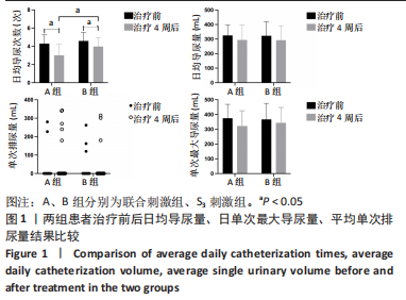
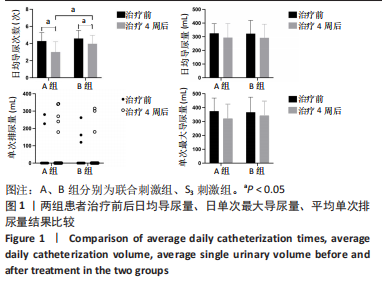
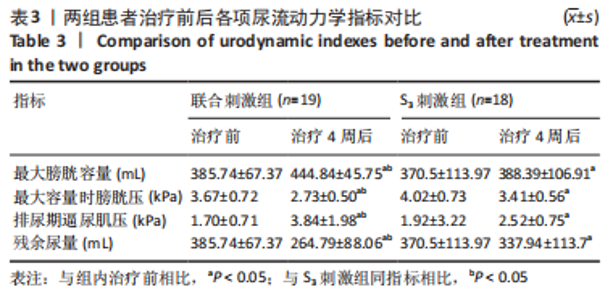
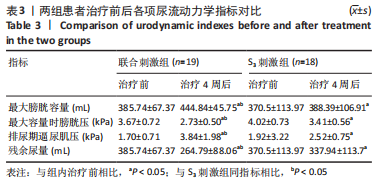
[1] SINGH A, TETREAULT L, KALSI-RYAN S, et al. Global prevalence and incidence of traumatic spinal cord injury. Clin Epidemiol. 2014;6:309-331.
[2] ECKERT MJ, MARTIN MJ. Trauma: Spinal Cord Injury. Surg Clin North Am. 2017;97(5):1031-1045.
[3] LOY K, BAREYRE FM. Rehabilitation following spinal cord injury: how animal models can help our understanding of exercise-induced neuroplasticity. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(3):405-412.
[4] ONG B, WILSON JR, HENZEL MK. Management of the patient with chronic spinal cord injury. Med Clin North Am.2020;104(2):263-278.
[5] Pettigrew RI, Heetderks WJ, Christine AK, et al. Epidural spinal stimulation to improve bladder, bowel, and sexual function in individuals with spinal cord injuries: a framework for clinical research. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2017;64(2):253-262.
[6] XU L, FU C, ZHANG Q, et al. Efficacy of biofeedback, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and pelvic floor muscle training for female neurogenic bladder dysfunction after spinal cord injury: a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2020;10(8):1-9.
[7] GAD P, CHOE J, SHAH P, et al. Sub-threshold spinal cord stimulation facilitates spontaneous motor activity in spinal rats. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2013;10:108.
[8] TSAI PY, WANG CP, HSIEH CY, et al. Long-term sacral magnetic stimulation for refractory stress urinary incontinence. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014;95(12):2231-2238.
[9] 王梦婷,秦义婷,程清,等.骶神经磁刺激对逼尿肌无力的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2020,42(8):729-733.
[10] YAO J, ZHANG Q, LIAO X, et al. A corticopontine circuit for initiation of urination. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21(11):1541-1550.
[11] 邓皓月,袁昌艳,王树琼,等.磁刺激初级运动皮层(M1区)对不完全性脊髓损伤患者膀胱功能的影响[J].重庆医科大学学报,2020,45(1):122-125.
[12] 陆飞,闫振壮,苏清伦,等.不同频率高频磁刺激对脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱患者治疗效果的比较[J].中国康复医学杂志,2021,36(7):852-854.
[13] 李建军,王方永.脊髓损伤神经学分类国际标准(2011年修订)[J].中国康复理论与实践,2011,17(10):963-972.
[14] IWATSUBO E. Bladder recovery in patients with traumatic cervical cord injury evaluated by voiding synchronous cystosphincterometry with uroflowmetry.J Urol. 1981;126 (4): 503-508.
[15] LI H, ZHOU CK, SONG J, et al. Curative efficacy of low frequency electrical stimulation in preventing urinary retention after cervical cancer operation.World J Surg Oncol. 2019;17(1):141.
