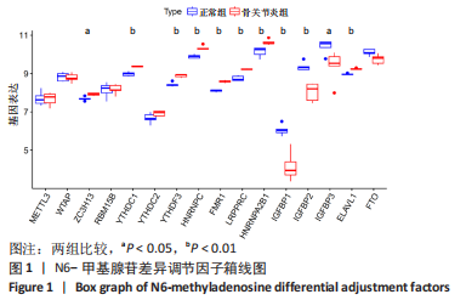
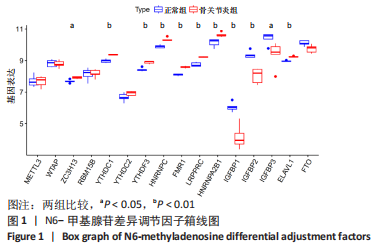
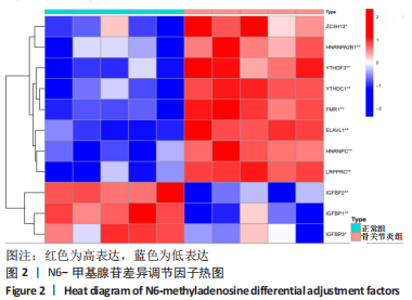
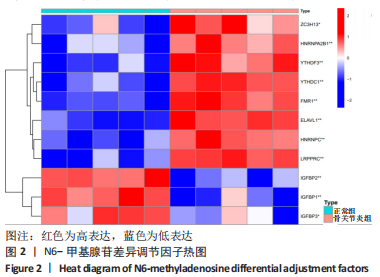
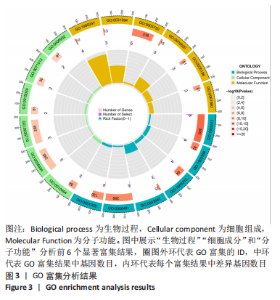
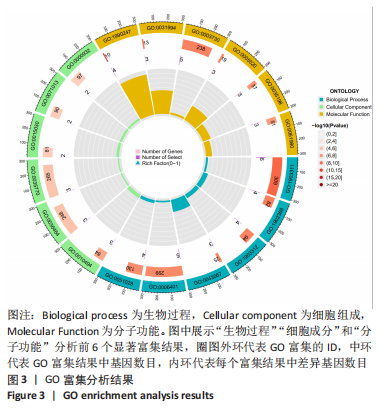
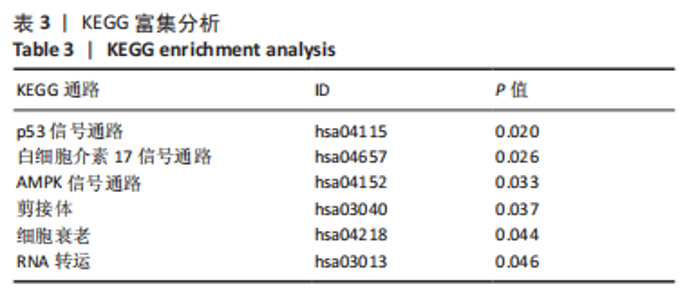
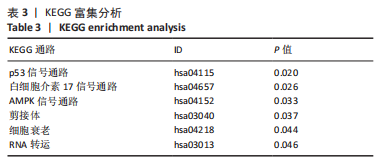
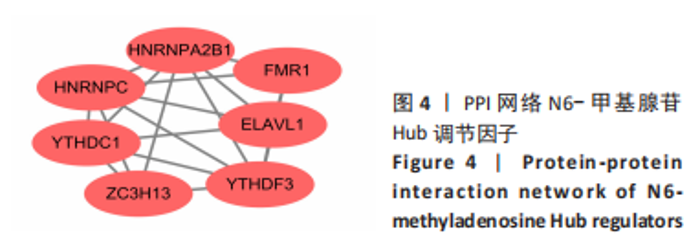
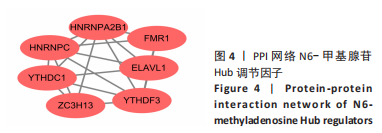
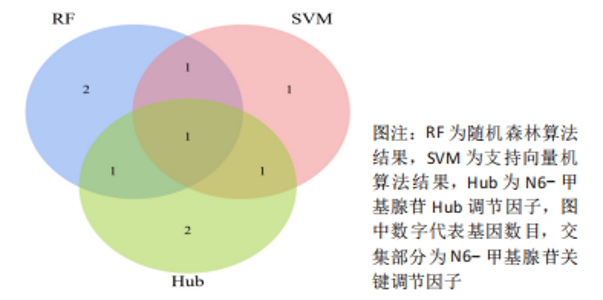
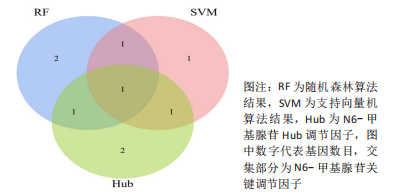
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (11): 1724-1729.doi: 10.12307/2024.224
Previous Articles Next Articles
N6-methyladenosine related regulatory factors in osteoarthritis: bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation
Yuan Changshen1, Liao Shuning2, Li Zhe2, Guan Yanbing2, Wu Siping2, Hu Qi2, Mei Qijie1, Duan Kan1
- 1Orthopedic Department of the Limbs, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-02-14Accepted:2023-03-22Online:2024-04-18Published:2023-07-27 -
Contact:Duan Kan, MD, Chief physician, Orthopedic Department of the Limbs, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Yuan Changshen, Master, Orthopedic Department of the Limbs, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 82060875 (to YCS) and 82160912 (to DK)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yuan Changshen, Liao Shuning, Li Zhe, Guan Yanbing, Wu Siping, Hu Qi, Mei Qijie, Duan Kan. N6-methyladenosine related regulatory factors in osteoarthritis: bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1724-1729.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] GLOBAL BURDEN OF DISEASE STUDY 2013 COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;386(9995):743-800. [2] HE Y, LI Z, ALEXANDER PG, et al. Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis: RiskFactors, Regulatory Pathways in Chondrocytes,and Experimental Model. Biology(Basel). 2020;9(8):194. [3] ZHENG HX, ZHANG XS, SUI N. Advances in the profiling of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications. Biotechnol Adv. 2020;45: 107656. [4] LIU Y, LU T, LIU Z, et al. Six macrophage-associated genes in synovium constitute a novel diagnostic signature for osteoarthritis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:936606. [5] ZHAO X, ZHAO Y, JIANG Y, et al. Deciphering the endometrial immune landscape of RIF during the window of implantation from cellular senescence by integrated bioinformatics analysis and machine learning. Front Immunol. 2022;13:952708. [6] GREENER JG, KANDATHIL SM, MOFFAT L, et al. A guide to machine learning for biologists. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022;23(1):40-55. [7] ZHU H, YAN X, ZHANG M, et al. miR-21-5p protects IL-1β-induced human chondrocytes from degradation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1): 118. [8] 魏丽杰.降钙素对IL-1β诱导的大鼠软骨细胞炎性反应的影响[D].唐山:河北联合大学,2014. [9] WU B, LI L, HUANG Y, et al. Readers, writers and erasers of N6-methylated adenosine modification. