo, Ren Qiang. Application and prospect of tissue engineering in treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1450-1456. |
| [4] | Wang Shanshan, Shu Qing, Tian Jun. Physical factors promote osteogenic differentiation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [5] | Mei Jingyi, Liu Jiang, Xiao Cong, Liu Peng, Zhou Haohao, Lin Zhanyi. Proliferation and metabolic patterns of smooth muscle cells during construction of tissue-engineered blood vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1043-1049. |
| [6] | Ning Tianliang, Wang Kun, Wang Lingbiao, Han Pengfei. Finite element analysis on correction effect of varus foot orthosis based on the three-point force principle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 891-899. |
| [7] | Shen Ziqing, Xia Tian, Shan Yibo, Zhu Ruijun, Wan Haoxin, Ding Hao, Pan Shu, Zhao Jun. Vascularized tracheal substitutes constructed by exosome-load hydrogel-modified 3D printed scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 697-705. |
| [8] | Zhu Liwei, Wang Jiangyue, Bai Ding. Application value of nanocomposite gelatin methacryloyl hydrogels in different bone defect environments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 753-758. |
| [9] | Chen Xiaofang, Zheng Guoshuang, Li Maoyuan, Yu Weiting. Preparation and application of injectable sodium alginate hydrogels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 789-794. |
| [10] | Wang Jiani, Chen Junyu. Angiogenesis mechanism of metal ions and their application in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 804-812. |
| [11] | Yang Yuqing, Chen Zhiyu. Role and application of early transient presence of M1 macrophages in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 594-601. |
| [12] | Gu Mingxi, Wang Changcheng, Tian Fengde, An Ning, Hao Ruihu, Guo Lin. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of a three-dimensional porous cartilage scaffold made of silk fibroin/gelatin/chitosan [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 366-372. |
| [13] | Xu Xiaodong, Zhou Jiping, Zhang Qi, Feng Chen, Zhu Mianshun, Shi Hongcan. 3D printing process of gelatin/oxidized nanocellulose skin scaffold with high elastic modulus and high porosity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 398-403. |
| [14] | Wang Xinmin, Yan Wenkai, Song Yahui, Liu Fei. Leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin with autologous hamstring tendon for traumatic patella dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 404-410. |
| [15] | Bi Yujie, Ma Dujun, Peng Liping, Zhou Ziqiong, Zhao Jing, Zhu Houjun, Zhong Qiuhui, Yang Yuxin. Strategy and significance of Chinese medicine combined with medical hydrogel for disease treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 419-425. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||