[16] 张怀期.骶神经根磁刺激对脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱的疗效观察[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2019.
[17] LIM, LIONG M, LEONG W, et al. Magnetic stimulation for stress urinary incontinence: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2015;16:279.
[18] ADRIAANSEN JJE, VAN ASBECK FWA, TEPPER M, et al. Bladder-emptying methods, neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction and impact on quality of life in people with long-term spinal cord injury. J Am Paraplegia Soc. 2017;40(1):43-53.
[19] BLAYNE W, SCHNEIDER MP, JEFFREY T, et al. Early urological care of patients with spinal cord injury. World J Urol. 2018;36(10):1537-1544.
[20] SINHA S. Follow-up urodynamics in patients with neurogenic bladder. Indian J Urol. 2017; 33(4):267-275.
[21] SEKIDO N, IGAWA Y, KAKIZAKI H, et al. Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of lower urinary tract dysfunction in patients with spinal cord injury. Int J Urol. 2020;27(4):276-288.
[22] FERGANY LA, SHAKER H, ARAFA M, et al. Does sacral pulsed electromagnetic field therapy have a better effect than transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in patients with neurogenic overactive bladder? Arab J Urol. 2017;15(2):148-152.
[23] LIAO KK, CHEN JT, LAI KL, et al. Effect of sacral-root stimulation on the motor cortex in patients with idiopathic overactive bladder syndrome. Neurophysiol Clin. 2008;38(1):39-43.
[24] NARDONE R, VERSACE V, SEBASTIANELLI L, et al. Transcranial magnetic stimulation and bladder function: A systematic review. Clin Neurophysiol. 2019;130(11):2032-2037.
[25] RODIC B, SCHLÄPFER A, CURT A, et al. Magnetic stimulation of sacral roots for assessing the efferent neuronal pathways of lower urinary tract. Muscle Nerve.2002;26(4):486-491.
[26] NIU T, BENNETT CJ, KELLER TL, et al. A Proof-of-concept study of transcutaneous magnetic spinal cord stimulation for neurogenic bladder. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):12549.
[27] BYCROFT JA, CRAGGS MD, SHERIFF M, et al. Does magnetic stimulation of sacral nerve roots cause contraction or suppression of the bladder? Neurourol Urodyn. 2004;23(3):241-245.
[28] EL-HABASHY H, NADA MM, MAHER EA, et al. The effect of cortical versus sacral repetitive magnetic stimulation on lower urinary tract dysfunction in patients with multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Belg. 2020;120(1):141-147.
[29] TAUBE W, LEUKEL C, NIELSEN JB, et al. Repetitive activation of the corticospinal pathway by means of rTMS may reduce the efficiency of corticomotoneuronal synapses. Cereb Cortex. 2015;25(6):1629-1637.
[30] BANNAGA A, GUO T, OUYANG X, et al. Magnetic stimulation accelerating rehabilitation of peripheral nerve injury. Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2002;22(2):135-139.
[31] THICKBROOM GW, BYRNES ML, EDWARDS DJ, et al. Repetitive paired-pulse TMS at I-wave periodicity markedly increases corticospinal excitability: a new technique for modulating synaptic plasticity.Clin Neurophysiol. 2006;117(1):61-66.
[32] JIANG JL, GUO XD, ZHANG SQ, et al. Repetitive magnetic stimulation affects the microenvironment of nerve regeneration and evoked potentials after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(5):816-822.
[33] BUNDAY KL, URBIN MA, PEREZ MA. Potentiating paired corticospinal-motoneuronal plasticity after spinal cord injury. Brain Stimul. 2018;11(5):1083-1092.
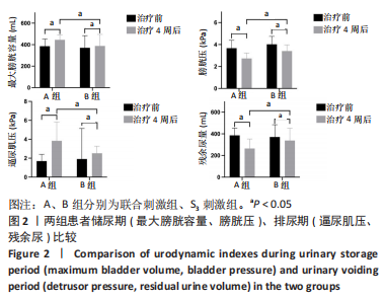
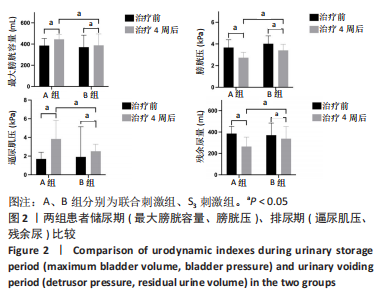
|