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2017;47: 67-76. [10] YANG Y, HSU PJ, CHEN YS, et al. Dynamic transcriptomic m6A decoration: writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res. 2018;28(6):616-624. [11] SANG W, XUE S, JIANG Y, et al. METTL3 involves the progression of osteoarthritis probably by affecting ECM degradation and regulating the inflammatory response. Life Sci. 2021;278:119528. [12] CHEN X, GONG W, SHAO X, et al. METTL3-mediated m6A modification of ATG7 regulates autophagy-GATA4 axis to promote cellular senescence and osteoarthritis progression. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;81(1): 87-99. [13] SHI H, WEI J, HE C. Where, When, and How: Context-Dependent Functions of RNA Methylation Writers, Readers, and Erasers. Mol Cell. 2019;74(4):640-650. [14] PEFFERS MJ, BALASKAS P, SMAGUL A. Osteoarthritis year in review 2017: genetics and epigenetics. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(3): 304-311. [15] ZHAI G, XIAO L, JIANG C, et al. Regulatory Role of N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) Modification in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10: 946219. [16] YANG J, ZHANG M, YANG D, et al. m6A-mediated upregulation of AC008 promotes osteoarthritis progression through the miR-328-3p-AQP1/ANKH axis. Exp Mol Med. 2021;53(11):1723-1734. [17] SWINGLER TE, NIU L, SMITH P, et al. The function of microRNAs in cartilage and osteoarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37 Suppl 120(5): 40-47. [18] ZHU J, YANG S, QI Y, et al. Stem cell-homing hydrogel-based miR-29b-5p delivery promotes cartilage regeneration by suppressing senescence in an osteoarthritis rat model. Sci Adv. 2022;8(13):eabk0011. [19] MASSICOTTE F, AUBRY I, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, et al. Abnormal insulin-like growth factor 1 signaling in human osteoarthritic subchondral bone osteoblasts. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(6):R177. [20] TROMPETER N, GARDINIER JD, DEBARROS V, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 regulates the mechanosensitivity of chondrocytes by modulating TRPV4. Cell Calcium. 2021;99:102467. [21] ENGELAND K. Cell cycle regulation: p53-p21-RB signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29(5):946-960. [22] KIRAZ Y, ADAN A, KARTAL YANDIM M, et al. Major apoptotic mechanisms and genes involved in apoptosis. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(7): 8471-8486. [23] ZHANG M, WANG Z, LI B, et al. Identification of microRNA‑363‑3p as an essential regulator of chondrocyte apoptosis in osteoarthritis by targeting NRF1 through the p53-signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2020;21(3):1077-1088. [24] NA HS, PARK JS, CHO KH, et al. Interleukin-1-Interleukin-17 Signaling Axis Induces Cartilage Destruction and Promotes Experimental Osteoarthritis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:730. [25] WANG K, XU J, CAI J, et al. Serum levels of resistin and interleukin-17 are associated with increased cartilage defects and bone marrow lesions in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2017; 27(2):339-344. [26] FAUST HJ, ZHANG H, HAN J, et al. IL-17 and immunologically induced senescence regulate response to injury in osteoarthritis. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(10):5493-5507. [27] POURSAMIMI J, SHARIATI-SARABI Z, TAVAKKOL-AFSHARI J, et al. Immunoregulatory Effects of Krocina™, a Herbal Medicine Made of Crocin, on Osteoarthritis Patients: A Successful Clinical Trial in Iran. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020;19(3):253-263. [28] LI J, ZHANG B, LIU WX, et al. Metformin limits osteoarthritis development and progression through activation of AMPK signalling. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(5):635-645. [29] ZHANG D, ZHANG D, YANG X, et al. Expression of m6A Methylation Regulator in Osteoarthritis and Its Prognostic Markers. Cartilage. 2022:19476035221137722. doi: 10.1177/19476035221137722. [30] XIE X, ZHANG Y, YU J, et al. Significance of m6A regulatory factor in gene expression and immune function of osteoarthritis. Front Physiol. 2022;13:918270. [31] WIDAGDO J, ANGGONO V, WONG JJ. The multifaceted effects of YTHDC1-mediated nuclear m6A recognition. Trends Genet. 2022;38(4): 325-332. [32] LIU J, GAO M, HE J, et al. The RNA m6A reader YTHDC1 silences retrotransposons and guards ES cell identity. Nature. 2021;591(7849): 322-326. [33] LI Y, ZHANG W, DAI Y, et al. Identification and verification of IGFBP3 and YTHDC1 as biomarkers associated with immune infiltration and mitophagy in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Front Genet. 2022;13: 986995. [34] CHEN H, LI Y, LI L, et al. YTHDC1 gene polymorphisms and hepatoblastoma susceptibility in Chinese children: A seven-center case-control study. J Gene Med. 2020;22(11):e3249. [35] LIN A, HUA RX, ZHOU M, et al. YTHDC1 gene polymorphisms and Wilms tumor susceptibility in Chinese children: A five-center case-control study. Gene. 2021;783:145571. [36] CAO D, GE S, LI M. MiR-451a promotes cell growth, migration and EMT in osteosarcoma by regulating YTHDC1-mediated m6A methylation to activate the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. J Bone Oncol. 2022;33: 100412. [37] XUE JF, SHI ZM, ZOU J, et al. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway promotes autophagy of articular chondrocytes and attenuates inflammatory response in rats with osteoarthritis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;89:1252-1261. [38] XU K, HE Y, MOQBEL SAA, et al. SIRT3 ameliorates osteoarthritis via regulating chondrocyte autophagy and apoptosis through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;175:351-360. [39] CAI C, MIN S, YAN B, et al. MiR-27a promotes the autophagy and apoptosis of IL-1β treated-articular chondrocytes in osteoarthritis through PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(16): 6371-6384. |
| [1] | Li Yongjie, Fu Shenyu, Xia Yuan, Zhang Dakuan, Liu Hongju. Correlation of knee extensor muscle strength and spatiotemporal gait parameters with peak knee flexion/adduction moment in female patients with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1354-1358. |
| [2] | Qi Haodong, Lu Chao, Xu Hanbo, Wang Mengfei, Hao Yangquan. Effect of diabetes mellitus on perioperative blood loss and pain after primary total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1383-1387. |
| [3] | Du Changling, Shi Hui, Zhang Shoutao, Meng Tao, Liu Dong, Li Jian, Cao Heng, Xu Chuang. Efficacy and safety of different applications of tranexamic acid in high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1409-1413. |
| [4] | Yu Weijie, Liu Aifeng, Chen Jixin, Guo Tianci, Jia Yizhen, Feng Huichuan, Yang Jialin. Advantages and application strategies of machine learning in diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1426-1435. |
| [5] | Huang Xiarong, Hu Lizhi, Sun Guanghua, Peng Xinke, Liao Ying, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Yin Linwei, Zhong Peirui, Peng Ting, Zhou Jun, Qu Mengjian. Effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of P53 and P21 in articular cartilage and subchondral bone of aged rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1174-1179. |
| [6] | Zhao Garida, Ren Yizhong, Han Changxu, Kong Lingyue, Jia Yanbo. Mechanism of Mongolian Medicine Erden-uril on osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1193-1199. |
| [7] | Li Rui, Zhang Guihong, Wang Tao, Fan Ping. Effect of ginseng polysaccharide on the expression of prostaglandin E2/6-keto-prostaglandin 1alpha in traumatic osteoarthritis model rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1235-1240. |
| [8] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [9] | Zhang Zeyi, Yang Yimin, Li Wenyan, Zhang Meizhen. Effect of foot progression angle on lower extremity kinetics of knee osteoarthritis patients of different ages: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 968-975. |
| [10] | Shen Feiyan, Yao Jixiang, Su Shanshan, Zhao Zhongmin, Tang Weidong. Knockdown of circRNA WD repeat containing protein 1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of chondrocytes in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 499-504. |
| [11] | Maisituremu·Heilili, Zhang Wanxia, Nijiati·Nuermuhanmode, Maimaitituxun·Tuerdi. Effect of intraarticular injection of different concentrations of ozone on condylar histology of rats with early temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 505-509. |
| [12] | Qiao Hujun, Wang Guoxiang. Evaluation of rat osteoarthritis chondrocyte models induced by interleukin-1beta [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 516-521. |
| [13] | Bu Xianzhong, Bu Baoxian, Xu Wei, Zhang Chi, Zhang Yisheng, Zhong Yuanming, Li Zhifei, Tang Fubo, Mai Wei, Zhou Jinyan. Analysis of serum differential proteomics in patients with acute cervical spondylotic radiculopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 535-541. |
| [14] | Liu Yuhan, Fan Yujiang, Wang Qiguang. Comparison of protocols for constructing animal models of early traumatic knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 542-549. |
| [15] | Zhang Yaru, Chen Yanjun, Zhang Xiaodong, Chen Shenghua, Huang Wenhua. Effect of ferroptosis mediated by glutathione peroxidase 4 in the occurrence and progression of synovitis in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 550-555. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||